事件传递在Android中有着举足轻重的作用,那么事件的传递在Android中又是怎么样实现的呢,在这里我们将进一步探讨Android的事件传递机制
从一个例子入手
首先是一个简单的onTouch和onClick事件的例子
public class TouchAndClickActivity extends AppCompatActivity implements View.OnTouchListener, View.OnClickListener {
private static final String TAG = "TouchAndClickActivity";
private LinearLayout linearLayout;
private Button button;
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_touch_and_click);
linearLayout = findViewById(R.id.linear_layout);
button = findViewById(R.id.button);
linearLayout.setOnTouchListener(this);
button.setOnTouchListener(this);
linearLayout.setOnClickListener(this);
button.setOnClickListener(this);
}
@Override
public boolean onTouch(View v, MotionEvent event) {
Log.d(TAG, "onTouch: view -> " + v.getClass().getSimpleName());
return false;
}
@Override
public void onClick(View v) {
Log.d(TAG, "onClick: view -> " + v.getClass().getSimpleName());
}
}
此时观察打印日志
D/TouchAndClickActivity: onTouch: view -> AppCompatButton
D/TouchAndClickActivity: onTouch: view -> AppCompatButton
D/TouchAndClickActivity: onClick: view -> AppCompatButton
D/TouchAndClickActivity: onTouch: view -> LinearLayout
D/TouchAndClickActivity: onTouch: view -> LinearLayout
D/TouchAndClickActivity: onClick: view -> LinearLayout
经过观察发现,控件的事件触发顺序是先onTouch再onClick,并且onTouch会在触摸和松开时各执行一次,并且onClick是在抬起时候执行的,相当于keyUp
然后我们修改onTouch的返回值为true,再次实验,观察输出日志
D/TouchAndClickActivity: onTouch: view -> AppCompatButton
D/TouchAndClickActivity: onTouch: view -> AppCompatButton
D/TouchAndClickActivity: onTouch: view -> LinearLayout
D/TouchAndClickActivity: onTouch: view -> LinearLayout
通过修改onTouch的返回值,我们得到这样的结论:当onTouch返回true时,代表事件被消费了,不会再向下传递,即onClick事件不会得到执行
那么为何会产生上面的现象呢,这其实是由于View的事件分发机制造成的,接下来就来看一看View的事件分发机制具体是怎么做的
View的事件分发
要知道View的事件分发机制是如何运行的,我们就需要到源码中去一探究竟,由于View的代码比较庞大,这里只需要重点关注的有如下四个点(这里以SDK25的源代码为例)
dispatchTouchEvent()
onTouchListener.onTouch()
onTouchEvent()
onClickListener.onClick()
首先到dispatchTouchEvent(),这里是处理事件的地方
/**
* Pass the touch screen motion event down to the target view, or this
* view if it is the target.
*
* @param event The motion event to be dispatched.
* @return True if the event was handled by the view, false otherwise.
*/
public boolean dispatchTouchEvent(MotionEvent event) {
// If the event should be handled by accessibility focus first.
if (event.isTargetAccessibilityFocus()) {
// We don't have focus or no virtual descendant has it, do not handle the event.
if (!isAccessibilityFocusedViewOrHost()) {
return false;
}
// We have focus and got the event, then use normal event dispatch.
event.setTargetAccessibilityFocus(false);
}
boolean result = false;
if (mInputEventConsistencyVerifier != null) {
mInputEventConsistencyVerifier.onTouchEvent(event, 0);
}
final int actionMasked = event.getActionMasked();
if (actionMasked == MotionEvent.ACTION_DOWN) {
// Defensive cleanup for new gesture
stopNestedScroll();
}
if (onFilterTouchEventForSecurity(event)) {
if ((mViewFlags & ENABLED_MASK) == ENABLED && handleScrollBarDragging(event)) {
result = true;
}
//noinspection SimplifiableIfStatement
ListenerInfo li = mListenerInfo;
if (li != null && li.mOnTouchListener != null
&& (mViewFlags & ENABLED_MASK) == ENABLED
&& li.mOnTouchListener.onTouch(this, event)) {
result = true;
}
if (!result && onTouchEvent(event)) {
result = true;
}
}
if (!result && mInputEventConsistencyVerifier != null) {
mInputEventConsistencyVerifier.onUnhandledEvent(event, 0);
}
// Clean up after nested scrolls if this is the end of a gesture;
// also cancel it if we tried an ACTION_DOWN but we didn't want the rest
// of the gesture.
