Image源码解读
接着我们来看看放在相同图集中的Sprite是如何合并DrawCall的,从原理上来讲,每个Mesh都需要给顶点设置UV信息,也就是说我们只需要将图集上的某个区域一一抠出来贴到Mesh正确的区域即可。如下代码所示,只要观察GenerateSimpleSprite()方法,UGUI通过Sprites.DataUtility.GetOuterUV(activeSprite)方法将当前待显示的Sprite的UV信息取出来,通过vh.AddVert()和vh.AddTriangle()来填充Mesh信息。
Image.cs(部分代码):
public class Image : MaskableGraphic, ISerializationCallbackReceiver, ILayoutElement, ICanvasRaycastFilter { //...略 protected override void OnPopulateMesh(VertexHelper toFill) { if (activeSprite == null) { base.OnPopulateMesh(toFill); return; } //Image有4种显示模式,正常、九宫、平铺、填充 //分别生成对应的顶点信息 switch (type) { case Type.Simple: if (!useSpriteMesh) GenerateSimpleSprite(toFill, m_PreserveAspect); else GenerateSprite(toFill, m_PreserveAspect); break; case Type.Sliced: GenerateSlicedSprite(toFill); break; case Type.Tiled: GenerateTiledSprite(toFill); break; case Type.Filled: GenerateFilledSprite(toFill, m_PreserveAspect); break; } } void GenerateSimpleSprite(VertexHelper vh, bool lPreserveAspect) { Vector4 v = GetDrawingDimensions(lPreserveAspect); //获取根据Sprite获取正确的UV信息 var uv = (activeSprite != null) ? Sprites.DataUtility.GetOuterUV(activeSprite) : Vector4.zero; var color32 = color; vh.Clear(); //填充顶点、颜色、uv vh.AddVert(new Vector3(v.x, v.y), color32, new Vector2(uv.x, uv.y)); vh.AddVert(new Vector3(v.x, v.w), color32, new Vector2(uv.x, uv.w)); vh.AddVert(new Vector3(v.z, v.w), color32, new Vector2(uv.z, uv.w)); vh.AddVert(new Vector3(v.z, v.y), color32, new Vector2(uv.z, uv.y)); //填充三角形顶点序列 vh.AddTriangle(0, 1, 2); vh.AddTriangle(2, 3, 0); } }
最终,不同的UI使用相同的材质、Shader、贴图,只是它们拥有不同的UV信息,这符合Draw Call合并的规则,所以就能合批。
Text源码解读
UGUI的Text就是位图字体,先通过TTF字体将字体形状生成在位图中,接着就是将正确的UV设置给字体的Mesh,这和前面介绍的Image组件几乎一样了。如下代码所示,首先需要根据文本的区域、字体、填充文字调用GetGenerationSettings()创建文本生成器,顶点、uv信息都会被填充好,由于每个文本都是一个Quad,所以还需要设置它们的位置。
Text.cs(部分代码):
public class Text : MaskableGraphic, ILayoutElement { //...略 //字体生成器 public TextGenerator cachedTextGenerator { get { return m_TextCache ?? (m_TextCache = (m_Text.Length != 0 ? new TextGenerator(m_Text.Length) : new TextGenerator())); } } readonly UIVertex[] m_TempVerts = new UIVertex[4]; protected override void OnPopulateMesh(VertexHelper toFill) { if (font == null) return; m_DisableFontTextureRebuiltCallback = true; Vector2 extents = rectTransform.rect.size; //获取字体的生成规则设置 var settings = GetGenerationSettings(extents); //根据待填充字体、生成规则,生成顶点信息 cachedTextGenerator.PopulateWithErrors(text, settings, gameObject); // IList<UIVertex> verts = cachedTextGenerator.verts; float unitsPerPixel = 1 / pixelsPerUnit; int vertCount = verts.Count - 4; if (vertCount <= 0) { toFill.Clear(); return; } Vector2 roundingOffset = new Vector2(verts[0].position.x, verts[0].position.y) * unitsPerPixel; roundingOffset = PixelAdjustPoint(roundingOffset) - roundingOffset; toFill.Clear(); if (roundingOffset != Vector2.zero) { for (int i = 0; i < vertCount; ++i) { int tempVertsIndex = i & 3; //填充顶点信息 m_TempVerts[tempVertsIndex] = verts[i]; //设置字体偏移 m_TempVerts[tempVertsIndex].position *= unitsPerPixel; m_TempVerts[tempVertsIndex].position.x += roundingOffset.x; m_TempVerts[tempVertsIndex].position.y += roundingOffset.y; if (tempVertsIndex == 3) toFill.AddUIVertexQuad(m_TempVerts); //填充UI顶点面片 } } else { for (int i = 0; i < vertCount; ++i) { int tempVertsIndex = i & 3; //填充顶点信息 m_TempVerts[tempVertsIndex] = verts[i]; //设置字体偏移 m_TempVerts[tempVertsIndex].position *= unitsPerPixel; if (tempVertsIndex == 3) toFill.AddUIVertexQuad(m_TempVerts);//填充UI顶点面片 } } m_DisableFontTextureRebuiltCallback = false; } public TextGenerationSettings GetGenerationSettings(Vector2 extents) { //字体设置信息 var settings = new TextGenerationSettings(); //下面对Text信息进行提取 settings.generationExtents = extents; if (font != null && font.dynamic) { settings.fontSize = m_FontData.fontSize; settings.resizeTextMinSize = m_FontData.minSize; settings.resizeTextMaxSize = m_FontData.maxSize; } settings.textAnchor = m_FontData.alignment; settings.alignByGeometry = m_FontData.alignByGeometry; settings.scaleFactor = pixelsPerUnit; settings.color = color; settings.font = font; settings.pivot = rectTransform.pivot; settings.richText = m_FontData.richText; settings.lineSpacing = m_FontData.lineSpacing; settings.fontStyle = m_FontData.fontStyle; settings.resizeTextForBestFit = m_FontData.bestFit; settings.updateBounds = false; settings.horizontalOverflow = m_FontData.horizontalOverflow; settings.verticalOverflow = m_FontData.verticalOverflow; return settings; } }
如下代码所示, 字体的贴图保存在Font.material.mainTexture中,Mesh信息准备好后将字体的材质贴上就可以将文字渲染出来了,最终字体和Image绘制完全一样,通过Graphic.UpdateMaterial()将材质贴上。

顶点辅助类VertexHelper
前面我们介绍的Image和Text 合并网格都用到了VertexHelper类,如下代码所示,它只是个普通的类对象,里面只保存了生成Mesh的基本信息并非Mesh对象,最后通过这些基本信息就可以生成Mesh网格了。
VertexHelper.cs(部分代码):
