Scrapy
Scrapy是一个为了爬取网站数据,提取结构性数据而编写的应用框架。 其可以应用在数据挖掘,信息处理或存储历史数据等一系列的程序中。
Scrapy囊括了爬取网站数据几乎所有的功能,是一个扩展性很强的一个框架,Scrapy在爬虫界里相当于web的Django
Scrapy 使用了 Twisted异步网络库来处理网络通讯。整体架构大致如下
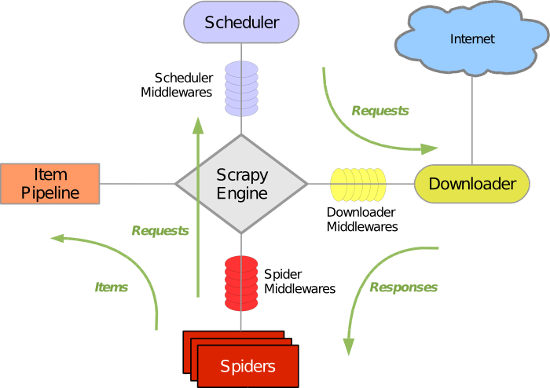
Scrapy主要包括了以下组件:
- 引擎(Scrapy)
用来处理整个系统的数据流处理, 触发事务(框架核心) - 调度器(Scheduler)
用来接受引擎发过来的请求, 压入队列中, 并在引擎再次请求的时候返回. 可以想像成一个URL(抓取网页的网址或者说是链接)的优先队列, 由它来决定下一个要抓取的网址是什么, 同时去除重复的网址 - 下载器(Downloader)
用于下载网页内容, 并将网页内容返回给蜘蛛(Scrapy下载器是建立在twisted这个高效的异步模型上的) - 爬虫(Spiders)
爬虫是主要干活的, 用于从特定的网页中提取自己需要的信息, 即所谓的实体(Item)。用户也可以从中提取出链接,让Scrapy继续抓取下一个页面 - 项目管道(Pipeline)
负责处理爬虫从网页中抽取的实体,主要的功能是持久化实体、验证实体的有效性、清除不需要的信息。当页面被爬虫解析后,将被发送到项目管道,并经过几个特定的次序处理数据。 - 下载器中间件(Downloader Middlewares)
位于Scrapy引擎和下载器之间的框架,主要是处理Scrapy引擎与下载器之间的请求及响应。 - 爬虫中间件(Spider Middlewares)
介于Scrapy引擎和爬虫之间的框架,主要工作是处理蜘蛛的响应输入和请求输出。 - 调度中间件(Scheduler Middewares)
介于Scrapy引擎和调度之间的中间件,从Scrapy引擎发送到调度的请求和响应。
Scrapy运行流程大概如下:
- 引擎从调度器中取出一个链接(URL)用于接下来的抓取
- 引擎把URL封装成一个请求(Request)传给下载器
- 下载器把资源下载下来,并封装成应答包(Response)
- 爬虫解析Response
- 解析出实体(Item),则交给实体管道进行进一步的处理
- 解析出的是链接(URL),则把URL交给调度器等待抓取
1.Scrapy的安装

Windows a. pip3 install wheel b. 下载twisted http://www.lfd.uci.edu/~gohlke/pythonlibs/#twisted c. 进入下载目录,执行 pip3 install Twisted‑17.1.0‑cp35‑cp35m‑win_amd64.whl d. pip3 install scrapy e. 下载并安装pywin32:https://sourceforge.net/projects/pywin32/files/
2.命令使用

