今天来更新下数据库。。。。
1.Redis中的数据库,Redis服务器将所有的数据库都保存在服务器状态都保存在redisServer的结构中。
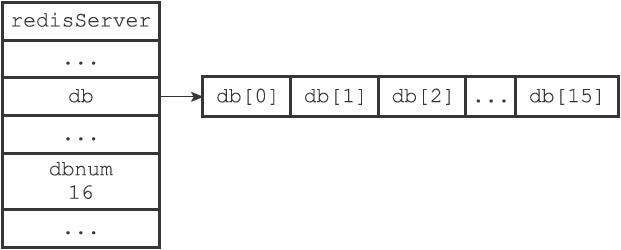
1.db数组的每一项是一个redisDb结构,代表一个数据库;
2.dbnum是表示数据库数目,有redis.conf里的配置决定。
typedef struct redisDb { dict *dict; /* The keyspace for this DB */ dict *expires; /* Timeout of keys with a timeout set */ dict *blocking_keys; /* Keys with clients waiting for data (BLPOP) */ dict *ready_keys; /* Blocked keys that received a PUSH */ dict *watched_keys; /* WATCHED keys for MULTI/EXEC CAS */ struct evictionPoolEntry *eviction_pool; /* Eviction pool of keys */ int id; /* Database ID */ long long avg_ttl; /* Average TTL, just for stats */ } redisDb;
2.切换数据库
Redis客户端用select方法进行数据库的切换。
redis中redisClient结构中的db属性记录客户端当前在那个数据库中,是一个指向redisDb结构的指针。
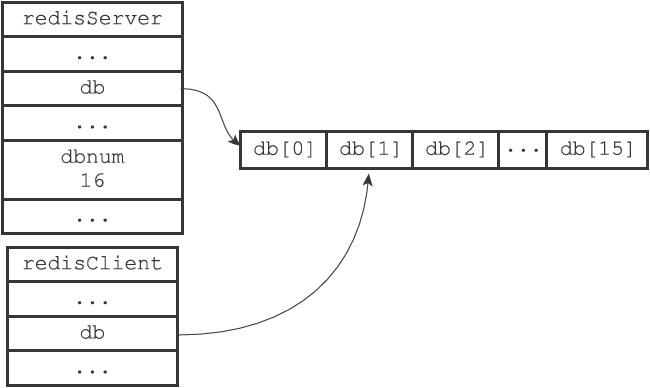
如果执行select 2,则redisClient里db的指针指向db[2]数据库,而实现数据库的切换。
2.数据库的键操作
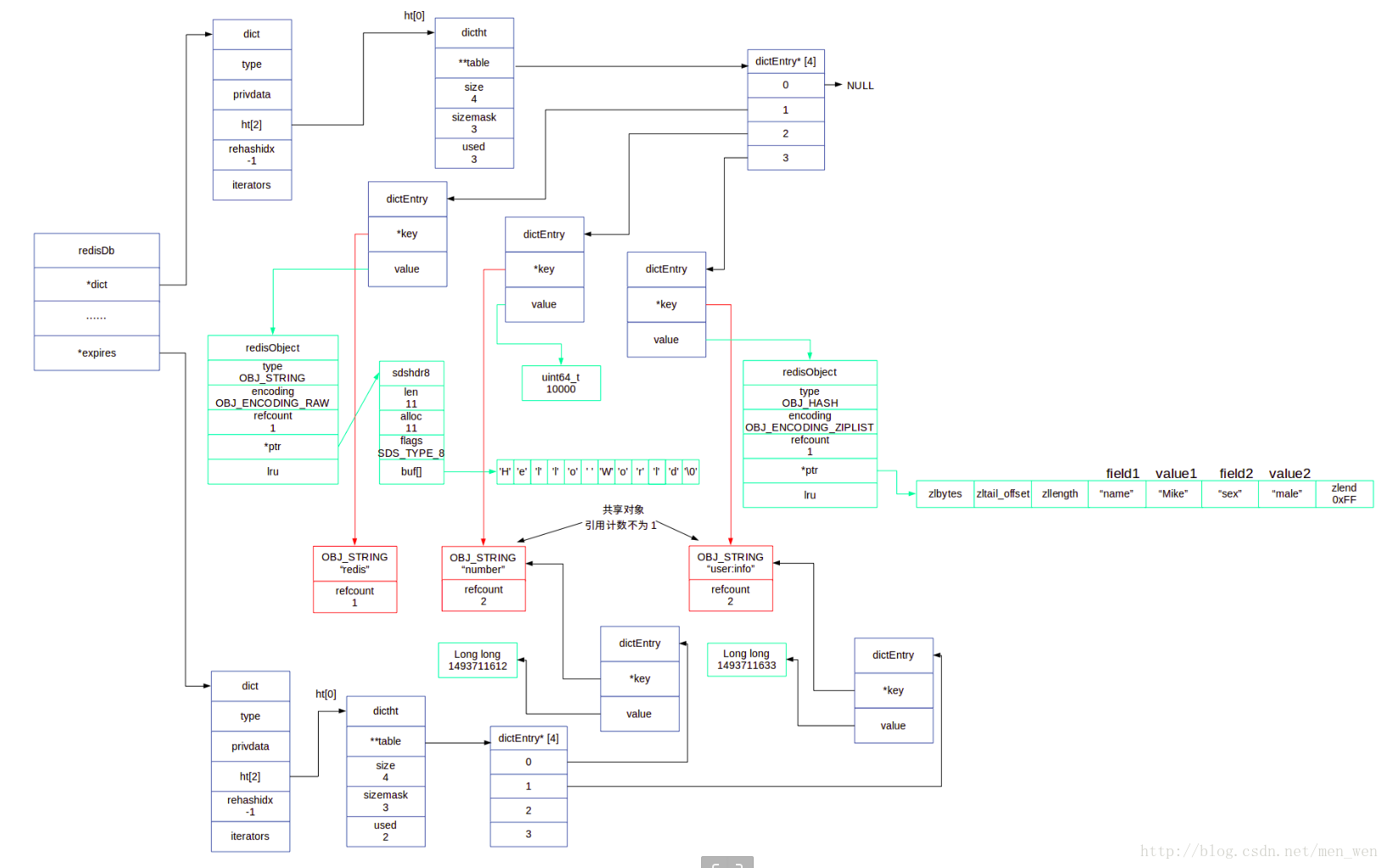
Redis是一个键值对数据库服务器,所有的键值对都是保存在字典(dict)这种数据结构中的。数据库redisDb定义在redis.h中。redisDb结构如上。
2.1 查找键值对
//从数据库db中 取出key的值对象 robj *lookupKey(redisDb *db, robj *key) { dictEntry *de = dictFind(db->dict,key->ptr); if (de) { robj *val = dictGetVal(de); /* Update the access time for the ageing algorithm. * Don't do it if we have a saving child, as this will trigger * a copy on write madness. */ //更新键的使用时间 在没有执行备份或者重写时 if (server.rdb_child_pid == -1 && server.aof_child_pid == -1) val->lru = LRU_CLOCK(); return val; } else { return NULL; } }
// 查找key dictEntry *dictFind(dict *d, const void *key) { dictEntry *he; unsigned int h, idx, table; if (d->ht[0].size == 0) return NULL; /* We don't have a table at all */ if (dictIsRehashing(d)) _dictRehashStep(d); h = dictHashKey(d, key); for (table = 0; table <= 1; table++) { idx = h & d->ht[table].sizemask; he = d->ht[table].table[idx]; while(he) { if (dictCompareKeys(d, key, he->key)) return he; he = he->next; } if (!dictIsRehashing(d)) return NULL; } return NULL; }
查找key,找到则更新使用时间,没找到返回null。
2.2 删除键
删除数据库中的一个键,实际上就是在键空间里面删除键所对应的键值对对象。
int dbDelete(redisDb *db, robj *key) { /* Deleting an entry from the expires dict will not free the sds of * the key, because it is shared with the main dictionary. */ if (dictSize(db->expires) > 0) dictDelete(db->expires,key->ptr); if (dictDelete(db->dict,key->ptr) == DICT_OK) { if (server.cluster_enabled) slotToKeyDel(key); return 1; } else { return 0; } }
