- 感知阶段
随着软件业的发展,互联网用户的日渐增多,并发这门艺术的兴起似乎是那么合情合理。每日PV十多亿的淘宝,处理并发的手段可谓是业界一流。用户访问淘宝首页的平均等待时间只有区区几秒,但是服务器所处理的流程十分复杂。首先负责首页的服务器就有好几千台,通过计算把与用户路由最近的服务器处理首页的返回。其次是网页上的资源,就JS和CSS文件就有上百个,还有图片资源等。它能在几秒内加载出来可见阿里几千名顶尖工程师的智慧是如何登峰造极。
而在大型电商网站中,他们的服务或者应用解耦之后,是通过消息队列在彼此间通信的。消息队列和应用之间的架构关系就是生产者消费者模型。
在介绍之前,先找找现实间的模型。笔者最近发觉,很多技术模型是和生活中的模型息息相关的。相信多数人都进过肯德基和麦当劳消费,笔者进店消费的时候发现他们的点单流程和并发模型十分接近。虽然每家店的流程有所差异,但是大概就只有两种模型。在肯德基里,你点单之后点单员会把所点的食物完成封装之后拿来你面前,然后让你结账,有时候有些耗时操作没完成就会留下一个餐台号稍后送来。而在麦当劳的点餐模型大致是,你点完快餐之后要求你立即付款,付完款之后下一位点餐,而取餐的是在旁边等待,另一个服务员专责负责配餐。
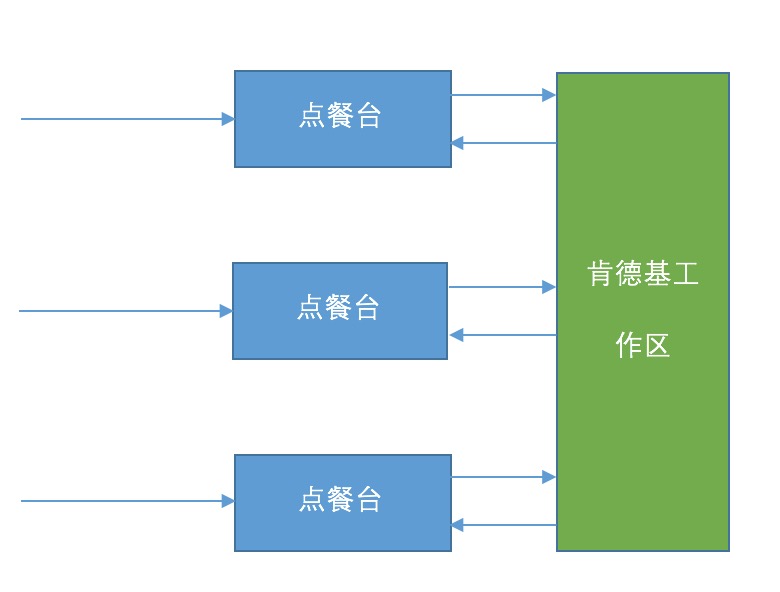
肯德基流程
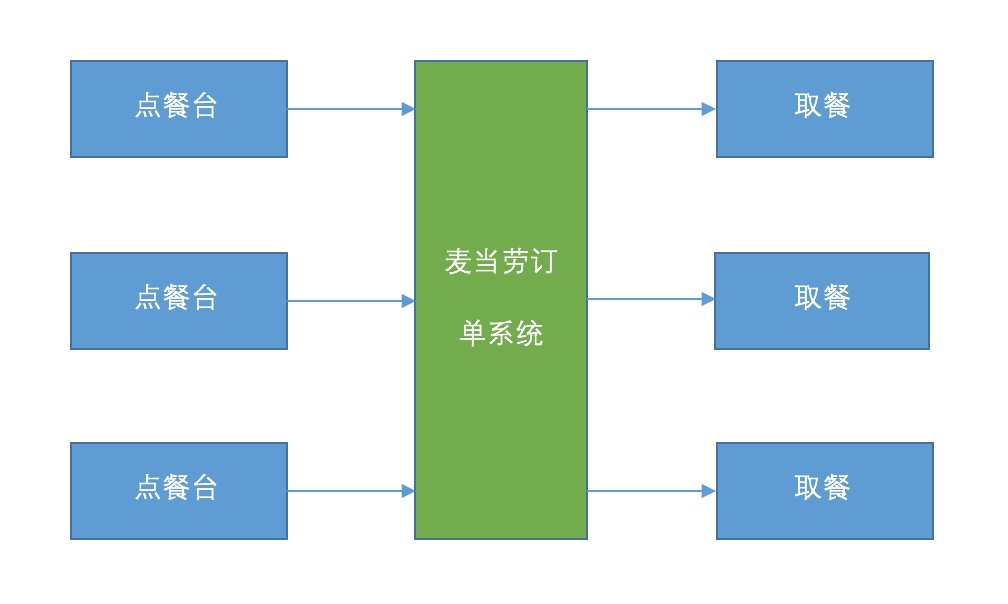
麦当劳点餐图
在并发模型中,肯德基比较倾向于一个线程把所有的服务都做完,而麦当劳倾向于服务解耦,让他们更专注于自己的业务。而肯德基的模型与BIO服务器的模型设计类似,麦当劳的模型则与生产者消费者模型十分相似。
- 生产消费者模型
生产者消费者模型具体来讲,就是在一个系统中,存在生产者和消费者两种角色,他们通过内存缓冲区进行通信,生产者生产消费者需要的资料,消费者把资料做成产品。生产消费者模式如下图。

在日益发展的服务类型中,譬如注册用户这种服务,它可能解耦成好几种独立的服务(账号验证,邮箱验证码,手机短信码等)。它们作为消费者,等待用户输入数据,在前台数据提交之后会经过分解并发送到各个服务所在的url,分发的那个角色就相当于生产者。消费者在获取数据时候有可能一次不能处理完,那么它们各自有一个请求队列,那就是内存缓冲区了。做这项工作的框架叫做消息队列。
- 生产者消费者模型的实现
生产者是一堆线程,消费者是另一堆线程,内存缓冲区可以使用List数组队列,数据类型只需要定义一个简单的类就好。关键是如何处理多线程之间的协作。这其实也是多线程通信的一个范例。
在这个模型中,最关键就是内存缓冲区为空的时候消费者必须等待,而内存缓冲区满的时候,生产者必须等待。其他时候可以是个动态平衡。值得注意的是多线程对临界区资源的操作时候必须保证在读写中只能存在一个线程,所以需要设计锁的策略。
下面这个例子是书上介绍的,生产者负责生产一个数字并存入缓冲区,消费者从缓冲区中取出数据并且求出它的平方并输出。
package ProducterAndConsumer.Version1; import java.util.Random; import java.util.concurrent.BlockingQueue; import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit; import java.util.concurrent.atomic.AtomicInteger; /** * 生产者 * @author ctk * 生产者消费者模型 */ public class Producer implements Runnable { private volatile boolean isRunning = true; private BlockingQueue<PCData> queue;// 内存缓冲区 private static AtomicInteger count = new AtomicInteger();// 总数 原子操作 private static final int SLEEPTIME = 1000; public Producer(BlockingQueue<PCData> queue) { this.queue = queue; } @Override public void run() { PCData data = null; Random r = new Random(); System.out.println("start producting id:" + Thread.currentThread().getId()); try { while (isRunning) { Thread.sleep(r.nextInt(SLEEPTIME)); data = new PCData(count.incrementAndGet()); System.out.println(data + " 加入队列"); if (!queue.offer(data, 2, TimeUnit.SECONDS)) { System.err.println(" 加入队列失败"); } } } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); Thread.currentThread().interrupt(); } } public void stop() { isRunning = false; } }
