WebView基本使用
WebView是View的一个子类,可以让你在activity中显示网页。
可以在布局文件中写入WebView:比如下面这个写了一个填满整个屏幕的WebView:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<WebView xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:id="@+id/webview"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="fill_parent"
/>
加载一个网页,使用loadUrl():
WebView myWebView = (WebView) findViewById(R.id.webview); myWebView.loadUrl(http://www.example.com);
注意要在manifest中加上访问网络的权限:
<manifest ... >
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.INTERNET" />
...
</manifest>
设置WebView要显示的网页
设置WevView要显示的网页方法有很多:
互联网页面直接用:
myWebView.loadUrl(“http://www.google.com“);
本地文件用:
myWebView.loadUrl(“file:///android_asset/XX.html“);
本地文件存放在:assets文件中。
还可以直接载入html的字符串,如:
String htmlString = "<h1>Title</h1><p>This is HTML text<br /><i>Formatted in italics</i><br />Anothor Line</p>"; // 载入这个html页面 myWebView.loadData(htmlString, "text/html", "utf-8");
在WebView中使用JavaScript
如果你想要载入的页面中用了JavaScript,你必须为你的WebView使能JavaScript。
一旦使能之后,你也可以自己创建接口在你的应用和JavaScript代码间进行交互。
使能JavaScript
可以通过getSettings()获得WebSettings,然后用setJavaScriptEnabled()使能JavaScript:
WebView myWebView = (WebView) findViewById(R.id.webview); WebSettings webSettings = myWebView.getSettings(); webSettings.setJavaScriptEnabled(true);
WebSettings中提供了很多有用的设置。
处理页面浏览
当用户点击了你的WebView中的一个链接,默认的行为是Android启动一个处理URL的应用,通常,默认的浏览器打开并下载目标URL。
但是,你可以在你的WebView中覆盖这一行为,使得连接仍在你的WebView中打开。
之后,根据在WebView中维护的网页浏览历史,你可以允许用户向前或向后浏览他们的网页。
在WebView中打开所有链接
要打开用户点击的链接,只需要用setWebViewClient()方法向你的WebView提供一个WebViewClient 比如:
WebView myWebView = (WebView) findViewById(R.id.webview); myWebView.setWebViewClient(new WebViewClient());
此时就OK了, 就可以在你的WebView中打开链接了。
关于打开链接位置的更多控制
如果你对在哪里打开链接需要更多的控制,你可以创建自己的类,继承 WebViewClient,然后覆写shouldOverrideUrlLoading() 方法。
比如下面这个:
private class MyWebViewClient extends WebViewClient
{
@Override
public boolean shouldOverrideUrlLoading(WebView view, String url)
{
if(Uri.parse(url).getHost().equals(www.example.com))
{
// This is my web site, so do not override; let my WebView load
// the page
return false;
}
// Otherwise, the link is not for a page on my site, so launch
// another Activity that handles URLs
Intent intent = new Intent(Intent.ACTION_VIEW, Uri.parse(url));
startActivity(intent);
return true;
}
}
将特定的链接用自己的WebView打开,其他链接用浏览器(intent启动了默认的处理URL的Activity)。
定义完之后把这个类的对象传入setWebViewClient()方法即可。
WebView myWebView = (WebView) findViewById(R.id.webview); myWebView.setWebViewClient(new MyWebViewClient());
实践验证:在直接设置setWebViewClient(new WebViewClient());时验证正确,即所有链接都是在WebView中打开。
在设置为自定义的WebViewClient子类对象时,发现链接仍然都是从默认浏览器中打开。
浏览网页历史回退
当你的WebView覆写了URL载入的行为,它会自动地对访问过的网页积累一个历史,你可以利用 goBack() 和 goForward()方法在这个历史中前进或后退。