if (actionMasked == MotionEvent.ACTION_UP ||
actionMasked == MotionEvent.ACTION_CANCEL ||
(actionMasked == MotionEvent.ACTION_DOWN && !result)) {
stopNestedScroll();
}
return result;
}
这其中需要重点关注的代码如下
if (onFilterTouchEventForSecurity(event)) {
if ((mViewFlags & ENABLED_MASK) == ENABLED && handleScrollBarDragging(event)) {
result = true;
}
//noinspection SimplifiableIfStatement
ListenerInfo li = mListenerInfo;
if (li != null && li.mOnTouchListener != null
&& (mViewFlags & ENABLED_MASK) == ENABLED
&& li.mOnTouchListener.onTouch(this, event)) {
result = true;
}
if (!result && onTouchEvent(event)) {
result = true;
}
}
这里面的ListenerInfo是一个内部类,保存了View的所有监听
再看这个判断条件
if (li != null && li.mOnTouchListener != null
&& (mViewFlags & ENABLED_MASK) == ENABLED
&& li.mOnTouchListener.onTouch(this, event)) {
result = true;
}
里面涉及到了onTouch方法,正是因为这样,当onTouch返回true的时候,result = true得以执行,并且这里一旦赋值,后面的判断条件就为false,即不会再执行onTouchEvent(event),并且最终返回的result就是true了,如果onTouch返回的是false,那么就会执行onTouchEvent(event),在onTouchEvent(event)里面主要涉及到以下四种状态
MotionEvent.ACTION_UP
MotionEvent.ACTION_DOWN
MotionEvent.ACTION_CANCEL
MotionEvent.ACTION_MOVE
而在UP中,我们找到了点击事件
mPerformClick -> new PerformClick() -> performClickInternal() -> performClick()
在performClick()里面,就看到了click方法
public boolean performClick() {
// We still need to call this method to handle the cases where performClick() was called
// externally, instead of through performClickInternal()
notifyAutofillManagerOnClick();
final boolean result;
final ListenerInfo li = mListenerInfo;
if (li != null && li.mOnClickListener != null) {
playSoundEffect(SoundEffectConstants.CLICK);
li.mOnClickListener.onClick(this);
result = true;
} else {
result = false;
}
sendAccessibilityEvent(AccessibilityEvent.TYPE_VIEW_CLICKED);
notifyEnterOrExitForAutoFillIfNeeded(true);
return result;
}
之所以绕这么大个弯,是要保证安全
通过以上的源代码分析,我们可以得出以下结论
- 当
onTouchListener的onTouch方法返回了true,那么view里面的onTouchEvent就不会被调用了,返回false时候才会调用onTouchEvent - 如果
view为disenable,则onTouchListener里面不会执行,但是会执行onTouchEvent(event)方法 onTouchEvent方法中的ACTION_UP分支中触发onclick事件监听- 其顺序为
dispatchTouchEvent() -> onTouchListener.onTouch()[return false] -> onTouchEvent() -> onClickListener.onClick()
到这里就解释了为何onTouch的返回值会控制到onClick的执行了
那么来验证下我们的猜想,自定义一个Button,主要打印dispatchTouchEvent()和onTouchEvent()的执行时机
public class MyButton extends AppCompatButton {
private static final String TAG = "cj5785";
public MyButton(Context context, AttributeSet attrs) {
super(context, attrs);
}
@Override
public boolean dispatchTouchEvent(MotionEvent event) {
Log.d(TAG, "dispatchTouchEvent : action -> " + event.getAction());
return super.dispatchTouchEvent(event);
}
@Override
public boolean onTouchEvent(MotionEvent event) {
Log.d(TAG, "onTouchEvent : action -> " + event.getAction());
return super.onTouchEvent(event);
}
}
在log中看到以下信息,完成了两次dispatchTouchEvent,一次按下,一次抬起(试验时,onTouch返回false)
D/cj5785: dispatchTouchEvent : action -> 0
D/TouchAndClickActivity: onTouch: view -> MyButton
D/cj5785: onTouchEvent : action -> 0
D/cj5785: dispatchTouchEvent : action -> 1
D/TouchAndClickActivity: onTouch: view -> MyButton
D/cj5785: onTouchEvent : action -> 1
D/TouchAndClickActivity: onClick: view -> MyButton
此时再来看看onTouchEvent(),如果该写为以下代码
@Override
public boolean onTouchEvent(MotionEvent event) {
Log.d(TAG, "onTouchEvent : action -> " + event.getAction());
super.onTouchEvent(event);
return true;
}
打印日志如下
D/cj5785: dispatchTouchEvent : action -> 0
D/TouchAndClickActivity: onTouch: view -> MyButton
D/cj5785: onTouchEvent : action -> 0
D/cj5785: dispatchTouchEvent : action -> 1
D/TouchAndClickActivity: onTouch: view -> MyButton
D/cj5785: onTouchEvent : action -> 1
D/TouchAndClickActivity: onClick: view -> MyButton
返回false时,打印如下
D/cj5785: dispatchTouchEvent : action -> 0
D/TouchAndClickActivity: onTouch: view -> MyButton