public class VertexHelper : IDisposable { //保存每个顶点的位置、颜色、UV、法线、切线 private List<Vector3> m_Positions; private List<Color32> m_Colors; private List<Vector2> m_Uv0S; private List<Vector2> m_Uv1S; private List<Vector2> m_Uv2S; private List<Vector2> m_Uv3S; private List<Vector3> m_Normals; private List<Vector4> m_Tangents; //记录三角形的索引 private List<int> m_Indices; //开始添加顶点的位置、颜色、UV、法线、切线数据 public void AddVert(Vector3 position, Color32 color, Vector2 uv0, Vector2 uv1, Vector3 normal, Vector4 tangent) { InitializeListIfRequired(); m_Positions.Add(position); m_Colors.Add(color); m_Uv0S.Add(uv0); m_Uv1S.Add(uv1); m_Uv2S.Add(Vector2.zero); m_Uv3S.Add(Vector2.zero); m_Normals.Add(normal); m_Tangents.Add(tangent); } //添加三角形的索引 public void AddTriangle(int idx0, int idx1, int idx2) { InitializeListIfRequired(); m_Indices.Add(idx0); m_Indices.Add(idx1); m_Indices.Add(idx2); } }
Graphic中有个静态对象s_VertexHelper保存每次生成的网格信息,使用完后会立即清理掉等待下个Graphic对象使用。
Graphic.cs(部分代码):
public abstract class Graphic : UIBehaviour, ICanvasElement { //...略 [NonSerialized] private static readonly VertexHelper s_VertexHelper = new VertexHelper(); private void DoMeshGeneration() { //...略 //s_VertexHelper中的数据信息,调用FillMesh()方法生成真正的网格信息。 s_VertexHelper.FillMesh(workerMesh); //s_VertexHelper.FillMesh内部实现 //就是Unity自己生成Mesh的API而已 //public void FillMesh(Mesh mesh) //{ // InitializeListIfRequired(); // mesh.Clear(); // if (m_Positions.Count >= 65000) // throw new ArgumentException("Mesh can not have more than 65000 vertices"); // mesh.SetVertices(m_Positions); // mesh.SetColors(m_Colors); // mesh.SetUVs(0, m_Uv0S); // mesh.SetUVs(1, m_Uv1S); // mesh.SetUVs(2, m_Uv2S); // mesh.SetUVs(3, m_Uv3S); // mesh.SetNormals(m_Normals); // mesh.SetTangents(m_Tangents); // mesh.SetTriangles(m_Indices, 0); // mesh.RecalculateBounds(); //} //最终提交网格信息,在C++底层中合并网格 canvasRenderer.SetMesh(workerMesh); } }
Layout源码解读
UGUI的布局功能确实很强大,只要挂在节点下就可以设置HorizontalLayoutGroup(横向)、VerticalLayoutGroup(纵向)、GridLayoutGroup(表格)的布局了。虽然使用方便,但是效率是不高的,这里我们以纵向来举例。无论横向还是纵向排列,首先得计算出每个子对象的区域才行。如下代码所示,在GetChildSizes()方法中拿到每个元素的区域。
HorizontalOrVerticalLayoutGroup.cs(部分代码):
public abstract class HorizontalOrVerticalLayoutGroup : LayoutGroup { //...略 private void GetChildSizes(RectTransform child, int axis, bool controlSize, bool childForceExpand, out float min, out float preferred, out float flexible) { //获取每个子元素的区域,min最小区域、preferred准确区域、flexible弹性区域 if (!controlSize) { min = child.sizeDelta[axis]; preferred = min; flexible = 0; } else { min = LayoutUtility.GetMinSize(child, axis); preferred = LayoutUtility.GetPreferredSize(child, axis); flexible = LayoutUtility.GetFlexibleSize(child, axis); } if (childForceExpand) flexible = Mathf.Max(flexible, 1); } }
