整理了一些Java方面的架构、面试资料(微服务、集群、分布式、中间件等),有需要的小伙伴可以关注公众号【程序员内点事】,无套路自行领取
引言
接着《一口气说出 9种 分布式ID生成方式,面试官有点懵了》来继续详细的介绍分布式ID生成器,大家比较感兴趣的美团(Leaf)、滴滴(Tinyid)、百度(uid-generator)三个开源项目,美团(Leaf)已经讲完,详见《9种分布式ID生成之美团(Leaf)实战》,今天结合实战搞一下滴滴开源的(Tinyid)。
Tinyid介绍
Tinyid是滴滴开发的一款分布式ID系统,Tinyid是在美团(Leaf)的leaf-segment算法基础上升级而来,不仅支持了数据库多主节点模式,还提供了tinyid-client客户端的接入方式,使用起来更加方便。但和美团(Leaf)不同的是,Tinyid只支持号段一种模式不支持雪花模式。
Tinyid的特性
- 全局唯一的long型ID
- 趋势递增的id
- 提供 http 和 java-client 方式接入
- 支持批量获取ID
- 支持生成1,3,5,7,9...序列的ID
- 支持多个db的配置
适用场景:只关心ID是数字,趋势递增的系统,可以容忍ID不连续,可以容忍ID的浪费
不适用场景:像类似于订单ID的业务,因生成的ID大部分是连续的,容易被扫库、或者推算出订单量等信息
Tinyid原理
Tinyid是基于号段模式实现,再简单啰嗦一下号段模式的原理:就是从数据库批量的获取自增ID,每次从数据库取出一个号段范围,例如 (1,1000] 代表1000个ID,业务服务将号段在本地生成1~1000的自增ID并加载到内存.。
Tinyid会将可用号段加载到内存中,并在内存中生成ID,可用号段在首次获取ID时加载,如当前号段使用达到一定比例时,系统会异步的去加载下一个可用号段,以此保证内存中始终有可用号段,以便在发号服务宕机后一段时间内还有可用ID。
原理图大致如下图:
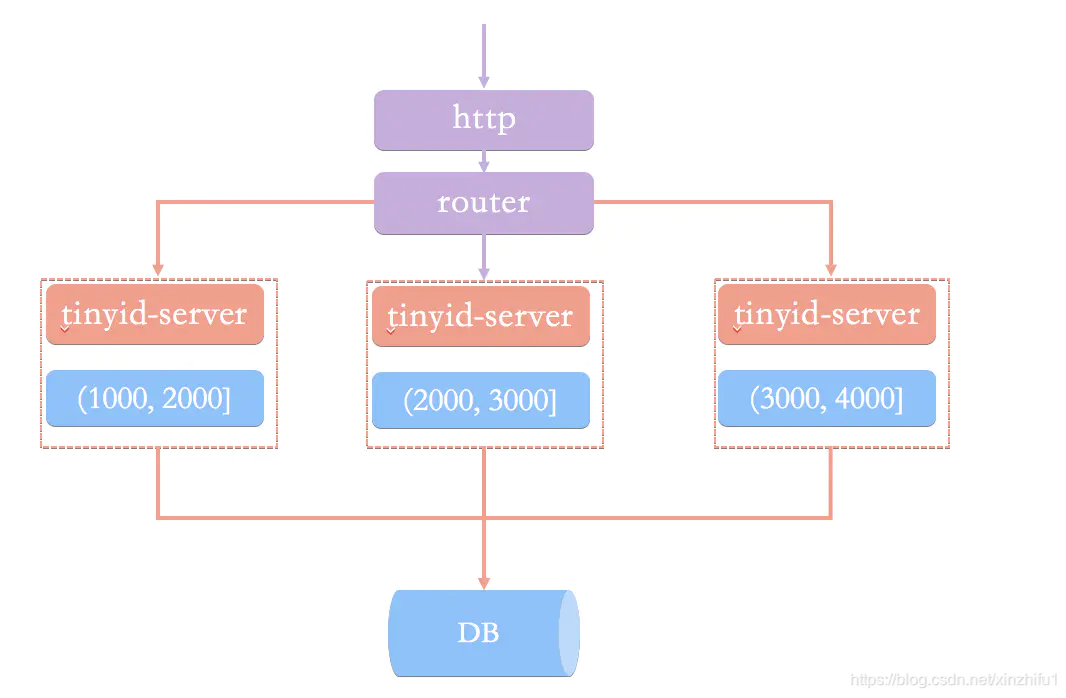
Tinyid实现
Tinyid的GitHub地址 : https://github.com/didi/tinyid.git
Tinyid提供了两种调用方式,一种基于Tinyid-server提供的http方式,另一种Tinyid-client客户端方式。
不管使用哪种方式调用,搭建Tinyid都必须提前建表tiny_id_info、tiny_id_token。
CREATE TABLE `tiny_id_info` (
`id` bigint(20) unsigned NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT COMMENT '自增主键',
`biz_type` varchar(63) NOT NULL DEFAULT '' COMMENT '业务类型,唯一',
`begin_id` bigint(20) NOT NULL DEFAULT '0' COMMENT '开始id,仅记录初始值,无其他含义。初始化时begin_id和max_id应相同',
`max_id` bigint(20) NOT NULL DEFAULT '0' COMMENT '当前最大id',
`step` int(11) DEFAULT '0' COMMENT '步长',
`delta` int(11) NOT NULL DEFAULT '1' COMMENT '每次id增量',
`remainder` int(11) NOT NULL DEFAULT '0' COMMENT '余数',
`create_time` timestamp NOT NULL DEFAULT '2010-01-01 00:00:00' COMMENT '创建时间',
`update_time` timestamp NOT NULL DEFAULT '2010-01-01 00:00:00' COMMENT '更新时间',
`version` bigint(20) NOT NULL DEFAULT '0' COMMENT '版本号',
PRIMARY KEY (`id`),
UNIQUE KEY `uniq_biz_type` (`biz_type`)
) ENGINE=InnoDB AUTO_INCREMENT=1 DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8 COMMENT 'id信息表';
CREATE TABLE `tiny_id_token` (
`id` int(11) unsigned NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT COMMENT '自增id',
`token` varchar(255) NOT NULL DEFAULT '' COMMENT 'token',
`biz_type` varchar(63) NOT NULL DEFAULT '' COMMENT '此token可访问的业务类型标识',
