缓存可以说是加速服务响应速度的一种非常有效并且简单的方式。在缓存领域,有很多知名的框架,如EhCache 、Guava、HazelCast等。Redis作为key-value型数据库,由于他的这一特性,Redis也成为一种流行的数据缓存工具。
在传统方式下对于缓存的处理代码是非常臃肿的。
例如:我们要把一个查询函数加入缓存功能,大致需要三步。
一、在函数执行前,我们需要先检查缓存中是否存在数据,如果存在则返回缓存数据
二、如果不存在,就需要在数据库的数据查询出来。
三、最后把数据存放在缓存中,当下次调用此函数时,就可以直接使用缓存数据,减轻了数据库压力。
那么实现上面的三步需要多少代码呢?下面是一个示例:
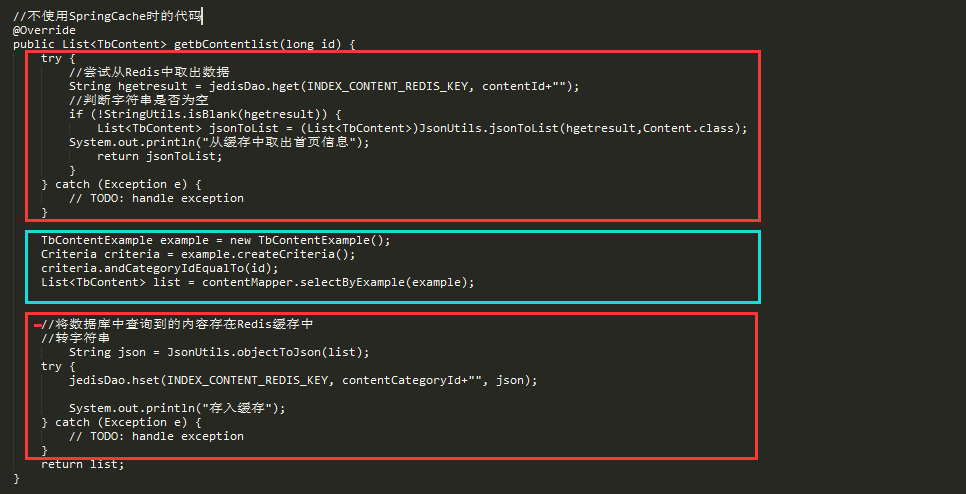
上图中的红色部分都是模板代码,真正与这个函数有关的代码却只占了1/5,对于所有需要实现缓存功能的函数,都需要加上臃肿的模板代码。可谓是一种极不优雅的解决方案。
那么如何让臃肿的代码重回清新的当初呢?
AOP不就是专门解决这种模板式代码的最佳方案吗,幸运的是我们不需要再自己实现切面了,SpringCache已经为我们提供好了切面,我们只需要进行简单的配置,就可以重回当初了,像下面这样:

只需要加一个注解就可以了,对于原来的代码连改都不需要改,是不是已经跃跃欲试了?
对于配置SpringCache只需要三步:
第一步:加入相关依赖:
<dependency> <groupId>redis.clients</groupId> <artifactId>jedis</artifactId> <version>2.9.0</version> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.data</groupId> <artifactId>spring-data-redis</artifactId> <version>1.6.0.RELEASE</version> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.apache.commons</groupId> <artifactId>commons-lang3</artifactId>
<version>3.3.2</version> </dependency>
第二步:配置SpringCache,Redis连接等信息
applicationContext-redis.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns:p="http://www.springframework.org/schema/p" xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context" xmlns:mvc="http://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc" xmlns:cache="http://www.springframework.org/schema/cache" xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-4.2.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context-4.2.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc http://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc/spring-mvc-4.2.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/cache http://www.springframework.org/schema/cache/spring-cache-4.2.xsd">
<!-- 配置文件加载 -->
<context:property-placeholder location="classpath:*.properties"/>
<cache:annotation-driven cache-manager="cacheManager"/> <!-- redis连接池 --> <bean id="poolConfig" class="redis.clients.jedis.JedisPoolConfig"> <property name="maxIdle" value="${redis.maxIdle}" /> <property name="maxWaitMillis" value="${redis.maxWait}" /> <property name="testOnBorrow" value="${redis.testOnBorrow}" /> </bean> <!-- 连接工厂 --> <bean id="JedisConnectionFactory" class="org.springframework.data.redis.connection.jedis.JedisConnectionFactory" p:host-name="${redis.host}" p:port="${redis.port}" p:password="${redis.pass}" p:pool-config-ref="poolConfig"/> <!-- redis模板 --> <bean id="redisTemplate" class="org.springframework.data.redis.core.RedisTemplate"> <property name="connectionFactory" ref="JedisConnectionFactory" /> </bean> <bean id="cacheManager" class="org.springframework.cache.support.SimpleCacheManager"> <property name="caches"> <set> <!-- 这里可以配置多个redis --> <bean class="com.cky.rest.utils.RedisCache"> <property name="redisTemplate" ref="redisTemplate" /> <property name="name" value="content"/> <!-- name对应的名称要在类或方法的注解中使用 --> </bean> </set> </property> </bean> </beans>
redis.properties文件:
# Redis settings
# server IP
redis.host=192.168.100.55
# server port
redis.port=6379
# server pass
redis.pass=
# use dbIndex
redis.database=0
#max idel instance of jedis
redis.maxIdle=300
#if wait too long ,throw JedisConnectionException
redis.maxWait=3000
#if true,it will validate before borrow jedis instance,what you get instance is all usefull
redis.testOnBorrow=true
第三步,编写Cache接口实现类
Spring对于缓存只是提供了抽象的接口,并且通过接口来调用功能,没有具体的实现类,所以需要我们自己实现具体的操作。
在上面配置中可知,每个实现类都会注入一个redisTemplate实例,我们就可以通过redisTemplate来操作redis