package ProducterAndConsumer.Version1; /** * 消费者 * @author ctk */ import java.text.MessageFormat; import java.util.Random; import java.util.concurrent.BlockingQueue; public class Consumer implements Runnable{ private BlockingQueue<PCData> queue; private static final int SLEEPTIME = 1000; public Consumer(BlockingQueue<PCData> queue){ this.queue = queue; } @Override public void run() { System.out.println("start Consumer id :"+Thread.currentThread().getId()); Random r = new Random(); try{ while(true){ PCData data = queue.take(); if(data != null) { int re = data.getData() * data.getData(); System.out.println(MessageFormat.format("{0}*{1}={2}", data.getData(),data.getData(),re)); Thread.sleep(r.nextInt(SLEEPTIME)); } } }catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); Thread.currentThread().interrupt(); } } }
package ProducterAndConsumer.Version1; import java.util.concurrent.BlockingQueue; import java.util.concurrent.ExecutorService; import java.util.concurrent.Executors; import java.util.concurrent.LinkedBlockingDeque; /** * 主函数 * @author ctk * */ public class Main { public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException { BlockingQueue<PCData> queue = new LinkedBlockingDeque<>(10); Producer p1 = new Producer(queue); Producer p2 = new Producer(queue); Producer p3 = new Producer(queue); Consumer c1 = new Consumer(queue); Consumer c2 = new Consumer(queue); Consumer c3 = new Consumer(queue); ExecutorService service = Executors.newCachedThreadPool(); service.execute(p1); service.execute(p2); service.execute(p3); service.execute(c1); service.execute(c2); service.execute(c3); Thread.sleep(10*1000); p1.stop(); p2.stop(); p3.stop(); Thread.sleep(3000); service.shutdown(); } }
package ProducterAndConsumer.Version1; /** * 容器数据类型 * @author ctk * */ public class PCData { private final int intData; public PCData(int d){ intData = d; } public PCData(String d){ intData = Integer.valueOf(d); } public int getData(){ return intData; } @Override public String toString(){ return "data:"+intData; } }
因为BlockingQueue是一个阻塞队列,它的存取可以保证只有一个线程在进行,所以根据逻辑,生产者在内存满的时候进行等待,并且唤醒消费者队列,反过来消费者在饥饿状态下等待并唤醒生产者进行生产。
下面的两个版本是使用notify/wait()和await()/signal()方法进行设计的。在结构上是一致遵从模型图的。
package ProducterAndConsumer.Version2; import java.util.List; /** * 消费者 * * @author ctk * */ public class Consumer implements Runnable { private List<PCData> queue; public Consumer(List<PCData> queue) { this.queue = queue; } @Override public void run() { try { while (true) { if (Thread.currentThread().isInterrupted()) break; PCData data = null; synchronized (queue) { if (queue.size() == 0) { queue.wait(); queue.notifyAll(); } data = queue.remove(0); } System.out.println( Thread.currentThread().getId() + " 消费了:" + data.get() + " result:" + (data.get() * data.get())); Thread.sleep(1000); } } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } } package ProducterAndConsumer.Version2; import java.util.List; import java.util.Random; /** * 生产者 * * @author MacBook * */ public class Producer implements Runnable { private List<PCData> queue; private int length; public Producer(List<PCData> queue, int length) { this.queue = queue; this.length = length; } @Override public void run() { try { while (true) { if (Thread.currentThread().isInterrupted()) break; Random r = new Random(); long temp = r.nextInt(100); System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getId() + " 生产了:" + temp); PCData data = new PCData(); data.set(temp); synchronized (queue) { if (queue.size() >= length) { queue.notifyAll(); queue.wait(); } else queue.add(data); } Thread.sleep(1000); } } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } } package ProducterAndConsumer.Version2; import java.util.ArrayList; import java.util.List; import java.util.concurrent.ExecutorService; import java.util.concurrent.Executors; public class Main { public static void main(String[] args) { List<PCData> queue = new ArrayList<PCData>(); int length = 10; Producer p1 = new Producer(queue,length); Producer p2 = new Producer(queue,length); Producer p3 = new Producer(queue,length); Consumer c1 = new Consumer(queue); Consumer c2 = new Consumer(queue); Consumer c3 = new Consumer(queue); ExecutorService service = Executors.newCachedThreadPool(); service.execute(p1); service.execute(p2); service.execute(p3); service.execute(c1); service.execute(c2); service.execute(c3); } } package ProducterAndConsumer.Version2; /** * 基本数据类型 * @author ctk * */ public class PCData { private long value; public void set(long value){ this.value = value; } public long get(){ return value; } }
package ProducterAndConsumer.Version3; import java.util.List; /** * 消费者 * @author ctk * */ public class Consumer implements Runnable{ private List<PCData> queue; public Consumer(List<PCData> queue){ this.queue = queue; } @Override public void run() { try { while (true) { if (Thread.currentThread().isInterrupted()) break; PCData data = null; Main.lock.lock(); if (queue.size() == 0){ Main.full.signalAll(); Main.empty.await(); } Thread.sleep(1000); data = queue.remove(0); Main.lock.unlock(); System.out.println("消费者ID:"+Thread.currentThread().getId()+" 消费了:"+data.getData()+" result:"+(data.getData()*data.getData())); } } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } } package ProducterAndConsumer.Version3; import java.util.List; import java.util.Random; /** * 生产者 * @author ctk * */ public class Producter implements Runnable{ private List<PCData> queue; private int len; public Producter(List<PCData> queue,int len){ this.queue = queue; this.len = len; } @Override public void run() { try{ while(true){ if(Thread.currentThread().isInterrupted()) break; Random r = new