如下代码所示,最核心的计算在LayoutUtility. GetLayoutProperty()方法中,把每个实现ILayoutElement接口的对象的信息取出来。
LayoutUtility.cs(部分代码):
public static class LayoutUtility { //...略 public static float GetMinWidth(RectTransform rect) { //计算最小宽度 return GetLayoutProperty(rect, e => e.minWidth, 0); } public static float GetLayoutProperty(RectTransform rect, System.Func<ILayoutElement, float> property, float defaultValue, out ILayoutElement source) { source = null; if (rect == null) return 0; float min = defaultValue; int maxPriority = System.Int32.MinValue; var components = ListPool<Component>.Get(); rect.GetComponents(typeof(ILayoutElement), components); //遍历每一个实现ILayoutElement接口的子对象(Image和Text都实现了ILayoutElement接口) //或者绑定了LayoutElement对象的脚本也实现了ILayoutElement接口 for (int i = 0; i < components.Count; i++) { //确保layoutComp对象有效 var layoutComp = components[i] as ILayoutElement; if (layoutComp is Behaviour && !((Behaviour)layoutComp).isActiveAndEnabled) continue; //确保当前优先级小于最大优先级 int priority = layoutComp.layoutPriority; if (priority < maxPriority) continue; float prop = property(layoutComp); if (prop < 0) continue; //如果有更高的优先级,那么就覆盖最小数值,并且覆盖最大优先级数值 if (priority > maxPriority) { min = prop; maxPriority = priority; source = layoutComp; } //如果组件有相同的优先级,取较大的值 else if (prop > min) { min = prop; source = layoutComp; } } ListPool<Component>.Release(components); //返回最小值 return min; } }
如下代码所示,由于Image和Text都实现了ILayoutElement接口,所以LayoutGroup下的Image和Text元素会自动布局,也可以绑定LayoutElement脚本主动设置区域。
public class Image : MaskableGraphic, ISerializationCallbackReceiver, ILayoutElement, ICanvasRaycastFilter public class Text : MaskableGraphic, ILayoutElement
但是Layout还有Min Wdith和Flexible Width可设置最小宽高和弹性宽高,这都需要进行额外的计算产生额外的开销,如果对效率要求比较高的UI,最好可以考虑自行封装一套布局组件。 如图9-1所示,有时候希望布局以后自动计算RectTransform的区域,那么就不得不再挂上一个Content Size Fitter组件了,它是在LayoutRebuilder中等待Rebuild()时调用,那么势必会再次造成Rebuild()。
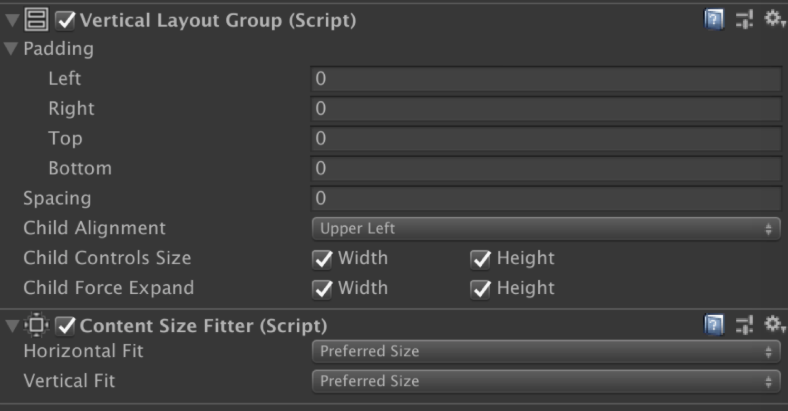
不得不说 Content Size Fitter、VerticalLayoutGroup、HorizontalLayoutGroup、 AspectRatioFitter、GridLayoutGroup组件效率是很低的,它们势必会导致所有元素的Rebuild()执行两次。
1、界面第一次打开需要进行第一次Rebuild()
2、Layout组件要算位置或者大小会强制再执行一次Rebuild()
很有可能有些元素是不需要Rebuild的,但是Layout组件也会强制执行,那么势必造成额外的开销。
遮罩:Mask与Mask2D
UGUI的裁切分为Mask和Mask2D两种,我们先来看Mask。它可以给Mask指定一张裁切图裁切子元素。如图10-1所示,我们给Mask指定了一张圆形图片,那么子节点下的元素都会被裁切在这个圆形区域中。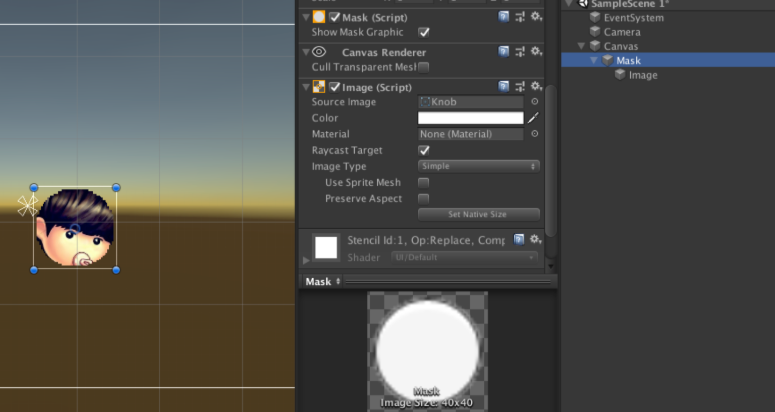
