本文接下来分析上文涉及到的ObjectIdentityCache接口及相关对象
先熟悉一下继承和依赖关系,简要UML类图如下:
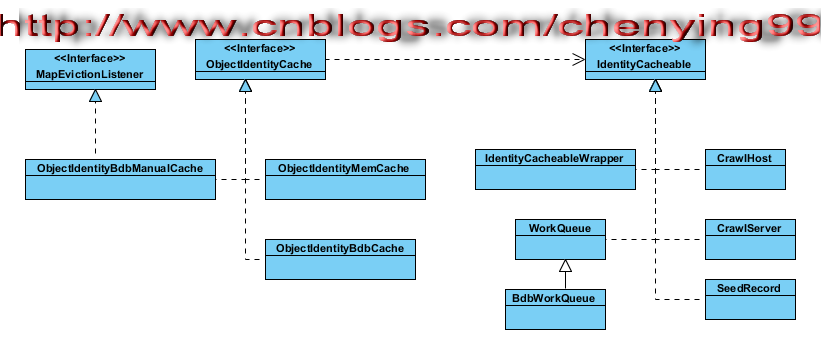
我们先来了解一下ObjectIdentityCache接口的源码(泛型接口)
/** * An object cache for create-once-by-name-and-then-reuse objects. * * Objects are added, but never removed. Subsequent get()s using the * same key will return the exact same object, UNLESS all such objects * have been forgotten, in which case a new object MAY be returned. * * This allows implementors (such as ObjectIdentityBdbCache or * CachedBdbMap) to page out (aka 'expunge') instances to * persistent storage while they're not being used. However, as long as * they are used (referenced), all requests for the same-named object * will share a reference to the same object, and the object may be * mutated in place without concern for explicitly persisting its * state to disk. * * @param <V> */ public interface ObjectIdentityCache<V extends IdentityCacheable> extends Closeable { /** get the object under the given key/name -- but should not mutate * object state*/ public abstract V get(final String key); /** get the object under the given key/name, using (and remembering) * the object supplied by the supplier if no prior mapping exists * -- but should not mutate object state */ public abstract V getOrUse(final String key, Supplier<V> supplierOrNull); /** force the persistent backend, if any, to be updated with all * live object state */ public abstract void sync(); /** force the persistent backend, if any, to eventually be updated with * live object state for the given key */ public abstract void dirtyKey(final String key); /** close/release any associated resources */ public abstract void close(); /** count of name-to-object contained */ public abstract int size(); /** set of all keys */ public abstract Set<String> keySet(); }
该接口是用来管理对象缓存的,而被管理的对象必须是实现了IdentityCacheable接口的对象(泛型)
在heritrix3.1.0系统里面,有三个类实现了ObjectIdentityCache接口,分别为ObjectIdentityBdbCache、ObjectIdentityMemCache、ObjectIdentityBdbManualCache
最重要的是ObjectIdentityBdbManualCache类,我们可以在BdbModule类找到它的初始化方法
/** * Get an ObjectIdentityBdbCache, backed by a BDB Database of the * given name, with the given value class type. If 'recycle' is true, * reuse values already in the database; otherwise start with an * empty cache. * * @param <V> * @param dbName * @param recycle * @param valueClass * @return * @throws DatabaseException */ public <V extends IdentityCacheable> ObjectIdentityBdbManualCache<V> getOIBCCache(String dbName, boolean recycle, Class<? extends V> valueClass) throws DatabaseException { if (!recycle) { try { bdbEnvironment.truncateDatabase(null, dbName, false); } catch (DatabaseNotFoundException e) { // ignored } } ObjectIdentityBdbManualCache<V> oic = new ObjectIdentityBdbManualCache<V>(); oic.initialize(bdbEnvironment, dbName, valueClass, classCatalog); oiCaches.put(dbName, oic); return oic; }
初始化方法里面传入了BDB数据库的环境变量、数据库名、要缓存的对象类名、StoredClassCatalog classCatalog变量(用于对象类型转换)
ObjectIdentityBdbManualCache类是一个泛型类,最重要的成员变量如下:
/** The BDB JE database used for this instance. */ protected transient Database db; /** in-memory map of new/recent/still-referenced-elsewhere instances */ protected transient ConcurrentMap<String,V> memMap; /** The Collection view of the BDB JE database used for this instance. */ protected transient StoredSortedMap<String, V> diskMap; protected transient ConcurrentMap<String,V> dirtyItems; protected AtomicLong count;
上面均为泛型容器(支持同步),其中被管理的对象为V类型(实现IdentityCacheable接口),每个被管理的对象以key/value的形式存储在上面容器中,其中最关键的容器是StoredSortedMap<String, V> diskMap
接下来查看它的初始化方法(它的构造方法很平庸,此处忽略贴出)
