vmalloc是一个接口函数, 内核代码使用它来分配在虚拟内存中连续但在物理内存中不一定连续的内存。
只需要一个参数,以字节为单位。
使用vmalloc的最著名的实例是内核对模块的实现. 因为模块可能在任何时候加载, 如果模块数据比较多, 那么无法保证有足够的连续内存可用, 特别是在系统已经运行了比较长时间的情况下.
如果能够用小块内存拼接出足够的内存, 那么使用vmalloc可以规避该问题。
因为用于vmalloc的内存页总是必须映射在内核地址空间中, 因此使用ZONE_HIGHMEM内存域的页要优于其他内存域. 这使得内核可以节省更宝贵的较低端内存域, 而又不会带来额外的坏处. 因此, vmalloc等映射函数是内核出于自身的目的(并非因为用户空间应用程序)使用高端内存页的少数情形之一.
内核在管理虚拟内存中的VMALLOC区域时, 内核必须跟踪哪些子区域被使用、哪些是空闲的. 为此定义了一个数据结构vm_struct:
31struct vm_struct { 32 struct vm_struct *next; 33 void *addr; 34 unsigned long size; 35 unsigned long flags; 36 struct page **pages; 37 unsigned int nr_pages; 38 phys_addr_t phys_addr; 39 const void *caller; 40};
一个vm_struct代表一个vmalloc区域。
通过next形成一个链表。
addr是映射的首地址,size为映射地址区间的大小。
pages是一组指针,这些指针描述映射到这个区间里面的一个个真实的物理页对应的page指针。
nr_pages表示该地址区间映射了多少物理页。
phys_addr仅当用ioremap映射了由物理地址描述的物理内存区域时才需要。该信息保存在phys_addr中。
caller指向调用__vmalloc_node_flags被调用的地址。
flags的取值如下:
12/* bits in flags of vmalloc's vm_struct below */ 13#define VM_IOREMAP 0x00000001 /* ioremap() and friends */ 14#define VM_ALLOC 0x00000002 /* vmalloc() */ 15#define VM_MAP 0x00000004 /* vmap()ed pages */ 16#define VM_USERMAP 0x00000008 /* suitable for remap_vmalloc_range */ 17#define VM_VPAGES 0x00000010 /* buffer for pages was vmalloc'ed */ 18#define VM_UNINITIALIZED 0x00000020 /* vm_struct is not fully initialized */ 19#define VM_NO_GUARD 0x00000040 /* don't add guard page */ 20#define VM_KASAN 0x00000080 /* has allocated kasan shadow memory */ 21/* bits [20..32] reserved for arch specific ioremap internals */
因为vmalloc的调用函数都在一起,贴上如下:
1710/** 1711 * __vmalloc_node - allocate virtually contiguous memory 1712 * @size: allocation size 1713 * @align: desired alignment 1714 * @gfp_mask: flags for the page level allocator 1715 * @prot: protection mask for the allocated pages 1716 * @node: node to use for allocation or NUMA_NO_NODE 1717 * @caller: caller's return address 1718 * 1719 * Allocate enough pages to cover @size from the page level 1720 * allocator with @gfp_mask flags. Map them into contiguous 1721 * kernel virtual space, using a pagetable protection of @prot. 1722 */ 1723static void *__vmalloc_node(unsigned long size, unsigned long align, 1724 gfp_t gfp_mask, pgprot_t prot, 1725 int node, const void *caller) 1726{ 1727 return __vmalloc_node_range(size, align, VMALLOC_START, VMALLOC_END, 1728 gfp_mask, prot, 0, node, caller); 1729} 1730 ... 1737 1738static inline void *__vmalloc_node_flags(unsigned long size, 1739 int node, gfp_t flags) 1740{ 1741 return __vmalloc_node(size, 1, flags, PAGE_KERNEL, 1742 node, __builtin_return_address(0)); 1743} 1744 1745/** 1746 * vmalloc - allocate virtually contiguous memory 1747 * @size: allocation size 1748 * Allocate enough pages to cover @size from the page level 1749 * allocator and map them into contiguous kernel virtual space. 1750 * 1751 * For tight control over page level allocator and protection flags 1752 * use __vmalloc() instead. 1753 */ 1754void *vmalloc(unsigned long size) 1755{ 1756 return __vmalloc_node_flags(size, NUMA_NO_NODE, 1757 GFP_KERNEL | __GFP_HIGHMEM); 1758} 1759EXPORT_SYMBOL(vmalloc);
