stream流类似于lambda表达式的函数式编程,集合使用过滤、添加元素等更加方便。
根据Collection获取流
-
Collection接口中有一个stream()方法,可以获取流 , default Stream<E> stream():获取一个Stream流
-
通过List集合获取: list.stream()
-
通过Set集合获取
-
根据Map获取流
-
使用所有键的集合来获取流
-
使用所有值的集合来获取流
-
使用所有键值对的集合来获取流
list.stream().map(p -> map.get(p.getType())).collect(Collectors.toList());
根据数组获取流
-
Stream流中有一个static <T> Stream<T> of(T... values)
-
通过数组获取: (Stream.of(arr))
-
通过直接给多个数据的方式
在上述介绍的各种方法中,凡是返回值仍然为Stream接口的为函数拼接方法,它们支持链式调用;而返回值不再为Stream接口的为终结方法,不再支持链式调用。如下表所示:
| 方法名 | 方法作用 | 方法种类 | 是否支持链式调用 |
说明 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| count | 统计个数 | 终结 | 否 | |
| forEach | 逐一处理 | 终结 | 否 | |
| filter | 过滤 | 函数拼接 | 是 | |
| limit | 取用前几个 | 函数拼接 | 是 | |
| skip | 跳过前几个 | 函数拼接 | 是 | |
| map | 映射 | 函数拼接 | 是 |
流中的元素映射到另外一个流中 (转换为其他类型) |
| concat | 组合 | 函数拼接 | 是 | 拼接两个流 |
收集Stream结果
1、收集到集合中
<R,A> R collect(Collector<? super T,A,R> collector): 把流中的数据收集到单列集合中
-
public static <T> Collector<T, ?, List<T>> toList():转换为List集合。
-
public static <T> Collector<T, ?, Set<T>
示例:stream.collect(collectors.toList())
stream.collect(collectors.toSet())
2、收集到数组中
Java中双冒号::的使用
使用范例
方法调用
person -> person.getAge();
可以替换成
Person::getAge
x -> System.out.println(x)
可以替换成
System.out::printlnout是一个PrintStream类的对象,println是该类的方法,依据x的类型来重载方法
创建对象
() -> new ArrayList<>();
可以替换为
ArrayList::newnew关键字实际上调用的是ArrayList的构造方法
----------------------------------更新-------------------------------------------
flapmap使用
参考https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/flatten-nested-list-iterator/
341. 扁平化嵌套列表迭代器
扁平化,拆解外层的option
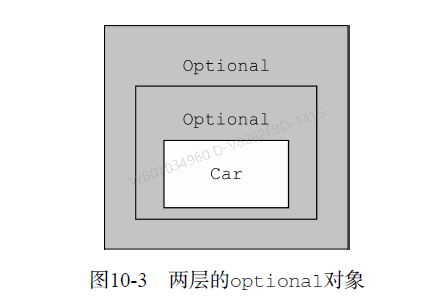
public String getCarInsuranceName(Optional<Person> person) {
return person.flatMap(Person::getCar)
.flatMap(Car::getInsurance)
.map(Insurance::getName)
.orElse("Unknown");
}
List<String> words = new ArrayList<>();
words.add("Hello");
words.add("World");
List<String> uniqueCharacters =
words.stream()
.map(w -> w.split(""))
.flatMap(Arrays::stream)
.distinct()
.collect(Collectors.toList());
List<Integer> numbers1 = Arrays.asList(1, 2, 3);
List<Integer> numbers2 = Arrays.asList(3, 4);
List<int[]> pairs = numbers1.stream()
.flatMap(i -> numbers2.stream()
.map(j -> new int[] {i, j})
)
.collect(toList());
输出[[1,3],[1,4],[2,3],[2,4],[3,3],[3,4]]
查找元素
menu.stream() .filter(Dish::isVegetarian) .findAny() .ifPresent(d -> System.out.println(d.getName());
reduce 归约
int sum = numbers.stream().reduce(0, (a, b) -> a + b);