//找到key 并且根据nofree标志是否free static int dictGenericDelete(dict *d, const void *key, int nofree) { unsigned int h, idx; dictEntry *he, *prevHe; int table; if (d->ht[0].size == 0) return DICT_ERR; /* d->ht[0].table is NULL */ if (dictIsRehashing(d)) _dictRehashStep(d); h = dictHashKey(d, key); for (table = 0; table <= 1; table++) { idx = h & d->ht[table].sizemask; he = d->ht[table].table[idx]; prevHe = NULL; while(he) { if (dictCompareKeys(d, key, he->key)) { /* Unlink the element from the list */ if (prevHe) prevHe->next = he->next; else d->ht[table].table[idx] = he->next; if (!nofree) { dictFreeKey(d, he); dictFreeVal(d, he); } zfree(he); d->ht[table].used--; return DICT_OK; } prevHe = he; he = he->next; } if (!dictIsRehashing(d)) break; } return DICT_ERR; /* not found */ } //删除key并释放 int dictDelete(dict *ht, const void *key) { return dictGenericDelete(ht,key,0); } //删除key 不释放 int dictDeleteNoFree(dict *ht, const void *key) { return dictGenericDelete(ht,key,1); }
2.3 更新键
对一个数据库键进行更新,实际上就是对键空间里面键所对应的值对象进行更新,根据值对象的类型不同,更新的具体方法也会不同。
/* Add the key to the DB. It's up to the caller to increment the reference * counter of the value if needed. * * The program is aborted if the key already exists. */ void dbAdd(redisDb *db, robj *key, robj *val) { sds copy = sdsdup(key->ptr); int retval = dictAdd(db->dict, copy, val); redisAssertWithInfo(NULL,key,retval == REDIS_OK); if (val->type == REDIS_LIST) signalListAsReady(db, key); if (server.cluster_enabled) slotToKeyAdd(key); }
2.4 键的生存时间或过期时间
通过expire命令或者pexpire命令,客户端可以以秒或者毫秒精度为数据库中的某个键设置生存时间,更过指定的秒或者毫秒之后,服务器就会自动删除生存时间为0的键。
redis删除key的方式有三种
-
-
-
定时删除:在设置键的过期时间的同时,创建一个定时器,该定时器在键的过期时间来临时,立即执行对键的删除操作。
-
惰性删除:放任键过期不管,每次从键空间中访问键时,都检查该键是否过期,如果过期的话,则删除该键。
-
定期删除:每隔一段时间,程序就对数据库进行一次检查,删除其中的过期键。至于要删除多少过期键,以及要检查多少个数据库,则由算法决定。
-
-
1.定时删除策略是对内存最友好的:通过使用定时器,定时删除策略可以保证过期键会尽可能快的被删除,并释放过期键所占用的内存。另一方面,定时删除策略的缺点是,他对cpu时间是最不友好的,在过期键比较多的情况下,删除过期键这一行为可能会占用相当一部分cpu时间,在内存不紧张但是cpu时间金正的情况下,将cpu时间用在删除和当前任务无关的过期键上,无疑会对服务器的响应时间和吞吐量造成影响。
2.惰性删除策略对CPU时间来说是最友好的:程序只会在访问键时才对键进行过期检查,这可以保证删除过期键的操作只会在非做不可的情况下进行,并且删除的目标仅限于当前处理的键,这个策略不会在删除其他无关的过期键上花费任何CPU时间。惰性删除策略的缺点是,它对内存是最不友好的:如果数据库中有非常多的过期键,而这些过期键又恰好没有被访问到的话,那么它们也许永远也不会被删除,这就类似于内存泄漏的情况了。
3.定期删除策略是前两种策略的一种折中:该策略每隔一段时间执行一次删除过期键操作,并通过限制删除操作执行的时长和频率来减少删除操作对CPU时间的影响。另一方面,定期删除策略有效地减少了因为过期键而带来的内存浪费。
Redis服务器实际使用的是惰性删除和定期删除两种策略,通过配合使用这两种删除策略,服务器可以很好地在合理使用CPU时间和避免浪费内存空间之间取得平衡。
设置了过期时间的数据库:图片来源
3..数据库相关实现
1.scan