1. scrapy startproject 项目名称 - 在当前目录中创建中创建一个项目文件(类似于Django) 2. scrapy genspider [-t template] <name> <domain> - 创建爬虫应用 如: scrapy gensipider -t basic oldboy oldboy.com scrapy gensipider -t xmlfeed autohome autohome.com.cn PS: 查看所有命令:scrapy gensipider -l 查看模板命令:scrapy gensipider -d 模板名称 3. scrapy list - 展示爬虫应用列表 4. scrapy crawl 爬虫应用名称 - 运行单独爬虫应用
3.Spiders介绍
Spiders里主要装的是爬虫的目录,和爬虫的编写。

name = 'chouti' #设置allowed_domains的含义是过滤爬取的域名,在插件OffsiteMiddleware启用的情况下(默认是启用的),不在此允许范围内的域名就会被过滤 allowed_domains = ['chouti.com'] #起始urls,在引擎调用调度器的时候,调度器会循环起始urls列表 start_urls = ['http://dig.chouti.com'] #在这里我们可以自定义起始url: 1. start_requests # def start_requests(self): # for url in self.start_urls: # yield Request(url=url,callback=self.parse) # # def start_requests(self): # req_list = [] # for url in self.start_urls: # req_list.append(Request(url=url,callback=self.parse)) # return req_list # 两种都是可以的 # 因为scrapy内部会将返回值转换成迭代器。
解析器
可以在Chrome 右击某个标签copy-->copyxpath可以获取该路径

#有两种执行解析器的方法 # 方式一: # response.xpath('//div[@id="content-list"]/div[@class="item"]') # 方式二: # from scrapy.selector import HtmlXPathSelector #hsx=HtmlXPathSelector(response=response) # div = hsx.xpath('//div[@id="content-list"]/div[@class="item"]') 查找规则: # // 代表子子孙孙 / 表示后代 .// 当前标签下的子子孙孙 # //a # //div/a # //a[re:test(@id, "id+")] # # items = hxs.xpath("//div[@id='content-list']/div[@class='item']") # for item in items: # item.xpath('.//div') # # text = row.xpath('.//div[@class="part1"]//a[1]/text()').extract_first() # texe是文本内容 # href = row.xpath('.//div[@class="part1"]//a[1]/@href').extract_first() # href是属性内容 # 解析: # 标签对象:xpath('/html/body/ul/li/a/@href') # 列表: xpath('/html/body/ul/li/a/@href').extract() # 值: xpath('//body/ul/li/a/@href').extract_first()
4.items
设置数据存储模板,用于结构化数据,如:Django的Model

class XianglongItem(scrapy.Item): # define the fields for your item here like: # name = scrapy.Field() title = scrapy.Field() href = scrapy.Field()
5.pipelines
数据处理行为,如:一般结构化的数据持久化

# class FilePipeline(object): # def process_item(self, item, spider): # print('写入文件',item['href']) # # 将item传递给下一个类 # return item # # def open_spider(self, spider): # """ # 爬虫开始执行时,调用 # :param spider: # :return: # """ # print('打开文件') # # def close_spider(self, spider): # """ # 爬虫关闭时,被调用 # :param spider: # :return: # """ # print('关闭文件')

如果想要丢弃,不给后续pipeline使用: # from scrapy.exceptions import DropItem # class FilePipeline(object): # # def process_item(self, item, spider): # print('写入文件',item['href']) # # # return item # raise DropItem()

# - 根据配置文件读取相关值,再进行pipeline处理 # class FilePipeline(object): # def __init__(self,path): # self.path = path # self.f = None # # @classmethod # def from_crawler(cls, crawler): # """ # 初始化时候,用于创建pipeline对象 # :param crawler: # :return: # """ # - 根据配置文件读取相关值,再进行pipeline处理 # path = crawler.settings.get('XL_FILE_PATH') # return cls(path) # # def process_item(self, item, spider): # self.f.write(item['href']+' ') # return item # # def open_spider(self, spider): # """ # 爬虫开始执行时,调用 # :param spider: # :return: # """ # self.f = open(self.path,'w') # # def close_spider(self, spider): # """ # 爬虫关闭时,被调用 # :param spider: # :return: # """ # self.f.close()

