1.1 工具变量法
OLS 有一个经典的假设:解释变量与随机误差项不相关,即 。如果存在解释变量违背了这个假设,则估计出的参数是有偏的,也是不一致的。
工具变量 (IV) 法为解决「内生解释变量」问题提供了一种可行的方法。为此,我们需要找到满足以下条件的「外生解释变量 (z)」:
- 与内生解释变量相关,即
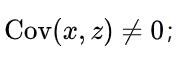
- 与随机误差项不相关,即
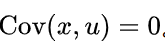
根据「内生解释变量」与「工具变量」间的数量关系,又可以分为以下几种情况:
- 不可识别 (unidentified):工具变量数小于内生解释变量数;
- 恰好识别 (just or exactly indentified):工具变量数等于内生解释变量数;
- 过度识别 (overindentified):工具变量数大于内生解释变量数。
在「恰好识别」的情况下,我们可以估计 ,而在「过度识别」的情况下,则需要通过两阶段最小二乘法 (Two Stage Least Square,2SLS 或 TSLS) 估计 。当然在「恰好识别」的情况下,我们也可以用 2SLS 进行估计。但是,在「不可识别」情况下,以上方法失效。2SLS 主要通过以下两阶段实现:
- 第一阶段,用内生解释变量对工具变量回归;
- 第二阶段,用被解释变量对第一阶段回归的拟合值回归。
值得注意, 2SLS 只有在「同方差」的情况下才是最优效率的,而在「过度识别」和「异方差」的情况下,广义矩估计 (Generalized Method of Moments, GMM) 才是最有效率的。关于 GMM 介绍详见:「Stata:GMM 简介及实现范例」和「GMM 简介与 Stata 实现」。
在使用工具变量之前,我们仍需进行若干检验:
- 解释变量内生性的检验;
- 弱工具变量检验;
- 过度识别检验。
在「恰好识别」的情况下,我们无法检验工具变量的外生性,只能进行「定性讨论或依赖专家意见」,详见「IV-估计:工具变量不外生时也可以用!」。因此,我们重点关注「过度识别检验」的方法和在 Stata 中实现。
1.2 两阶段最小二乘法
两阶段最小二乘法其本质上是属于工具变量,回归分两个阶段进行,因此而得名。具体机理是:
第一步,将结构方程先转换为简化式模型(约简型方程),简化式模型里的每一个方程都不存在随机解释变量问题,可以直接采用普通最小二乘法进行估计。
第二步,由第一步得出的估计量替换 Y 。该方程中不存在随机解释变量问题,也可以直接用普通最小二乘法进行估计。
例子:一般 IV 回归模型为:
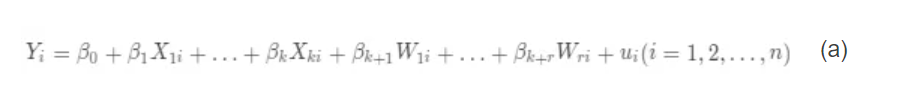

以单内生回归变量的 2SLS 为例,当只有一个内生回归变量 X 和一些其他的包含的外生变量时,感兴趣的方程为:


2. 过度识别检验
2.1过度识别检验原理
上面提到了,只有恰好识别和过度识别才能用 IV 方法估计。假设待估参数的个数为 k ,矩条件的个数为 l 。当 k=l 时,称为“恰好识别”,当 k<l 时,称为="过度识别"。
一个很重要的命题是:只有过度识别情况下才能检验工具变量的外生性,而恰好识别情况下无法检验。

为基于所有工具变量的 2SLS 回归估计残差(由于抽样变异性因此是近似的而不是精确地,注意到这些残差是利用 X 值而不是用其第一阶段的预测值得到的。)

