本篇文章首发于头条号Flink程序是如何执行的?通过源码来剖析一个简单的Flink程序,欢迎关注头条号和微信公众号“大数据技术和人工智能”(微信搜索bigdata_ai_tech)获取更多干货,也欢迎关注我的CSDN博客。
在这之前已经介绍了如何在本地搭建Flink环境和如何创建Flink应用和如何构建Flink源码,这篇文章用官方提供的SocketWindowWordCount例子来解析一下一个常规Flink程序的每一个基本步骤。
示例程序
public class SocketWindowWordCount {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
// the host and the port to connect to
final String hostname;
final int port;
try {
final ParameterTool params = ParameterTool.fromArgs(args);
hostname = params.has("hostname") ? params.get("hostname") : "localhost";
port = params.getInt("port");
} catch (Exception e) {
System.err.println("No port specified. Please run 'SocketWindowWordCount " +
"--hostname <hostname> --port <port>', where hostname (localhost by default) " +
"and port is the address of the text server");
System.err.println("To start a simple text server, run 'netcat -l <port>' and " +
"type the input text into the command line");
return;
}
// get the execution environment
final StreamExecutionEnvironment env = StreamExecutionEnvironment.getExecutionEnvironment();
// get input data by connecting to the socket
DataStream<String> text = env.socketTextStream(hostname, port, "
");
// parse the data, group it, window it, and aggregate the counts
DataStream<WordWithCount> windowCounts = text
.flatMap(new FlatMapFunction<String, WordWithCount>() {
@Override
public void flatMap(String value, Collector<WordWithCount> out) {
for (String word : value.split("\s")) {
out.collect(new WordWithCount(word, 1L));
}
}
})
.keyBy("word")
.timeWindow(Time.seconds(5))
.reduce(new ReduceFunction<WordWithCount>() {
@Override
public WordWithCount reduce(WordWithCount a, WordWithCount b) {
return new WordWithCount(a.word, a.count + b.count);
}
});
// print the results with a single thread, rather than in parallel
windowCounts.print().setParallelism(1);
env.execute("Socket Window WordCount");
}
// ------------------------------------------------------------------------
/**
* Data type for words with count.
*/
public static class WordWithCount {
public String word;
public long count;
public WordWithCount() {}
public WordWithCount(String word, long count) {
this.word = word;
this.count = count;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return word + " : " + count;
}
}
}
上面这个是官网的SocketWindowWordCount程序示例,它首先从命令行中获取socket连接的host和port,然后获取执行环境、从socket连接中读取数据、解析和转换数据,最后输出结果数据。
每个Flink程序都包含以下几个相同的基本部分:
- 获得一个execution environment,
