控制反转(Inversion of Control,缩写为IoC),是面向对象编程中的一种设计原则,可以用来减低计算机代码之间的耦合度。其中最常见的方式叫做依赖注入(Dependency Injection,简称DI),还有一种方式叫“依赖查找”(Dependency Lookup)。通过控制反转,对象在被创建的时候,由一个调控系统内所有对象的外界实体,将其所依赖的对象的引用传递给它。也可以说,依赖被注入到对象中
注入布局
首先是注入布局,这也是注入中相对简单的注入
在没有使用注入的时候,会使用setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);去加载布局,而使用注入以后就可以直接注入布局了
首先需要一个注入注解
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Target(ElementType.TYPE)
public @interface ContentView {
int value();
}
然后编写一个BaseActivity,让MainActivity继承BaseActivity,在BaseActivity中完成注入说明
public class BaseActivity extends Activity {
@Override
protected void onCreate(@Nullable Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
InjectUtils.injectLayout(this);
}
}
去掉MainActivity中的setContentView()方法,使用注解
@ContentView(R.layout.activity_main)
public class MainActivity extends BaseActivity {
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
}
}
编写注入方法类InjectUtils
public class InjectUtils {
public static void injectLayout(Context context) {
int layoutId = 0;
Class<?> clazz = context.getClass();
//拿到类上面的注解
ContentView contentView = clazz.getAnnotation(ContentView.class);
if (contentView != null) {
layoutId = contentView.value();
try {
Method method = clazz.getMethod("setContentView", int.class);
method.invoke(context,layoutId);