scan,sscan,hscan,zsan统一的入口函数:scanGenericCommand;
//计算第一个参数的下标
// scan 0
// sscan myset 0 mastch *
//scan一类命令的实现 void scanGenericCommand(redisClient *c, robj *o, unsigned long cursor) { int i, j; list *keys = listCreate(); listNode *node, *nextnode; //创建一个list long count = 10; sds pat; int patlen, use_pattern = 0; dict *ht; /* Object must be NULL (to iterate keys names), or the type of the object * must be Set, Sorted Set, or Hash. */ //输入类型的检查 要么迭代键名 要么当前集合对象 要么迭代哈希对象 要么迭代有序集合对象 redisAssert(o == NULL || o->type == REDIS_SET || o->type == REDIS_HASH || o->type == REDIS_ZSET); /* Set i to the first option argument. The previous one is the cursor. */ //计算第一个参数的下标 // scan 0 // sscan myset 0 mastch * // i指向count的下标 i = (o == NULL) ? 2 : 3; /* Skip the key argument if needed. */ /* Step 1: Parse options. */ //解析选项 while (i < c->argc) { j = c->argc - i; //count值 if (!strcasecmp(c->argv[i]->ptr, "count") && j >= 2) { //获取count选项 是从第二个值开始的 if (getLongFromObjectOrReply(c, c->argv[i+1], &count, NULL) != REDIS_OK) { goto cleanup; } if (count < 1) { addReply(c,shared.syntaxerr); goto cleanup; } i += 2; } else if (!strcasecmp(c->argv[i]->ptr, "match") && j >= 2) { //match 选项 pat = c->argv[i+1]->ptr; //获取到匹配规则 patlen = sdslen(pat); /* The pattern always matches if it is exactly "*", so it is * equivalent to disabling it. */ //如果匹配模式是 * 贪婪匹配 则match不生效 use_pattern = !(pat[0] == '*' && patlen == 1); i += 2; } else { addReply(c,shared.syntaxerr); goto cleanup; } } /* Step 2: Iterate the collection. * * Note that if the object is encoded with a ziplist, intset, or any other * representation that is not a hash table, we are sure that it is also * composed of a small number of elements. So to avoid taking state we * just return everything inside the object in a single call, setting the * cursor to zero to signal the end of the iteration. */ /* Handle the case of a hash table. */ // //如果对象是ziplist intset或者其他而不是哈希表 那么这些类型只是包含少量的元素 //一次将所有的元素全部返回给调用者 并设置cursor为0 标识scan迭代完成 ht = NULL; if (o == NULL) { ht = c->db->dict; } else if (o->type == REDIS_SET && o->encoding == REDIS_ENCODING_HT) { ht = o->ptr; } else if (o->type == REDIS_HASH && o->encoding == REDIS_ENCODING_HT) { ht = o->ptr; count *= 2; /* We return key / value for this type. */ } else if (o->type == REDIS_ZSET && o->encoding == REDIS_ENCODING_SKIPLIST) { zset *zs = o->ptr; ht = zs->dict; count *= 2; /* We return key / value for this type. */ } if (ht) { void *privdata[2]; /* We set the max number of iterations to ten times the specified * COUNT, so if the hash table is in a pathological state (very * sparsely populated) we avoid to block too much time at the cost * of returning no or very few elements. */ //最大迭代次数是 10 * count long maxiterations = count*10; /* We pass two pointers to the callback: the list to which it will * add new elements, and the object containing the dictionary so that * it is possible to fetch more data in a type-dependent way. */ //回调的两个指针 一个是将向其中添加新元素的列表 //另一个是包含dictionary的对象,一遍能够以类型相关的方式获取更过数据 privdata[0] = keys; privdata[1] = o; do { cursor = dictScan(ht, cursor, scanCallback, privdata); } while (cursor && maxiterations-- && listLength(keys) < (unsigned long)count); } else if (o->type == REDIS_SET) { //如果是set 则将set里面的数据全部返回 int pos = 0; int64_t ll; while(intsetGet(o->ptr,pos++,&ll)) listAddNodeTail(keys,createStringObjectFromLongLong(ll)); cursor = 0; } else if (o->type == REDIS_HASH || o->type == REDIS_ZSET) { // ziplist 或者hash 字符串标识的数据结构 unsigned char *p = ziplistIndex(o->ptr,0); unsigned char *vstr; unsigned int vlen; long long vll; while(p) { ziplistGet(p,&vstr,&vlen,&vll); listAddNodeTail(keys, (vstr != NULL) ? createStringObject((char*)vstr,vlen) : createStringObjectFromLongLong(vll)); p = ziplistNext(o->ptr,p); } cursor = 0; } else { redisPanic("Not handled encoding in SCAN."); } /* Step 3: Filter elements. */ //过滤元素 遍历第二步构造的list node = listFirst(keys); //链表首节点地址 while (node) { robj *kobj = listNodeValue(node); // key nextnode = listNextNode(node); // next node int filter = 0; /* Filter element if it does not match the pattern. */ //不匹配 则过滤掉 if (!filter && use_pattern) { if (sdsEncodedObject(kobj)) { if (!stringmatchlen(pat, patlen, kobj->ptr, sdslen(kobj->ptr), 0)) filter = 1; } else { char buf[REDIS_LONGSTR_SIZE]; int len; redisAssert(kobj->encoding == REDIS_ENCODING_INT); len = ll2string(buf,sizeof(buf),(long)kobj->ptr); if (!stringmatchlen(pat, patlen, buf, len, 0)) filter = 1; } } /* Filter element if it is an expired key. */ //删除掉过期key if (!filter && o == NULL && expireIfNeeded(c->db, kobj)) filter = 1; /* Remove the element and its associted value if needed. */ if (filter) { decrRefCount(kobj); listDelNode(keys, node); } /* If this is a hash or a sorted set, we have a