- 加载/创建初始数据,
- 指定此数据的转换,
- 指定放置计算结果的位置,
- 触发程序执行
Flink执行环境
final StreamExecutionEnvironment env = StreamExecutionEnvironment.getExecutionEnvironment();
Flink程序都是从这句代码开始,这行代码会返回一个执行环境,表示当前执行程序的上下文。如果程序是独立调用的,则此方法返回一个由createLocalEnvironment()创建的本地执行环境LocalStreamEnvironment。从其源码里可以看出来:
//代码目录:org/apache/flink/streaming/api/environment/StreamExecutionEnvironment.java
public static StreamExecutionEnvironment getExecutionEnvironment() {
if (contextEnvironmentFactory != null) {
return contextEnvironmentFactory.createExecutionEnvironment();
}
ExecutionEnvironment env = ExecutionEnvironment.getExecutionEnvironment();
if (env instanceof ContextEnvironment) {
return new StreamContextEnvironment((ContextEnvironment) env);
} else if (env instanceof OptimizerPlanEnvironment || env instanceof PreviewPlanEnvironment) {
return new StreamPlanEnvironment(env);
} else {
return createLocalEnvironment();
}
}
获取输入数据
DataStream<String> text = env.socketTextStream(hostname, port, "
");
这个例子里的源数据来自于socket,这里会根据指定的socket配置创建socket连接,然后创建一个新数据流,包含从套接字无限接收的字符串,接收的字符串由系统的默认字符集解码。当socket连接关闭时,数据读取会立即终止。通过查看源码可以发现,这里实际上是通过指定的socket配置来构造一个SocketTextStreamFunction实例,然后源源不断的从socket连接里读取输入的数据创建数据流。
//代码目录:org/apache/flink/streaming/api/environment/StreamExecutionEnvironment.java
@PublicEvolving
public DataStreamSource<String> socketTextStream(String hostname, int port, String delimiter, long maxRetry) {
return addSource(new SocketTextStreamFunction(hostname, port, delimiter, maxRetry),
"Socket Stream");
}
SocketTextStreamFunction的类继承关系如下:
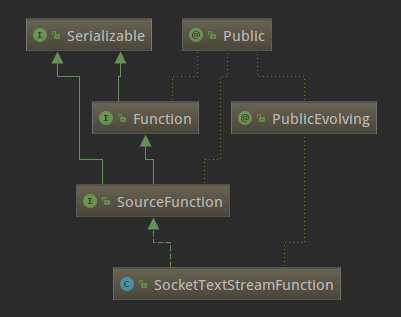
可以看出SocketTextStreamFunction是SourceFunction的子类,SourceFunction是Flink中所有流数据源的基本接口。SourceFunction的定义如下:
//代码目录:org/apache/flink/streaming/api/functions/source/SourceFunction.java
@Public
public interface SourceFunction<T> extends Function, Serializable {
void run(SourceContext<T> ctx) throws Exception;
void cancel();
@Public
interface SourceContext<T> {
void collect(T element);
@PublicEvolving
void collectWithTimestamp(T element, long timestamp);
@PublicEvolving
void emitWatermark(Watermark mark);
@PublicEvolving
void markAsTemporarilyIdle();
Object getCheckpointLock();
void close();
}
}
SourceFunction定义了run和cancel两个方法和SourceContext内部接口。
- run(SourceContex):实现数据获取逻辑,并可以通过传入的参数ctx进行向下游节点的数据转发。
- cancel():用来取消数据源,一般在run方法中,会存在一个循环来持续产生数据,cancel方法则可以使该循环终止。
- SourceContext:source函数用于发出元素和可能的watermark的接口,返回source生成的元素的类型。