} catch (NoSuchMethodException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IllegalAccessException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (InvocationTargetException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
之后再运行就可以不使用setContentView完成布局注入了
控件注入
控件注入如同布局注入一样,不使用findViewById()方法,再要注入的控件加入id即可
控件注入注解
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Target(ElementType.FIELD)
public @interface ViewInject {
int value();
}
再InjectUtils中加入控件注入方法
public static void injectView(Context context) {
Class<?> aClass = context.getClass();
//获取Activity里面的所有成员变量
Field[] fields=aClass.getDeclaredFields();
for (Field field : fields) {
//得到需要注入的View
ViewInject viewInject = field.getAnnotation(ViewInject.class);
if (viewInject != null) {
//获取ID
int valueId = viewInject.value();
try {
Method method = aClass.getMethod("findViewById", int.class);
//反射调用方法
View view = (View) method.invoke(context, valueId);
field.setAccessible(true);
field.set(context, view);
} catch (NoSuchMethodException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IllegalAccessException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (InvocationTargetException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
最后再调用即可
@ContentView(R.layout.activity_main)
public class MainActivity extends BaseActivity {
@ViewInject(R.id.text_view)
private TextView textView;
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
//InjectUtils.injectLayout(this); //BaseActivity中已经执行过
InjectUtils.injectView(this);
textView.setText("IOC View Inject");
}
}
此处必须要有一个id,在注入完成以后,界面正常显示,并且TextView的显示文字变为IOC View Inject,完成布局和控件的注入
效果如下

事件注入
在之前,监听一个事件,其操作还是相对来说比较繁琐的,比如Button按键的监听就使用如下方法
button.setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(View v) {
}
});
这里使用注入,其过程比布局和控件注入稍微复杂一点,这是考虑到了扩展性,不能单一使用id完成注解
事件的监听包含事件源,事件和回调,因此其注解就稍微复杂一点,这里设计一个监听各种点击事件的监听,包括普通单击,长按,itemclick等
首先依旧是需要一个注解
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Target(ElementType.ANNOTATION_TYPE)
public @interface EventInject {
//设置监听
String listenerSetter();
//事件类型
Class<?> listenerType();
//回调方法
String callBackMethod();
}
这是为了拓展方便的一个接口,用在注解上,接下来是单击和长按的注解
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Target(ElementType.METHOD)
@EventInject(listenerSetter = "setOnClickListener",
listenerType = View.OnClickListener.class,
callBackMethod = "onClick")
public @interface OnClick {
int[] value() default -1;
}
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Target(ElementType.METHOD)
@EventInject(listenerSetter = "setOnLongClickListener",
listenerType = View.OnLongClickListener.class,
callBackMethod = "onLongClick")
public @interface OnLongClick {
int[] value() default -1;
}