2.2.1 Sargan 检验


2.2.2 Hansen J 检验


2.2.3 C 统计量

3. 过度识别检验的 Stata 实现
3.1 ivreg2 命令
以官方 griliches76.dta 数据为例,lw 为工资对数,s 为受教育年限,expr 为工龄,tenure 为现单位工作年数,rns 为美国南方虚拟变量 (住在南方 = 1),smsa 为大城市虚拟变量 (住在大城市 = 1),iq 为智商,med 为母亲受教育年限,kww 为一项职业测试成绩 (score on knowledge in world of work test),age 为年龄,mrt 为婚姻状况 (已婚 = 1)。
在研究「智商」对「工资」的影响时,「智商」通常会被认为是一个内生的解释变量,因此我们需要为「智商」寻找工具变量。当然外生解释变量可以被看作自身的工具变量。在这里,我们将母亲受教育年限 (med)、职业测试成绩 (kww)、年龄 (age) 和婚姻状况 (mrt)作为「智商」的工具变量,并进行「过度识别」检验。
在使用 ivreg2 命令进行工具变量回归时,默认提供 Sargan 统计量,而在命令后加入 robust、bw、cluster 等选项时,Stata 默认提供 Hansen J 统计量。若要报告 统计量,只需在命令后加入 orthog(varlist_ex) 选项,其中 varlist_ex 为需要检验外生性的变量。关于 ivreg2 更多介绍,详见 help ivreg2。
*-安装命令 ssc install ivreg2, replace *-Sargan 检验 use http://fmwww.bc.edu/ec-p/data/hayashi/griliches76.dta ivreg2 lw s expr tenure rns smsa i.year (iq=med kww age mrt) *-Hansen J 检验 ivreg2 lw s expr tenure rns smsa i.year (iq=med kww age mrt), robust *-C 统计量 ivreg2 lw s expr tenure rns smsa i.year (iq=med kww age mrt), orthog(s)
. ivreg2 lw s expr tenure rns smsa i.year (iq=med kww age mrt) IV (2SLS) estimation -------------------- Estimates efficient for homoskedasticity only Statistics consistent for homoskedasticity only Number of obs = 758 F( 12, 745) = 45.91 Prob > F = 0.0000 Total (centered) SS = 139.2861498 Centered R2 = 0.4255 Total (uncentered) SS = 24652.24662 Uncentered R2 = 0.9968 Residual SS = 80.0182337 Root MSE = .3249 ------------------------------------------------------------------------------ lw | Coef. Std. Err. z P>|z| [95% Conf. Interval] -------------+---------------------------------------------------------------- iq | .0001747 .0039035 0.04 0.964 -.007476 .0078253 s | .0691759 .0129366 5.35 0.000 .0438206 .0945312 expr | .029866 .0066393 4.50 0.000 .0168533 .0428788 tenure | .0432738 .0076271 5.67 0.000 .0283249 .0582226 rns | -.1035897 .029481 -3.51 0.000 -.1613715 -.0458079 smsa | .1351148 .0266573 5.07 0.000 .0828674 .1873623 | year | 67 | -.052598 .0476924 -1.10 0.270 -.1460734 .0408774 68 | .0794686 .0447194 1.78 0.076 -.0081797 .1671169 69 | .2108962 .0439336 4.80 0.000 .1247878 .2970045 70 | .2386338 .0509733 4.68 0.000 .1387281 .3385396 71 | .2284609 .0437436 5.22 0.000 .1427251 .3141967 73 | .3258944 .0407181 8.00 0.000 .2460884 .4057004 | _cons | 4.39955 .2685443 16.38 0.000 3.873213 4.925887 ------------------------------------------------------------------------------ Underidentification test (Anderson canon. corr. LM statistic): 52.436 Chi-sq(4) P-val = 0.0000 ------------------------------------------------------------------------------ Weak identification test (Cragg-Donald Wald F statistic): 13.786 Stock-Yogo weak ID test critical values: 5% maximal IV relative bias 16.85 10% maximal IV relative bias 10.27 20% maximal IV relative bias 6.71 30% maximal IV relative bias 5.34 10% maximal IV size 24.58 15% maximal IV size 13.96 20% maximal IV size 10.26 25% maximal IV size 8.31 Source: Stock-Yogo (2005). Reproduced by permission. ------------------------------------------------------------------------------ Sargan statistic (overidentification test of all instruments): 87.655 Chi-sq(3) P-val = 0.0000 ------------------------------------------------------------------------------ Instrumented: iq Included instruments: s expr tenure rns smsa 67.year 68.year 69.year 70.year 71.year 73.year Excluded instruments: med kww age mrt ------------------------------------------------------------------------------
*-Hansen J 检验 . ivreg2 lw s expr tenure rns smsa i.year (iq=med kww age mrt), robust IV (2SLS) estimation -------------------- Estimates efficient for homoskedasticity only Statistics robust to heteroskedasticity Number of obs = 758 F( 12, 745) = 46.94 Prob > F = 0.0000 Total (centered) SS = 139.2861498 Centered R2 = 0.4255 Total (uncentered) SS = 24652.24662 Uncentered R2 = 0.9968 Residual SS = 80.0182337 Root MSE = .3249 ------------------------------------------------------------------------------ | Robust lw | Coef. Std. Err. z P>|z| [95% Conf. Interval] -------------+---------------------------------------------------------------- iq | .0001747 .0041241 0.04 0.966 -.0079085 .0082578 s | .0691759 .0132907 5.20 0.000 .0431266 .0952253 expr | .029866 .0066974 4.46 0.000 .0167394 .0429926 tenure | .0432738 .0073857 5.86 0.000 .0287981 .0577494 rns | -.1035897 .029748 -3.48 0.000 -.1618947 -.0452847 smsa | .1351148 .026333 