Random(); PCData data = new PCData(); data.setData(r.nextInt(500)); Main.lock.lock(); if(queue.size() >= len) { Main.empty.signalAll(); Main.full.await(); } Thread.sleep(1000); queue.add(data); Main.lock.unlock(); System.out.println("生产者ID:"+Thread.currentThread().getId()+" 生产了:"+data.getData()); } }catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } } package ProducterAndConsumer.Version3; import java.util.ArrayList; import java.util.List; import java.util.concurrent.ExecutorService; import java.util.concurrent.Executors; import java.util.concurrent.locks.Condition; import java.util.concurrent.locks.ReentrantLock; public class Main { public static ReentrantLock lock = new ReentrantLock(); public static Condition empty = lock.newCondition(); public static Condition full = lock.newCondition(); public static void main(String[] args) { List<PCData> queue = new ArrayList<PCData>(); int length = 10; Producter p1 = new Producter(queue,length); Producter p2 = new Producter(queue,length); Producter p3 = new Producter(queue,length); Consumer c1 = new Consumer(queue); Consumer c2 = new Consumer(queue); Consumer c3 = new Consumer(queue); ExecutorService service = Executors.newCachedThreadPool(); service.execute(p1); service.execute(p2); service.execute(p3); service.execute(c1); service.execute(c2); service.execute(c3); } } package ProducterAndConsumer.Version3; public class PCData { private int data; public int getData() { return data; } public void setData(int data) { this.data = data; } }
await的版本我个人写出来之后感觉,每次控制台只输出了一句话,说明在同一时间内生产者或者消费者只有一个是激活的,而wait的版本,一次可能有多个生成者激活。我个人觉得wait的版本更接近我的构想。
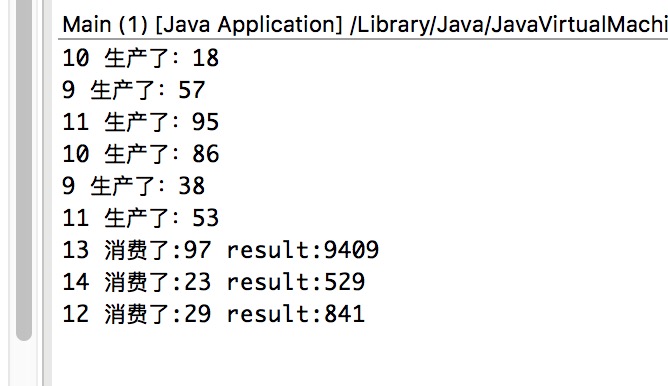
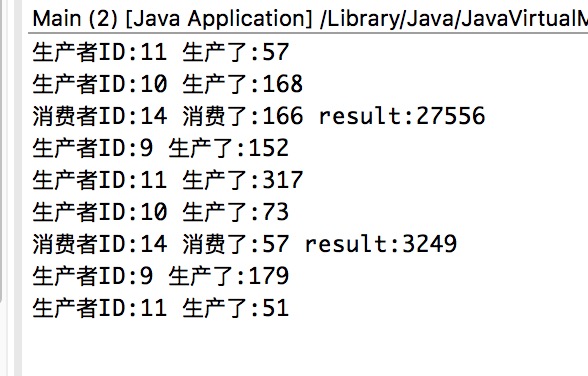
-----update 2019-03-30
之前的实现review了一下,感觉有点累赘,在线程中加同步关键字,又使用阻塞队列;西餐讲究从最基础的食材进行调味,那我们自己写一个阻塞队列吧,大体上的设计是这样。


参考了阻塞队列BlockingQueue的实现,加上一些线程同步的思想,自己写一个BlokingQueue非常简单。
import java.util.concurrent.atomic.AtomicInteger; import java.util.concurrent.locks.Condition; import java.util.concurrent.locks.ReentrantLock; /** * Created by ctk on 2019/3/29. */ public class MyBlockingQueue<E> { private Object[] data; private ReentrantLock lock; private Condition full; private Condition empty; private int takeIndex; private int putIndex; private AtomicInteger size ; private static final int DEFAULT_CAPACITY = 10; public MyBlockingQueue (){ this(DEFAULT_CAPACITY); } public MyBlockingQueue(int initCapacity){ if(initCapacity < 0){ throw new IllegalStateException("initCapacity must not be negative"); } data = new Object[initCapacity]; size = new AtomicInteger(0); takeIndex = putIndex = 0; lock = new ReentrantLock(); full = lock.newCondition(); empty = lock.newCondition(); } public