这里还需要一个动态代理
public class ListenerInvocationHandler implements InvocationHandler {
//真实对象引用
private Context context;
//可能存在多个方法
private Map<String, Method> methodMap;
public ListenerInvocationHandler(Context context, Map<String, Method> methodMap) {
this.context = context;
this.methodMap = methodMap;
}
@Override
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable {
String name = method.getName();
//决定是否需要代理
Method method1 = methodMap.get(name);
if (method1 != null) {
return method1.invoke(context, args);
} else {
return method.invoke(proxy,args);
}
}
}
具体的注入方法
//注入事件
public static void injectEvent(Context context) {
Class<?> aClass = context.getClass();
//获取所有方法
Method[] methods = aClass.getDeclaredMethods();
for (Method method : methods) {
//获取方法上所有注解
Annotation[] annotations = method.getAnnotations();
for (Annotation annotation : annotations) {
//获取annotationType注解
Class<?> annotationType = annotation.annotationType();
EventInject eventInject = annotationType.getAnnotation(EventInject.class);
if (eventInject == null) {
continue;
}
//获取事件三要素,进行注入
String listenerSetter = eventInject.listenerSetter();
Class<?> listenerType = eventInject.listenerType();
String callBackMethod = eventInject.callBackMethod();
Map<String, Method> methodMap = new HashMap<>();
methodMap.put(callBackMethod, method);
