P(wi | wi-1) = count(wi-1, wi) / count(wi-1)
simplify, we can get
p(wi | wi-1) = c(wi-1, wi) / c(wi-1)
Well, we can have a example.

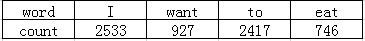
then we can get the probility
P(I want to eat) = P(want| I) * P(to | want) * P(eat | to)
P(want | I) = c(I want) / c(I) = 0.33
P(to | want) = c(want to) / c(want) = 0.66
P(eat | to) = c(to eat) / c(to) = 0.28
In practical, we do everything in log space, because one is avoid underflow, and the other is adding is faster than multiplying.
p1 * p2 * p3 * p4 = logp1 + logp2 + logp3 + logp4
Language toolkit
1. we can download SRILM http://www.speech.sri.com/projects/srilm/
2.Goolge N-Gram Release http://ngrams.googlelabs.com/
3. Google Book N-grams http://googleresearch.blogspot.com/2006/08/all-our-n-gram-are-belong-to-you.html