/** * Call this method when you have an instance when you used the * default constructor or when you have a deserialized instance that you * want to reconnect with an extant bdbje environment. Do not * call this method if you used the * {@link #CachedBdbMap(File, String, Class, Class)} constructor. * @param env * @param keyClass * @param valueClass * @param classCatalog * @throws DatabaseException */ @SuppressWarnings("unchecked") public void initialize(final Environment env, String dbName, final Class valueClass, final StoredClassCatalog classCatalog) throws DatabaseException { // TODO: tune capacity for actual threads, expected size of key caches? this.memMap = new MapMaker().concurrencyLevel(64).initialCapacity(8192).softValues().makeMap(); this.db = openDatabase(env, dbName); this.diskMap = createDiskMap(this.db, classCatalog, valueClass); // keep a record of items that must be persisted; auto-persist if // unchanged after 5 minutes, or more than 10K would collect this.dirtyItems = new MapMaker().concurrencyLevel(64) .maximumSize(10000).expireAfterWrite(5,TimeUnit.MINUTES) .evictionListener(this).makeMap(); this.count = new AtomicLong(diskMap.size()); }
初始化数据库Database db、内存容器ConcurrentMap<String,V> memMap、BDB容器StoredSortedMap<String, V> diskMap、临时容器ConcurrentMap<String,V> dirtyItems等
Database openDatabase(final Environment environment,final String dbName)方法为根据BDB环境和数据库名创建数据库
protected Database openDatabase(final Environment environment, final String dbName) throws DatabaseException { DatabaseConfig dbConfig = new DatabaseConfig(); dbConfig.setTransactional(false); dbConfig.setAllowCreate(true); dbConfig.setDeferredWrite(true); return environment.openDatabase(null, dbName, dbConfig); }
StoredSortedMap<String, V> createDiskMap(Database database,StoredClassCatalog classCatalog, Class valueClass)方法根据创建的数据库,数据项转换对象以及要存储的类型创建StoredSortedMap<String, V> diskMap对象,显然该对象依赖于BDB数据库(容器里面的项存储于BDB数据库)
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
protected StoredSortedMap<String, V> createDiskMap(Database database,
StoredClassCatalog classCatalog, Class valueClass) {
EntryBinding keyBinding = TupleBinding.getPrimitiveBinding(String.class);
EntryBinding valueBinding = TupleBinding.getPrimitiveBinding(valueClass);
if(valueBinding == null) {
valueBinding =
new KryoBinding<V>(valueClass);
// new SerialBinding(classCatalog, valueClass);
// new BenchmarkingBinding<V>(new EntryBinding[] {
// new KryoBinding<V>(valueClass),
// new RecyclingSerialBinding<V>(classCatalog, valueClass),
// }, valueClass);
}
return new StoredSortedMap<String,V>(database, keyBinding, valueBinding, true);
}
那么Heritrix3.1.0系统里面是怎样重用容器中的被缓存的对象呢?我们在BdbFrontier类的方法里面可以看到如下方法
/** * Return the work queue for the given classKey, or null * if no such queue exists. * * @param classKey key to look for * @return the found WorkQueue */ protected WorkQueue getQueueFor(final String classKey) { WorkQueue wq = allQueues.getOrUse( classKey, new Supplier<WorkQueue>() { public BdbWorkQueue get() { String qKey = new String(classKey); // ensure private minimal key BdbWorkQueue q = new BdbWorkQueue(qKey, BdbFrontier.this); q.setTotalBudget(getQueueTotalBudget()); //-1 System.out.println(getQueuePrecedencePolicy().getClass().getName()); getQueuePrecedencePolicy().queueCreated(q); return q; }}); return wq; }
BdbWorkQueue类即为被管理的对象,该类间接实现了IdentityCacheable接口,从上面我们可以看到,外部类通过调用ObjectIdentityBdbManualCache对象的V getOrUse(final String key, Supplier<V> supplierOrNull)方法获取被缓存的对象