D/cj5785: onTouchEvent : action -> 0
D/TouchAndClickActivity: onTouch: view -> LinearLayout
D/TouchAndClickActivity: onTouch: view -> LinearLayout
D/TouchAndClickActivity: onClick: view -> LinearLayout
直接使用true,不使用super
@Override
public boolean onTouchEvent(MotionEvent event) {
Log.d(TAG, "onTouchEvent : action -> " + event.getAction());
return true;
}
打印日志如下
D/cj5785: dispatchTouchEvent : action -> 0
D/TouchAndClickActivity: onTouch: view -> MyButton
D/cj5785: onTouchEvent : action -> 0
D/cj5785: dispatchTouchEvent : action -> 1
D/TouchAndClickActivity: onTouch: view -> MyButton
D/cj5785: onTouchEvent : action -> 1
如果直接返回false,打印如下
D/cj5785: dispatchTouchEvent : action -> 0
D/TouchAndClickActivity: onTouch: view -> MyButton
D/cj5785: onTouchEvent : action -> 0
D/TouchAndClickActivity: onTouch: view -> LinearLayout
D/TouchAndClickActivity: onTouch: view -> LinearLayout
D/TouchAndClickActivity: onClick: view -> LinearLayout
通过以上实验发现,onTouchEvent的返回值决定是否继续传递事件,第一个super+true,代表调用父类方法,然后返回true,也就是说在调完父类方法以后,消费此次事件,不再传递。第二个super+false,表示不消费此次事件,继续传递,此时传递给父布局,所以打印出LinearLayout,同时事件在后面被处理了,第三个true,表示消费此次事件,不再传递,由于没有super,自然也就没有click方法调用,第四个,表示不消费此次事件,继续传递,父布局继续处理
再来,如果dispatchTouchEvent()的返回值直接返回true,而不使用super,那么将会什么都执行不到,这也从另一侧说明了dispatchTouchEvent()是事件分发的入口
其实dispatchTouchEvent()的返回值的作用可以从调用处看出
public final boolean dispatchPointerEvent(MotionEvent event) {
if (event.isTouchEvent()) {
return dispatchTouchEvent(event);
} else {
return dispatchGenericMotionEvent(event);
}
}
ViewGroup和View的事件分发
这里我们关注的三个方法为
dispatchTouchEvent()
onTouchEvent()
onInterceptTouchEvent()
自定义一个LinearLayout,然后包裹自定义的Button,自定义Button中返回的是super
public class MyLinearLayout extends LinearLayout {
private static final String TAG = "cj5785";
public MyLinearLayout(Context context, @Nullable AttributeSet attrs) {
super(context, attrs);
}
@Override
public boolean dispatchTouchEvent(MotionEvent ev) {
Log.d(TAG, "dispatchTouchEvent: view->" + getClass().getSimpleName() + ",action->" + ev.getAction());
return super.dispatchTouchEvent(ev);
}
@Override
public boolean onInterceptTouchEvent(MotionEvent ev) {
Log.d(TAG, "onInterceptTouchEvent: view->" + getClass().getSimpleName() + ",action->" + ev.getAction());
return super.onInterceptTouchEvent(ev);
}
@Override
public boolean onTouchEvent(MotionEvent event) {
Log.d(TAG, "onTouchEvent: view->" + getClass().getSimpleName() + ",action->" + event.getAction());
return super.onTouchEvent(event);
}
}
得到的打印日志
D/cj5785: dispatchTouchEvent: view->MyLinearLayout,action->0
D/cj5785: onInterceptTouchEvent: view->MyLinearLayout,action->0
D/cj5785: dispatchTouchEvent: view->MyButton,action->0
D/TouchAndClickActivity: onTouch: view -> MyButton
D/cj5785: onTouchEvent: view->MyButton,action->0
D/cj5785: dispatchTouchEvent: view->MyLinearLayout,action->1
D/cj5785: onInterceptTouchEvent: view->MyLinearLayout,action->1
D/cj5785: dispatchTouchEvent: view->MyButton,action->1
D/TouchAndClickActivity: onTouch: view -> MyButton
D/cj5785: onTouchEvent: view->MyButton,action->1
D/TouchAndClickActivity: onClick: view -> MyButton
由打印信息得知,先得到事件的是MyLinearLayout,然后再传递给MyButton
先执行dispatchTouchEvent,再执行onInterceptTouchEvent(),由于MyButton消费了事件,所以MyLinearLayout没有执行到onTouchEvent()
此时如果点击的是MyLinearLayout,那么onTouchEvent()就会得到执行
D/cj5785: dispatchTouchEvent: view->MyLinearLayout,action->0
D/cj5785: onInterceptTouchEvent: view->MyLinearLayout,action->0
D/TouchAndClickActivity: onTouch: view -> MyLinearLayout
D/cj5785: onTouchEvent: view->MyLinearLayout,action->0
D/cj5785: dispatchTouchEvent: view->MyLinearLayout,action->1
D/TouchAndClickActivity: onTouch: view -> MyLinearLayout
D/cj5785: onTouchEvent: view->MyLinearLayout,action->1
D/TouchAndClickActivity: onClick: view -> MyLinearLayout
接下来去看看源代码,由于源代码较多,这里就只贴出关键代码
在方法里面,有这样一段代码
// Check for interception.