功能确实很强大,我们来看看它的效率如何呢?由于裁切需要同时裁切图片和文本,所以Image和Text都会派生自MaskableGraphic。如果要让Mask节点下的元素裁切,那么它需要占一个DrawCall,因为这些元素需要一个新的Shader参数来渲染。如下代码所示,MaskableGraphic实现了IMaterialModifier接口, 而StencilMaterial.Add()就是设置Shader中的裁切参数。
MaskableGraphic.cs(部分代码):
public abstract class MaskableGraphic : Graphic, IClippable, IMaskable, IMaterialModifier { //...略 public virtual Material GetModifiedMaterial(Material baseMaterial) { var toUse = baseMaterial; //获取模板缓冲值 if (m_ShouldRecalculateStencil) { var rootCanvas = MaskUtilities.FindRootSortOverrideCanvas(transform); m_StencilValue = maskable ? MaskUtilities.GetStencilDepth(transform, rootCanvas) : 0; m_ShouldRecalculateStencil = false; } //确保Mask组件有效 Mask maskComponent = GetComponent<Mask>(); if (m_StencilValue > 0 && (maskComponent == null || !maskComponent.IsActive())) { //设置模板缓冲值,并且设置在该区域内的显示,不在的裁切掉 var maskMat = StencilMaterial.Add(toUse, (1 << m_StencilValue) - 1, StencilOp.Keep, CompareFunction.Equal, ColorWriteMask.All, (1 << m_StencilValue) - 1, 0); StencilMaterial.Remove(m_MaskMaterial); m_MaskMaterial = maskMat; //并且更换新的材质 toUse = m_MaskMaterial; } return toUse; } }
如下代码所示,Image对象在进行Rebuild()时,UpdateMaterial()方法中会获取需要渲染的材质,并且判断当前对象的组件是否有继承IMaterialModifier接口,如果有那么它就是绑定了Mask脚本,接着调用上面提到的GetModifiedMaterial方法修改材质上Shader的参数。
Graphic.cs(部分代码):
public abstract class Graphic : UIBehaviour,ICanvasElement { //...略 public virtual void Rebuild(CanvasUpdate update) { if (canvasRenderer.cull) return; switch (update) { case CanvasUpdate.PreRender: if (m_VertsDirty) { //开始更新网格 UpdateGeometry(); m_VertsDirty = false; } if (m_MaterialDirty) { //开始更新材质 UpdateMaterial(); m_MaterialDirty = false; } break; } } public virtual Material materialForRendering { get { //遍历UI中的每个Mask组件 var components = ListPool<Component>.Get(); GetComponents(typeof(IMaterialModifier), components); //并且更新每个Mask组件的模板缓冲材质 var currentMat = material; for (var i = 0; i < components.Count; i++) currentMat = (components[i] as IMaterialModifier).GetModifiedMaterial(currentMat); ListPool<Component>.Release(components); //返回新的材质,用于裁切 return currentMat; } } protected virtual void UpdateMaterial() { if (!IsActive()) return; //更新刚刚替换的新的模板缓冲的材质 canvasRenderer.materialCount = 1; canvasRenderer.SetMaterial(materialForRendering, 0); canvasRenderer.SetTexture(mainTexture); } }
Mask的原理就是利用了StencilBuffer(模板缓冲),它里面记录了一个ID,被裁切元素也有StencilBuffer(模板缓冲)的ID,并且和Mask里的比较,相同才会被渲染。因为模板缓冲可以提供模板的区域,也就是前面设置的圆形图片,所以最终会将元素裁切到这个圆心图片中。 如图10-2所示,在Mask外面放一个普通的图片,默认情况下Stencil Ref的值是0,所以它不会被裁切,永远会显示出来。
