第一级配置器是对C的内存分配函数malloc,free,realloc的简单封装,用来分配大于128bytes的区块。
第二级配置器管理16个free-lists链表,各自管理8-128bytes的小额区块。
链表节点结构如下:
union obj //free_list节点 { union obj* free_list_link; };
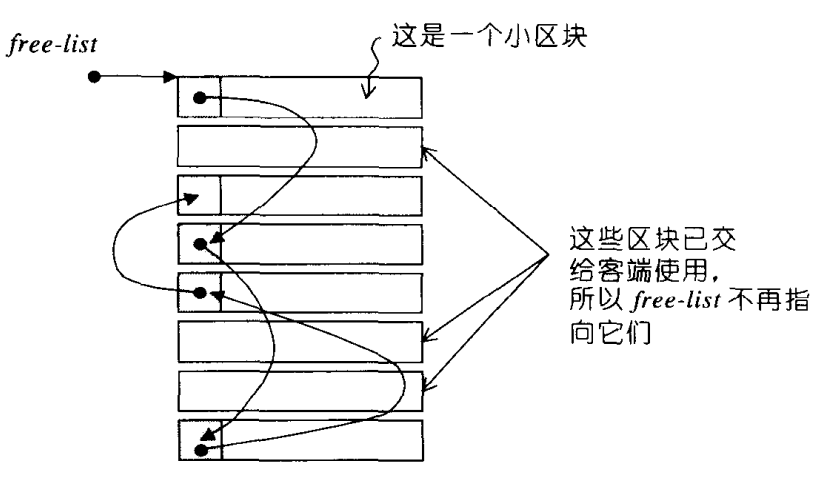
当一个区块未被使用时,其前端sizeof(obj)的空间用于存放union obj,因此可通过free_list_link指针找到下一个区块。
当需要一个区块时,直接将该区块的首地址(即指向该区块的free_list_link)返回,使用过程中,该区块的前部union被覆盖,因此不会造成空间的浪费。
代码如下:
class alloc { private: static size_t ROUND_UP(size_t bytes) //将bytes上调至8的倍数 { return (((bytes)+__ALIGN - 1)&~(__ALIGN - 1)); } private: union obj //free_list节点 { union obj* free_list_link; }; private: static obj* volatile free_list[__NFREELISTS]; static size_t FREELIST_INDEX(size_t bytes) { return (((bytes)+__ALIGN - 1) / __ALIGN - 1); } static void* refill(size_t n); //返回大小为n的对象,并可能加入大小为n的其他区块到free_list static char* chunk_alloc(size_t size, int &nodejs); static char* start_free; //内存池起始 static char* end_free; //内存池结束 static size_t heap_size; //? public: static void* allocate(size_t n); static void deallocate(void* p, size_t n); static void* reallocate(void* p, size_t old_sz, size_t new_sz); }; char* alloc::start_free = 0; char* alloc::end_free = 0; size_t alloc::heap_size = 0; alloc::obj* volatile alloc::free_list[__NFREELISTS] = { nullptr }; void* alloc::allocate(size_t n) { obj* volatile* my_free_list; // volatile修饰的是*my_free_list obj* result; if (n > static_cast<size_t>(__MAX_BYTES)) { return malloc(n); } my_free_list = free_list + FREELIST_INDEX(n); result = *my_free_list; if (result == nullptr) //没找到可用free_list { void* r = refill(ROUND_UP(n)); return r; } *my_free_list = result->free_list_link; return result; } void alloc::deallocate(void* p, size_t n) { obj* q = (obj*)p; obj* volatile* my_free_list; if (n > (size_t)__MAX_BYTES) { free(p); return; } my_free_list = free_list + FREELIST_INDEX(n); q->free_list_link = *my_free_list; *my_free_list = q; } void* alloc::refill(size_t n) { int nobjs = 20; char* chunk = chunk_alloc(n, nobjs); obj* volatile* my_free_list; obj* result; obj* current_obj, *next_obj; if (nobjs == 1)return (chunk); my_free_list = free_list + FREELIST_INDEX(n); result = (obj*)chunk; //这一块返回给客端 *my_free_list = next_obj = next_obj = (obj*)(chunk + n); //chunk~chunk+n已经分配给客户端 //将free list的各节点串接起来 for (int i = 1;; ++i) { current_obj = next_obj; next_obj = (obj*)((char*)next_obj + n); if (nobjs - 1 == i) { current_obj->free_list_link = nullptr; break; } else { current_obj->free_list_link = next_obj; } } return result; } char* alloc::chunk_alloc(size_t size, int& nobjs) //尝试从内存池分配单个大小为size,数量为nobjs的区块 { char* result; size_t total_bytes = size*nobjs; size_t bytes_left = end_free - start_free; if (bytes_left >= total_bytes) //内存剩余空间完全满足需求 { result = start_free; start_free += total_bytes; return result; } else if (bytes_left>=size) //不能完全满足需求,但能供应>=1个区块 { nobjs = bytes_left / size; total_bytes = size*nobjs; result = start_free; start_free += total_bytes; return result; } else { size_t bytes_to_get = 2 * total_bytes + ROUND_UP(heap_size >> 4); if (bytes_left > 0) { obj* volatile* my_free_list = free_list + FREELIST_INDEX(bytes_left); ((obj*)start_free)->free_list_link = *my_free_list; *my_free_list = (obj*)start_free; } start_free = (char*)malloc(bytes_to_get); //配置heap空间 if (start_free == nullptr) //heap空间不足 { obj* volatile* my_free_list, *p; for (int i = size; i <= __MAX_BYTES; i += __ALIGN) //寻找尚未使用的足够大(至少>=size)的区块, { my_free_list = free_list + FREELIST_INDEX(i); //寻找大小为i的区块所在地 p = *my_free_list; if (p) { *my_free_list = p->free_list_link; //将该区块取出 start_free = (char*)p; //将其编入内存池 end_free = start_free + i; return chunk_alloc(size, nobjs); //递归调用,修正nobjs } } end_free = 0; //彻底没内存 throw; //抛出异常 } heap_size += bytes_to_get; //从堆里获取的空间 end_free = start_free + bytes_to_get; return (chunk_alloc(size, nobjs)); } }