int sum = numbers.stream().reduce(0, Integer::sum);
Optional<Integer> max = numbers.stream().reduce(Integer::max);
分组groupingBy
public enum CaloricLevel { DIET, NORMAL, FAT }
Map<CaloricLevel, List<Dish>> dishesByCaloricLevel = menu.stream().collect(
groupingBy(dish -> {
if (dish.getCalories() <= 400) return CaloricLevel.DIET;
else if (dish.getCalories() <= 700) return
CaloricLevel.NORMAL;
else return CaloricLevel.FAT;
} ));
//多级分组
Map<Dish.Type, Map<CaloricLevel, List<Dish>>> dishesByTypeCaloricLevel =
menu.stream().collect(
groupingBy(Dish::getType,
groupingBy(dish -> {
if (dish.getCalories() <= 400) {
return CaloricLevel.DIET;
} else if (dish.getCalories() <= 700) {
return CaloricLevel.NORMAL;
} else {
return CaloricLevel.FAT;
}
})
)
);
分区partitioningBy
Map<Boolean, List<Dish>> partitionedMenu =
menu.stream().collect(partitioningBy(Dish::isVegetarian));
这会返回下面的Map:
{false=[pork, beef, chicken, prawns, salmon],
true=[french fries, rice, season fruit, pizza]}
partitioningBy工厂方法有一个重载版本,可以像下面这样传递第二个收集器:
Map<Boolean, Map<Dish.Type, List<Dish>>> vegetarianDishesByType =
menu.stream().collect(
partitioningBy(Dish::isVegetarian,
groupingBy(Dish::getType)));
这将产生一个二级Map:
{false={FISH=[prawns, salmon], MEAT=[pork, beef, chicken]},true={OTHER=[french fries, rice, season fruit, pizza]}}
这里,对于分区产生的素食和非素食子流,分别按类型对菜肴分组,得到了一个二级Map,
二级分组得到的结果类似。再举一个例子,你可以重用前面的代码来找到素食和非素
食中热量最高的菜:
Map<Boolean, Dish> mostCaloricPartitionedByVegetarian =
menu.stream().collect(
partitioningBy(Dish::isVegetarian,
collectingAndThen(
maxBy(comparingInt(Dish::getCalories)),
Optional::get)));
这将产生以下结果:
{false=pork, true=pizza}
optional对象
我们决定采用orElse方法读取这个变量的值,使用这种方式你还可以定义一个默认值,遭
遇空的Optional变量时,默认值会作为该方法的调用返回值。Optional类提供了多种方法读取
Optional实例中的变量值。
get()是这些方法中最简单但又最不安全的方法。如果变量存在,它直接返回封装的变量
值,否则就抛出一个NoSuchElementException异常。所以,除非你非常确定Optional
变量一定包含值,否则使用这个方法是个相当糟糕的主意。此外,这种方式即便相对于
嵌套式的null检查,也并未体现出多大的改进。
orElse(T other)是我们在代码清单10-5中使用的方法,正如之前提到的,它允许你在
Optional对象不包含值时提供一个默认值。
orElseGet(Supplier<? extends T> other)是orElse方法的延迟调用版,Supplier
方法只有在Optional对象不含值时才执行调用。如果创建默认值是件耗时费力的工作,
你应该考虑采用这种方式(借此提升程序的性能),或者你需要非常确定某个方法仅在
Optional为空时才进行调用,也可以考虑该方式(这种情况有严格的限制条件)。
orElseThrow(Supplier<? extends X> exceptionSupplier)和get方法非常类似,
它们遭遇Optional对象为空时都会抛出一个异常,但是使用orElseThrow你可以定制希
望抛出的异常类型。
ifPresent(Consumer<? super T>)让你能在变量值存在时执行一个作为参数传入的
方法,否则就不进行任何操作。
Optional类和Stream接口的相似之处,远不止map和flatMap这两个方法