最终调到__vmalloc_node_range,并把VMALLOC_START和VMALLOC_END传入,该函数是vmalloc的主要实现,用来从(start, end)中申请一段大小为size的虚拟地址空间,并给这块虚拟地址空间申请物理内存(基本是不连续的),并写入页表。
VMALLOC_START和VMALLOC_END在arm中的定义如下:
36/* 37 * Just any arbitrary offset to the start of the vmalloc VM area: the 38 * current 8MB value just means that there will be a 8MB "hole" after the 39 * physical memory until the kernel virtual memory starts. That means that 40 * any out-of-bounds memory accesses will hopefully be caught. 41 * The vmalloc() routines leaves a hole of 4kB between each vmalloced 42 * area for the same reason. ;) 43 */ 44#define VMALLOC_OFFSET (8*1024*1024) 45#define VMALLOC_START (((unsigned long)high_memory + VMALLOC_OFFSET) & ~(VMALLOC_OFFSET-1)) 46#define VMALLOC_END 0xff800000UL 47
可以看出VMALLOC_END为0xff800000UL,但VMALLOC_START与high_memory有关。high_memory在sanity_check_meminfo中被确定:
static void * __initdata vmalloc_min = 1082 (void *)(VMALLOC_END - (240 << 20) - VMALLOC_OFFSET); 1083 1084/* 1085 * vmalloc=size forces the vmalloc area to be exactly 'size' 1086 * bytes. This can be used to increase (or decrease) the vmalloc 1087 * area - the default is 240m. 1088 */ 1089static int __init early_vmalloc(char *arg) 1090{ 1091 unsigned long vmalloc_reserve = memparse(arg, NULL); 1092 1093 if (vmalloc_reserve < SZ_16M) { 1094 vmalloc_reserve = SZ_16M; 1095 pr_warn("vmalloc area too small, limiting to %luMB ", 1096 vmalloc_reserve >> 20); 1097 } 1098 1099 if (vmalloc_reserve > VMALLOC_END - (PAGE_OFFSET + SZ_32M)) { 1100 vmalloc_reserve = VMALLOC_END - (PAGE_OFFSET + SZ_32M); 1101 pr_warn("vmalloc area is too big, limiting to %luMB ", 1102 vmalloc_reserve >> 20); 1103 } 1104 1105 vmalloc_min = (void *)(VMALLOC_END - vmalloc_reserve); 1106 return 0; 1107} 1108early_param("vmalloc", early_vmalloc); 1109 1110phys_addr_t arm_lowmem_limit __initdata = 0; 1111 1112void __init sanity_check_meminfo(void) 1113{ 1114 phys_addr_t memblock_limit = 0; 1115 int highmem = 0; 1116 phys_addr_t vmalloc_limit = __pa(vmalloc_min - 1) + 1; 1117 struct memblock_region *reg; 1118 bool should_use_highmem = false; 1119 1120 for_each_memblock(memory, reg) { 1121 phys_addr_t block_start = reg->base; 1122 phys_addr_t block_end = reg->base + reg->size; 1123 phys_addr_t size_limit = reg->size; 1124 1125 if (reg->base >= vmalloc_limit) 1126 highmem = 1; 1127 else 1128 size_limit = vmalloc_limit - reg->base; 1129 1130 1131 if (!IS_ENABLED(CONFIG_HIGHMEM) || cache_is_vipt_aliasing()) { 1132 1133 if (highmem) { 1134 pr_notice("Ignoring RAM at %pa-%pa (!CONFIG_HIGHMEM) ", 1135 &block_start, &block_end); 1136 memblock_remove(reg->base, reg->size); 1137 should_use_highmem = true; 1138 continue; 1139 } 1140 1141 if (reg->size > size_limit) { 1142 phys_addr_t overlap_size = reg->size - size_limit; 1143 1144 pr_notice("Truncating RAM at %pa-%pa to -%pa", 1145 &block_start, &block_end, &vmalloc_limit); 1146 memblock_remove(vmalloc_limit, overlap_size); 1147 block_end = vmalloc_limit; 1148 should_use_highmem = true; 1149 } 1150 } 1151 1152 if (!highmem) { 1153 if (block_end > arm_lowmem_limit) { 1154 if (reg->size > size_limit) 1155 arm_lowmem_limit = vmalloc_limit; 1156 else 1157 arm_lowmem_limit = block_end; 1158 } 1159 1160 /* 1161 * Find the first non-pmd-aligned page, and point 1162 * memblock_limit at it. This relies on rounding the 1163 * limit down to be pmd-aligned, which happens at the 1164 * end of this function. 