void add(E e){ try{ offer(e); }catch (InterruptedException exp){ throw new RuntimeException("add interrupted"); } } public E get(){ try{ return take(); }catch (InterruptedException exp){ throw new RuntimeException("add interrupted"); } } private int reset(int index){ if(index > data.length - 1){ return 0; }else { return index; } } private void offer(E e) throws InterruptedException{ try{ lock.lockInterruptibly(); while (size.get() == data.length){ full.await(); } data[putIndex++] = e; putIndex = reset(putIndex); // if(size.incrementAndGet() == data.length){ // empty.signalAll(); // } size.incrementAndGet(); empty.signal(); return ; }finally { lock.unlock(); } } private E take() throws InterruptedException{ try{ lock.lockInterruptibly(); while (size.get() == 0){ empty.await(); } E e = (E)data[takeIndex]; data[takeIndex++] = null; takeIndex = reset(takeIndex); // if(size.decrementAndGet() == 0){ // full.signalAll(); // } size.decrementAndGet(); full.signal(); return e; }finally { lock.unlock(); } } }
在这个队列中,入队时候如果size达到最大则自旋阻塞,如果成功入队可以选择唤醒一个消费者,或者唤醒所有消费者;而出队操作时候,如果队列为空,则自旋阻塞,如果出队成功,则唤醒一个(所有)生产者;
/** * Created by ctk on 2019/3/30. */ public abstract class Worker<E> implements Runnable{ private MyBlockingQueue<E> queue; public Worker(MyBlockingQueue queue){ this.queue = queue; } @Override public void run() { handler(); } protected abstract void handler(); public MyBlockingQueue<E> getQueue() { return queue; } }
这里用了抽象的方法定义了Worker,只需要实现handler就好了;
import java.util.Random;
/** * Created by ctk on 2019/3/30. */ public class Provider extends Worker<Integer>{ private Random random; public Provider(MyBlockingQueue queue) { super(queue); random = new Random(); } @Override protected void handler() { for (int i=0;i<100;i++){ int seed = random.nextInt(100); getQueue().add(seed); System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+" send ["+seed+"] to queue"); // // try{ // Thread.sleep(1500); // }catch (Exception e){ // e.printStackTrace(); // } } } }
/** * Created by ctk on 2019/3/30. */ public class Consumer extends Worker<Integer>{ public Consumer(MyBlockingQueue queue) { super(queue); } @Override protected void handler() { try{ for(int i=0;i<100;i++){ int seed = getQueue().get(); int count = seed * 2 + 1; System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+" consumer ["+seed+"],count 2n+1 result :"+count); } }catch (Exception e){ e.printStackTrace(); } } }
生产消费模型,本质上是一种线程间通信的方法,而且使用的是共同内存区,只需要处理好线程同步的关系就好了。
-----update 2019-03-30
-----update 2019-04-13
我们考虑,是否可以不使用锁,于是我读了一篇lock-free的论文,初步使用了无锁数组实现并发队列。
我定义这个无锁环形数组,使用的是非空元素集合,而空作为数组EMPTY的情况。有兴趣可以看一下最新一篇,Lock-Free论文实践。
/**
* Created by MacBook on 2019/4/13.