了解了SourceFunction这个接口,再来看下SocketTextStreamFunction的具体实现(主要是run方法),逻辑就已经很清晰了,就是从指定的hostname和port持续不断的读取数据,按回车换行分隔符划分成一个个字符串,然后再将数据转发到下游。现在回到StreamExecutionEnvironment的socketTextStream方法,它通过调用addSource返回一个DataStreamSource实例。思考一下,例子里的text变量是DataStream类型,为什么源码里的返回类型却是DataStreamSource呢?这是因为DataStream是DataStreamSource的父类,下面的类关系图可以看出来,这也体现出了Java的多态的特性。
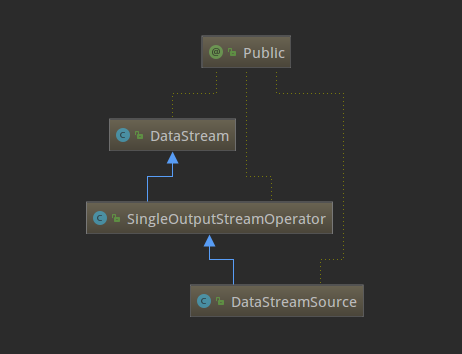
数据流操作
对上面取到的DataStreamSource,进行flatMap、keyBy、timeWindow、reduce转换操作。
DataStream<WordWithCount> windowCounts = text
.flatMap(new FlatMapFunction<String, WordWithCount>() {
@Override
public void flatMap(String value, Collector<WordWithCount> out) {
for (String word : value.split("\s")) {
out.collect(new WordWithCount(word, 1L));
}
}
})
.keyBy("word")
.timeWindow(Time.seconds(5))
.reduce(new ReduceFunction<WordWithCount>() {
@Override
public WordWithCount reduce(WordWithCount a, WordWithCount b) {
return new WordWithCount(a.word, a.count + b.count);
}
});
这段逻辑中,对上面取到的DataStreamSource数据流分别做了flatMap、keyBy、timeWindow、reduce四个转换操作,下面说一下flatMap转换,其他三个转换操作读者可以试着自己查看源码理解一下。
先看一下flatMap方法的源码吧,如下。
//代码目录:org/apache/flink/streaming/api/datastream/DataStream.java
public <R> SingleOutputStreamOperator<R> flatMap(FlatMapFunction<T, R> flatMapper) {
TypeInformation<R> outType = TypeExtractor.getFlatMapReturnTypes(clean(flatMapper),
getType(), Utils.getCallLocationName(), true);
return transform("Flat Map", outType, new StreamFlatMap<>(clean(flatMapper)));
}
这里面做了两件事,一是用反射拿到了flatMap算子的输出类型,二是生成了一个operator。flink流式计算的核心概念就是将数据从输入流一个个传递给operator进行链式处理,最后交给输出流的过程。对数据的每一次处理在逻辑上成为一个operator。上面代码中的最后一行transform方法的作用是返回一个SingleOutputStreamOperator,它继承了Datastream类并且定义了一些辅助方法,方便对流的操作。在返回之前,transform方法还把它注册到了执行环境中。下面这张图是一个由Flink程序映射为Streaming Dataflow的示意图:
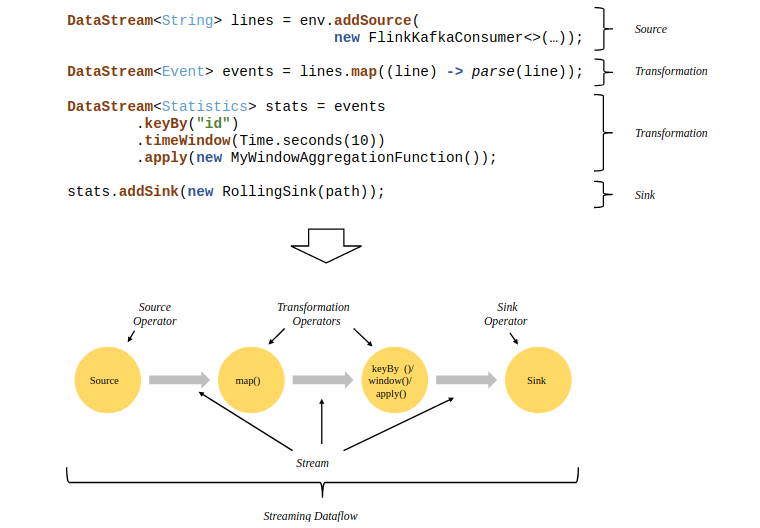
结果输出
windowCounts.print().setParallelism(1);
每个Flink程序都是以source开始以sink结尾,这里的print方法就是把计算出来的结果sink标准输出流。在实际开发中,一般会通过官网提供的各种Connectors或者自定义的Connectors把计算好的结果数据sink到指定的地方,比如Kafka、HBase、FileSystem、Elasticsearch等等。这里的setParallelism是设置此接收器的并行度的,值必须大于零。
执行程序
env.execute("Socket Window WordCount");
Flink有远程模式和本地模式两种执行模式,这两种模式有一点不同,这里按本地模式来解析。先看下execute方法的源码,如下:
//代码目录:org/apache/flink/streaming/api/environment/LocalStreamEnvironment.java
@Override
public JobExecutionResult execute(String jobName) throws Exception {
// transform the streaming program into a JobGraph
StreamGraph streamGraph = getStreamGraph();
streamGraph.setJobName(jobName);