1165 * 1166 * With this algorithm, the start or end of almost any 1167 * bank can be non-pmd-aligned. The only exception is 1168 * that the start of the bank 0 must be section- 1169 * aligned, since otherwise memory would need to be 1170 * allocated when mapping the start of bank 0, which 1171 * occurs before any free memory is mapped. 1172 */ 1173 if (!memblock_limit) { 1174 if (!IS_ALIGNED(block_start, PMD_SIZE)) 1175 memblock_limit = block_start; 1176 else if (!IS_ALIGNED(block_end, PMD_SIZE)) 1177 memblock_limit = arm_lowmem_limit; 1178 } 1179 1180 } 1181 } 1182 1183 if (should_use_highmem) 1184 pr_notice("Consider using a HIGHMEM enabled kernel. "); 1185 1186 high_memory = __va(arm_lowmem_limit - 1) + 1; 1187 1188 if (!memblock_limit) 1189 memblock_limit = arm_lowmem_limit; 1190 1191 /* 1192 * Round the memblock limit down to a pmd size. This 1193 * helps to ensure that we will allocate memory from the 1194 * last full pmd, which should be mapped. 1195 */ 1196 memblock_limit = round_down(memblock_limit, PMD_SIZE); 1197 1198 memblock_set_current_limit(memblock_limit); 1199}
如果在bootargs里面没有vmalloc=的字段,vmalloc占用的虚拟地址空间为240MB,如果设置了该参数大小为P,会用VMALLOC_END-P赋给vmalloc_min。
sanity_check_meminfo对于vmalloc来讲最重要的作用就是根据memblock里面的内存块确定arm_lowmem_limit的地址,使其不会与vmalloc区间重叠。
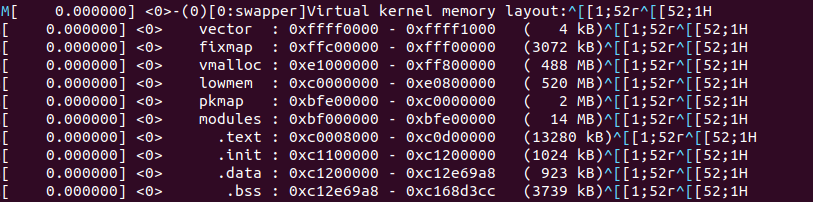
OK, VMALLOC_START与VMALLOC_END确定。
下面来看下这个函数的实现:
1649/** 1650 * __vmalloc_node_range - allocate virtually contiguous memory 1651 * @size: allocation size 1652 * @align: desired alignment 1653 * @start: vm area range start 1654 * @end: vm area range end 1655 * @gfp_mask: flags for the page level allocator 1656 * @prot: protection mask for the allocated pages 1657 * @vm_flags: additional vm area flags (e.g. %VM_NO_GUARD) 1658 * @node: node to use for allocation or NUMA_NO_NODE 1659 * @caller: caller's return address 1660 * 1661 * Allocate enough pages to cover @size from the page level 1662 * allocator with @gfp_mask flags. Map them into contiguous 1663 * kernel virtual space, using a pagetable protection of @prot. 1664 */ 1665void *__vmalloc_node_range(unsigned long size, unsigned long align, 1666 unsigned long start, unsigned long end, gfp_t gfp_mask, 1667 pgprot_t prot, unsigned long vm_flags, int node, 1668 const void *caller) 1669{ 1670 struct vm_struct *area; 1671 void *addr; 1672 unsigned long real_size = size; 1673 1674 size = PAGE_ALIGN(size); 1675 if (!size || (size >> PAGE_SHIFT) > totalram_pages) 1676 goto fail; 1677 1678 area = __get_vm_area_node(size, align, VM_ALLOC | VM_UNINITIALIZED | 1679 vm_flags, start, end, node, gfp_mask, caller); 1680 if (!area) 1681 goto fail; 1682 1683 addr = __vmalloc_area_node(area, gfp_mask, prot, node); 1684 if (!addr) 1685 return NULL; 1686 1687 /* 1688 * In this function, newly allocated vm_struct has VM_UNINITIALIZED 1689 * flag. It means that vm_struct is not fully initialized. 