题面
题解
因为这道题目我也不太会做,所以借鉴了一下大佬heyujun的博客
如果不强制在线,这道题目是树上莫队练手题
我们知道莫队是离线的,但是万一强制在线就凉凉了
于是我们就需要一些操作:树分块
看到这个图:
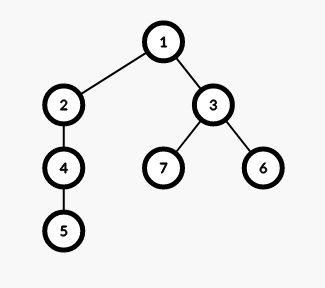
这里有(7)个点,我们每隔(2)深度分块
但是我们要保证分块的连续性,于是分成了((1,2)(7,6,3)(4,5))三块
现在给了你两个将询问的点(u,v(dep[u]>dep[v])),分类讨论:
-
两个点在同一个块内
直接暴力
-
两个点不在同一个块内
这种情况比较复杂,记一个块的根为(rt[i]),则它到另外所有点的答案我们可以很轻松地
统计出来,只需要对于每个(rt[i])暴力统计一遍就可以了。那么现在我们要考虑的只有(u)到它的块的根(x)路径上是否会对答案产生贡献:
对于这个,我们可以将这个分块可持久化,维护这个点的颜色在它的祖先中出现最深的位置
的深度,那么一个块只需继承上面的块,并将在这个块中颜色的答案更新,因为那个颜色如
果出现在这个位置,那么答案肯定更优。有了上面的铺垫,那我们只需对(u o x)上的点暴力算它的深度是否超过(mathrm{LCA}(u, v))即可
代码
#include<cstdio>
#include<cstring>
#include<cctype>
#include<cmath>
#include<algorithm>
#define RG register
#define file(x) freopen(#x".in", "r", stdin), freopen(#x".out", "w", stdout)
#define clear(x, y) memset(x, y, sizeof(x))
inline int read()
{
int data = 0, w = 1; char ch = getchar();
while(ch != '-' && (!isdigit(ch))) ch = getchar();
if(ch == '-') w = -1, ch = getchar();
while(isdigit(ch)) data = data * 10 + (ch ^ 48), ch = getchar();
return data * w;
}
const int maxn(40010), SQRT(210);
struct edge { int next, to; } e[maxn << 1];
int head[maxn], e_num;
inline void add_edge(int from, int to)
{
e[++e_num] = (edge) {head[from], to};
head[from] = e_num;
}
int n, m, Len, a[maxn], b[maxn], _a[maxn], r[maxn];
int P[maxn][SQRT], A[SQRT][maxn], fa[maxn], dep[maxn];
int q[maxn], belong[maxn], top, cnt, SIZE, root[maxn];
int c[maxn], Ans;
struct Block
{
int a[SQRT]; void insert(const Block&, int, int);
int &operator [] (const int &x) { return P[a[b[x]]][r[x]]; }
const int &operator [] (const int &x) const { return P[a[b[x]]][r[x]]; }
} s[maxn];
void Block::insert(const Block &rhs, int x, int d)
{
int blk = b[x], t = r[x];
memcpy(a, rhs.a, sizeof(a));
memcpy(P[++SIZE], P[a[blk]], sizeof(P[0]));
P[a[blk] = SIZE][t] = d;
}
namespace Tree
{
int belong[maxn], heavy[maxn], size[maxn];
void dfs(int x, int chain)
{
belong[x] = chain;
if(!heavy[x]) return;
dfs(heavy[x], chain);
for(RG int i = head[x]; i; i = e[i].next)
{
int to = e[i].to;
if(to == fa[x] || to == heavy[x]) continue;
dfs(to, to);
}
}
int LCA(int x, int y)
{
while(belong[x] != belong[y])
{
if(x[belong][dep] < y[belong][dep]) std::swap(x, y);
x = x[belong][fa];
}
return dep[x] < dep[y] ? x : y;
}
}
int dfs(int x, int f)
{
using Tree::size; using Tree::heavy;
fa[x] = f, size[x] = 1;
s[x].insert(s[f], a[x], dep[x] = dep[f] + 1);
q[++top] = x; int maxd = dep[x], p = top;
for(RG int i = head[x]; i; i = e[i].next)
{
int to = e[i].to; if(to == f) continue;
maxd = std::max(maxd, dfs(to, x)); size[x] += size[to];
if(size[heavy[x]] < size[to]) heavy[x] = to;
}
if(maxd - dep[x] >= Len || p == 1)
{
root[++cnt] = x;
for(RG int i = p; i <= top; i++) belong[q[i]] = cnt;
top = p - 1; return dep[x] - 1;
}
return maxd;
}
void Pre(int x, int f, int *s)
{
if(!c[a[x]]++) ++Ans; s[x] = Ans;
for(RG int i = head[x]; i; i = e[i].next) if(e[i].to != f)
Pre(e[i].to, x, s);
if(!--c[a[x]]) --Ans;
}
int Solve1(int x, int y)
{
for(top = Ans = 0; x != y; x = fa[x])
{
if(dep[x] < dep[y]) std::swap(x, y);
if(!c[q[++top] = a[x]]) c[a[x]] = 1, ++Ans;
}
for(Ans += !c[a[x]]; top;) c[q[top--]] = 0;
return Ans;
}
int Solve2(int x, int y)
{
if(dep[root[belong[x]]] < dep[root[belong[y]]]) std::swap(x, y);
int x1 = root[belong[x]], d = dep[Tree::LCA(x, y)]; Ans = A[belong[x]][y];
for(top = 0; x != x1; x = fa[x])
if(!c[a[x]] && s[x1][a[x]] < d && s[y][a[x]] < d)
c[q[++top] = a[x]] = 1, ++Ans;
while(top) c[q[top--]] = 0;
return Ans;
}
int main()
{
#ifndef ONLINE_JUDGE
freopen("cpp.in", "r", stdin);
#endif
n = read(), m = read(), Len = sqrt(n) - 1;
for(RG int i = 1; i <= n; i++) b[i] = (i - 1) / Len + 1, r[i] = i % Len;
for(RG int i = 1; i <= n; i++) a[i] = _a[i] = read();
std::sort(_a + 1, _a + n + 1);
int tot = std::unique(_a + 1, _a + n + 1) - _a - 1;
for(RG int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
a[i] = std::lower_bound(_a + 1, _a + tot + 1, a[i]) - _a;
for(RG int i = 1, x, y; i < n; i++) x = read(), y = read(),
add_edge(x, y), add_edge(y, x);
top = 0, dfs(1, 0), Tree::dfs(1, 1);
for(RG int i = 1; i <= cnt; i++) Pre(root[i], 0, A[i]);
int ans = 0; while(m--)
{
int x = ans ^ read(), y = read();
printf("%d
", ans = (belong[x] == belong[y] ?
Solve1(x, y) : Solve2(x, y)));
}
return 0;
}