###配置文件### ITEM_PIPELINES = { 'xianglong.pipelines.FilePipeline': 300, 'xianglong.pipelines.DBPipeline': 301, } #数字越小优先级越高 class FilePipeline(object): def process_item(self, item, spider): ''' :param item: :param spider: :return: ''' print('写入文件') # 返回值会返回给下一个process_item return item raise DropItem() # 后续的pipeline不能在使用item (丢弃item) def open_spider(self,spider): ''' :param spider: 开始时被调用 :return: ''' print('打开文件') def close_spider(self,spider): ''' :param spider:爬虫关闭时被调用 :return: ''' print('关闭文件') class DBPipeline(object): def process_item(self, item, spider): print('写入数据库') return item def open_spider(self, spider): print('打开数据库') def close_spider(self, spider): print('关闭数据库') #执行顺序,先执行FilePipeline的open_spider--->DBPipeline的open_spider FilePipeline的process_item---->DBPipeline的process_item FilePipeline的close_spider--->DBPipeline的close_spider
6.post访问/请求头的设置/cookies

自动登录抽屉+点赞 # # POST+请求头: # from scrapy.http import Request # req = Request( # url='http://dig.chouti.com/login', # method='POST', # body='phone=8613121758648&password=woshiniba&oneMonth=1', # headers={'Content-Type': 'application/x-www-form-urlencoded; charset=UTF-8'}, # cookies={}, # callback=self.parse_check_login, # )

# cookies: # 手动: # from scrapy.http.cookies import CookieJar # cookie_dict = {} # cookie_jar = CookieJar() # cookie_jar.extract_cookies(response, response.request) # for k, v in cookie_jar._cookies.items(): # for i, j in v.items(): # for m, n in j.items(): # cookie_dict[m] = n.value # # req = Request( # url='http://dig.chouti.com/login', # method='POST', # headers={'Content-Type': 'application/x-www-form-urlencoded; charset=UTF-8'}, # body='phone=8615131255089&password=pppppppp&oneMonth=1', # cookies=cookie_dict, # 手动携带 # callback=self.check_login # ) # yield req

# 自动:****meta={'cookiejar': True}***** # class ChoutiSpider(scrapy.Spider): # name = 'chouti' # allowed_domains = ['chouti.com'] # start_urls = ['http://dig.chouti.com/',] # # def start_requests(self): # for url in self.start_urls: # yield Request(url=url,callback=self.parse_index,meta={'cookiejar':True}) # # def parse_index(self,response): # req = Request( # url='http://dig.chouti.com/login', # method='POST', # headers={'Content-Type': 'application/x-www-form-urlencoded; charset=UTF-8'}, # body='phone=8613121758648&password=woshiniba&oneMonth=1', # callback=self.parse_check_login, # meta={'cookiejar': True} # ) # yield req # # def parse_check_login(self,response): # # print(response.text) # yield Request( # url='https://dig.chouti.com/link/vote?linksId=19440976', # method='POST', # callback=self.parse_show_result, # meta={'cookiejar': True} # ) # # def parse_show_result(self,response): # print(response.text) # # 配置文件制定是否允许操作cookie: # # Disable cookies (enabled by default) # # COOKIES_ENABLED = False
7.去重
访问过的url不再访问,减少不必要的资源浪费。

