Linux内核的三种调度策略
SCHED_OTHER
分时调度策略。
它是默认的线程分时调度策略,所有的线程的优先级别都是0,线程的调度是通过分时来完成的。简单地说,如果系统使用这种调度策略,程序将无法设置线程的优先级。请注意,这种调度策略也是抢占式的,当高优先级的线程准备运行的时候,当前线程将被抢占并进入等待队列。这种调度策略仅仅决定线程在可运行线程队列中的具有相同优先级的线程的运行次序。
SCHED_FIFO
实时调度策略,
先到先服务。一旦占用cpu则一直运行。一直运行直到有更高优先级任务到达或自己放弃。
它是一种实时的先进先出调用策略,且只能在超级用户下运行。这种调用策略仅仅被使用于优先级大于0的线程。它意味着,使用SCHED_FIFO的可运行线程将一直抢占使用SCHED_OTHER的运行线程J。此外SCHED_FIFO是一个非分时的简单调度策略,当一个线程变成可运行状态,它将被追加到对应优先级队列的尾部。当所有高优先级的线程终止或者阻塞时,它将被运行。对于相同优先级别的线程,按照简单的先进先运行的规则运行。我们考虑一种很坏的情况,如果有若干相同优先级的线程等待执行,然而最早执行的线程无终止或者阻塞动作,那么其他线程是无法执行的,除非当前线程调用如pthread_yield之类的函数,所以在使用SCHED_FIFO的时候要小心处理相同级别线程的动作。
SCHED_RR
实时调度策略,时间片轮转。
当进程的时间片用完,系统将重新分配时间片,并置于就绪队列尾。放在队列尾保证了所有具有相同优先级的RR任务的调度公平。
鉴于SCHED_FIFO调度策略的一些缺点,SCHED_RR对SCHED_FIFO做出了一些增强功能。从实质上看,它还是SCHED_FIFO调用策略。它使用最大运行时间来限制当前进程的运行,当运行时间大于等于最大运行时间的时候,当前线程将被切换并放置于相同优先级队列的最后。这样做的好处是其他具有相同级别的线程能在“自私“线程下执行。
系统创建线程时,默认的线程是SCHED_OTHER。所以如果我们要改变线程的调度策略的话,可以通过下面的这个函数实现:
int pthread_attr_setschedpolicy(pthread_attr_t *attr, int policy);
Linux线程优先级设置
首先,可以通过以下两个函数来获得线程可以设置的最高和最低优先级,函数中的策略即上述三种策略的宏定义:
int sched_get_priority_max(int policy);
int sched_get_priority_min(int policy);
SCHED_OTHER是不支持优先级使用的,而SCHED_FIFO和SCHED_RR支持优先级的使用,他们分别为1和99,数值越大优先级越高。
设置和获取优先级通过以下两个函数:
int pthread_attr_setschedparam(pthread_attr_t *attr, const struct sched_param *param);
int pthread_attr_getschedparam(const pthread_attr_t *attr, struct sched_param *param);
上面的param使用了下面的这个数据结构:
struct sched_param
{
int __sched_priority; //所要设定的线程优先级
};
例如:
param.sched_priority = 51; //设置优先级
测试程序
#include <stdio.h>
#include <pthread.h>
#include <sched.h>
#include <assert.h>
//打印当前的线程调度策略
static int get_thread_policy(pthread_attr_t *attr)
{
int policy;
int rs = pthread_attr_getschedpolicy(attr,&policy);
assert(rs==0);
switch(policy)
{
case SCHED_FIFO:
printf("policy= SCHED_FIFO
");
break;
case SCHED_RR:
printf("policy= SCHED_RR
");
break;
case SCHED_OTHER:
printf("policy=SCHED_OTHER
");
break;
default:
printf("policy=UNKNOWN
");
break;
}
return policy;
}
//打印当前调度策略线程的最高和最低优先级
static void show_thread_priority(pthread_attr_t *attr,int policy)
{
int priority = sched_get_priority_max(policy);
assert(priority!=-1);
printf("max_priority=%d
",priority);
priority= sched_get_priority_min(policy);
assert(priority!=-1);
printf("min_priority=%d
",priority);
}
//打印当前线程的优先级
static int get_thread_priority(pthread_attr_t *attr)
{
struct sched_param param;
int rs = pthread_attr_getschedparam(attr,¶m);
assert(rs==0);
printf("priority=%d
",param.__sched_priority);
return param.__sched_priority;
}
//设置线程线程的调度策略
static void set_thread_policy(pthread_attr_t *attr,int policy)
{
int rs = pthread_attr_setschedpolicy(attr,policy);
assert(rs==0);
get_thread_policy(attr);
}
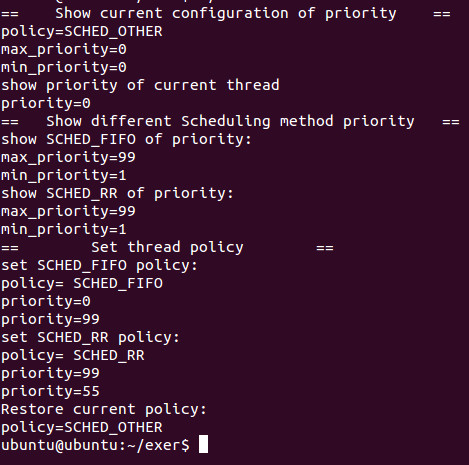
int main(void)
{
pthread_attr_t attr;
struct sched_param sched;
int rs;
rs = pthread_attr_init(&attr);
assert(rs==0);
//获取默认的线程调度策略
printf("== Show current configuration of priority ==
");
int policy = get_thread_policy(&attr);
show_thread_priority(&attr,policy);
//打印当前线程的优先级
printf("show priority of current thread
");
int priority = get_thread_priority(&attr);
printf("== Show different Scheduling method priority ==
");
//获取SCHED_FIFO调度策略的最高和最低优先级
printf("show SCHED_FIFO of priority:
");
show_thread_priority(&attr,SCHED_FIFO);
//获取SCHED_RR调度策略的最高和最低优先级
printf("show SCHED_RR of priority:
");
show_thread_priority(&attr,SCHED_RR);
printf("== Set thread policy ==
");
//设置线程的调度属性为SCHED_FIFO
printf("set SCHED_FIFO policy:
");
set_thread_policy(&attr,SCHED_FIFO);
priority = get_thread_priority(&attr);
sched.__sched_priority = 99;
pthread_attr_setschedparam(&attr,&sched);
priority = get_thread_priority(&attr);
//设置线程的调度属性为SCHED_FIFO
printf("set SCHED_RR policy:
");
set_thread_policy(&attr,SCHED_RR);
priority = get_thread_priority(&attr);
sched.__sched_priority = 55;
pthread_attr_setschedparam(&attr,&sched);
priority = get_thread_priority(&attr);
//恢复线程的调度策略
printf("Restore current policy:
");
set_thread_policy(&attr,policy);
rs = pthread_attr_destroy(&attr);
assert(rs==0);
return 0;
}