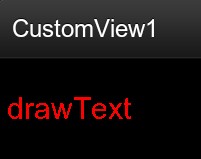
书接上回
在xml里建立属性,然后java代码里用typedArray获得这些属性,得到属性后,利用属性做一些事.例:得到xml里的color,赋给paint.
1.在res/values/下新建attrs.xml
- <?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
- <resources>
- <declare-styleable name="CustomView2">
- <attr name="textColor" format="color" />
- <attr name="textSize" format="dimension" />
- </declare-styleable>
- </resources>
- <!-- name="CustomView1"控件名称 得到TypedArray时用 -->
- <!-- name="textColor" 对应test:textColor -->
- <!-- format="color" 对应构造方法里a.getColor(R.styleable.CustomView2_textColor, 0xFFFFFFFF); -->
format详解可参照http://blog.csdn.net/ethan_xue/article/details/7315064
2.主要看构造函数
- public class CustomView2 extends View {
- private Paint mPaint2;
- private String mText = "drawText";
- public CustomView2(Context context, AttributeSet attrs) {
- super(context, attrs);
- mPaint2 = new Paint();
- // TypedArray是存放资源的array,1.通过上下文得到这个数组,attrs是构造函数传进来的,对应attrs.xml
- TypedArray a = context.obtainStyledAttributes(attrs, R.styleable.CustomView2);
- // 获得xml里定义的属性,格式为 名称_属性名 后面是默认值
- int textColor = a.getColor(R.styleable.CustomView2_textColor, 0xFFFFFFFF);
- float textSize = a.getDimension(R.styleable.CustomView2_textSize, 35);
- mPaint2.setColor(textColor);
- mPaint2.setTextSize(textSize);
- // 为了保持以后使用该属性一致性,返回一个绑定资源结束的信号给资源
- a.recycle();
- }
- @Override
- protected void onDraw(Canvas canvas) {
- super.onDraw(canvas);
- mPaint2.setStyle(Style.FILL);
- canvas.drawText(mText, 10, 60, mPaint2);
- }
- }
3.布局
- <?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
- <!-- xmlns:test="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/ethan.customview1" 包名 -->
- <LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
- xmlns:test="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/ethan.customview1"
- android:orientation="vertical"
- android:layout_width="fill_parent"
- android:layout_height="fill_parent"
- >
- <ethan.customview1.CustomView2
- android:layout_width="wrap_content"
- android:layout_height="wrap_content"
- test:textColor="#f00"
- test:textSize="20sp"
- />
- </LinearLayout>
4.效果图