package com.cky.rest.utils; import java.io.Serializable; import org.apache.commons.lang3.SerializationUtils; import org.springframework.cache.Cache; import org.springframework.cache.support.SimpleValueWrapper; import org.springframework.dao.DataAccessException; import org.springframework.data.redis.connection.RedisConnection; import org.springframework.data.redis.core.RedisCallback; import org.springframework.data.redis.core.RedisTemplate; public class RedisCache implements Cache { private RedisTemplate<String, Object> redisTemplate; private String name; @Override public void clear() { System.out.println("-------緩存清理------"); redisTemplate.execute(new RedisCallback<String>() { @Override public String doInRedis(RedisConnection connection) throws DataAccessException { connection.flushDb(); return "ok"; } }); } @Override public void evict(Object key) { System.out.println("-------緩存刪除------"); final String keyf=key.toString(); redisTemplate.execute(new RedisCallback<Long>() { @Override public Long doInRedis(RedisConnection connection) throws DataAccessException { return connection.del(keyf.getBytes()); } }); } @Override public ValueWrapper get(Object key) { System.out.println("------缓存获取-------"+key.toString()); final String keyf = key.toString(); Object object = null; object = redisTemplate.execute(new RedisCallback<Object>() { @Override public Object doInRedis(RedisConnection connection) throws DataAccessException { byte[] key = keyf.getBytes(); byte[] value = connection.get(key); if (value == null) { System.out.println("------缓存不存在-------"); return null; } return SerializationUtils.deserialize(value); } }); ValueWrapper obj=(object != null ? new SimpleValueWrapper(object) : null); System.out.println("------获取到内容-------"+obj); return obj; } @Override public void put(Object key, Object value) { System.out.println("-------加入缓存------"); System.out.println("key----:"+key); System.out.println("key----:"+value); final String keyString = key.toString(); final Object valuef = value; final long liveTime = 86400; redisTemplate.execute(new RedisCallback<Long>() { @Override public Long doInRedis(RedisConnection connection) throws DataAccessException { byte[] keyb = keyString.getBytes(); byte[] valueb = SerializationUtils.serialize((Serializable) valuef); connection.set(keyb, valueb); if (liveTime > 0) { connection.expire(keyb, liveTime); } return 1L; } }); } @Override public <T> T get(Object arg0, Class<T> arg1) { // TODO Auto-generated method stub return null; } @Override public String getName() { return this.name; } @Override public Object getNativeCache() { return this.redisTemplate; } @Override public ValueWrapper putIfAbsent(Object arg0, Object arg1) { // TODO Auto-generated method stub return null; } public RedisTemplate<String, Object> getRedisTemplate() { return redisTemplate; } public void setRedisTemplate(RedisTemplate<String, Object> redisTemplate) { this.redisTemplate = redisTemplate; } public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } }
在配置过程中曾经出现过两次错误:
1.Xxxx.ClassNotFoundException 最后发现是jar下载不完整,把maven本地仓库的对应jar包文件夹删除完从新下载就好了
2.Xxxx.MethodNotFoundException 这种情况是版本不对,换成第一步中的版本就可以了
SpringCache中常见注解的使用:
@Cacheable注解
最常用的注解,会把被注解方法的返回值缓存。工作原理是:首先在缓存中查找,如果没有执行方法并缓存结果,然后返回数据。此注解的缓存名必须指定,和cacheManager中的caches中的某一个Cache的name值相对应。可以使用value或cacheNames指定。
如果没有指定key属性,spring会使用默认的主键生成器产生主键。也可以自定义主键,在key中可以使用SpEL表达式。如下:
@Cacheable(cacheNames=”content”,key=”#user.userId”) Public User getUser(User user){ xxxxx }
可以使用condition属性,来给缓存添加条件,如下:
@Cacheable(cacheNames=”content”,key=”#user.userId”,condition=”#user.age<40”) Public User getUser(User user){xxxxx}
@CachePut注解
先执行方法,然后将返回值放回缓存。可以用作缓存的更新。
@CacheEvict注解
该注解负责从缓存中显式移除数据,通常缓存数据都有有效期,当过期时数据也会被移除。
此注解多了两个属性:
allEntries是否移除所有缓存条目。
beforeInvocation:在方法调用前还是调用后完成移除操作。true/false
