<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="utf-8"> <style> table td{ border-spacing:0; padding: 5px 10px; border: 1px solid #ddd; } </style> </head> <body> <table> <thead> <td>姓名</td> <td>年龄</td> </thead> <tr> <td>张三</td> <td>12</td> </tr> <tr> <td>李四</td> <td>11</td> </tr> </table> <ul> <li> <p>文字1</p> <p>文字1</p> </li> <li> <p>文字2</p> <p>文字2</p> </li> <li> <p>文字3</p> <p>文字3</p> </li> </ul> </body> <script src="jquery-3.1.0.min.js"></script> <script> console.log(document.getElementsByTagName('table')[0].innerHTML); // <thead> // <tr><td>姓名</td> // <td>年龄</td> // </tr></thead> // <tbody><tr> // <td>张三</td> // <td>12</td> // </tr> // <tr> // <td>李四</td> // <td>11</td> // </tr> // </tbody> //错误示范 // $('table').children('tr').children('td').eq(0).css({ // 'background': 'blue', // 'border-bottom': '1px solid red' // }); console.log($('ul').children('p').eq(0).html());//undefined console.log($('table').children('tr').html());//undefined //正确示范1 console.log($('table').find('tr').children('td').eq(0));//长度为6的数组里面的第一个值 $('table').find('tr').children('td').eq(0).css({ 'color': 'blue' }); //正确示范2 $('table tr td:nth-child(1)').css({ 'background': 'pink', 'border-bottom': '1px solid red' }); $('ul').children('li').children('p').eq(0).css('border','1px solid blue'); $('ul').children('li').children('p:nth-child(1)').css('color','red'); </script> </html>
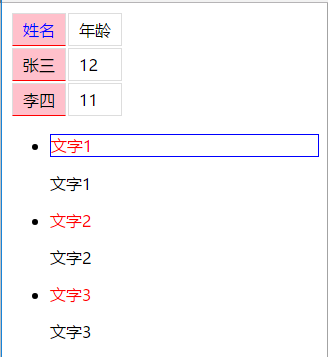
总结:
一、table结构
如以上代码所示,对于table表格而言,thead标签里面会默认自动加上一层tr标签,同时,与thead相并列的tbody标签,如果不加,也是会自动默认加上的,tbody里面的td外如果没有tr,那么也会被默认加上。所以,在使用选择器来选择table里面的元素时一定要注意,别忘了由于默认添加上的标签而导致的结构的变化。
二、children()与find()的区别
选择器children()只是用来选择子代元素的,无法选择到后代元素。而选择器find()既可以选择到子代元素,也可以选择到后代元素,通常的话,习惯确定是后代元素的话就用选择器find()。所以,如果用children()来选择一个后代元素,必然得到的结果是undefined了。所以,清楚结构是很重要的。
三、选择器eq(n)与nth-child(n)的差异
$('ul').children('li').children('p') 得到的是 [p, p, p, p, p, p, prevObject: r.fn.init(3)], .eq(0)之后,获得的是第一个p,因此只有第一个p加上了蓝色边框。
$('ul').children('li').children('p:nth-child(1)') 得到的是[p, p, p, prevObject: r.fn.init(3)],即p的父元素(各自依属的三个li标签)下的第一个子节点,因此有三个p标签里面的文字变成了红色。
以上三点都是比较容易忽视的地方,以后要注意了,不能再同一块石头上摔倒两次哟!