/* (non-Javadoc) * @see org.archive.util.ObjectIdentityCache#get(java.lang.String, org.archive.util.ObjectIdentityBdbCache) */ public V getOrUse(final String key, Supplier<V> supplierOrNull) { countOfGets.incrementAndGet(); if (countOfGets.get() % 10000 == 0) { logCacheSummary(); } // check mem cache V val = memMap.get(key); if(val != null) { // the concurrent garden path: in memory and valid cacheHit.incrementAndGet(); val.setIdentityCache(this); return val; } val = diskMap.get(key); V prevVal; if(val == null) { // never yet created, consider creating if(supplierOrNull==null) { return null; } val = supplierOrNull.get(); supplierUsed.incrementAndGet(); // putting initial value directly into diskMap // (rather than just the memMap until page-out) // ensures diskMap.keySet() provides complete view prevVal = diskMap.putIfAbsent(key, val); if(prevVal!=null) { // we lost a race; discard our local creation in favor of disk version diskHit.incrementAndGet(); val = prevVal; } else { // we uniquely added a new key count.incrementAndGet(); } } else { diskHit.incrementAndGet(); } prevVal = memMap.putIfAbsent(key, val); // fill memMap or lose race gracefully if(prevVal != null) { val = prevVal; } val.setIdentityCache(this); return val; }
上述方法跟我们以前的缓存管理有点类似,首先根据key从缓存获取对象,如果没有则将新对象加入缓存(以后复用)
接下来看后面的方法
void dirtyKey(String key)方法为将指定key的V类型对象从memMap容器同时添加到dirtyItems容器
@Override public void dirtyKey(String key) { V val = memMap.get(key); if(val==null) { logger.severe("dirty key not in memory should be impossible"); } dirtyItems.put(key,val); }
void onEviction(String key, V val)方法将key/value对象添加到diskMap容器(MapEvictionListener接口方法)
@Override public void onEviction(String key, V val) { evictions.incrementAndGet(); diskMap.put(key, val); }
void sync()方法将dirtyItems容器中的对象同步到BDB数据库
/** * Sync all in-memory map entries to backing disk store. */ public synchronized void sync() { String dbName = null; // Sync. memory and disk. useStatsSyncUsed.incrementAndGet(); long startTime = 0; if (logger.isLoggable(Level.FINE)) { dbName = getDatabaseName(); startTime = System.currentTimeMillis(); logger.fine(dbName + " start sizes: disk " + this.diskMap.size() + ", mem " + this.memMap.size()); } Iterator<Entry<String, V>> iter = dirtyItems.entrySet().iterator(); while(iter.hasNext()) { Entry<String, V> entry = iter.next(); iter.remove(); diskMap.put(entry.getKey(), entry.getValue()); } try { this.db.sync(); } catch (DatabaseException e) { throw new RuntimeException(e); } if (logger.isLoggable(Level.FINE)) { logger.fine(dbName + " sync took " + (System.currentTimeMillis() - startTime) + "ms. " + "Finish sizes: disk " + this.diskMap.size() + ", mem " + this.memMap.size()); } }
接下来分析IdentityCacheable接口及相关类, IdentityCacheable接口声明的方法很简单,其源码如下:
/** * Common interface for objects held in ObjectIdentityCaches. * * @contributor gojomo */ public interface IdentityCacheable extends Serializable { public void setIdentityCache(ObjectIdentityCache<?> cache); public String getKey(); public void makeDirty(); }
实现该接口的类必须实现上面三方法,我这里主要介绍WorkQueue类(抽象类),它的实现上面方法的相关代码如下
// // IdentityCacheable support // transient private ObjectIdentityCache<?> cache; @Override public String getKey() { return getClassKey(); } @Override public void makeDirty() { cache.dirtyKey(getKey()); } @Override public void setIdentityCache(ObjectIdentityCache<?> cache) { this.cache = cache; }
从这里可以看出,void setIdentityCache(ObjectIdentityCache<?> cache)方法是设置管理当前被缓存的对象的缓存管理类(ObjectIdentityCache类型对象)
在void makeDirty()方法里面是回调ObjectIdentityCache类型对象的方法
---------------------------------------------------------------------------
本系列Heritrix 3.1.0 源码解析系本人原创
转载请注明出处 博客园 刺猬的温驯
本文链接 http://www.cnblogs.com/chenying99/archive/2013/04/18/3027679.html