比如说使用后退键进行网页后退:
/**
* 按键响应,在WebView中查看网页时,按返回键的时候按浏览历史退回,如果不做此项处理则整个WebView返回退出
*/
@Override
public boolean onKeyDown(int keyCode, KeyEvent event)
{
// Check if the key event was the Back button and if there's history
if ((keyCode == KeyEvent.KEYCODE_BACK) && myWebView.canGoBack())
{
// 返回键退回
myWebView.goBack();
return true;
}
// If it wasn't the Back key or there's no web page history, bubble up
// to the default
// system behavior (probably exit the activity)
return super.onKeyDown(keyCode, event);
}
canGoBack() 方法在网页可以后退时返回true。
类似的,canGoForward()方法可以检查是否有可以前进的历史记录。
如果你不执行这种检查,一旦 goBack() 和 goForward()方法到达历史记录顶端,它们将什么也不做。
如果不加这种设置,在用户按下Back键时,如果是WebView显示网页,则会将WebView作为整体返回。
程序实例
附上完整的程序:

import android.annotation.SuppressLint;
import android.app.Activity;
import android.content.Intent;
import android.net.Uri;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.view.KeyEvent;
import android.view.Menu;
import android.webkit.WebSettings;
import android.webkit.WebView;
import android.webkit.WebViewClient;
@SuppressLint("SetJavaScriptEnabled")
public class WebActivity extends Activity
{
private WebView myWebView = null;
@Override
public void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState)
{
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_web);
// 打开网页
myWebView = (WebView) findViewById(R.id.webview);
//
// myWebView.loadUrl("http://www.cnblogs.com/mengdd/");// 博客链接
myWebView.loadUrl("http://www.baidu.com/");// 百度链接
// JavaScript使能(如果要加载的页面中有JS代码,则必须使能JS)
WebSettings webSettings = myWebView.getSettings();
webSettings.setJavaScriptEnabled(true);
// 在WebView中打开链接(默认行为是使用浏览器,设置此项后都用WebView打开)
// myWebView.setWebViewClient(new WebViewClient());
// 这样设置后所有的链接都会在当前WebView中打开
// 更强的打开链接控制:自己覆写一个WebViewClient类:除了指定链接从WebView打开,其他的链接默认打开
myWebView.setWebViewClient(new MyWebViewClient());
}
@Override
public boolean onCreateOptionsMenu(Menu menu)
{
getMenuInflater().inflate(R.menu.activity_web, menu);
return true;
}
/**
* 自定义的WebViewClient类,将特殊链接从WebView打开,其他链接仍然用默认浏览器打开
*
* @author 1
*
*/
private class MyWebViewClient extends WebViewClient
{
@Override
public boolean shouldOverrideUrlLoading(WebView view, String url)
{
if (Uri.parse(url)
.getHost()
.equals("http://www.cnblogs.com/mengdd/archive/2013/02/27/2935811.html")
|| Uri.parse(url).getHost()
.equals("http://music.baidu.com/"))
{
// This is my web site, so do not override; let my WebView load
// the page
// 这是官网上的例子,但是我点击特定链接的时候仍然是用浏览器而不是用自己的WebView打开,加上下面这句view.loadUrl(url)仍然是用浏览器,无解,不知道哪里出了问题
// view.loadUrl(url);
return false;
}
// Otherwise, the link is not for a page on my site, so launch
// another Activity that handles URLs