`remark` varchar(255) NOT NULL DEFAULT '' COMMENT '备注',
`create_time` timestamp NOT NULL DEFAULT '2010-01-01 00:00:00' COMMENT '创建时间',
`update_time` timestamp NOT NULL DEFAULT '2010-01-01 00:00:00' COMMENT '更新时间',
PRIMARY KEY (`id`)
) ENGINE=InnoDB AUTO_INCREMENT=1 DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8 COMMENT 'token信息表';
INSERT INTO `tiny_id_info` (`id`, `biz_type`, `begin_id`, `max_id`, `step`, `delta`, `remainder`, `create_time`, `update_time`, `version`)
VALUES
(1, 'test', 1, 1, 100000, 1, 0, '2018-07-21 23:52:58', '2018-07-22 23:19:27', 1);
INSERT INTO `tiny_id_info` (`id`, `biz_type`, `begin_id`, `max_id`, `step`, `delta`, `remainder`, `create_time`, `update_time`, `version`)
VALUES
(2, 'test_odd', 1, 1, 100000, 2, 1, '2018-07-21 23:52:58', '2018-07-23 00:39:24', 3);
INSERT INTO `tiny_id_token` (`id`, `token`, `biz_type`, `remark`, `create_time`, `update_time`)
VALUES
(1, '0f673adf80504e2eaa552f5d791b644c', 'test', '1', '2017-12-14 16:36:46', '2017-12-14 16:36:48');
INSERT INTO `tiny_id_token` (`id`, `token`, `biz_type`, `remark`, `create_time`, `update_time`)
VALUES
(2, '0f673adf80504e2eaa552f5d791b644c', 'test_odd', '1', '2017-12-14 16:36:46', '2017-12-14 16:36:48');
tiny_id_info表是具体业务方号段信息数据表
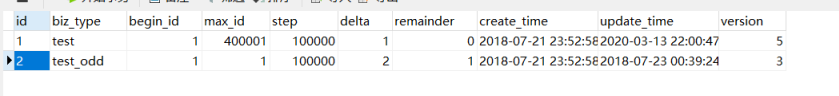
max_id :号段的最大值
step:步长,即为号段的长度
biz_type:业务类型
号段获取对max_id字段做一次update操作,update max_id= max_id + step,更新成功则说明新号段获取成功,新的号段范围是(max_id ,max_id +step]。
tiny_id_token是一个权限表,表示当前token可以操作哪些业务的号段信息。

修改tinyid-server中 offlineapplication.properties 文件配置数据库,由于tinyid支持数据库多master模式,可以配置多个数据库信息。启动 TinyIdServerApplication 测试一下。
datasource.tinyid.primary.driver-class-name=com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
datasource.tinyid.primary.url=jdbc:mysql://127.0.0.1:3306/xin-master?autoReconnect=true&useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=UTF-8
datasource.tinyid.primary.username=junkang
datasource.tinyid.primary.password=junkang
datasource.tinyid.primary.testOnBorrow=false
datasource.tinyid.primary.maxActive=10
datasource.tinyid.secondary.driver-class-name=com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
datasource.tinyid.secondary.url=jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/db2?autoReconnect=true&useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=UTF-8