# 5. 去重规则 # 配置: # DUPEFILTER_CLASS = 'xianglong.dupe.MyDupeFilter' # 编写类: # class MyDupeFilter(BaseDupeFilter): # def __init__(self): # self.record = set() # # @classmethod # def from_settings(cls, settings): # return cls() # # def request_seen(self, request): # if request.url in self.record: # print('已经访问过了', request.url) # return True # self.record.add(request.url) # # def open(self): # can return deferred # pass # # def close(self, reason): # can return a deferred # pass # # 问题:为请求创建唯一标识 # # # http://www.oldboyedu.com?id=1&age=2 # http://www.oldboyedu.com?age=2&id=1 # # from scrapy.utils.request import request_fingerprint # from scrapy.http import Request # # # u1 = Request(url='http://www.oldboyedu.com?id=1&age=2') # u2 = Request(url='http://www.oldboyedu.com?age=2&id=1') # # result1 = request_fingerprint(u1) # result2 = request_fingerprint(u2) # print(result1,result2) # 其内部将url用哈希加密成一个64位的字符串,那么建立索引的时候就可#以用char字段 result1=result2 # 问题:记录到低要不要放在数据库?【使用redis集合存储】 # 访问记录可以放在redis中。 # # # 补充:dont_filter到低在哪里? # from scrapy.core.scheduler import Scheduler # def enqueue_request(self, request): # # request.dont_filter=False # # self.df.request_seen(request): # # - True,已经访问 # # - False,未访问 # # request.dont_filter=True,全部加入到调度器 # if not request.dont_filter and self.df.request_seen(request): # self.df.log(request, self.spider) # return False # # 如果往下走,把请求加入调度器 # dqok = self._dqpush(request)
8.中间件
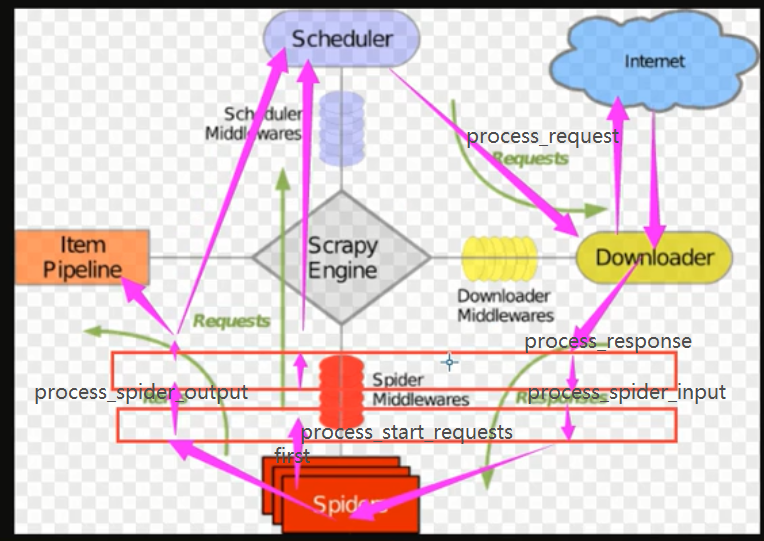
1.下载中间件
下载中间件的作用?
在每次下载前和下载后对请求和响应可以定制功能。例如:user-agent/代理/cookie
代理实例:

# 1. 下载中间件 # 问题:scrapy中如何添加代理? # 解决方案: # 方式一:内置添加代理功能 # # -*- coding: utf-8 -*- # import os # import scrapy # from scrapy.http import Request # # class ChoutiSpider(scrapy.Spider): # name = 'chouti' # allowed_domains = ['chouti.com'] # start_urls = ['https://dig.chouti.com/'] # # def start_requests(self): # os.environ['HTTP_PROXY'] = "http://192.168.11.11" # # for url in self.start_urls: # yield Request(url=url,callback=self.parse) # # def parse(self, response): # print(response) # # 方式二:自定义下载中间件 # import random # import base64 # import six # def to_bytes(text, encoding=None, errors='strict'): # """Return the binary representation of `text`. If `text` # is already a bytes object, return it as-is.""" # if isinstance(text, bytes): # return text # if not isinstance(text, six.string_types): # raise TypeError('to_bytes must receive a unicode, str or bytes ' # 'object, got %s' % type(text).__name__) # if encoding is None: # encoding = 'utf-8' # return text.encode(encoding, errors) # # class MyProxyDownloaderMiddleware(object): # def process_request(self, request, spider): # proxy_list = [ # {'ip_port': '111.11.228.75:80', 'user_pass': 'xxx:123'}, # {'ip_port': '120.198.243.22:80', 'user_pass': ''}, # {'ip_port': '111.8.60.9:8123', 'user_pass': ''}, # {'ip_port': '101.71.27.120:80', 'user_pass': ''}, # {'ip_port': '122.96.59.104:80', 'user_pass': ''}, # {'ip_port': '122.224.249.122:8088', 'user_pass': ''}, # ] # proxy = random.choice(proxy_list) # if proxy['user_pass'] is not None: # request.meta['proxy'] = to_bytes("http://%s" % proxy['ip_port']) # encoded_user_pass = base64.encodestring(to_bytes(proxy['user_pass'])) # request.headers['Proxy-Authorization'] = to_bytes('Basic ' + encoded_user_pass) # else: # request.meta['proxy'] = to_bytes("http://%s" % proxy['ip_port']) # # # # 配置: # DOWNLOADER_MIDDLEWARES = { # # 'xiaohan.middlewares.MyProxyDownloaderMiddleware': 543, # } #
2.爬虫中间件