1690 * Now, it is fully initialized, so remove this flag here. 1691 */ 1692 clear_vm_uninitialized_flag(area); 1693 1694 /* 1695 * A ref_count = 2 is needed because vm_struct allocated in 1696 * __get_vm_area_node() contains a reference to the virtual address of 1697 * the vmalloc'ed block. 1698 */ 1699 kmemleak_alloc(addr, real_size, 2, gfp_mask); 1700 1701 return addr; 1702 1703fail: 1704 warn_alloc_failed(gfp_mask, 0, 1705 "vmalloc: allocation failure: %lu bytes ", 1706 real_size); 1707 return NULL; 1708} 1709
先调用__get_vm_area_node在vmap_area组成的红黑树中找到一个位置,把由该空间组成的vmap_area插入红黑树。
然后调用setup_vmalloc_vm 把该空间保存在vm_struct中。
1317static void setup_vmalloc_vm(struct vm_struct *vm, struct vmap_area *va, 1318 unsigned long flags, const void *caller) 1319{ 1320 spin_lock(&vmap_area_lock); 1321 vm->flags = flags; 1322 vm->addr = (void *)va->va_start; 1323 vm->size = va->va_end - va->va_start; 1324 vm->caller = caller; 1325 va->vm = vm; 1326 va->flags |= VM_VM_AREA; 1327 spin_unlock(&vmap_area_lock); 1328}
然后回到__vmalloc_node_range中,申请完虚拟地址空间后,接着调用__vmalloc_area_node 来申请具体的物理页,并把这些页和对应的虚拟地址填入页表。
1591static void *__vmalloc_area_node(struct vm_struct *area, gfp_t gfp_mask, 1592 pgprot_t prot, int node) 1593{ 1594 const int order = 0; 1595 struct page **pages; 1596 unsigned int nr_pages, array_size, i; 1597 const gfp_t nested_gfp = (gfp_mask & GFP_RECLAIM_MASK) | __GFP_ZERO; 1598 const gfp_t alloc_mask = gfp_mask | __GFP_NOWARN; 1599 1600 nr_pages = get_vm_area_size(area) >> PAGE_SHIFT; 1601 array_size = (nr_pages * sizeof(struct page *)); 1602 1603 area->nr_pages = nr_pages; 1604 /* Please note that the recursion is strictly bounded. */ 1605 if (array_size > PAGE_SIZE) { 1606 pages = __vmalloc_node(array_size, 1, nested_gfp|__GFP_HIGHMEM, 1607 PAGE_KERNEL, node, area->caller); 1608 area->flags |= VM_VPAGES; 1609 } else { 1610 pages = kmalloc_node(array_size, nested_gfp, node); 1611 } 1612 area->pages = pages; 1613 if (!area->pages) { 1614 remove_vm_area(area->addr); 1615 kfree(area); 1616 return NULL; 1617 } 1618 1619 for (i = 0; i < area->nr_pages; i++) { 1620 struct page *page; 1621 1622 if (node == NUMA_NO_NODE) 1623 page = alloc_page(alloc_mask); 1624 else 1625 page = alloc_pages_node(node, alloc_mask, order); 1626 1627 if (unlikely(!page)) { 1628 /* Successfully allocated i pages, free them in __vunmap() */ 1629 area->nr_pages = i; 1630 goto fail; 1631 } 1632 area->pages[i] = page; 1633 if (gfpflags_allow_blocking(gfp_mask)) 1634 cond_resched(); 1635 } 1636 1637 if (map_vm_area(area, prot, pages)) 1638 goto fail; 1639 return area->addr; 1640 1641fail: 1642 warn_alloc_failed(gfp_mask, order, 1643 "vmalloc: allocation failure, allocated %ld of %ld bytes ", 1644 (area->nr_pages*PAGE_SIZE), area->size); 1645 vfree(area->addr); 1646 return NULL; 1647} 1648
首先为pages数组申请一段连续的虚拟地址空间(小于1页,使用kmalloc,大于1页,调vmalloc来保证虚拟地址空间的连续性),用来存入申请的物理页对应的page结构体,然后会申请nr_pages个物理页(注意是一次申请一页,因此申请到的页基本是不连续的)。
最终通过map_vm_area把这些物理页和虚拟地址空间对应起来,写入页表。
另外,社区还有对vmalloc的页面进行区分的patch。如下:
