1.官网:
2.什么是vuex?
Vuex 是一个专为 Vue.js 应用程序开发的状态管理模式。它采用集中式存储管理应用的所有组件的状态,并以相应的规则保证状态以一种可预测的方式发生变化。Vuex 也集成到 Vue 的官方调试工具 devtools extension (opens new window),提供了诸如零配置的 time-travel 调试、状态快照导入导出等高级调试功能。
3.安装
npm
npm i vuex --save
yarn
npm i yarn -g
yarn add vuex
4.创建仓库
src/store/index.js
import Vue from 'vue'
import Vuex from "vuex"
Vue.use(Vuex)
export default new Vuex.Store({
//状态【数据】
state: {
name:"妲己",
age:10,
arr:[],//从后端取回来的数据
},
//只有mutations才直接修改state,mutations做的是同步操作
mutations: {
changeName(state,name){
state.name=name;
},
changeAge(state,age){
state.age=age;
},
changeArr(state,arr){
state.arr=arr;
}
},
//可以做异步操作|逻辑操作,一般情况下主要做ajax
actions: {
// context是仓库本身
asyncChangeName(context,name){
setTimeout(()=>{
context.commit('changeName',name)
},1000)
},
reqArr(context){
/*
axios().then(res=>{
context.commit("changeArr",res.data.list)
})*/
}
},
//类似计算属性 computed,导出数据给组件的
getters:{
name(state){
return state.name;
},
age(state){
return state.age
},
arr(state){
return state.arr;
},
info(state){
return `我叫${state.name},年龄${state.age}`
}
},
})
组件使用方法:
1.组价取值:$store.state.name
2.触发mutations中的方法:$store.commit('changeName','王昭君')
3.触发actions中的方法:$store.dispatch('asyncChangeName','王昭君')
4.this.$store.getters.name
5.小结
vuex是单向数据流,表单是双向数据绑定,所以有表单的地方就不要使用vuex。
state—(getters)—>组件展示的数据——(actions)——>mutations—(修改)—>state---(getters)—>组件展示—>…..
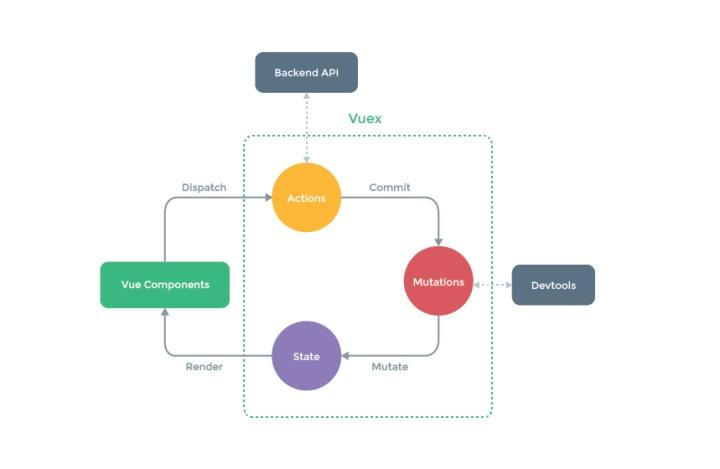
6.辅助函数
可以通过mapGetters将getters上的数据导入给组件的computed
可以通过mapActions将actions上的方法导入给组件的methods
<template>
<div class="box">
<h3>this is D</h3>
<div> getters name:{{name}}</div>
<div> getters info:{{info}}</div>
<button @click="changeName('鲁班')">鲁班</button>
<button @click="asyncChangeName('宫本')">宫本</button>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import {mapGetters,mapActions} from "vuex"
export default {
computed:{
//...mapGetters(["name","info"]),
...mapGetters({
name:"name",
info:"info"
}),
a(){
return 10;
}
},
methods:{
//...mapActions(["changeName","asyncChangeName"])
...mapActions({
changeName:"changeName",
asyncChangeName:"asyncChangeName"
}),
}
}
</script>
7.mutations VS actions
mutations 同步操作、 可以修改state $store.commit()触发
actions 异步操作、逻辑 不可以修改state $store.dispatch()触发
8.Vuex VS 本地存储
(需要整理下代码,上传)
vuex 刷新数据没有了 ,方便组件取值,数据改变可以实时渲染
本地存储 刷新数据还在 ,取值不方便,不会实时渲染
9.vuex中数组变了,页面不渲染,怎么解决?
