决策树
优点:计算复杂度不高,输出结果易于理解,对中间值的缺失不敏感,可以处理不相关特征数据。
缺点:可能会产生过度匹配问题。
适用数据类型:数值型和标称型
决策树的一般流程
(1) 收集数据:可以使用任何方法。
(2) 准备数据:树构造算法只适用于标称型数据,因此数值型数据必须离散化。
(3) 分析数据:可以使用任何方法,构造树完成之后,我们应该检查图形是否符合预期。
(4) 训练算法:构造树的数据结构。
(5) 测试算法:使用经验树计算错误率。
(6) 使用算法:此步骤可以适用于任何监督学习算法,而使用决策树可以更好地理解数据的内在含义。
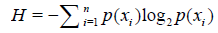
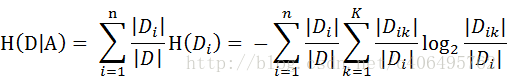
from math import log import operator """ Parameters: dataSet - 数据集 Returns: shannonEnt - 经验熵(香农熵) """ # 函数说明:计算给定数据集的经验熵(香农熵) def calcShannonEnt(dataSet): numEntires = len(dataSet) #返回数据集的行数 labelCounts = {} #保存每个标签(Label)出现次数的字典 for featVec in dataSet: #对每组特征向量进行统计 currentLabel = featVec[-1] #提取标签(Label)信息 if currentLabel not in labelCounts.keys(): #如果标签(Label)没有放入统计次数的字典,添加进去 labelCounts[currentLabel] = 0 labelCounts[currentLabel] += 1 #Label计数 shannonEnt = 0.0 #经验熵(香农熵) for key in labelCounts: #计算香农熵 prob = float(labelCounts[key]) / numEntires#选择该标签(Label)的概率 shannonEnt -= prob * log(prob, 2) #利用公式计算 return shannonEnt #返回经验熵(香农熵) """ Parameters: 无 Returns: dataSet - 数据集 labels - 特征标签 """ # 函数说明:创建测试数据集 def createDataSet(): dataSet = [[0, 0, 0, 0, 'no'],#数据集 [0, 0, 0, 1, 'no'], [0, 1, 0, 1, 'yes'], [0, 1, 1, 0, 'yes'], [0, 0, 0, 0, 'no'], [1, 0, 0, 0, 'no'], [1, 0, 0, 1, 'no'], [1, 1, 1, 1, 'yes'], [1, 0, 1, 2, 'yes'], [1, 0, 1, 2, 'yes'], [2, 0, 1, 2, 'yes'], [2, 0, 1, 1, 'yes'], [2, 1, 0, 1, 'yes'], [2, 1, 0, 2, 'yes'], [2, 0, 0, 0, 'no']] labels = ['年龄', '有工作', '有自己的房子', '信贷情况']#特征标签 return dataSet, labels#返回数据集和分类属性 """ Parameters: dataSet - 待划分的数据集 axis - 划分数据集的特征 value - 需要返回的特征的值 Returns: 无 """ # 函数说明:按照给定特征划分数据集 def splitDataSet(dataSet, axis, value): retDataSet = [] #创建返回的数据集列表 for featVec in dataSet: #遍历数据集 if featVec[axis] == value: reducedFeatVec = featVec[:axis] #去掉axis特征 reducedFeatVec.extend(featVec[axis+1:])#将符合条件的添加到返回的数据集 retDataSet.append(reducedFeatVec) return retDataSet #返回划分后的数据集 """ Parameters: dataSet - 数据集 Returns: bestFeature - 信息增益最大的(最优)特征的索引值 """ # 函数说明:选择最优特征 def chooseBestFeatureToSplit(dataSet): numFeatures = len(dataSet[0]) - 1 #特征数量 baseEntropy = calcShannonEnt(dataSet) #计算数据集的香农熵 bestInfoGain = 0.0 #信息增益 bestFeature = -1 #最优特征的索引值 for i in range(numFeatures): #遍历所有特征 #获取dataSet的第i个所有特征 featList = [example[i] for example in dataSet] uniqueVals = set(featList) #创建set集合{},元素不可重复 newEntropy = 0.0 #经验条件熵 for value in uniqueVals: #计算信息增益 subDataSet = splitDataSet(dataSet, i, value) #subDataSet划分后的子集 prob = len(subDataSet) / float(len(dataSet)) #计算子集的概率 newEntropy += prob * calcShannonEnt(subDataSet)#根据公式计算经验条件熵 infoGain = baseEntropy - newEntropy #信息增益 # print("第%d个特征的增益为%.3f" % (i, infoGain)) #打印每个特征的信息增益 if (infoGain > bestInfoGain): #计算信息增益 bestInfoGain = infoGain #更新信息增益,找到最大的信息增益 bestFeature = i #记录信息增益最大的特征的索引值 return bestFeature #返回信息增益最大的特征的索引值 """ Parameters: classList - 类标签列表 Returns: sortedClassCount[0][0] - 出现此处最多的元素(类标签) """ # 函数说明:统计classList中出现此处最多的元素(类标签) def majorityCnt(classList): classCount = {} for vote in classList:#统计classList中每个元素出现的次数 if vote not in classCount.keys():classCount[vote] = 0 classCount[vote] += 1 sortedClassCount = sorted(classCount.items(), key = operator.itemgetter(1), reverse = True)#根据字典的值降序排序 return sortedClassCount[0][0]#返回classList中出现次数最多的元素 """ Parameters: dataSet - 训练数据集 labels - 分类属性标签 featLabels - 存储选择的最优特征标签 Returns: myTree - 决策树 """ # 函数说明:创建决策树 def createTree(dataSet, labels, featLabels): classList = [example[-1] for example in dataSet] #取分类标签(是否放贷:yes or no) if classList.count(classList[0]) == len(classList): #如果类别完全相同则停止继续划分 return classList[0] if len(dataSet[0]) == 1: #遍历完所有特征时返回出现次数最多的类标签 return majorityCnt(classList) bestFeat = chooseBestFeatureToSplit(dataSet) #选择最优特征 bestFeatLabel = labels[bestFeat] #最优特征的标签 featLabels.append(bestFeatLabel) myTree = {bestFeatLabel:{}} #根据最优特征的标签生成树 del(labels[bestFeat]) #删除已经使用特征标签 featValues = [example[bestFeat] for example in dataSet]#得到训练集中所有最优特征的属性值 uniqueVals = set(featValues) #去掉重复的属性值 for value in uniqueVals: #遍历特征,创建决策树。 myTree[bestFeatLabel][value] = createTree(splitDataSet(dataSet, bestFeat, value), labels, featLabels) return myTree if __name__ == '__main__': dataSet, labels = createDataSet() featLabels = [] myTree = createTree(dataSet, labels, featLabels) print(myTree)