Intent intent = new Intent(Intent.ACTION_VIEW, Uri.parse(url));
startActivity(intent);
return true;
}
}
/**
* 按键响应,在WebView中查看网页时,按返回键的时候按浏览历史退回,如果不做此项处理则整个WebView返回退出
*/
@Override
public boolean onKeyDown(int keyCode, KeyEvent event)
{
// Check if the key event was the Back button and if there's history
if ((keyCode == KeyEvent.KEYCODE_BACK) && myWebView.canGoBack())
{
// 返回键退回
myWebView.goBack();
return true;
}
// If it wasn't the Back key or there's no web page history, bubble up
// to the default
// system behavior (probably exit the activity)
return super.onKeyDown(keyCode, event);
}
}
绑定JavaScript与Android代码
当你为你的Android应用中的WebView专门开发一个网页应用时,你可以创建你的JavaScript代码和你的客户端的Android代码之间的接口。
比如,你可以用JavaScript代码调用Android代码中的方法,来展现一个对话框之类,而不是使用alert()方法(JS中的对话框方法)。
在JS和Android代码间绑定一个新的接口,需要调用 addJavascriptInterface()方法。
方法参数传入一个Java对象实例和一个字符串,该字符串是一个名字(interface name,注意此接口不是通常所说的那个用来实现的接口,而是传入的这个对象在JS中的别名),在JS代码中用此名字调用该Java对象的方法。
注意这个方法可以让JS代码控制宿主程序,这是一个非常有力的特性,但是同时也存在一些安全问题,因为进一步JS代码可以通过反射访问到注入对象的公有域。攻击者可能会在HTML和JavaScript中包含了有威胁性的代码。
所以Android 4.1,API 17,也就是JELLY_BEAN 开始,只有被JavascriptInterface 注解标识的公有方法可以被JS代码访问。
另外,因为JS代码和Java对象在这个WebView所私有的后台线程交互,所以还需要注意线程安全性问题。
注意,与JS代码绑定的的这个Java对象运行在另一个线程中,与创建它的线程不是一个线程。
注意,这个Java对象的域是不可访问的。
绑定JavaScript与Android代码的例子
比如可以定义这么一个类:
/**
* 自定义的Android代码和JavaScript代码之间的桥梁类
*
* @author 1
*
*/
public class WebAppInterface
{
Context mContext;
/** Instantiate the interface and set the context */
WebAppInterface(Context c)
{
mContext = c;
}
/** Show a toast from the web page */
// 如果target 大于等于API 17,则需要加上如下注解
// @JavascriptInterface
public void showToast(String toast)
{
// Toast.makeText(mContext, toast, Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show();
Toast.makeText(mContext, toast, Toast.LENGTH_LONG).show();
}
}
然后将这个类和你的WebView中的JS代码绑定:
WebView webView = (WebView) findViewById(R.id.webview); webView.addJavascriptInterface(new WebAppInterface(this), "Android");
给这个对象起的别名叫“Android”。
这个就创立了一个接口名,叫“Android”,运行在WebView中的JS代码可以通过这个名字调用WebAppInterface类中的showToast()方法:
<input type="button" value="Say hello" onClick="showAndroidToast('Hello Android!')" />
<script type="text/javascript">
function showAndroidToast(toast)
{
Android.showToast(toast);
}
</script>
特别注意:需要设置chrome handler
这个问题让我纳闷了好久,因为开始的时候我写的程序,JS代码中的按钮会出现在WebView中,但是点击下去后,不会弹出相应的对话框之类。
也就是说JS代码调用自己也没有执行?
同样的代码在别的地方执行可以正常弹出啊。所以我还提问来着:http://q.cnblogs.com/q/47060/
后来找了半天原因,才发现两个问题:
1.网页按钮按下后不出现JS对话框是因为没有设置chrome handler,需要设置如下:
// 如果不设置这个,JS代码中的按钮会显示,但是按下去却不弹出对话框
// Sets the chrome handler. This is an implementation of WebChromeClient
// for use in handling JavaScript dialogs, favicons, titles, and the
// progress. This will replace the current handler.
