1. 概述
1.1. 已知算法
将一条线段栅格化的最简单的算法思路是根据其斜率,按X或Y方向步进取值:
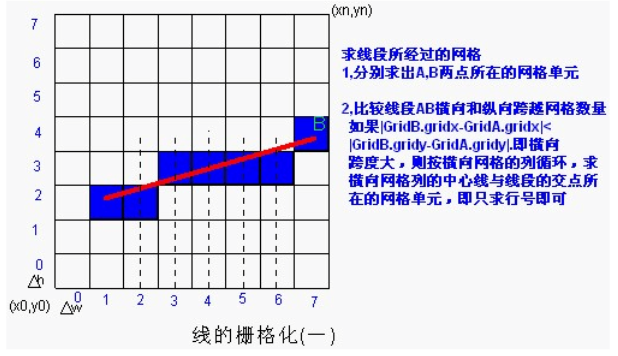
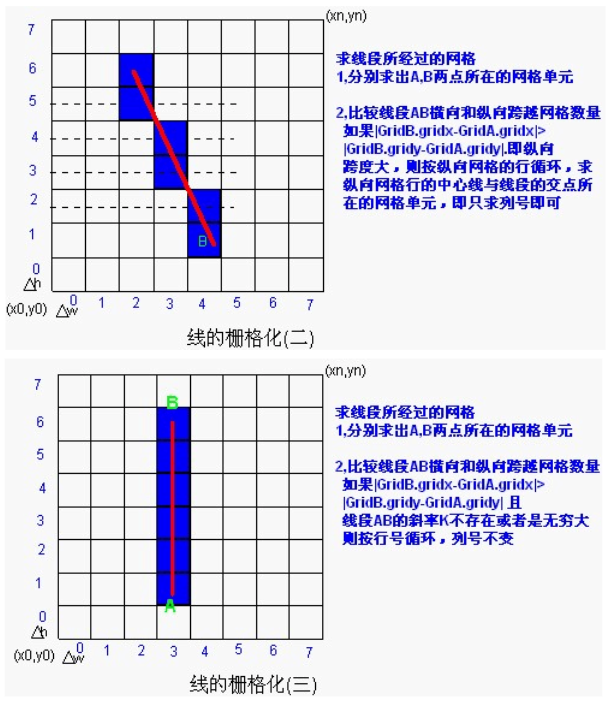
除此之外还有一种算法是利用计算机图形学中绘制直线的Bresenham算法,这种算法的效率很高,原理就是用遍历的办法规避乘法和除法,只用加减法就能完成线段的栅格化。
1.2. 本文算法
上述两种算法有个问题就是都要经过一系列繁复的判断,才能得到比较严密的结果,所以我并没有采用。我这里采用的算法也是逐渐步进求值的办法,只不过不再沿着X或者Y方向求值,而是沿着射线方向步进。这里的射线指的是从线段的起点开始,以1像素为步进单位,步进到线段的终点。因为线段的方向性问题,步进得到的点总会有重复的值,最后再进行去重操作即可。
算法过程简述如下:
- 设线段的起点为(O),终点为(E),则方向向量为(D=E-O);
- 线段的长度L为向量(D)的模。以0为初值,L为终值,以1为步进值建立一个for循环,每次取的长度为d;
- 令(t=d/L),则线段上相应的点为(P=O+tD)。这个公式是根据射线向量方程推导出来的,可以参看这篇文章《已知线段上某点与起点的距离,求该点的坐标》;
- 将取的点都保存到容器中;
- 对容器中的点进行去重操作。
最终得到的点即为直线栅格化后的点。
2. 实现
具体的C++实现代码如下:
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
const double EPSILON = 0.000001;
// 2D Point
struct Vector2d
{
public:
Vector2d()
{
}
Vector2d(double dx, double dy)
{
x = dx;
y = dy;
}
// 矢量赋值
void set(double dx, double dy)
{
x = dx;
y = dy;
}
// 矢量相加
Vector2d operator + (const Vector2d& v) const
{
return Vector2d(x + v.x, y + v.y);
}
// 矢量相减
Vector2d operator - (const Vector2d& v) const
{
return Vector2d(x - v.x, y - v.y);
}
//矢量数乘
Vector2d Scalar(double c) const
{
return Vector2d(c*x, c*y);
}
// 矢量点积
double Dot(const Vector2d& v) const
{
return x * v.x + y * v.y;
}
//向量的模
double Mod() const
{
return sqrt(x * x + y * y);
}
bool Equel(const Vector2d& v) const
{
if (abs(x - v.x) < EPSILON && abs(y - v.y) < EPSILON)
{
return true;
}
return false;
}
double x, y;
};
//栅格化一条线段
void RasterLine(std::pair<Vector2d, Vector2d> line, std::vector<Vector2d>& linePointList)
{
Vector2d vecLine = line.second - line.first;
double lineLength = vecLine.Mod();
double step = 1.0;
//根据距离逐步取
vector<Vector2d> tmpPointList;
double curLength = 0;
while (curLength < lineLength)
{
curLength = curLength + step;
Vector2d P = line.first + vecLine.Scalar(curLength / lineLength);
P.x = (int)(P.x + 0.5);
P.y = (int)(P.y + 0.5);
tmpPointList.push_back(P);
}
//与最后一个值比较,去重
linePointList.push_back(line.first);
for (size_t i = 0; i < tmpPointList.size(); i++)
{
//与最后一个值比较,去重
if (!tmpPointList[i].Equel(linePointList[linePointList.size() - 1]))
{
linePointList.push_back(tmpPointList[i]);
}
}
if (!linePointList[linePointList.size() - 1].Equel(line.second))
{
linePointList.push_back(line.second);
}
}
int main()
{
Vector2d O(30, 60);
Vector2d E(88, 104);
std::pair<Vector2d, Vector2d> line(O, E);
vector<Vector2d> linePointList;
RasterLine(line, linePointList);
for (size_t i = 0; i < linePointList.size(); i++)
{
cout << linePointList[i].x << ',' << linePointList[i].y << ' ';
}
}
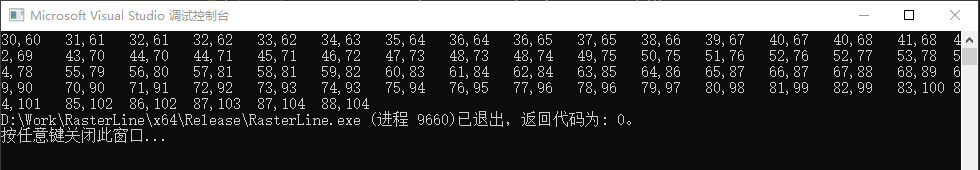
其运行的结果如下:
3. 参考
[1].矢量数据栅格化
[2].Bresenham算法