datasource.tinyid.secondary.username=root
datasource.tinyid.secondary.password=123456
datasource.tinyid.secondary.testOnBorrow=false
datasource.tinyid.secondary.maxActive=10
1、Http方式
tinyid 内部一共提供了四个http接口来获取ID和号段。
package com.xiaoju.uemc.tinyid.server.controller;
/**
* @author du_imba
*/
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/id/")
public class IdContronller {
private static final Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(IdContronller.class);
@Autowired
private IdGeneratorFactoryServer idGeneratorFactoryServer;
@Autowired
private SegmentIdService segmentIdService;
@Autowired
private TinyIdTokenService tinyIdTokenService;
@Value("${batch.size.max}")
private Integer batchSizeMax;
@RequestMapping("nextId")
public Response<List<Long>> nextId(String bizType, Integer batchSize, String token) {
Response<List<Long>> response = new Response<>();
try {
IdGenerator idGenerator = idGeneratorFactoryServer.getIdGenerator(bizType);
List<Long> ids = idGenerator.nextId(newBatchSize);
response.setData(ids);
} catch (Exception e) {
response.setCode(ErrorCode.SYS_ERR.getCode());
response.setMessage(e.getMessage());
logger.error("nextId error", e);
}
return response;
}
@RequestMapping("nextIdSimple")
public String nextIdSimple(String bizType, Integer batchSize, String token) {
String response = "";
try {
IdGenerator idGenerator = idGeneratorFactoryServer.getIdGenerator(bizType);
if (newBatchSize == 1) {
Long id = idGenerator.nextId();
response = id + "";
} else {
List<Long> idList = idGenerator.nextId(newBatchSize);
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
for (Long id : idList) {
sb.append(id).append(",");
}
response = sb.deleteCharAt(sb.length() - 1).toString();
}
} catch (Exception e) {
logger.error("nextIdSimple error", e);
}
return response;
}
@RequestMapping("nextSegmentId")
public Response<SegmentId> nextSegmentId(String bizType, String token) {
try {
SegmentId segmentId = segmentIdService.getNextSegmentId(bizType);
response.setData(segmentId);
} catch (Exception e) {
response.setCode(ErrorCode.SYS_ERR.getCode());
response.setMessage(e.getMessage());