myWebView.setWebChromeClient(new WebChromeClient()
{
@Override
public boolean onJsAlert(WebView view, String url, String message,
JsResult result)
{
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
return super.onJsAlert(view, url, message, result);
}
});
2.调用Android代码的那个按钮也没有出现Toast是因为我把别名写错了(大小写没有注意)。(这个错误可以忽略,但是大家也要引以为戒。。Orz。。。)
Android调用JavaScript代码
这个还比较简单,需要调用的时候只需要一行代码:
myWebView.loadUrl("javascript:myFunction()");
其中myFunction()是JS函数。
这里要补充一下,如果JavaScript函数是带参数的,那么调用时要特别注意。
比如下面这个JS函数,在原来内容上加入一行:
function writeLine(string)
{
console.log("Write a new Line");//调试信息
document.getElementById("content").innerHTML += string + "<br />";//在content标签段落加入新行
}
注:其中content是自定义的标签,html中有一个段落是:
<p id="content"></p>
那么在Android代码中调用这个writeLine()函数时,需要传入一个字符串参数,比如,想要传入一个叫name的String:
myWebView.loadUrl("javascript:writeLine('"+name+"')");//JS代码要是带参数
还有就是要注意双引号中的函数名一定不要写错。
程序实例
做了一个程序:
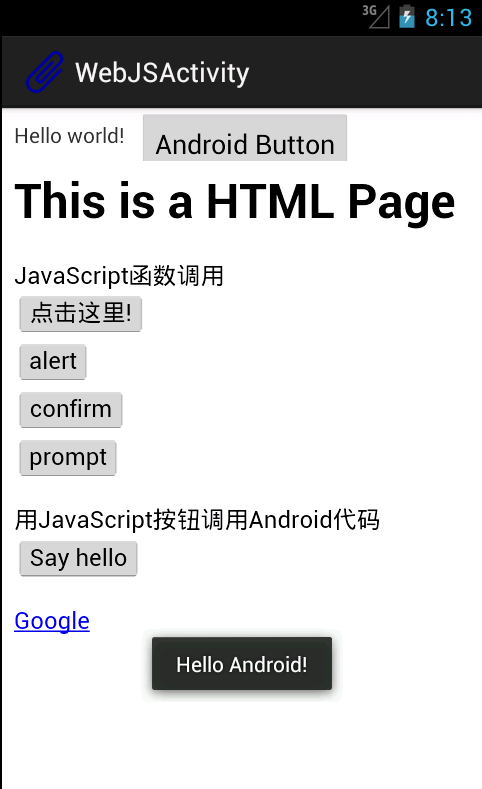
界面中包含一个TextView,旁边一个Button,下面整个是一个WebView。
在WebView中载入了一个本地html文件,本地文件存放在assets文件夹中。
网页中前四个按钮调用的是JavaScript函数,显示各种对话框。
SayHello按钮调用Android代码中的一个方法,显示一个Toast,如图中所示。
为了证明Android也可以调用JS代码,最上方的Android Button按下后和“点击这里”那个按钮的效果一致,都是出现JS的对话框。
Activity代码:

package com.example.hellowebjs;
import android.annotation.SuppressLint;
import android.app.Activity;
import android.content.Context;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.view.View;
import android.webkit.JsResult;
import android.webkit.WebChromeClient;
import android.webkit.WebSettings;
import android.webkit.WebView;
import android.webkit.WebViewClient;
import android.widget.Button;
import android.widget.Toast;
public class WebJSActivity extends Activity
{
private WebView myWebView = null;
private Button myButton = null;
@SuppressLint("SetJavaScriptEnabled")
@Override
public void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState)
{
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_web_js);
myWebView = (WebView) findViewById(R.id.myWebView);
// 得到设置属性的对象
WebSettings webSettings = myWebView.getSettings();
// 使能JavaScript
webSettings.setJavaScriptEnabled(true);
// 支持中文,否则页面中中文显示乱码
webSettings.setDefaultTextEncodingName("GBK");
// 限制在WebView中打开网页,而不用默认浏览器
myWebView.setWebViewClient(new WebViewClient());
// 如果不设置这个,JS代码中的按钮会显示,但是按下去却不弹出对话框
// Sets the chrome handler. This is an implementation of WebChromeClient
// for use in handling JavaScript dialogs, favicons, titles, and the
// progress. This will replace the current handler.