final boolean intercepted;
if (actionMasked == MotionEvent.ACTION_DOWN
|| mFirstTouchTarget != null) {
final boolean disallowIntercept = (mGroupFlags & FLAG_DISALLOW_INTERCEPT) != 0;
if (!disallowIntercept) {
intercepted = onInterceptTouchEvent(ev);
ev.setAction(action); // restore action in case it was changed
} else {
intercepted = false;
}
} else {
// There are no touch targets and this action is not an initial down
// so this view group continues to intercept touches.
intercepted = true;
}
也就是说,onInterceptTouchEvent()是在这里调用的,查看代码,也只有这一处调用,而在这段代码后面,有很多需要使用intercepted去做判断的地方,onInterceptTouchEvent()源代码如下,其作用就是拦截触摸事件,返回false表示不拦截
public boolean onInterceptTouchEvent(MotionEvent ev) {
if (ev.isFromSource(InputDevice.SOURCE_MOUSE)
&& ev.getAction() == MotionEvent.ACTION_DOWN
&& ev.isButtonPressed(MotionEvent.BUTTON_PRIMARY)
&& isOnScrollbarThumb(ev.getX(), ev.getY())) {
return true;
}
return false;
}
当onInterceptTouchEvent()的返回值为false时候,表示不拦截,就会进入到以下判断,最终调用dispatchTransformedTouchEvent()
if (!canceled && !intercepted) {
···
if (actionMasked == MotionEvent.ACTION_DOWN
|| (split && actionMasked == MotionEvent.ACTION_POINTER_DOWN)
|| actionMasked == MotionEvent.ACTION_HOVER_MOVE) {
···
if (newTouchTarget == null && childrenCount != 0) {
···
for (int i = childrenCount - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
···
if (dispatchTransformedTouchEvent(ev, false, child, idBitsToAssign)) {
...
}
}
}
}
}
而在dispatchTransformedTouchEvent()中,根据其是否有子控件,从而决定调用的dispatchTouchEvent(),到底是将事件交给子控件还是自己处理,其判断就是在这里做出的,事件分发的重难点也就在这,很绕,涉及到ViewGroup的递归和子控件的dispatchTouchEvent()返回值,简单来说就是这里会得到子空间时候会消费事件,如果要消费事件,那么就返回true
private boolean dispatchTransformedTouchEvent(MotionEvent event, boolean cancel,
View child, int desiredPointerIdBits) {
final boolean handled;
···
// Perform any necessary transformations and dispatch.
if (child == null) {
handled = super.dispatchTouchEvent(transformedEvent);
} else {
final float offsetX = mScrollX - child.mLeft;
final float offsetY = mScrollY - child.mTop;
transformedEvent.offsetLocation(offsetX, offsetY);
if (! child.hasIdentityMatrix()) {
transformedEvent.transform(child.getInverseMatrix());
}
handled = child.dispatchTouchEvent(transformedEvent);
}
// Done.
transformedEvent.recycle();
return handled;
}
分析到这,我们也就知道了之前打印出的日志原因了,ViewGroup的事件分发流程也差不多就是这样
ViewGroup的一些细节
上面分析了ViewGroup的事件分发,那么在时间分发时候有哪些是值得注意的呢
第一个地方,在按下时候会清除之前的一些状态
// Handle an initial down.
if (actionMasked == MotionEvent.ACTION_DOWN) {
// Throw away all previous state when starting a new touch gesture.
// The framework may have dropped the up or cancel event for the previous gesture
// due to an app switch, ANR, or some other state change.