2. 爬虫中间件 # 编写: # middlewares.py # class XiaohanSpiderMiddleware(object): # # Not all methods need to be defined. If a method is not defined, # # scrapy acts as if the spider middleware does not modify the # # passed objects. # def __init__(self): # pass # @classmethod # def from_crawler(cls, crawler): # # This method is used by Scrapy to create your spiders. # s = cls() # return s # # # 每次下载完成之后,未执行parse函数之前。 # def process_spider_input(self, response, spider): # # Called for each response that goes through the spider # # middleware and into the spider. # # # Should return None or raise an exception. # print('process_spider_input',response) # return None # # def process_spider_output(self, response, result, spider): # # Called with the results returned from the Spider, after # # it has processed the response. # # # Must return an iterable of Request, dict or Item objects. # print('process_spider_output',response) # for i in result: # yield i # # def process_spider_exception(self, response, exception, spider): # # Called when a spider or process_spider_input() method # # (from other spider middleware) raises an exception. # # # Should return either None or an iterable of Response, dict # # or Item objects. # pass # # # 爬虫启动时,第一次执行start_requests时,触发。(只执行一次) # def process_start_requests(self, start_requests, spider): # # Called with the start requests of the spider, and works # # similarly to the process_spider_output() method, except # # that it doesn’t have a response associated. # # # Must return only requests (not items). # # print('process_start_requests') # for r in start_requests: # yield r # # 应用: # SPIDER_MIDDLEWARES = { # 'xiaohan.middlewares.XiaohanSpiderMiddleware': 543, # } #
9.自定义扩展

engine_started = object() engine_stopped = object() spider_opened = object() spider_idle = object() spider_closed = object() spider_error = object() request_scheduled = object() request_dropped = object() response_received = object() response_downloaded = object() item_scraped = object() item_dropped = object()
扩展方法:

# 3. 扩展:信号 # 单纯扩展: # extends.py # class MyExtension(object): # def __init__(self): # pass # # @classmethod # def from_crawler(cls, crawler): # obj = cls() # return obj # 配置: # EXTENSIONS = { # 'xiaohan.extends.MyExtension':500, # } # # 扩展+信号: # extends.py # from scrapy import signals # # # class MyExtension(object): # def __init__(self): # pass # # @classmethod # def from_crawler(cls, crawler): # obj = cls() # # 在爬虫打开时,触发spider_opened信号相关的所有函数:xxxxxxxxxxx # crawler.signals.connect(obj.xxxxxxxxxxx1, signal=signals.spider_opened) # # 在爬虫关闭时,触发spider_closed信号相关的所有函数:xxxxxxxxxxx # crawler.signals.connect(obj.uuuuuuuuuu, signal=signals.spider_closed) # return obj # # def xxxxxxxxxxx1(self, spider): # print('open') # # def uuuuuuuuuu(self, spider): # print('close') # # return obj # 配置: # EXTENSIONS = { # 'xiaohan.extends.MyExtension':500, # } #
10.settings详解

