基础
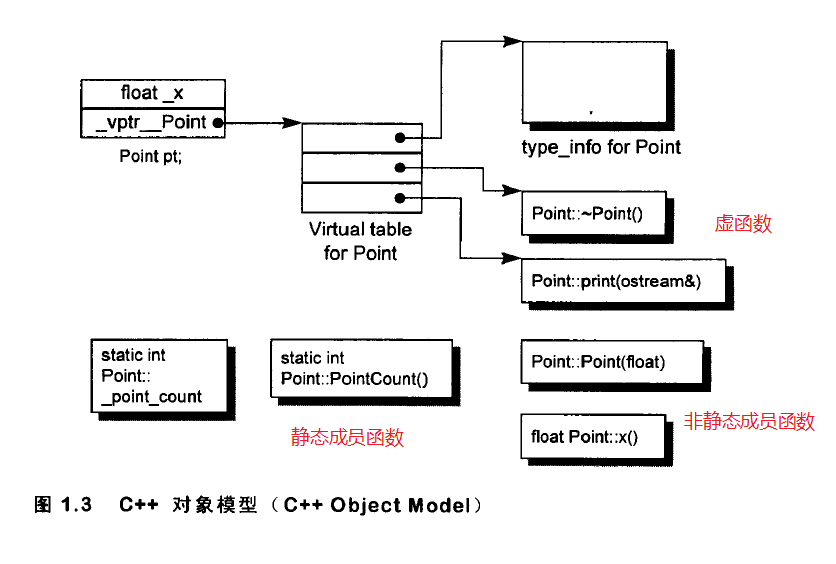
C++的类支持三种member function:static,nonstatic,virtual。
nonstatic member function
编译器会将nonstatic member function转换为普通外部函数。
1 #include <iostream> 2 3 using namespace std; 4 5 class A{ 6 public: 7 int x = 5; 8 int y = 6; 9 int add() 10 { 11 return x + y; 12 } 13 }; 14 15 int main() 16 { 17 A a; 18 a.add(); 19 return 0; 20 }
以上述代码为例,具体步骤如下:
- 改写函数原型,插入额外参数this指针。即int add(this)。
- 函数中对nonstatic data member的操作改为经由this指针来完成。即return this->x + this ->y。
- 加其重写为外部函数,并保证其函数名为独一无二的(区分类成员函数和普通函数、不同类中的同名成员函数、同类中的重载成员函数)。
virtual member function
对虚函数的调用会经由vptr及其偏移量来定位,并插入this指针。
1 #include <iostream> 2 2 3 3 using namespace std; 4 4 5 5 class A{ 6 6 public: 7 7 int x = 5; 8 8 int y = 6; 9 9 virtual int add() 10 10 { 11 11 return x + y; 12 12 } 13 13 }; 14 14 15 15 int main() 16 16 { 17 17 A a; 18 18 a.add(); 19 19 return 0; 20 20 }
以上述代码为例,a.add()会被编译器转换为(*(&a->vptr[1])) (this)。
引入了RTTI后,能在执行期确定对象类型。在编译期,只知道通过&a或者指向a的指针能够找到对象的virtual table,以及函数在表中的偏移量。
static member function
static member function的主要特性是没有this指针,所以它不能直接存取nonstatic member data,不能将static member function定义为const,volatile或virtual。
1 #include <iostream> 2 3 using namespace std; 4 5 class A{ 6 public: 7 int x = 5; 8 int y = 6; 9 static int add() 10 { 11 cout << "static member function" << endl; 12 } 13 }; 14 15 int main() 16 { 17 A a; 18 A* p = &a; 19 a.add(); //通过对象调用 20 p->add(); //通过对象指针调用 21 A::add(); //通过类调用 22 return 0; 23 }
其他
- 静态类型:对象在声明时采用的类型,在编译期既已确定;
- 动态类型:通常是指一个指针或引用目前所指对象的类型,是在运行期决定的;
- 静态绑定:绑定的是静态类型,所对应的函数或属性依赖于对象的静态类型,发生在编译期;
- 动态绑定:绑定的是动态类型,所对应的函数或属性依赖于对象的动态类型,发生在运行期;
参考
《深度探索C++对象模型》