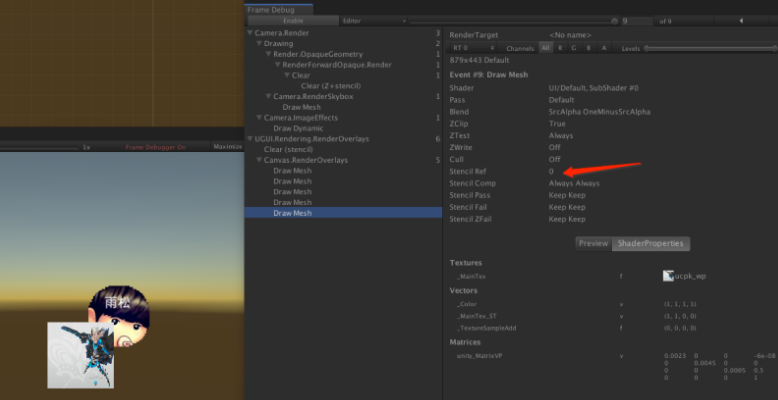
如图10-3所示,因为Mask的Stencil Ref 值是1,所需被裁切的元素它的Stencil Ref 值也应该是1就会被裁切。
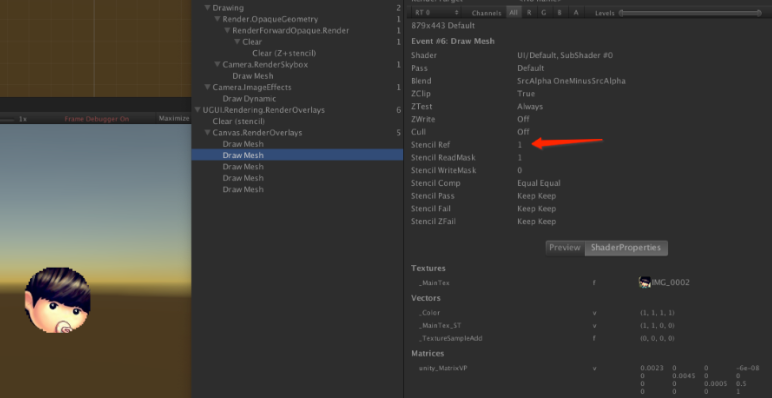
接着我们再来看看Mask2D的原理,在前面介绍Canvas.willRenderCanvases()时在PerformUpdate方法中会调用ClipperRegistry.instance.Cull();来处理界面中所有的Mask2D裁切。

ClipperRegistry.instance.Cull();的原理就是遍历界面中的所有Mask2D组件,并且调用每个组件的PerformClipping();方法。

如下代码所示,Mask2D会在OnEnable()方法中,将当前组件注册ClipperRegistry.Register(this);这样在上面ClipperRegistry.instance.Cull();方法时就可以遍历所有Mask2D组件并且调用它们的PerformClipping()方法了。
PerformClipping()方法,需要找到所有需要裁切的UI元素,因为Image和Text都继承了IClippable接口,最终将调用Cull()进行裁切。
RectMask2D.cs(部分代码):
public class RectMask2D : UIBehaviour, IClipper, ICanvasRaycastFilter { //...略 protected override void OnEnable() { //注册当前RectMask2D裁切对象,保证下次Rebuild时可进行裁切。 base.OnEnable(); m_ShouldRecalculateClipRects = true; ClipperRegistry.Register(this); MaskUtilities.Notify2DMaskStateChanged(this); } public virtual void PerformClipping() { if (ReferenceEquals(Canvas, null)) { return; } //重新计算裁切区域 if (m_ShouldRecalculateClipRects) { MaskUtilities.GetRectMasksForClip(this, m_Clippers); m_ShouldRecalculateClipRects = false; } //由于裁切可能有多个区域,这里会计算出正确包含重复的一个区域 bool validRect = true; Rect clipRect = Clipping.FindCullAndClipWorldRect(m_Clippers, out validRect); RenderMode renderMode = Canvas.rootCanvas.renderMode; bool maskIsCulled = (renderMode == RenderMode.ScreenSpaceCamera || renderMode == RenderMode.ScreenSpaceOverlay) && !clipRect.Overlaps(rootCanvasRect, true); bool clipRectChanged = clipRect != m_LastClipRectCanvasSpace; bool forceClip = m_ForceClip; // Avoid looping multiple times. foreach (IClippable clipTarget in m_ClipTargets) { if (clipRectChanged || forceClip) { //准备把裁切区域传到每个UI元素的Shader中 clipTarget.SetClipRect(clipRect, validRect); } //确保裁切可用 var maskable = clipTarget as MaskableGraphic; if (maskable != null && !maskable.canvasRenderer.hasMoved && !clipRectChanged) continue; //准备开始裁切,准备重建裁切的UI clipTarget.Cull( maskIsCulled ? Rect.zero : clipRect, maskIsCulled ? false : validRect); } m_LastClipRectCanvasSpace = clipRect; m_ForceClip = false; } }
如图10-4所示,RectMask2D会将RectTransform的区域作为_ClipRect传入Shader中,并且激活UNITY_UI_CLIP_RECT的Keywords。Stencil Ref 的值是0 表示它并没有使用模板缓冲比较,如果只是矩形裁切,RectMask2D并且它不需要一个无效的渲染用于模板比较,所以RectMask2D的效率会比Mask要高。
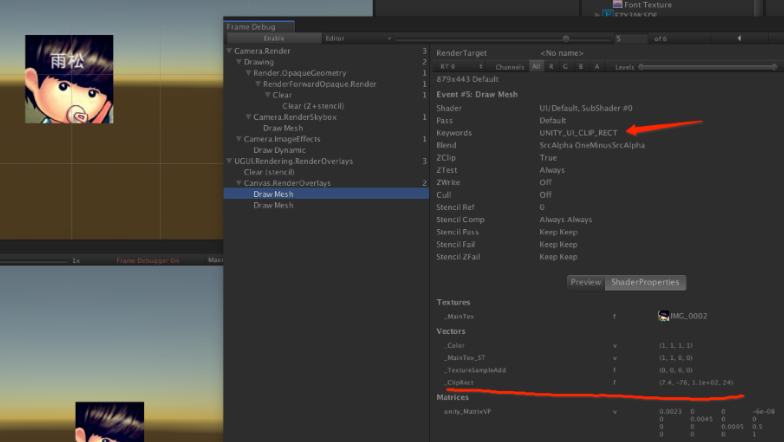
如下代码所示,在Shader的Frag处理像素中,被裁切掉的区域是通过UnityGet2DClipping()将Color.a变成了透明。
RectMask2D.cs(部分代码):
