法老讲课讲到的一道妙题,觉得很有趣就写了下
首先我们观察题意,发现原问题可以转化为一个排序问题
考虑我们求出(f_{i,j})表示在((i,j))格子上,最多可以保证顶上的(f_{i,j})个数有序
考虑对于所有的((i',j'),i'in[1,i],j'in[1,j],i' ot =ior j' ot= j),利用多路归并的思想,这上面的盘子都可以摆到((i,j))上
换句话说就是(f_{x,y}=sum_{i=1}^xsum_{j=1}^y f_{i,j} (i ot =xor j ot= y))
然后(f_{6,6})上就是最后能排好序的盘子数目了,我们打个表看看:
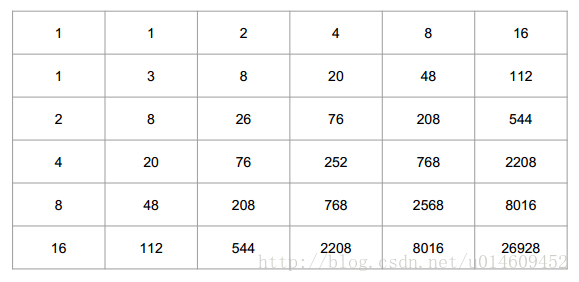
woc好像不行的亚子,难道就这样GG了?
我们再仔细想一下,其实对于(f_{1,2})和(f_{2,1}),它们其实是可以通过讨论来做到(f_{1,2}=f_{2,1}=2)的,这样一来还是按照上面的式子我们算一算:
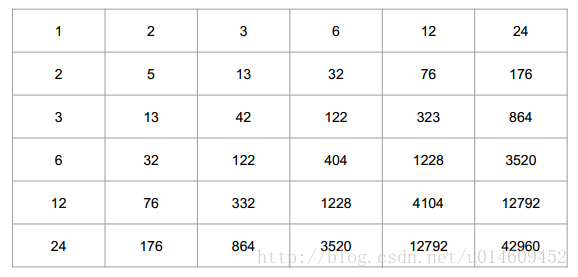
和数据范围完美契合,可以通过此题
然后稍微讲下实现吧,首先我们肯定是考虑递归完成这个问题,设一个函数solve(x,y,tp)表示做到((x,y))且这个位置上要放成升序还是降序
至于为什么要升降序,因为考虑我们归并的时候由于每个格子相当于是一个栈,因此之前的格子的升降序就要与后面的相反
然后多路归并的话就直接用堆来维护即可,有一些小细节
总复杂度应该是(O(6^6+36 imes n imes log 36))
#include<cstdio>
#include<utility>
#include<queue>
#include<stack>
#include<iostream>
#define RI register int
#define CI const int&
#define mp make_pair
#define fi first
#define se second
using namespace std;
typedef pair <int,int> pi;
typedef pair <int,pi> ipi;
const int N=10;
priority_queue <ipi,vector<ipi>,less<ipi> > big;
priority_queue <ipi,vector<ipi>,greater<ipi> > small;
stack <int> A[N][N],B[N][N]; int n,x;
inline void move(const pi& A,const pi& B) //move the top disk of A to B
{
int x=A.fi; while (x<B.fi) printf("%d %d D 1
",x++,A.se);
int y=A.se; while (y<B.se) printf("%d %d R 1
",x,y++);
}
inline void sort_greater(CI x,CI y)
{
for (RI i=1,j;i<=x;++i) for (j=1;j<=y;++j)
if ((i!=x||j!=y)&&!A[i][j].empty()) big.push(mp(A[i][j].top(),mp(i,j)));
while (!big.empty())
{
pi nw=big.top().se; A[x][y].push(big.top().fi); big.pop(); move(nw,mp(x,y));
if (A[nw.fi][nw.se].pop(),!A[nw.fi][nw.se].empty()) big.push(mp(A[nw.fi][nw.se].top(),nw));
}
}
inline void sort_less(CI x,CI y)
{
for (RI i=1,j;i<=x;++i) for (j=1;j<=y;++j)
if ((i!=x||j!=y)&&!A[i][j].empty()) small.push(mp(A[i][j].top(),mp(i,j)));
while (!small.empty())
{
pi nw=small.top().se; A[x][y].push(small.top().fi); small.pop(); move(nw,mp(x,y));
if (A[nw.fi][nw.se].pop(),!A[nw.fi][nw.se].empty()) small.push(mp(A[nw.fi][nw.se].top(),nw));
}
}
inline void solve(int x,int y,bool tp) // tp=0 less otherwise greater
{
if (x==1&&y==1)
{
if (!B[x][y].empty()) A[x][y].push(B[x][y].top()),B[x][y].pop(); return;
}
if ((x==1&&y==2)||(x==2&&y==1))
{
if (B[1][1].empty()) return; int a=B[1][1].top(); B[1][1].pop();
if (B[1][1].empty()) return A[x][y].push(a),move(mp(1,1),mp(x,y));
int b=B[1][1].top(); B[1][1].pop();
if ((a>b)^tp) printf("%d %d %c 2
",1,1,x==1?'R':'D');
else printf("%d %d %c 1
%d %d %c 1
",1,1,x==1?'R':'D',1,1,x==1?'R':'D');
if (tp) A[x][y].push(max(a,b)),A[x][y].push(min(a,b));
else A[x][y].push(min(a,b)),A[x][y].push(max(a,b)); return;
}
for (RI i=x,j;i;--i) for (j=y;j;--j) if (i!=x||j!=y) solve(i,j,tp^1);
if (tp) sort_greater(x,y); else sort_less(x,y);
}
int main()
{
scanf("%d",&n); for (RI i=1;i<=n;++i)
scanf("%d",&x),B[1][1].push(x); return solve(6,6,1),0;
}