flat list of * key-value elements, so if this element was filtered, remove the * value, or skip it if it was not filtered: we only match keys. */ if (o && (o->type == REDIS_ZSET || o->type == REDIS_HASH)) { node = nextnode; nextnode = listNextNode(node); if (filter) { kobj = listNodeValue(node); decrRefCount(kobj); listDelNode(keys, node); } } node = nextnode; } /* Step 4: Reply to the client. */ addReplyMultiBulkLen(c, 2); addReplyBulkLongLong(c,cursor); addReplyMultiBulkLen(c, listLength(keys)); while ((node = listFirst(keys)) != NULL) { robj *kobj = listNodeValue(node); addReplyBulk(c, kobj); decrRefCount(kobj); listDelNode(keys, node); } cleanup: listSetFreeMethod(keys,decrRefCountVoid); listRelease(keys); }
代码略长,首先是解析命令,解析count和match参数,如果没有指定count,则默认返回10条数据,返回的索引是下次查询的下标。
开始迭代集合,如果是key保存为ziplist或者intset,则一次性返回所有数据,没有游标(游标值直接返回0).由于redis设计只有数据量比较小的时候才会保存为ziplist或者intset,,然后根据根据match参数过滤返回值,并且如果这个键已经过期也会直接过滤掉(redis中键过期之后并不会立即删除),最后返回结果给客户端。
dictScan代码如下:
unsigned long dictScan(dict *d, unsigned long v, dictScanFunction *fn, void *privdata) { dictht *t0, *t1; const dictEntry *de; unsigned long m0, m1; if (dictSize(d) == 0) return 0; //是否在进行rehash if (!dictIsRehashing(d)) { //没有进行rehash t0 = &(d->ht[0]); m0 = t0->sizemask; /* Emit entries at cursor */ //遍历同一个bucket上后面的链表 de = t0->table[v & m0]; while (de) { fn(privdata, de); de = de->next; } } else { //在进行rehash t0 = &d->ht[0]; t1 = &d->ht[1]; /* Make sure t0 is the smaller and t1 is the bigger table */ if (t0->size > t1->size) { t0 = &d->ht[1]; t1 = &d->ht[0]; } m0 = t0->sizemask; m1 = t1->sizemask; /* Emit entries at cursor */ de = t0->table[v & m0]; while (de) { //遍历同一个bucket上面链接的链表 fn(privdata, de); de = de->next; } /* Iterate over indices in larger table that are the expansion * of the index pointed to by the cursor in the smaller table */ do { /* Emit entries at cursor */ de = t1->table[v & m1]; while (de) { fn(privdata, de); de = de->next; } /* Increment bits not covered by the smaller mask */ v = (((v | m0) + 1) & ~m0) | (v & m0); //下一个游标的取值 /* Continue while bits covered by mask difference is non-zero */ } while (v & (m0 ^ m1)); //判断条件 } /* Set unmasked bits so incrementing the reversed cursor * operates on the masked bits of the smaller table */ v |= ~m0; /* Increment the reverse cursor */ v = rev(v); v++; v = rev(v); return v; }
推荐博客:Redis scan命令原理将scan讲的很详细