cancelAndClearTouchTargets(ev);
resetTouchState();
}
在cancelAndClearTouchTargets()和resetTouchState()里面都调用了clearTouchTargets(),这个方法用来清除TouchTarget,防止触摸操作的干扰,这是调用dispatchTouchEvent()最开始就会执行的代码,保证了mFirstTouchTarget为空
private void clearTouchTargets() {
TouchTarget target = mFirstTouchTarget;
if (target != null) {
do {
TouchTarget next = target.next;
target.recycle();
target = next;
} while (target != null);
mFirstTouchTarget = null;
}
}
第二个地方就是是否拦截,在按下,移动,抬起时候都会做判断,源代码中这样写到
final boolean disallowIntercept = (mGroupFlags & FLAG_DISALLOW_INTERCEPT) != 0;
if (!disallowIntercept) {
intercepted = onInterceptTouchEvent(ev);
ev.setAction(action); // restore action in case it was changed
} else {
intercepted = false;
}
而intercepted代表着是否拦截,而intercepted的赋值取决于disallowIntercept,那么在使用时候会发现有这么一个方法,可以指定是否拦截,而在这里设置的的mGroupFlags会决定disallowIntercept的真假,从而影响intercepted
@Override
public void requestDisallowInterceptTouchEvent(boolean disallowIntercept) {
if (disallowIntercept == ((mGroupFlags & FLAG_DISALLOW_INTERCEPT) != 0)) {
// We're already in this state, assume our ancestors are too
return;
}
if (disallowIntercept) {
mGroupFlags |= FLAG_DISALLOW_INTERCEPT;
} else {
mGroupFlags &= ~FLAG_DISALLOW_INTERCEPT;
}
// Pass it up to our parent
if (mParent != null) {
mParent.requestDisallowInterceptTouchEvent(disallowIntercept);
}
}
第三个是重叠控件的执行问题,有这样一段代码
// Find a child that can receive the event.
// Scan children from front to back.
final ArrayList<View> preorderedList = buildTouchDispatchChildList();
这个方法最终会调用如下方法,也就是按照Z轴的大小从大到小排序,这也就是为何上面的空间会相应
ArrayList<View> buildOrderedChildList() {
final int childrenCount = mChildrenCount;
if (childrenCount <= 1 || !hasChildWithZ()) return null;
if (mPreSortedChildren == null) {
mPreSortedChildren = new ArrayList<>(childrenCount);
} else {
// callers should clear, so clear shouldn't be necessary, but for safety...
mPreSortedChildren.clear();
mPreSortedChildren.ensureCapacity(childrenCount);
}
final boolean customOrder = isChildrenDrawingOrderEnabled();
for (int i = 0; i < childrenCount; i++) {
// add next child (in child order) to end of list
final int childIndex = getAndVerifyPreorderedIndex(childrenCount, i, customOrder);
final View nextChild = mChildren[childIndex];
final float currentZ = nextChild.getZ();
// insert ahead of any Views with greater Z
int insertIndex = i;
while (insertIndex > 0 && mPreSortedChildren.get(insertIndex - 1).getZ() > currentZ) {
insertIndex--;
}
mPreSortedChildren.add(insertIndex, nextChild);
}
return mPreSortedChildren;
}
这段代码就是用来添加view,形成按Z轴大小排序的集合,那么就会先先执行到上面的控件,如果拦截了,下面的控件就得不到执行,不拦截则会执行下去
第四个就是ViewGroup的事件消费问题了
其主要处理逻辑在下列代码中
// Dispatch to touch targets.
if (mFirstTouchTarget == null) {
// No touch targets so treat this as an ordinary view.
handled = dispatchTransformedTouchEvent(ev, canceled, null,
TouchTarget.ALL_POINTER_IDS);
} else {
// Dispatch to touch targets, excluding the new touch target if we already
// dispatched to it. Cancel touch targets if necessary.
TouchTarget predecessor = null;
TouchTarget target = mFirstTouchTarget;
while (target != null) {
final TouchTarget next = target.next;
if (alreadyDispatchedToNewTouchTarget && target == newTouchTarget) {
handled = true;
} else {
final boolean cancelChild = resetCancelNextUpFlag(target.child)
|| intercepted;
if (dispatchTransformedTouchEvent(ev, cancelChild,
target.child, target.pointerIdBits)) {
handled = true;
}
if (cancelChild) {
if (predecessor == null) {
mFirstTouchTarget = next;
} else {
predecessor.next = next;
}
target.recycle();
target = next;
continue;
}
}
predecessor = target;
target = next;
}
}
这里主要是判断,而判断条件在前面做了赋值
newTouchTarget = addTouchTarget(child, idBitsToAssign);
/**
* Adds a touch target for specified child to the beginning of the list.
* Assumes the target child is not already present.
*/
private TouchTarget addTouchTarget(@NonNull View child, int pointerIdBits) {
final TouchTarget target = TouchTarget.obtain(child, pointerIdBits);
target.next = mFirstTouchTarget;
mFirstTouchTarget = target;
return target;
}
在这里就得到了target,如果说此时mFirstTouchTarget为空,那么就是一个普通控件,传递的子控件为nul,不包含touch事件,如果不为空,那么会将touch事件从mFirstTouchTarget链表中一个一个取出来,得到最后能相应事件的View
那么用一张图来说明这个过程

在这里面,省略了dispatchTouchEvent()的返回值,无论dispatchTouchEvent()返回真假,都会告诉调用者
细细品味,细思极恐,这段代码是真的经典!!!