JobGraph jobGraph = streamGraph.getJobGraph();
jobGraph.setAllowQueuedScheduling(true);
Configuration configuration = new Configuration();
configuration.addAll(jobGraph.getJobConfiguration());
configuration.setString(TaskManagerOptions.MANAGED_MEMORY_SIZE, "0");
// add (and override) the settings with what the user defined
configuration.addAll(this.configuration);
if (!configuration.contains(RestOptions.BIND_PORT)) {
configuration.setString(RestOptions.BIND_PORT, "0");
}
int numSlotsPerTaskManager = configuration.getInteger(TaskManagerOptions.NUM_TASK_SLOTS, jobGraph.getMaximumParallelism());
MiniClusterConfiguration cfg = new MiniClusterConfiguration.Builder()
.setConfiguration(configuration)
.setNumSlotsPerTaskManager(numSlotsPerTaskManager)
.build();
if (LOG.isInfoEnabled()) {
LOG.info("Running job on local embedded Flink mini cluster");
}
MiniCluster miniCluster = new MiniCluster(cfg);
try {
miniCluster.start();
configuration.setInteger(RestOptions.PORT, miniCluster.getRestAddress().get().getPort());
return miniCluster.executeJobBlocking(jobGraph);
}
finally {
transformations.clear();
miniCluster.close();
}
}
这个方法包含三部分:将流程序转换为JobGraph、使用用户定义的内容添加(或覆盖)设置、启动一个miniCluster并执行任务。关于JobGraph暂先不讲,这里就只说一下执行任务,跟进下return miniCluster.executeJobBlocking(jobGraph);这行的源码,如下:
//代码目录:org/apache/flink/runtime/minicluster/MiniCluster.java
@Override
public JobExecutionResult executeJobBlocking(JobGraph job) throws JobExecutionException, InterruptedException {
checkNotNull(job, "job is null");
final CompletableFuture<JobSubmissionResult> submissionFuture = submitJob(job);
final CompletableFuture<JobResult> jobResultFuture = submissionFuture.thenCompose(
(JobSubmissionResult ignored) -> requestJobResult(job.getJobID()));
final JobResult jobResult;
try {
jobResult = jobResultFuture.get();
} catch (ExecutionException e) {
throw new JobExecutionException(job.getJobID(), "Could not retrieve JobResult.", ExceptionUtils.stripExecutionException(e);
}
try {
return jobResult.toJobExecutionResult(Thread.currentThread().getContextClassLoader());
} catch (IOException | ClassNotFoundException e) {
throw new JobExecutionException(job.getJobID(), e);
}
}
这段代码的核心逻辑就是final CompletableFuture<JobSubmissionResult> submissionFuture = submitJob(job);,调用了MiniCluster类的submitJob方法,接着看这个方法:
//代码目录:org/apache/flink/runtime/minicluster/MiniCluster.java
public CompletableFuture<JobSubmissionResult> submitJob(JobGraph jobGraph) {
