题面
题解
这个题目主要是连边很奇怪,但是我们可以发现一个性质:权值是递增的。
于是像下图的连边:(加边方式为((A_1, B_1, 1)))
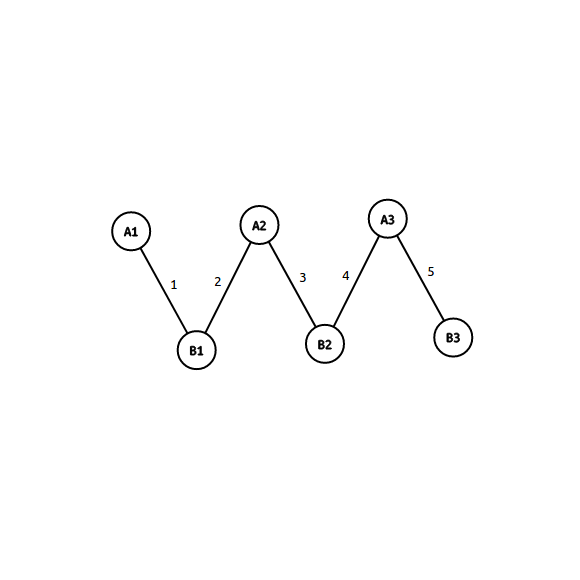
其实可以等价于如下连边:
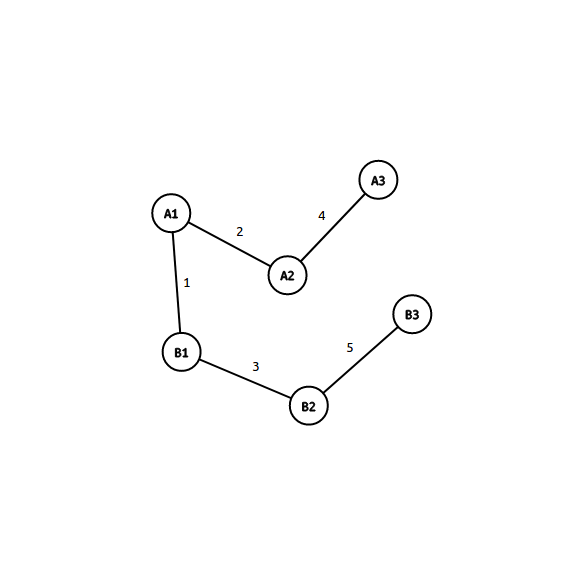
于是我们将其变成了在环上连边。
在环上连边有一点好,就是可以知道边((i,i+1))的边权最小值。
于是将这些边和之前的三元组((a, b, c))放到边集中去,跑kruskal即可。
代码
#include<cstdio>
#include<cstring>
#include<cctype>
#include<algorithm>
#define RG register
#define int long long
inline int read()
{
int data = 0, w = 1; char ch = getchar();
while(ch != '-' && (!isdigit(ch))) ch = getchar();
if(ch == '-') w = -1, ch = getchar();
while(isdigit(ch)) data = data * 10 + (ch ^ 48), ch = getchar();
return data * w;
}
const int maxn(2e5 + 10);
struct edge { int x, y, w; } e[maxn << 2];
inline int cmp(const edge &lhs, const edge &rhs) { return lhs.w < rhs.w; }
int dis[maxn], n, Q, e_num, fa[maxn], ans;
int find(int x) { return fa[x] == x ? x : fa[x] = find(fa[x]); }
template<typename T> inline void chkmin(T &x, const T &y) { if(y < x) x = y; }
inline void add_edge(int x, int y, int w) { e[++e_num] = (edge) {x, y, w}; }
signed main()
{
n = read(), Q = read(); memset(dis, 0x3f, sizeof dis);
for(RG int i = 1, a, b, c; i <= Q; i++)
a = read(), b = read(), c = read(),
add_edge(a, b, c), chkmin(dis[a], c + 1), chkmin(dis[b], c + 2);
for(RG int i = 0; i < n; i++) chkmin(dis[i], dis[(i - 1 + n) % n] + 2);
for(RG int i = 0; i < n; i++) chkmin(dis[i], dis[(i - 1 + n) % n] + 2);
for(RG int i = 0; i < n; i++) add_edge(i, (i + 1) % n, dis[i]), fa[i] = i;
std::sort(e + 1, e + e_num + 1, cmp);
for(RG int i = 1; i <= e_num; i++)
{
if(find(e[i].x) == find(e[i].y)) continue;
fa[find(e[i].x)] = find(e[i].y); ans += e[i].w;
}
printf("%lld
", ans);
return 0;
}