事件分发冲突问题
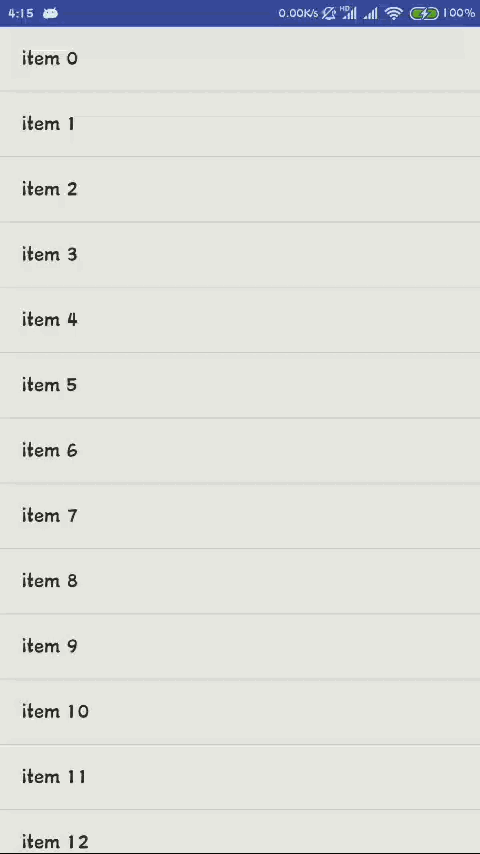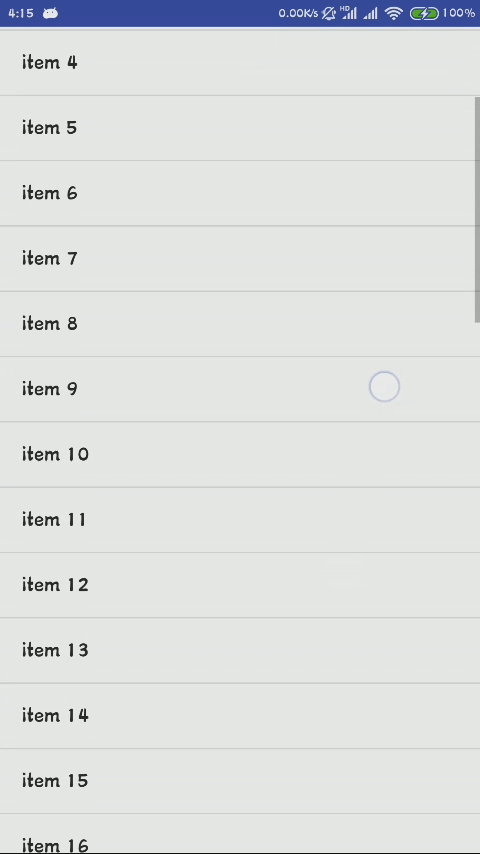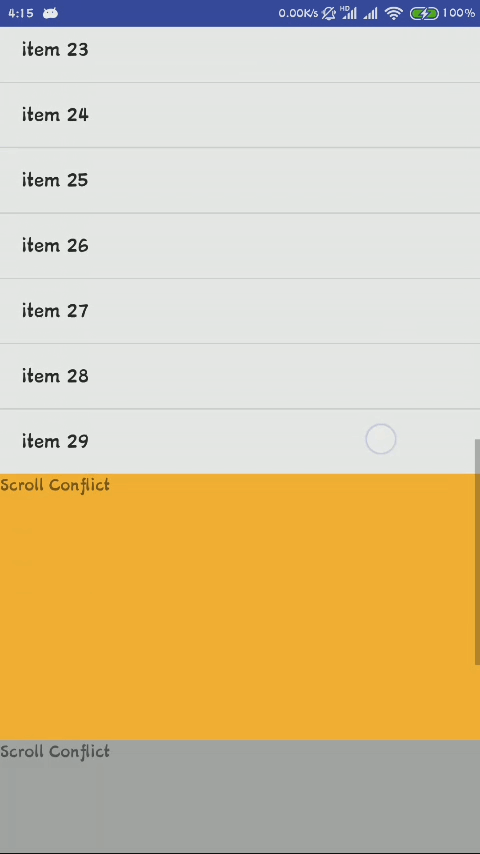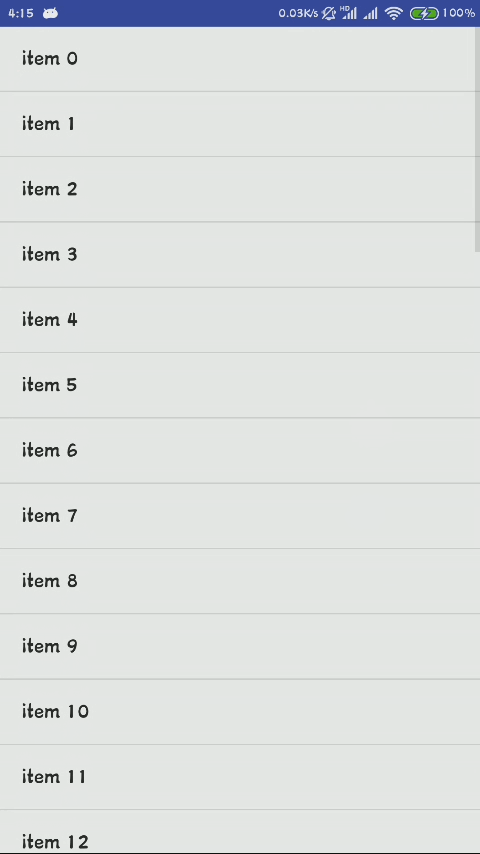
在ScrollView嵌套ListView类似这种情况并且其总高度超过屏幕的时候,会产生冲突
下面来展示这种冲突
首先是一个布局,ScrollView里面嵌套了ListView
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<ScrollView xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:id="@+id/scroll_view"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent">
<LinearLayout
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:orientation="vertical">
<ListView
android:id="@+id/list_view"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="500dp" />
<TextView
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="200dp"
android:background="@android:color/holo_orange_light"
android:text="@string/scroll_conflict" />
<TextView
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="200dp"
android:background="@android:color/darker_gray"
android:text="@string/scroll_conflict" />
<TextView
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="200dp"
