中介者模式是关于数据交互的设计模式,该模式的核心是一个中介者对象,负责协调一系列对象之间的不同的数据请求,这一系列对象成为同事类。如房产中介(简直不想提它),买房的卖房的,租房的放租的都到房产中介那里去登记。如果有卖房的就会通知买房的去买房,如果有放租的就会通知租房的去租房。所有的事物都是通过中介进行通知转换,这样就形成了一个典型的星型结构,说道星型结构,网络中的交换机路由器不就是个大大的中介者么。
作用
中介者模式包装了一系列对象相互作用的方式,使得这些对象不必相互明显作用。从而使它们可以松散耦合。当某些对象之间的作用发生改变时,不会立即影响其他的一些对象之间的作用。保证这些作用可以彼此独立的变化。
类视图
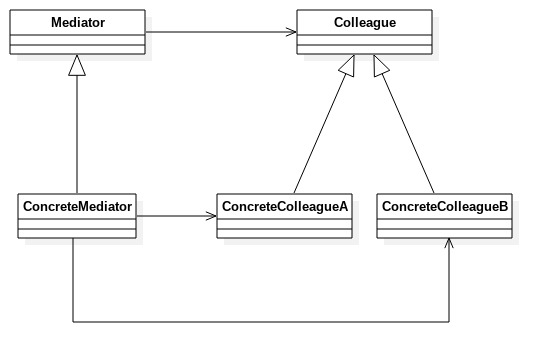
实现
中介者模式为拍卖行角色,负责买家、卖家和货币转换的协调工作,其中印度买家和法国买家想拍卖美国卖家的东西,印度使用的是卢比,法国使用的是美元,而美国使用的是美元,所有的出价都要以美元进行结算;这样就需要拍卖行来协调进行价格换算,拍卖竞价等工作。
//头文件mediator.h
#include <string>
class Mediator;
class Colleage //同事类
{
public:
Colleage(Mediator* md);
protected:
Mediator *m_mediator;
};
class IndianBuyer: public Colleage
{
public:
IndianBuyer(Mediator* md);
void setTotalMoney(float fall);
int Purchase(float bid);
private:
float m_total_money; //买家的心理价位
};
class FrenchBuyer: public Colleage
{
public:
FrenchBuyer(Mediator* md);
void setTotalMoney(float fall);
int Purchase(float bid);
private:
float m_total_money;
};
class AmericanSeller: public Colleage
{
public:
AmericanSeller(Mediator* md);
void SetWantPrice(float price);
bool IsBidAccept(float bidInDollars);
private:
float m_priceInDollars; //卖家的心理价位
};
class DollorConver: public Colleage
{
public:
DollorConver(Mediator* md);
float ConverToDollars(float bid, std::string strName);
private:
float ConverRupeetoDollar(float bid);
float ConverEurotoDollar(float bid);
private:
float dollor_unit; //美元换算比例
float euro_unit; //欧元换算比例
float rupee_unit;//卢比换算比例
};
class Mediator
{
public:
Mediator();
void RegisterIndianBuyer(IndianBuyer* buyer);
void RegisterFrenchBuyer(FrenchBuyer* buyer);
void RegisterAmericanSeller(AmericanSeller* seller);
void RegisterDollorConver(DollorConver* conver);
bool placeBid(float bid,std::string strName);
private:
IndianBuyer* m_pIndian;
FrenchBuyer* m_pFrench;
AmericanSeller* m_pAmerican;
DollorConver* m_pConver;
};
mediator.cpp
#include <iostream>
#include "mediator.h"
using namespace std;
Colleage::Colleage(Mediator* md):m_mediator(md)
{
}
IndianBuyer::IndianBuyer(Mediator* md):Colleage(md),m_total_money(-1){
m_mediator->RegisterIndianBuyer(this);
}
void IndianBuyer::setTotalMoney(float fall)
{
m_total_money = fall;
}
int IndianBuyer::Purchase(float bid)
{
//价格合适就出价一次
if (m_total_money<0 || bid<= m_total_money)
{
return (int)m_mediator->placeBid(bid,"RUPEE");
}
else
{
return 2;//价格太高了 不要啦
}
}
FrenchBuyer::FrenchBuyer(Mediator* md):Colleage(md),m_total_money(-1){
m_mediator->RegisterFrenchBuyer(this);
}
void FrenchBuyer::setTotalMoney(float fall)
{
m_total_money = fall;
}
int FrenchBuyer::Purchase(float bid)
{
if (m_total_money<0 || bid<= m_total_money)