(需要整理下代码,上传)
arr.splice()
Vue.set()
10.模块化
new Vuex.Store({
state:{},
mutations:{},
actions:{},
getters:{},
modules:{
home:{
state:{},
mutations:{},
actions:{},
getters:{},
namespaced:true,//命名空间
}
}
})
3.案例 组件层(vue)和状态层(vuex)解耦
(未上传)
1.轮播图数据
store/index.js
export default new Vuex.Store({
state: {
//轮播图数据
bannerList: []
},
mutations: {
//修改bannerList
changeBannerList(state, arr) {
state.bannerList = arr;
}
},
actions: {
//发请求bannerList
reqBannerList(context){
//发请求
reqBanner().then(res=>{
//修改bannerList
context.commit("changeBannerList",res.data.list)
})
}
},
getters:{
//导出数据给组件用
bannerList(state){
return state.bannerList;
}
},
modules: {
}
})
home.vue
import {mapGetters,mapActions} from "vuex"
export default {
computed:{
...mapGetters(["bannerList"])
},
methods:{
...mapActions(["reqBannerList"])
},
mounted(){
//进来发请求
this.reqBannerList()
}
}
2.首页分类数据
store/index.js
export default new Vuex.Store({
state: {
//首页分类数据
cateList: []
},
mutations: {
//修改分类列表
changeCateList(state, arr) {
state.cateList = arr;
}
},
actions: {
//请求分类列表
reqCateList(context){
//发请求
reqCate().then(res=>{
//修改分类列表
context.commit("changeCateList",res.data.list)
})
}
},
getters: {
//导出分类列表
cateList(state){
return state.cateList
}
},
})
home.vue
import {mapGetters,mapActions} from "vuex"
export default {
computed:{
...mapGetters(["cateList"])
},
methods:{
...mapActions(["reqCateList"])
},
mounted(){
//获取分类
this.reqCateList()
}
}
3.首页商品数据
store/index.js
export default new Vuex.Store({
state: {
//商品
goodsList: [],
//导航数据
navs:["热门推荐","上新推荐","所有商品"],
n:0
},
mutations: {
changeGoodsList(state, arr) {
state.goodsList = arr;
},
//修改n
changeN(state,n){
state.n=n;
}
},
actions: {
//请求goodsList
reqGoodsList(context){
//发请求
reqGoods().then(res=>{
//修改分类列表
context.commit("changeGoodsList", res.data.list)
})
},
//修改n
changeN(context,n){
context.commit("changeN",n)
}
},
getters: {
//导出goodsList
goodsList(state){
return state.goodsList
},
//导出navs
navs(state){
return state.navs
},
//导出n
n(state){
return state.n
},
},
})
home.vue引入使用
import {mapGetters,mapActions} from "vuex"
export default {
computed:{
...mapGetters(["goodsList","navs","n"])
},
methods:{
...mapActions([reqGoodsList","changeN"])
},
mounted(){
//获取商品
this.reqGoodsList();//[{content:[{},{}]},{content:[{},{}]},{content:[{},{}]}]
}
}
4.状态层分模块
目录:
-src
-store
index.js //创建仓库对象,并导出
mutations.js //根上的state、getters、mutations
actions.js //根上的状态的逻辑
-modules //模块
home.js
list.js
list.js
import { reqList } from '../../request';
let state = {
//商品列表页面的数据
list: []
}
let mutations = {
//修改商品列表页面的数据
changeList(state, arr) {
state.list = arr;
}
}
let actions = {
//请求商品列表页面的数据
reqList(context, id) {
//发请求
reqList(id).then(res => {
context.commit("changeList", res.data.list.goodData)
})
}
}
let getters = {
//导出list
list(state) {
return state.list
},
}
export default {
state,
mutations,
actions,
getters,
//命名空间
namespaced: true
}
index.js
import actions from "./actions"
import {state,mutations,getters} from "./mutations"
import home from "./modules/home"
import list from "./modules/list"
export default new Vuex.Store({
state,
mutations,
actions,
getters,
modules: {
home,
list,
}
})
list.vue取数据
import {mapGetters,mapActions} from "vuex"
export default {
computed:{
...mapGetters({
d:"list/list"
})
},
methods:{
...mapActions({
getList:"list/reqList"
})
},
mounted(){
this.getList(this.$route.query.id)
}
}
4.登录
store/mutations.js
export let state={
userInfo:localStorage.getItem("userInfo")?JSON.parse(localStorage.getItem('userInfo')):{}
}
export let mutations= {
changeUserInfo(state,obj){
state.userInfo=obj
}
}
export let getters={
userInfo(state){
return state.userInfo;
}
}
store/actions.js
export default {
//修改userInfo
changeUserInfo(context,obj){
//提交mutations
context.commit("changeUserInfo",obj)
//本地存储存一份
localStorage.setItem("userInfo",JSON.stringify(obj))
}
}
login.vue
methods: {
...mapActions(["changeUserInfo"]),
login() {
reqLogin(this.user).then((res) => {
if(res.data.code==200){
//存入vuex
this.changeUserInfo(res.data.list)
this.$router.push("/")
}
});
},
},
home.vue退出登录
logout(){
this.changeUserInfo({})
}