final CompletableFuture<DispatcherGateway> dispatcherGatewayFuture = getDispatcherGatewayFuture();
// we have to allow queued scheduling in Flip-6 mode because we need to request slots
// from the ResourceManager
jobGraph.setAllowQueuedScheduling(true);
final CompletableFuture<InetSocketAddress> blobServerAddressFuture = createBlobServerAddress(dispatcherGatewayFuture);
final CompletableFuture<Void> jarUploadFuture = uploadAndSetJobFiles(blobServerAddressFuture, jobGraph);
final CompletableFuture<Acknowledge> acknowledgeCompletableFuture = jarUploadFuture
.thenCombine(
dispatcherGatewayFuture,
(Void ack, DispatcherGateway dispatcherGateway) -> dispatcherGateway.submitJob(jobGraph, rpcTimeout))
.thenCompose(Function.identity());
return acknowledgeCompletableFuture.thenApply(
(Acknowledge ignored) -> new JobSubmissionResult(jobGraph.getJobID()));
}
这里的Dispatcher组件负责接收作业提交,持久化它们,生成JobManagers来执行作业并在主机故障时恢复它们。Dispatcher有两个实现,在本地环境下启动的是MiniDispatcher,在集群环境上启动的是StandaloneDispatcher。下面是类结构图:
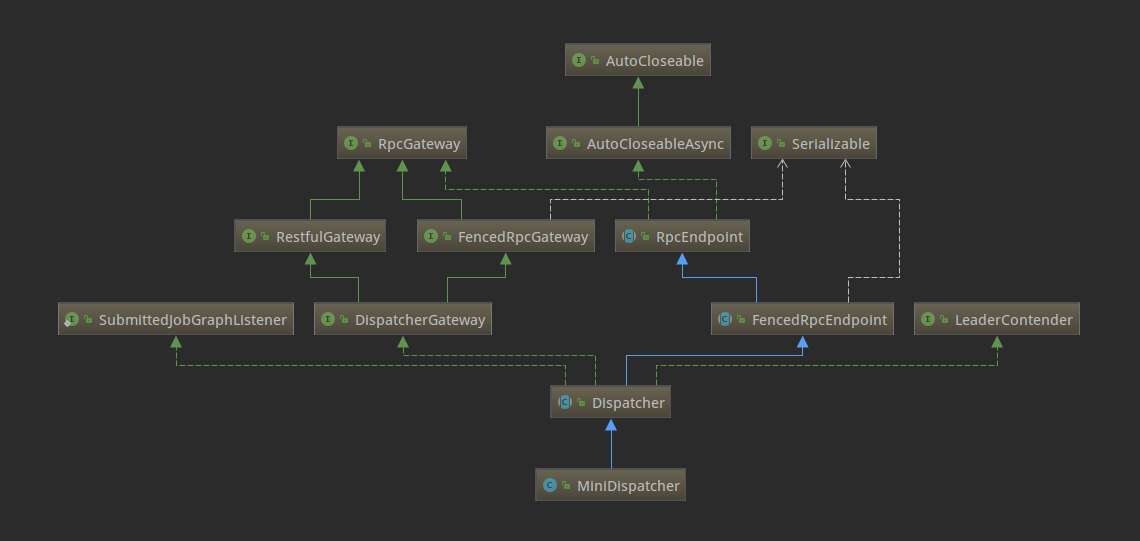
这里的Dispatcher启动了一个JobManagerRunner,委托JobManagerRunner去启动该Job的JobMaster。对应的代码如下:
//代码目录:org/apache/flink/runtime/jobmaster/JobManagerRunner.java
private CompletableFuture<Void> verifyJobSchedulingStatusAndStartJobManager(UUID leaderSessionId) {
final CompletableFuture<JobSchedulingStatus> jobSchedulingStatusFuture = getJobSchedulingStatus();
return jobSchedulingStatusFuture.thenCompose(
jobSchedulingStatus -> {
if (jobSchedulingStatus == JobSchedulingStatus.DONE) {
return jobAlreadyDone();
} else {
return startJobMaster(leaderSessionId);
}
});
}
JobMaster经过一系列方法嵌套调用之后,最终执行到下面这段逻辑:
//代码目录:org/apache/flink/runtime/jobmaster/JobMaster.java
private void scheduleExecutionGraph() {
checkState(jobStatusListener == null);
// register self as job status change listener
jobStatusListener = new JobManagerJobStatusListener();
executionGraph.registerJobStatusListener(jobStatusListener);
try {
executionGraph.scheduleForExecution();
}
catch (Throwable t) {
executionGraph.failGlobal(t);
}
}
这里executionGraph.scheduleForExecution();调用了ExecutionGraph的启动方法。在Flink的图结构中,ExecutionGraph是真正被执行的地方,所以到这里为止,一个任务从提交到真正执行的流程就结束了,下面再回顾一下本地环境下的执行流程:
- 客户端执行
execute方法; MiniCluster完成了大部分任务后把任务直接委派给MiniDispatcher;Dispatcher接收job之后,会实例化一个JobManagerRunner,然后用这个实例启动job;JobManagerRunner接下来把job交给JobMaster去处理;JobMaster使用ExecutionGraph的方法启动整个执行图,整个任务就启动起来了。