android:background="@android:color/holo_green_light"
android:text="@string/scroll_conflict" />
<TextView
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="200dp"
android:background="@android:color/holo_blue_light"
android:text="@string/scroll_conflict" />
</LinearLayout>
</ScrollView>
然后简单的准备ListView的数据
public class ScrollConflictActivity extends AppCompatActivity {
private ListView listView;
private List<String> list;
private ArrayAdapter<String> adapter;
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_scroll_conflict);
listView = findViewById(R.id.list_view);
list = new ArrayList<>();
for (int i = 0; i < 30; i++) {
list.add("item " + i);
}
adapter = new ArrayAdapter<>(this, android.R.layout.simple_list_item_1, list);
listView.setAdapter(adapter);
}
}
然后…
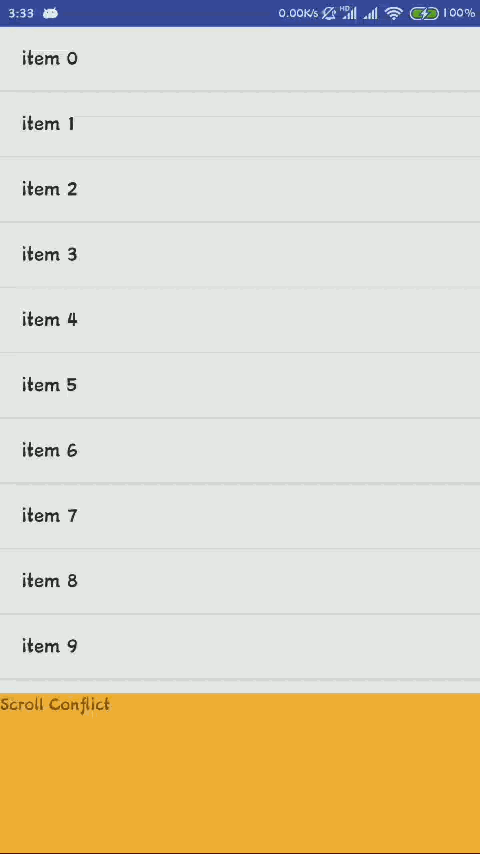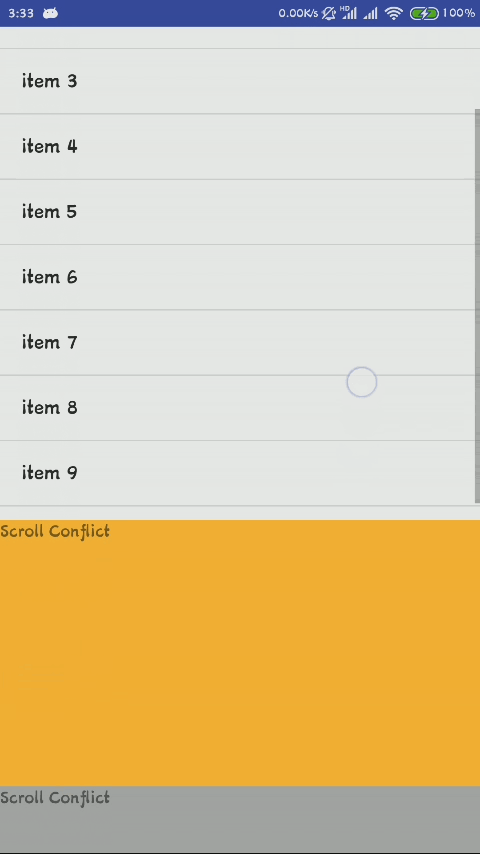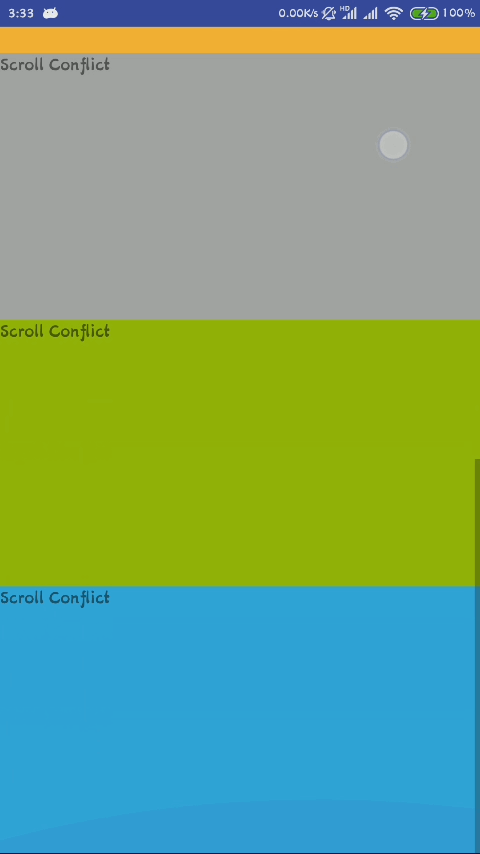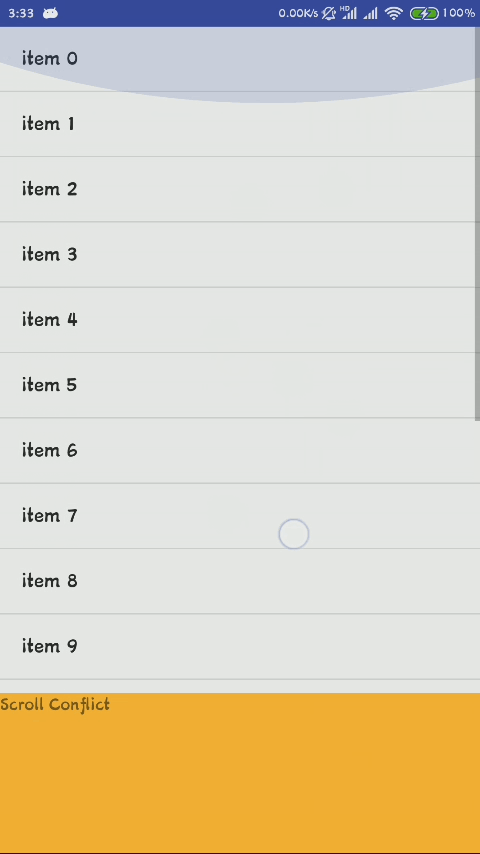
这时候只能滑动整个布局,也就是ScrollView,里面的ListView无法滑动,通过上面源代码的分析,我们知道了造成这种现象的原因就是ScrollView拦截了ListView的滑动,造成ListView无法滑动