# -*- coding: utf-8 -*- # Scrapy settings for step8_king project # # For simplicity, this file contains only settings considered important or # commonly used. You can find more settings consulting the documentation: # # http://doc.scrapy.org/en/latest/topics/settings.html # http://scrapy.readthedocs.org/en/latest/topics/downloader-middleware.html # http://scrapy.readthedocs.org/en/latest/topics/spider-middleware.html # 1. 爬虫名称 BOT_NAME = 'step8_king' # 2. 爬虫应用路径 SPIDER_MODULES = ['step8_king.spiders'] NEWSPIDER_MODULE = 'step8_king.spiders' # Crawl responsibly by identifying yourself (and your website) on the user-agent # 3. 客户端 user-agent请求头 # USER_AGENT = 'step8_king (+http://www.yourdomain.com)' # Obey robots.txt rules # 4. 禁止爬虫配置 # ROBOTSTXT_OBEY = False # Configure maximum concurrent requests performed by Scrapy (default: 16) # 5. 并发请求数 # CONCURRENT_REQUESTS = 4 # Configure a delay for requests for the same website (default: 0) # See http://scrapy.readthedocs.org/en/latest/topics/settings.html#download-delay # See also autothrottle settings and docs # 6. 延迟下载秒数 # DOWNLOAD_DELAY = 2 # The download delay setting will honor only one of: # 7. 单域名访问并发数,并且延迟下次秒数也应用在每个域名 # CONCURRENT_REQUESTS_PER_DOMAIN = 2 # 单IP访问并发数,如果有值则忽略:CONCURRENT_REQUESTS_PER_DOMAIN,并且延迟下次秒数也应用在每个IP # CONCURRENT_REQUESTS_PER_IP = 3 # Disable cookies (enabled by default) # 8. 是否支持cookie,cookiejar进行操作cookie # COOKIES_ENABLED = True # COOKIES_DEBUG = True # Disable Telnet Console (enabled by default) # 9. Telnet用于查看当前爬虫的信息,操作爬虫等... # 使用telnet ip port ,然后通过命令操作 # TELNETCONSOLE_ENABLED = True # TELNETCONSOLE_HOST = '127.0.0.1' # TELNETCONSOLE_PORT = [6023,] # 10. 默认请求头 # Override the default request headers: # DEFAULT_REQUEST_HEADERS = { # 'Accept': 'text/html,application/xhtml+xml,application/xml;q=0.9,*/*;q=0.8', # 'Accept-Language': 'en', # } # Configure item pipelines # See http://scrapy.readthedocs.org/en/latest/topics/item-pipeline.html # 11. 定义pipeline处理请求 # ITEM_PIPELINES = { # 'step8_king.pipelines.JsonPipeline': 700, # 'step8_king.pipelines.FilePipeline': 500, # } # 12. 自定义扩展,基于信号进行调用 # Enable or disable extensions # See http://scrapy.readthedocs.org/en/latest/topics/extensions.html # EXTENSIONS = { # # 'step8_king.extensions.MyExtension': 500, # } # 13. 爬虫允许的最大深度,可以通过meta查看当前深度;0表示无深度 # DEPTH_LIMIT = 3 # 14. 爬取时,0表示深度优先Lifo(默认);1表示广度优先FiFo # 后进先出,深度优先 # DEPTH_PRIORITY = 0 # SCHEDULER_DISK_QUEUE = 'scrapy.squeue.PickleLifoDiskQueue' # SCHEDULER_MEMORY_QUEUE = 'scrapy.squeue.LifoMemoryQueue' # 先进先出,广度优先 # DEPTH_PRIORITY = 1 # SCHEDULER_DISK_QUEUE = 'scrapy.squeue.PickleFifoDiskQueue' # SCHEDULER_MEMORY_QUEUE = 'scrapy.squeue.FifoMemoryQueue' # 15. 调度器队列 # SCHEDULER = 'scrapy.core.scheduler.Scheduler' # from scrapy.core.scheduler import Scheduler # 16. 访问URL去重 # DUPEFILTER_CLASS = 'step8_king.duplication.RepeatUrl' # Enable and configure the AutoThrottle extension (disabled by default) # See http://doc.scrapy.org/en/latest/topics/autothrottle.html """ 17. 