myWebView.setWebChromeClient(new WebChromeClient()
{
@Override
public boolean onJsAlert(WebView view, String url, String message,
JsResult result)
{
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
return super.onJsAlert(view, url, message, result);
}
});
// 用JavaScript调用Android函数:
// 先建立桥梁类,将要调用的Android代码写入桥梁类的public函数
// 绑定桥梁类和WebView中运行的JavaScript代码
// 将一个对象起一个别名传入,在JS代码中用这个别名代替这个对象,可以调用这个对象的一些方法
myWebView.addJavascriptInterface(new WebAppInterface(this),
"myInterfaceName");
// 载入页面:本地html资源文件
myWebView.loadUrl("file:///android_asset/sample.html");
// 这里用一个Android按钮按下后调用JS中的代码
myButton = (Button) findViewById(R.id.button1);
myButton.setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener()
{
@Override
public void onClick(View v)
{
// 用Android代码调用JavaScript函数:
myWebView.loadUrl("javascript:myFunction()");
// 这里实现的效果和在网页中点击第一个按钮的效果一致
}
});
}
/**
* 自定义的Android代码和JavaScript代码之间的桥梁类
*
* @author 1
*
*/
public class WebAppInterface
{
Context mContext;
/** Instantiate the interface and set the context */
WebAppInterface(Context c)
{
mContext = c;
}
/** Show a toast from the web page */
// 如果target 大于等于API 17,则需要加上如下注解
// @JavascriptInterface
public void showToast(String toast)
{
// Toast.makeText(mContext, toast, Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show();
Toast.makeText(mContext, toast, Toast.LENGTH_LONG).show();
}
}
}
HTML文件:

<html>
<head>
<h1>
This is a HTML Page
</h1>
<!-- JavaScript脚本,主要包括了按钮要执行的函数,显示对话框等 -->
<script type="text/javascript">
//JavaScript方法,弹出对话框显示信息
function myFunction()
{
alert("Hello World!");
}
function onAlert()
{
console.log("onAlert method");//显示调试信息
alert("This is a alert sample from html");
}
function onConfirm()
{
console.log("onConfirm method");
var b = confirm("are you sure to login?");
alert("your choice is " + b);
}
function onPrompt()
{
console.log("onPrompt method");
var b = prompt("please input your password", "aaa");
alert("your input is " + b);
}
//调用绑定的Java对象的方法,即调用Android代码显示对话框
function showAndroidToast(toast)
{
console.log("showAndroidToast method");
myInterfaceName.showToast(toast);//注意此处的myInterfaceName要和外部传入的名字一致,大小写正确
}
</script>
</head>
<body>
<p>
<!-- 前四个按钮调用JS函数 -->
JavaScript函数调用 <br />
<button onclick="myFunction()">点击这里!</button>
<br />
<input type="button" value="alert" onclick="onAlert()" /> <br />
<input type="button" value="confirm" onclick="onConfirm()" /> <br />
<input type="button" value="prompt" onclick="onPrompt()" /><br />
<!-- 上面用了两种定义按钮的方式,效果一样的 -->
</p>
<p>
<!-- 这个Say hello 按钮调用Android代码中的方法 -->
用JavaScript按钮调用Android代码 <br />
<input type="button"
value="Say hello" onClick="showAndroidToast('Hello Android!')" />
</p>
<a href="http://www.google.com" />Google
</a>
</body>
</html>
Activity布局文件:

<RelativeLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:id="@+id/myRelativeLayout"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent" >
<TextView
android:id="@+id/textView1"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:padding="@dimen/padding_medium"
android:text="@string/hello_world"
tools:context=".WebJSActivity" />
<Button
android:id="@+id/button1"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_toRightOf="@id/textView1"
android:text="@string/btn1_text" />
<WebView
android:id="@+id/myWebView"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="fill_parent"
android:layout_below="@id/textView1" />
</RelativeLayout>