*/
public class MyLockFreeQueue<E> implements MyQueue<E>{
private Object[] data;
private AtomicInteger takeIndex;
private AtomicInteger putIndex;
private AtomicInteger size;
private static final int DEFAULT_CAPACITY = 10;
public MyLockFreeQueue (){
this(DEFAULT_CAPACITY);
}
public MyLockFreeQueue(int initCapacity){
if(initCapacity < 0){
throw new IllegalStateException("initCapacity must not be negative");
}
data = new Object[initCapacity];
takeIndex = new AtomicInteger(0);
putIndex = new AtomicInteger(0);
size = new AtomicInteger(0);
}
public boolean add(E e){
if(e == null){
throw new NullPointerException("the element you put can't be null");
}
for(int index = putIndex.get();;){
if(size.get() == data.length){
return false;
}
int expect = (index == data.length - 1)?0:(index+1);
if(putIndex.compareAndSet(index,expect)){
data[index] = e;
size.incrementAndGet();
return true;
}
}
}
public E take(){
for(int index = takeIndex.get();;){
if(size.get() == 0){
return null;
}
int expect = (index == data.length - 1)?0:(index+1);
E e = (E)data[index];
if(takeIndex.compareAndSet(index,expect)){
size.decrementAndGet();
return e;
}
}
}
}
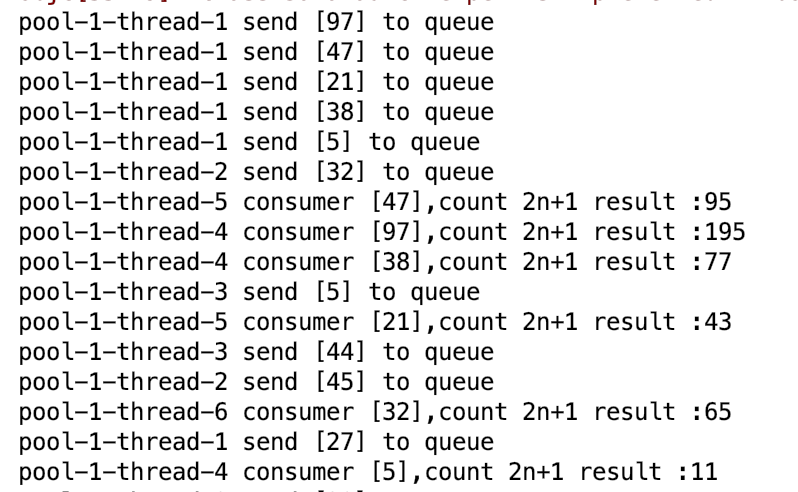
而生产消费者,对应的代码应该是。这样会在cpu中进行无效循环,不过使用CAS(论文说的CSW,醉了)就是要承担cpu自旋的成本。
for (int i=0;i<100;){
int seed = random.nextInt(100);
if(getQueue().add(seed)){
i++;
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+" send ["+seed+"] to queue"+"; total "+Worker.count1.incrementAndGet());
}
}
for(int i=0;i<100;){
Integer seed = getQueue().take();
if(seed != null){
i++;
int count = seed * 2 + 1;
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+" consumer ["+seed+"],count 2n+1 result :"+count+"; total "+Worker.count2.incrementAndGet());
}
}
pool-1-thread-1 send [77] to queue; total 1
pool-1-thread-1 send [86] to queue; total 2
pool-1-thread-1 send [18] to queue; total 3
pool-1-thread-1 send [30] to queue; total 4
pool-1-thread-1 send [28] to queue; total 5
pool-1-thread-3 consumer [77],count 2n+1 result :155; total 1
pool-1-thread-3 consumer [86],count 2n+1 result :173; total 2
pool-1-thread-2 send [72] to queue; total 6
pool-1-thread-1 send [80] to queue; total 7
pool-1-thread-3 consumer [18],count 2n+1 result :37; total 3
pool-1-thread-1 send [3] to queue; total 8
pool-1-thread-3 consumer [30],count 2n+1 result :61; total 4
pool-1-thread-1 send [15] to queue; total 9
pool-1-thread-3 consumer [28],count 2n+1 result :57; total 5
pool-1-thread-2 send [69] to queue; total 10
pool-1-thread-3 consumer [72],count 2n+1 result :145; total 6
pool-1-thread-3 consumer [80],count 2n+1 result :161; total 7
pool-1-thread-3 consumer [23],count 2n+1 result :47; total 8
pool-1-thread-3 consumer [15],count 2n+1 result :31; total 9
pool-1-thread-2 send [0] to queue; total 11
pool-1-thread-1 send [23] to queue; total 12
pool-1-thread-2 send [78] to queue; total 13
pool-1-thread-3 consumer [69],count 2n+1 result :139; total 10
pool-1-thread-2 send [14] to queue; total 15
pool-1-thread-1 send [12] to queue; total 14
...