{
return (int)m_mediator->placeBid(bid,"EURO");
}
else
{
return 2;
}
}
AmericanSeller::AmericanSeller(Mediator* md):Colleage(md),m_priceInDollars(0){
m_mediator->RegisterAmericanSeller(this);
}
void AmericanSeller::SetWantPrice(float price)
{
m_priceInDollars = price;
}
bool AmericanSeller::IsBidAccept(float bidInDollars)
{
if (bidInDollars>=m_priceInDollars)
{
//当遇到价格增长时记录最高的价格,没有人超过这个价格就按照这个价格出售
m_priceInDollars = bidInDollars;
return true;
}
return false;
}
DollorConver::DollorConver(Mediator* md):Colleage(md)
,dollor_unit(1.0),euro_unit(0.7),rupee_unit(45.0){
m_mediator->RegisterDollorConver(this);
}
float DollorConver::ConverToDollars(float bid, std::string strName)
{
if (strName.compare("RUPEE")==0)
{
return ConverRupeetoDollar(bid);
}
else
{
return ConverEurotoDollar(bid);
}
}
float DollorConver::ConverRupeetoDollar(float bid)
{
return bid*(dollor_unit/rupee_unit);
}
float DollorConver::ConverEurotoDollar(float bid)
{
return bid*(dollor_unit/euro_unit);
}
Mediator::Mediator():m_pIndian(NULL),m_pFrench(NULL)
,m_pAmerican(NULL),m_pConver(NULL){
}
void Mediator::RegisterIndianBuyer(IndianBuyer* buyer)
{
m_pIndian = buyer;
}
void Mediator::RegisterFrenchBuyer(FrenchBuyer* buyer)
{
m_pFrench = buyer;
}
void Mediator::RegisterAmericanSeller(AmericanSeller* seller)
{
m_pAmerican = seller;
}
void Mediator::RegisterDollorConver(DollorConver* conver)
{
m_pConver = conver;
}
bool Mediator::placeBid(float bid,std::string strName)
{
float dollars = m_pConver->ConverToDollars(bid,strName);
return m_pAmerican->IsBidAccept(dollars);
}
int main(int argc,char *argv[])
{
Mediator mediatior;
IndianBuyer indian(&mediatior);
FrenchBuyer french(&mediatior);
AmericanSeller american(&mediatior);
DollorConver conver(&mediatior);
indian.setTotalMoney(6000);
french.setTotalMoney(100);
american.SetWantPrice(50);
int nIndian = 0;
int nFrench = 0;
float IndianBid = 2000;
float FrenchBid = 30;
//一轮一轮进行出价,当有一个出不起的时候,就结束竞价。
while(nIndian+nFrench<=2)
{
do{
nIndian = indian.Purchase(IndianBid);
IndianBid+=100;
if (nIndian == 1)
{
cout<<"indian purchase : "<< IndianBid <<endl;
}
}
while(nIndian==0);
do{
nFrench = french.Purchase(FrenchBid);
FrenchBid+=1.5;
if (nFrench == 1)
{
cout<<"french purchase : "<< FrenchBid <<endl;
}
}
while(nFrench==0);
}
return 0;
}
当我们开始任何产品研发的时候总会有一些类,这些类会使用到之前产品的研发成果,随着功能的增加,逻辑会变得更加复杂,我们会添加更多的类和之前的类互相作用,知道难以维护所有的代码。中介者模式关心的就是这个问题,它会使代码更容易维护。它能够实现类之间的松散耦合。只有中介者这一个类知道所有的类,其他类只需要与中介者进行交互即可,当然更加集中的控制也会带来中枢的庞大,还是需要避免过度的集成。
应用场景
- 一组对象使用了标准的通信方式,但整体通信的连接都非常复杂,由此产生的相互依赖的结构导致系统难以结构化,也很难理解;
- 由于对象之间的通信和相互引用,导致对象难以重用。
- 分布于对个类中间的行为能够统一定制化,而无需创建过多的子类。