logger.error("nextSegmentId error", e);
}
return response;
}
@RequestMapping("nextSegmentIdSimple")
public String nextSegmentIdSimple(String bizType, String token) {
String response = "";
try {
SegmentId segmentId = segmentIdService.getNextSegmentId(bizType);
response = segmentId.getCurrentId() + "," + segmentId.getLoadingId() + "," + segmentId.getMaxId()
+ "," + segmentId.getDelta() + "," + segmentId.getRemainder();
} catch (Exception e) {
logger.error("nextSegmentIdSimple error", e);
}
return response;
}
}
nextId、nextIdSimple都是获取下一个ID,nextSegmentIdSimple、getNextSegmentId是获取下一个可用号段。区别在于接口是否有返回状态。
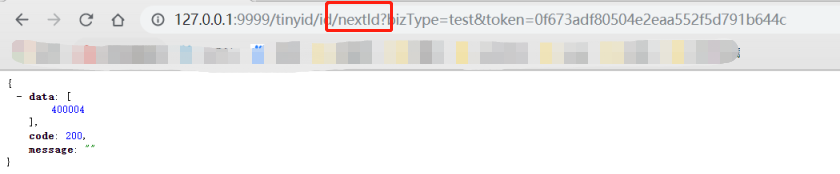
nextId:
'http://localhost:9999/tinyid/id/nextId?bizType=test&token=0f673adf80504e2eaa552f5d791b644c'
response :
{
"data": [2],
"code": 200,
"message": ""
}
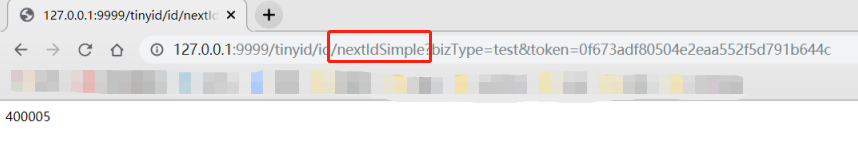
nextId Simple:
'http://localhost:9999/tinyid/id/nextIdSimple?bizType=test&token=0f673adf80504e2eaa552f5d791b644c'
response: 3
2、Tinyid-client客户端
如果不想通过http方式,Tinyid-client客户端也是一种不错的选择。
引用 tinyid-server 包
<dependency>
<groupId>com.xiaoju.uemc.tinyid</groupId>
<artifactId>tinyid-client</artifactId>
<version>${tinyid.version}</version>
</dependency>
启动 tinyid-server 项目打包后得到 tinyid-server-0.1.0-SNAPSHOT.jar ,设置版本 ${tinyid.version}为0.1.0-SNAPSHOT。
在我们的项目 application.properties 中配置 tinyid-server 服务的请求地址 和 用户身份token
tinyid.server=127.0.0.1:9999
tinyid.token=0f673adf80504e2eaa552f5d791b644c```
在Java代码调用TinyId也很简单,只需要一行代码。
// 根据业务类型 获取单个ID
Long id = TinyId.nextId("test");
// 根据业务类型 批量获取10个ID
List<Long> ids = TinyId.nextId("test", 10);
Tinyid整个项目的源码实现也是比较简单,像与数据库交互更直接用jdbcTemplate实现
@Override
public TinyIdInfo queryByBizType(String bizType) {
String sql = "select id, biz_type, begin_id, max_id," +
" step, delta, remainder, create_time, update_time, version" +
" from tiny_id_info where biz_type = ?";
List<TinyIdInfo> list = jdbcTemplate.query(sql, new Object[]{bizType}, new TinyIdInfoRowMapper());
if(list == null || list.isEmpty()) {
return null;
}
return list.get(0);
}
总结
两种方式推荐使用Tinyid-client,这种方式ID为本地生成,号段长度(step)越长,支持的qps就越大,如果将号段设置足够大,则qps可达1000w+。而且tinyid-client 对 tinyid-server 访问变的低频,减轻了server端的压力。
整理了一些Java方面的架构、面试资料(微服务、集群、分布式、中间件等),有需要的小伙伴可以关注公众号【程序员内点事】,无套路自行领取