自动限速算法 from scrapy.contrib.throttle import AutoThrottle 自动限速设置 1. 获取最小延迟 DOWNLOAD_DELAY 2. 获取最大延迟 AUTOTHROTTLE_MAX_DELAY 3. 设置初始下载延迟 AUTOTHROTTLE_START_DELAY 4. 当请求下载完成后,获取其"连接"时间 latency,即:请求连接到接受到响应头之间的时间 5. 用于计算的... AUTOTHROTTLE_TARGET_CONCURRENCY target_delay = latency / self.target_concurrency new_delay = (slot.delay + target_delay) / 2.0 # 表示上一次的延迟时间 new_delay = max(target_delay, new_delay) new_delay = min(max(self.mindelay, new_delay), self.maxdelay) slot.delay = new_delay """ # 开始自动限速 # AUTOTHROTTLE_ENABLED = True # The initial download delay # 初始下载延迟 # AUTOTHROTTLE_START_DELAY = 5 # The maximum download delay to be set in case of high latencies # 最大下载延迟 # AUTOTHROTTLE_MAX_DELAY = 10 # The average number of requests Scrapy should be sending in parallel to each remote server # 平均每秒并发数 # AUTOTHROTTLE_TARGET_CONCURRENCY = 1.0 # Enable showing throttling stats for every response received: # 是否显示 # AUTOTHROTTLE_DEBUG = True # Enable and configure HTTP caching (disabled by default) # See http://scrapy.readthedocs.org/en/latest/topics/downloader-middleware.html#httpcache-middleware-settings """ 18. 启用缓存 目的用于将已经发送的请求或相应缓存下来,以便以后使用 from scrapy.downloadermiddlewares.httpcache import HttpCacheMiddleware from scrapy.extensions.httpcache import DummyPolicy from scrapy.extensions.httpcache import FilesystemCacheStorage """ # 是否启用缓存策略 # HTTPCACHE_ENABLED = True # 缓存策略:所有请求均缓存,下次在请求直接访问原来的缓存即可 # HTTPCACHE_POLICY = "scrapy.extensions.httpcache.DummyPolicy" # 缓存策略:根据Http响应头:Cache-Control、Last-Modified 等进行缓存的策略 # HTTPCACHE_POLICY = "scrapy.extensions.httpcache.RFC2616Policy" # 缓存超时时间 # HTTPCACHE_EXPIRATION_SECS = 0 # 缓存保存路径 # HTTPCACHE_DIR = 'httpcache' # 缓存忽略的Http状态码 # HTTPCACHE_IGNORE_HTTP_CODES = [] # 缓存存储的插件 # HTTPCACHE_STORAGE = 'scrapy.extensions.httpcache.FilesystemCacheStorage'
11.自定义命令
- 在spiders同级创建任意目录,如:commands
- 在其中创建 crawlall.py 文件 (此处文件名就是自定义的命令)
-
- 在settings.py 中添加配置 COMMANDS_MODULE = '项目名称.目录名称'
- 在项目目录执行命令:scrapy crawlall

5. 自定义命令 # from scrapy.commands import ScrapyCommand # from scrapy.utils.project import get_project_settings # # # class Command(ScrapyCommand): # requires_project = True # # def syntax(self): # return '[options]' # # def short_desc(self): # return 'Runs all of the spiders' # # def run(self, args, opts): # spider_list = self.crawler_process.spiders.list() # for name in spider_list: # self.crawler_process.crawl(name, **opts.__dict__) # self.crawler_process.start() # # # PS:源码 # def run(self, args, opts): # from scrapy.crawler import CrawlerProcess # CrawlerProcess.crawl # CrawlerProcess.start # """ # self.crawler_process对象中含有:_active = {d,} # """ # self.crawler_process.crawl('chouti',**opts.__dict__) # self.crawler_process.crawl('cnblogs',**opts.__dict__) # # # self.crawler_process.start()
参考:http://www.cnblogs.com/wupeiqi/articles/6229292.html