所以这时候我们就要让ScrollView不拦截ListView
那么根据对源代码的分析,这里就有很多种解决办法
最简单粗暴的方法就是自定义ScrollView,然后复写dispatchTouchEvent(),调用requestDisallowInterceptTouchEvent(),设置为true
public class MyScrollView extends ScrollView {
public MyScrollView(Context context, AttributeSet attrs) {
super(context, attrs);
}
@Override
public boolean dispatchTouchEvent(MotionEvent ev) {
//不拦截
requestDisallowInterceptTouchEvent(true);
return super.dispatchTouchEvent(ev);
}
}
这样便解决了这个滑动冲突问题
随之而来的又一个问题产生了,要如何展开ListView呢,在这里使用match_parent是没有效果的,那么此时就需要展开ListView了
其实这个的解决办法也是很多的,例如计算每一个条目的高度,相加得到总高度,还有重写onMearsure()方法都可以实现这个效果
public class MyListView extends ListView {
public MyListView(Context context, AttributeSet attrs) {
super(context, attrs);
}
@Override
protected void onMeasure(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec) {
int expandHeight = MeasureSpec.makeMeasureSpec(Integer.MAX_VALUE >> 2, MeasureSpec.AT_MOST);
super.onMeasure(widthMeasureSpec, expandHeight);
}
}
这里只使用自定义ListView,而不使用自定义ScrollView