diff --git a/fs/proc/page.c b/fs/proc/page.c index 792c78a49174..fc83dae1af7b 100644 --- a/fs/proc/page.c +++ b/fs/proc/page.c @@ -156,6 +156,8 @@ u64 stable_page_flags(struct page *page) u |= 1 << KPF_BALLOON; if (PageTable(page)) u |= 1 << KPF_PGTABLE; + if (PageVMalloc(page)) + u |= 1 << KPF_VMALLOC; if (page_is_idle(page)) u |= 1 << KPF_IDLE; diff --git a/include/linux/mm_types.h b/include/linux/mm_types.h index 42619e16047f..c51ddd27bfb4 100644 --- a/include/linux/mm_types.h +++ b/include/linux/mm_types.h @@ -141,6 +141,11 @@ struct page { spinlock_t ptl; #endif }; + struct { /* VMalloc pages */ + struct vm_struct *vm_area; + unsigned long vm_offset; + unsigned long _vm_id; /* MAPPING_VMalloc */ + }; /** @rcu_head: You can use this to free a page by RCU. */ struct rcu_head rcu_head; diff --git a/include/linux/page-flags.h b/include/linux/page-flags.h index 901943e4754b..5232433175c1 100644 --- a/include/linux/page-flags.h +++ b/include/linux/page-flags.h @@ -699,6 +699,31 @@ PAGE_TYPE_OPS(Kmemcg, kmemcg) */ PAGE_TYPE_OPS(Table, table) +/* + * vmalloc pages may be mapped to userspace, so we need some other way + * to distinguish them from other kinds of pages. Use page->mapping + * for this purpose. Values below 0x1000 cannot be real pointers. + */ +#define MAPPING_VMalloc (void *)0x440 + +#define PAGE_MAPPING_OPS(name) +static __always_inline int Page##name(struct page *page) +{ + return page->mapping == MAPPING_##name; +} +static __always_inline void __SetPage##name(struct page *page) +{ + VM_BUG_ON_PAGE(page->mapping != NULL, page); + page->mapping = MAPPING_##name; +} +static __always_inline void __ClearPage##name(struct page *page) +{ + VM_BUG_ON_PAGE(page->mapping != MAPPING_##name, page); + page->mapping = NULL; +} + +PAGE_MAPPING_OPS(VMalloc) + extern bool is_free_buddy_page(struct page *page); __PAGEFLAG(Isolated, isolated, PF_ANY); diff --git a/include/uapi/linux/kernel-page-flags.h b/include/uapi/linux/kernel-page-flags.h index 21b9113c69da..6800968b8f47 100644 --- a/include/uapi/linux/kernel-page-flags.h +++ b/include/uapi/linux/kernel-page-flags.h @@ -36,5 +36,6 @@ #define KPF_ZERO_PAGE 24 #define KPF_IDLE 25 #define KPF_PGTABLE 26 +#define KPF_VMALLOC 27 #endif /* _UAPILINUX_KERNEL_PAGE_FLAGS_H */ diff --git a/mm/vmalloc.c b/mm/vmalloc.c index 5fbf27e7f956..98bc690d472d 100644 --- a/mm/vmalloc.c +++ b/mm/vmalloc.c @@ -1535,7 +1535,7 @@ static void __vunmap(const void *addr, int deallocate_pages) for (i = 0; i < area->nr_pages; i++) { struct page *page = area->pages[i]; - BUG_ON(!page); + __ClearPageVMalloc(page); __free_pages(page, 0); } @@ -1704,6 +1704,9 @@ static void *__vmalloc_area_node(struct vm_struct *area, gfp_t gfp_mask, area->nr_pages = i; goto fail; } + __SetPageVMalloc(page); + page->vm_area = area; + page->vm_offset = i; area->pages[i] = page; if (gfpflags_allow_blocking(gfp_mask)) cond_resched(); diff --git a/tools/vm/page-types.c b/tools/vm/page-types.c index cce853dca691..25cc21855be4 100644 --- a/tools/vm/page-types.c +++ b/tools/vm/page-types.c @@ -132,6 +132,7 @@ static const char * const page_flag_names[] = { [KPF_THP] = "t:thp", [KPF_BALLOON] = "o:balloon", [KPF_PGTABLE] = "g:pgtable", + [KPF_VMALLOC] = "V:vmalloc", [KPF_ZERO_PAGE] = "z:zero_page", [KPF_IDLE] = "i:idle_page",