效果还不错,如果消费者跟不上,可能会引起生产者阻塞,一直无法退出,不过这个可以自行优化。
-----update 2019-04-13
- 生产消费者模型思维
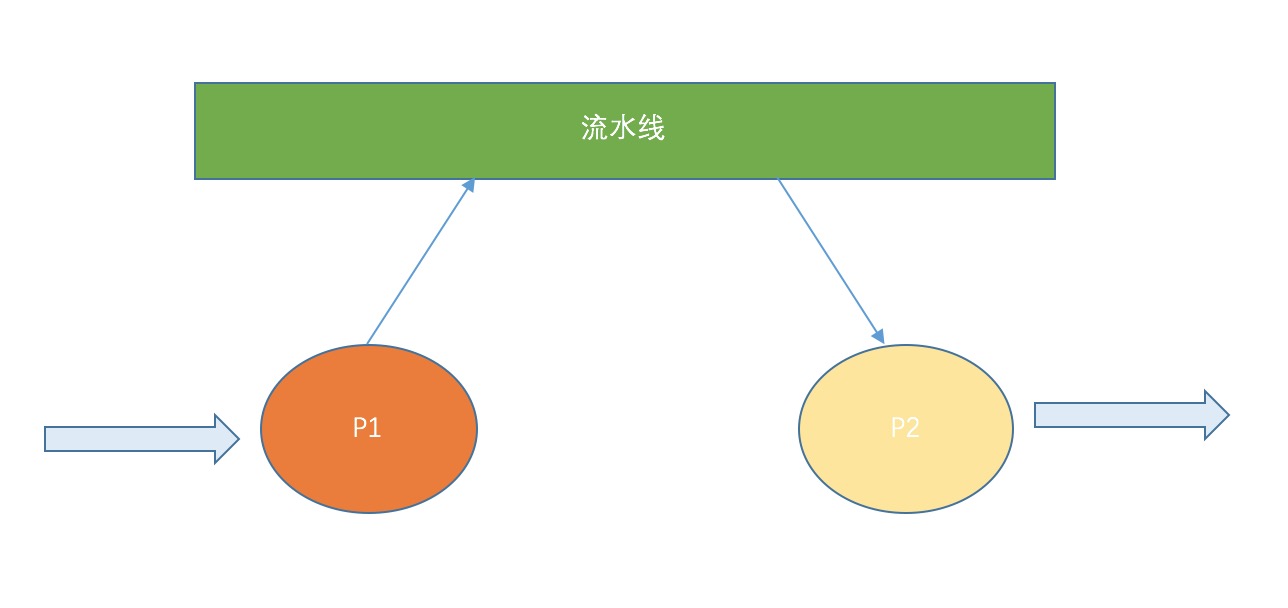
下午翻书,偶然发现并行计算的流水线思维。并行计算的要点就是分治法思维,如果能证明分割的两部分在因果上没有关联,则可以进行并行计算。譬如书上的例子(A+B)*C,这个算式是不能使用并行计算分割的,因为它的结果是A+B之后的结果乘以C。但是并行流水线的思维是,我们可以请两个工人,每个工人负责一步的处理。
分解后的架构是:P1:D = A + B;P2:R = D*3;
在这两个线程处理中并不需要存在因果,所以他们可以并行计算了。
设计这个模式是基于生产消费者模型的,流水线需要使用流水线传递半成品,流水线就是内存缓冲区,对于P2来说,P1就是生产者,而对于系统需要的结果来说,P2就是生产者。
- 后记
偶然读到一本书,上面提到的建立高速公路的学习方法是十分高效的学习方法,在学习新的技术的时候它们或多或少都会在现实中有所映射,所以读万卷书行万里路,经历和学术需要并行增长。技术模型不仅应用在技术领域,管理领域也可以参照思考,learn more,study less。