try {
Method valueMethod = annotationType.getDeclaredMethod("value");
int[] valueIds = (int[]) valueMethod.invoke(annotation);
for (int valueId : valueIds) {
Method findViewById = aClass.getMethod("findViewById", int.class);
View view = (View) findViewById.invoke(context, valueId);
if (view == null) {
continue;
}
Method setListener = view.getClass().getMethod(listenerSetter, listenerType);
//使用动态代理
ListenerInvocationHandler handler = new ListenerInvocationHandler(context, methodMap);
Object proxy = Proxy.newProxyInstance(listenerType.getClassLoader(),
new Class[]{listenerType}, handler);
setListener.invoke(view, proxy);
}
} catch (NoSuchMethodException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IllegalAccessException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (InvocationTargetException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
由于三个注入都使用了,所以在InjectUtils添加静态方法,在BaseActivity中调用
public static void inject(Context context){
injectLayout(context);
injectView(context);
injectEvent(context);
}
在Activity中调用
@ContentView(R.layout.activity_main)
public class MainActivity extends BaseActivity {
@ViewInject(R.id.text_view)
private TextView textView;
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
textView.setText("IOC View Inject");
}
@OnClick({R.id.onclick_button_one, R.id.onclick_button_two})
public void click(View view) {
switch (view.getId()) {
case R.id.onclick_button_one:
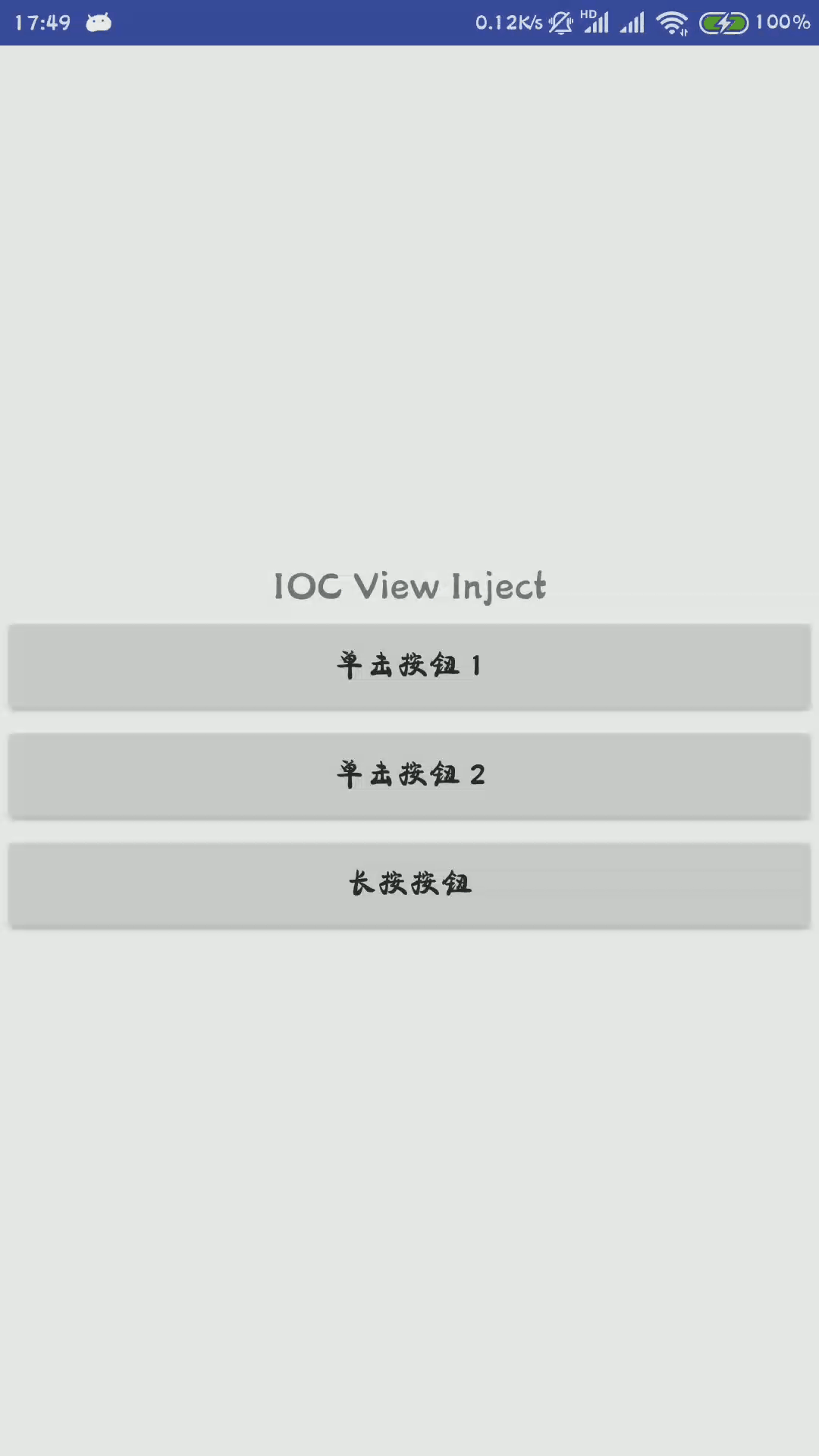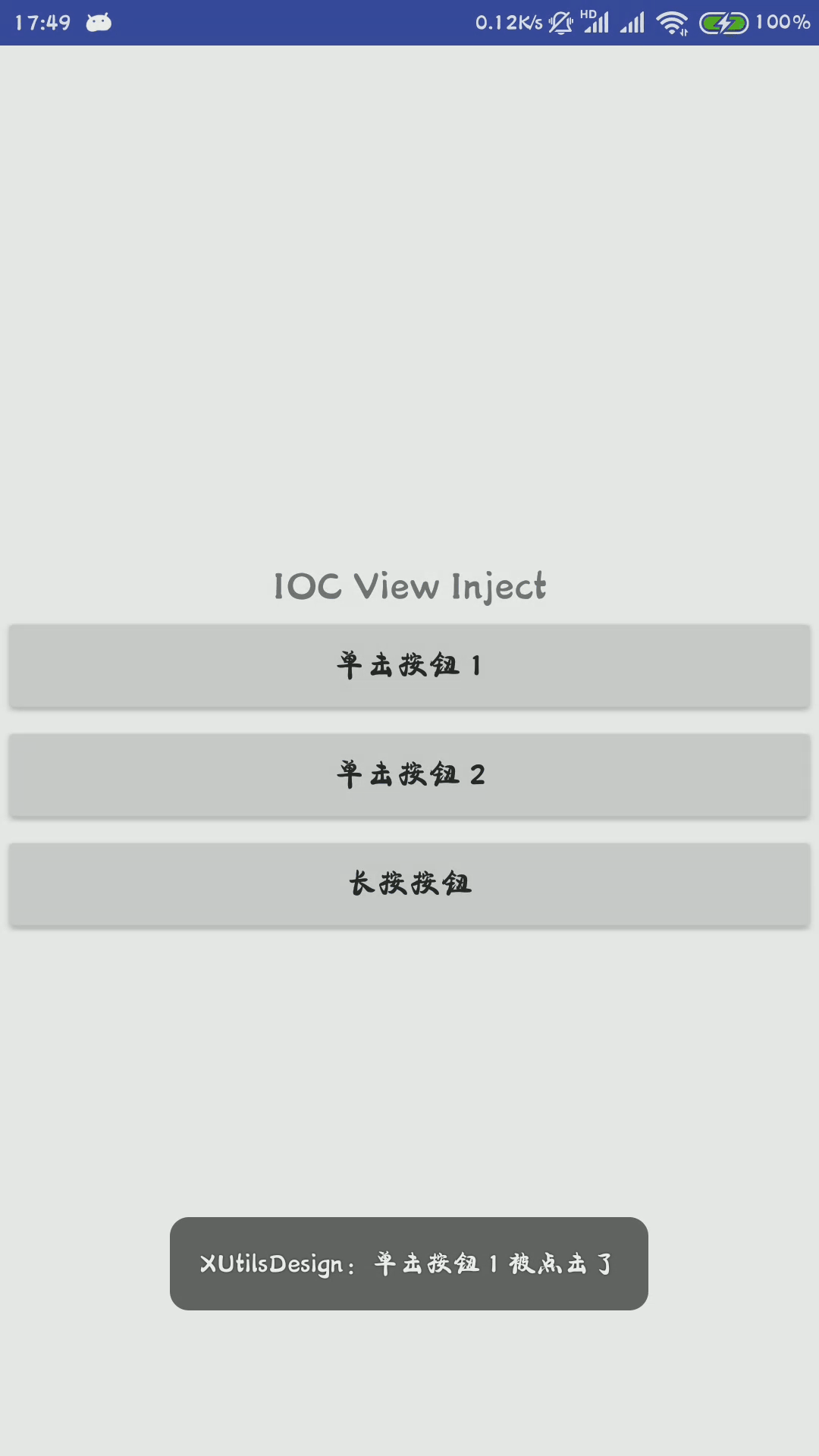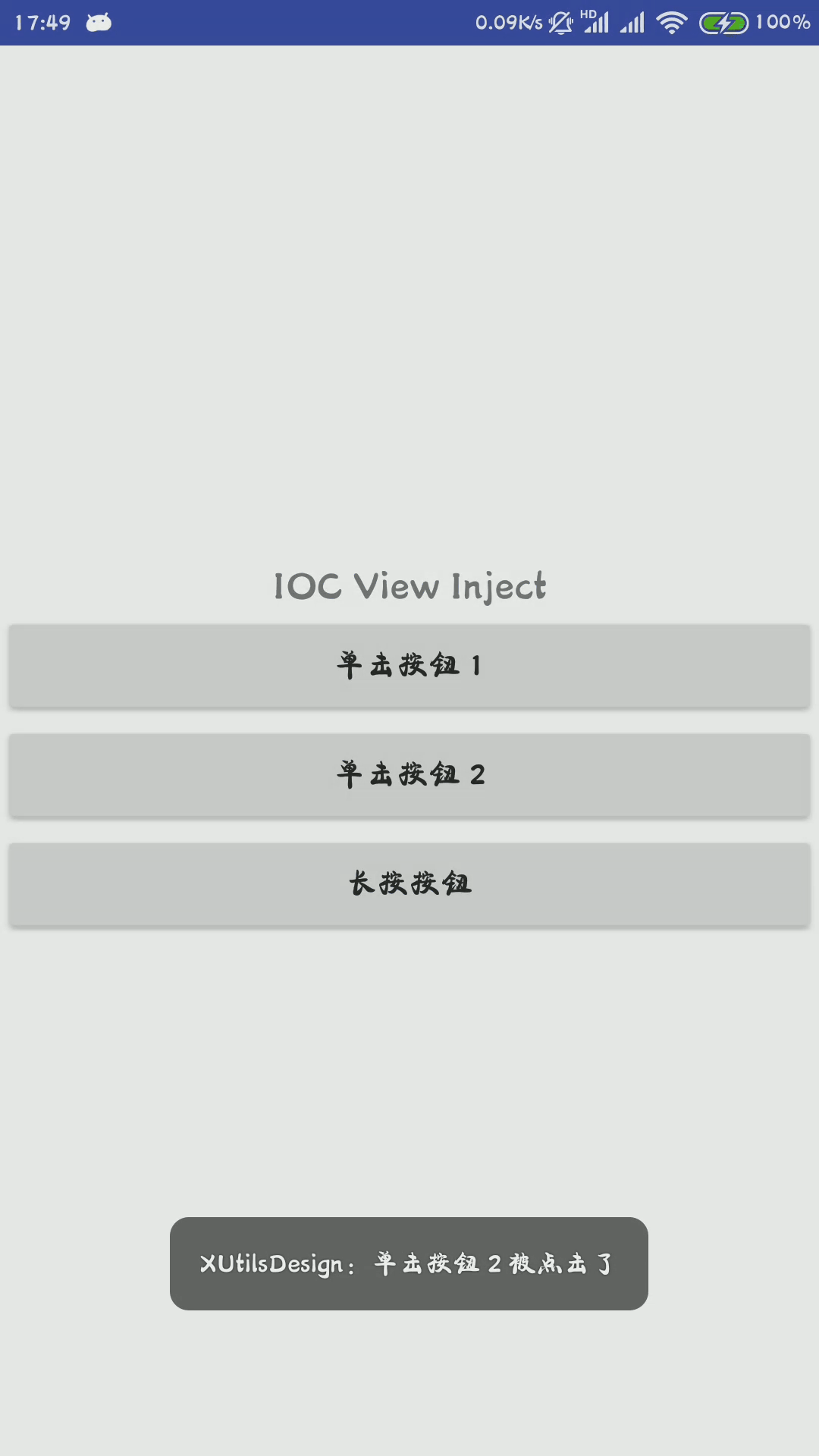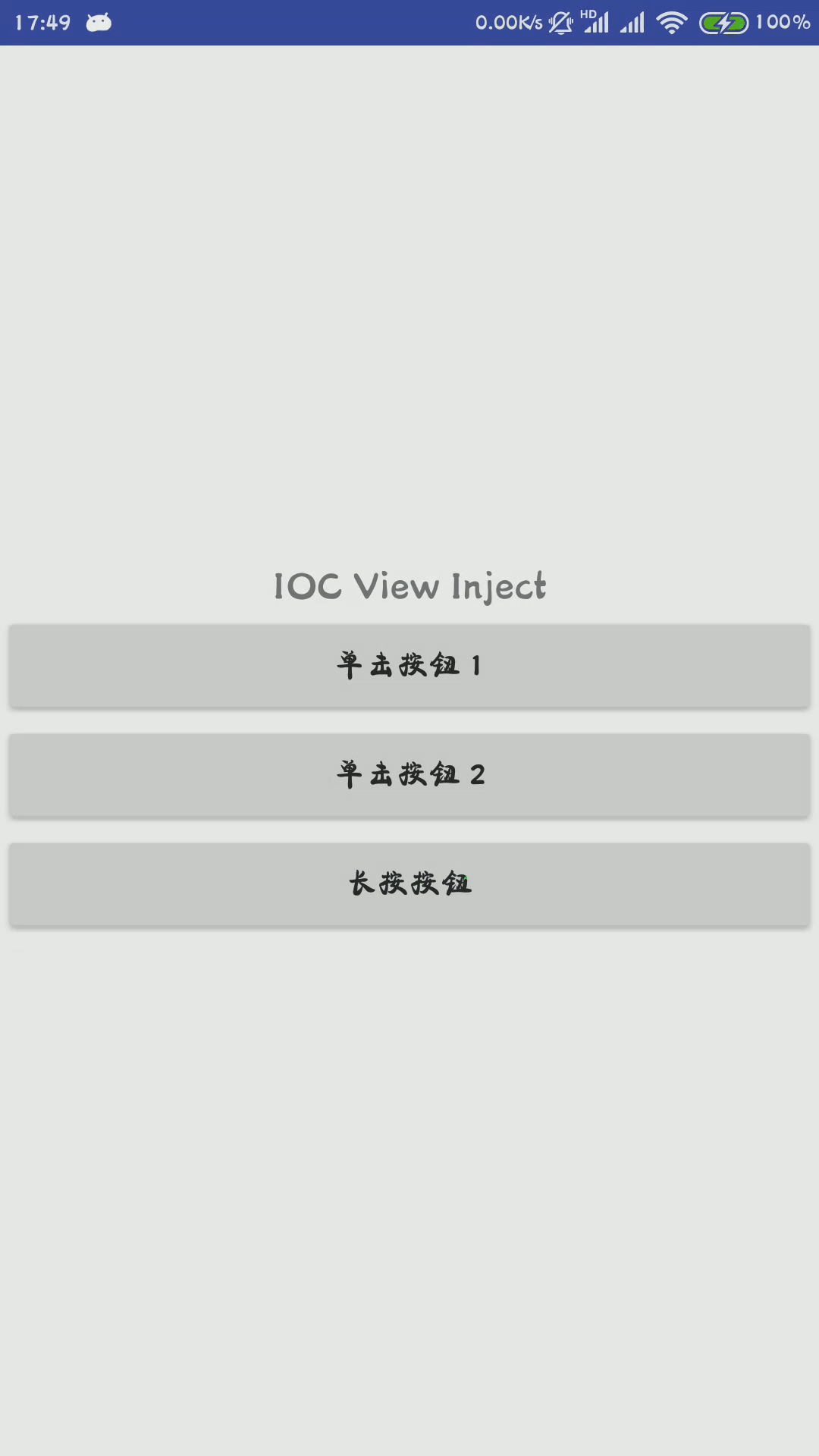
Toast.makeText(this, "单击按钮 1 被点击了", Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show();
break;
case R.id.onclick_button_two:
Toast.makeText(this, "单击按钮 2 被点击了", Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show();
break;
}
}
@OnLongClick(R.id.onlongclick_button)
public boolean longClick(View view) {
Toast.makeText(this, "长按被点击了", Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show();
return false;
}
}
布局如下,就是一个文本,三个按钮
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:orientation="vertical"
android:gravity="center">
<TextView
android:id="@+id/text_view"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:gravity="center"
android:text="Hello World!"
android:textSize="18sp" />
<Button
android:id="@+id/onclick_button_one"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="单击按钮 1" />
<Button
android:id="@+id/onclick_button_two"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="单击按钮 2" />
<Button
android:id="@+id/onlongclick_button"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="长按按钮" />
</LinearLayout>
其实现的效果如下