1、路由:
route() 装饰器用于把一个函数绑定到一个 URL,可以动态变化 URL 的某些部分,还可以为一个函数指定多个规则,从而方便用户访问与记忆。
例子:
@app.route('/') #调用一个app的route方法 def hello_work(): #定义一个处理方法 return '<h1>hello world</h1>'
@app.route('/test') #创建第二个应用,并指定访问路径 def index(): return 'index page'
全部代码为:

1 #coding=utf-8 2 from flask import Flask #导入flask类 3 app = Flask(__name__) #生成该类的一个实例 4 5 @app.route('/') #调用一个app的route方法 6 def hello_work(): #定义一个处理方法 7 return '<h1>hello world</h1>' 8 9 @app.route('/test') #创建第二个应用,并指定访问路径 10 def index(): 11 return 'index page' 12 13 if __name__ == '__main__': #确保服务器只会在使用python解释器运行代码的情况下运行 14 #app.debug = True #第一种方式:在应用对象上设置标志 15 #app.run(host='0.0.0.0') #用host参数,设定全网段可以访问 16 app.run(debug=True,host='0.0.0.0') #第二种方式:作为参数传递给run方法
执行程序,状态为:

# python hello.py * Running on http://0.0.0.0:5000/ (Press CTRL+C to quit) * Restarting with stat 192.168.168.80 - - [09/Apr/2015 15:12:46] "GET / HTTP/1.1" 200 - 192.168.168.80 - - [09/Apr/2015 15:12:51] "GET /test HTTP/1.1" 200 -
两次访问在浏览器中的表现为:
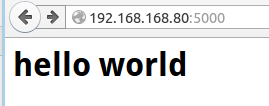
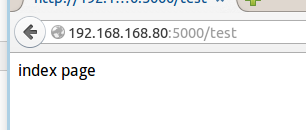
2、变量规则:
第一个例子:
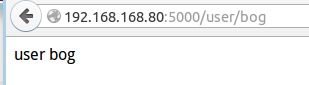
"第三个应用:标记url的一部分<username>,它可以添加变量,作为关键字参数传递给函数。" @app.route('/user/<username>') def show_user_message(username): return 'user %s' % username
效果截图:

第二个例子:
"第四个应用"
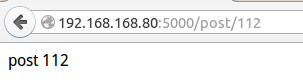
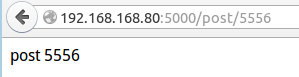
@app.route('/post/<int:post_id>') #转换器有:int、float、path(和缺省状况相同,也接受/ def show_post(post_id): return 'post %d' % post_id
效果截图:
第三个例子:
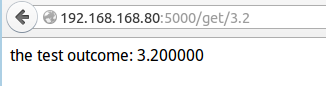
"第五个应用" @app.route('/get/<float:get_nu>') def test(get_nu): return 'the test outcome: %f' % get_nu
效果截图:
至此,全部代码为:

8 return '<h1>hello world</h1>' 9 10 @app.route('/test') #创建第二个应用,并指定访问路径 11 def index(): 12 return 'index page' 13 14 "-------------------------------------二、变量规则例子----------------------------------------" 15 "第三个应用:标记url的一部分<username>,它可以添加变量,作为关键字参数传递给函数。" 16 @app.route('/user/<username>') 17 def show_user_message(username): 18 return 'user %s' % username 19 20 " 第四个应用" 21 @app.route('/post/<int:post_id>') #转换器有:int、float、path(和缺省状况相同,也接受/ 22 def show_post(post_id): 23 return 'post %d' % post_id 24 25 "第五个应用" 26 @app.route('/get/<float:get_nu>') 27 def test(get_nu): 28 return 'the test outcome: %f' % get_nu 29 30 31 if __name__ == '__main__': #确保服务器只会在使用python解释器运行代码的情况下运行 32 #app.debug = True #第一种方式:在应用对象上设置标志 33 #app.run(host='0.0.0.0') #用host参数,设定全网段可以访问 34 app.run(debug=True,host='0.0.0.0') #第二种方式:作为参数传递给run方法
3、url重定向
第一个例子:
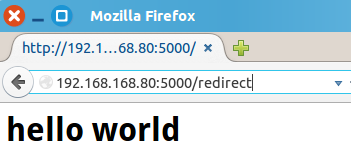
"第六个应用" @app.route('/redirect/') #行为像文件夹,(若末尾没有斜杠,Flask会自动重定向加上) def redirect(): return 'The redirect page'
效果:
 访问后的效果:
访问后的效果: 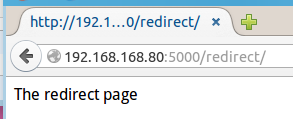
第二个例子:
"第七个应用" @app.route('/redirec') #行为像文件,若访问时在末尾加上斜杠,会得到404错误 def redirect(): return 'The second redirect page'
效果:
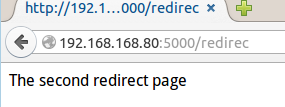 末尾加上斜杠后的效果:
末尾加上斜杠后的效果: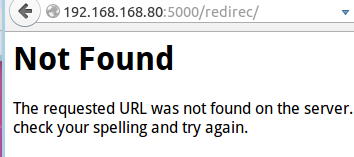
至此,全部代码为:

1 #coding=utf-8 2 from flask import Flask #导入flask类 3 app = Flask(__name__) #生成该类的一个实例 4 5 "------------------------------------一、URL例子--------------------------------------------" 6 @app.route('/') #调用一个app的route方法 7 def hello_work(): #定义一个处理方法 8 return '<h1>hello world</h1>' 9 10 @app.route('/test') #创建第二个应用,并指定访问路径 11 def index(): 12 return 'index page' 13 14 "-------------------------------------二、变量规则例子----------------------------------------" 15 "第三个应用:标记url的一部分<username>,它可以添加变量,作为关键字参数传递给函数。" 16 @app.route('/user/<username>') 17 def show_user_message(username): 18 return 'user %s' % username 19 20 " 第四个应用" 21 @app.route('/post/<int:post_id>') #转换器有:int、float、path(和缺省状况相同,也接受/ 22 def show_post(post_id): 23 return 'post %d' % post_id 24 25 "第五个应用" 26 @app.route('/get/<float:get_nu>') 27 def test(get_nu): 28 return 'the test outcome: %f' % get_nu 29 30 "--------------------------------------三、唯一的URL/重定向行为-----------------------------" 31 #"第六个应用 32 #@app.route('/redirect/') #行为像文件夹,(若末尾没有斜杠,Flask会自动重定向加上) 33 #def redirect(): 34 # return 'The redirect page' 35 #" 36 "第七个应用" 37 @app.route('/redirec') #行为像文件,若访问时在末尾加上斜杠,会得到404错误 38 def redirect(): 39 return 'The second redirect page' 40 41 42 if __name__ == '__main__': #确保服务器只会在使用python解释器运行代码的情况下运行 43 #app.debug = True #第一种方式:在应用对象上设置标志 44 #app.run(host='0.0.0.0') #用host参数,设定全网段可以访问 45 app.run(debug=True,host='0.0.0.0') #第二种方式:作为参数传递给run方法