5.13 0.000 .0835032 .1867265 | year | 67 | -.052598 .0457261 -1.15 0.250 -.1422195 .0370235 68 | .0794686 .0428231 1.86 0.063 -.0044631 .1634003 69 | .2108962 .0408774 5.16 0.000 .1307779 .2910144 70 | .2386338 .0529825 4.50 0.000 .1347901 .3424776 71 | .2284609 .0426054 5.36 0.000 .1449558 .311966 73 | .3258944 .0405569 8.04 0.000 .2464044 .4053844 | _cons | 4.39955 .290085 15.17 0.000 3.830994 4.968106 ------------------------------------------------------------------------------ Underidentification test (Kleibergen-Paap rk LM statistic): 41.537 Chi-sq(4) P-val = 0.0000 ------------------------------------------------------------------------------ Weak identification test (Cragg-Donald Wald F statistic): 13.786 (Kleibergen-Paap rk Wald F statistic): 12.167 Stock-Yogo weak ID test critical values: 5% maximal IV relative bias 16.85 10% maximal IV relative bias 10.27 20% maximal IV relative bias 6.71 30% maximal IV relative bias 5.34 10% maximal IV size 24.58 15% maximal IV size 13.96 20% maximal IV size 10.26 25% maximal IV size 8.31 Source: Stock-Yogo (2005). Reproduced by permission. NB: Critical values are for Cragg-Donald F statistic and i.i.d. errors. ------------------------------------------------------------------------------ Hansen J statistic (overidentification test of all instruments): 74.165 Chi-sq(3) P-val = 0.0000 ------------------------------------------------------------------------------ Instrumented: iq Included instruments: s expr tenure rns smsa 67.year 68.year 69.year 70.year 71.year 73.year Excluded instruments: med kww age mrt ------------------------------------------------------------------------------
. *-C 统计量 . ivreg2 lw s expr tenure rns smsa i.year (iq=med kww age mrt), orthog(age) IV (2SLS) estimation -------------------- Estimates efficient for homoskedasticity only Statistics consistent for homoskedasticity only Number of obs = 758 F( 12, 745) = 45.91 Prob > F = 0.0000 Total (centered) SS = 139.2861498 Centered R2 = 0.4255 Total (uncentered) SS = 24652.24662 Uncentered R2 = 0.9968 Residual SS = 80.0182337 Root MSE = .3249 ------------------------------------------------------------------------------ lw | Coef. Std. Err. z P>|z| [95% Conf. Interval] -------------+---------------------------------------------------------------- iq | .0001747 .0039035 0.04 0.964 -.007476 .0078253 s | .0691759 .0129366 5.35 0.000 .0438206 .0945312 expr | .029866 .0066393 4.50 0.000 .0168533 .0428788 tenure | .0432738 .0076271 5.67 0.000 .0283249 .0582226 rns | -.1035897 .029481 -3.51 0.000 -.1613715 -.0458079 smsa | .1351148 .0266573 5.07 0.000 .0828674 .1873623 | year | 67 | -.052598 .0476924 -1.10 0.270 -.1460734 .0408774 68 | .0794686 .0447194 1.78 0.076 -.0081797 .1671169 69 | .2108962 .0439336 4.80 0.000 .1247878 .2970045 70 | .2386338 .0509733 4.68 0.000 .1387281 .3385396 71 | .2284609 .0437436 5.22 0.000 .1427251 .3141967 73 | .3258944 .0407181 8.00 0.000 .2460884 .4057004 | _cons | 4.39955 .2685443 16.38 0.000 3.873213 4.925887 ------------------------------------------------------------------------------ Underidentification test (Anderson canon. corr. LM statistic): 52.436 Chi-sq(4) P-val = 0.0000 ------------------------------------------------------------------------------ Weak identification test (Cragg-Donald Wald F statistic): 13.786 Stock-Yogo weak ID test critical values: 5% maximal IV relative bias 16.85 10% maximal IV relative bias 10.27 20% maximal IV relative bias 6.71 30% maximal IV relative bias 5.34 10% maximal IV size 24.58 15% maximal IV size 13.96 20% maximal IV size 10.26 25% maximal IV size 8.31 Source: Stock-Yogo (2005). Reproduced by permission. ------------------------------------------------------------------------------ Sargan statistic (overidentification test of all instruments): 87.655 Chi-sq(3) P-val = 0.0000 -orthog- option: Sargan statistic (eqn. excluding suspect orthogonality conditions): 47.413 Chi-sq(2) P-val = 0.0000 C statistic (exogeneity/orthogonality of suspect instruments): 40.242 Chi-sq(1) P-val = 0.0000 Instruments tested: age ------------------------------------------------------------------------------ Instrumented: iq Included instruments: s expr tenure rns smsa 67.year 68.year 69.year 70.year 71.year 73.year Excluded instruments: med kww age mrt ------------------------------------------------------------------------------
可以看出,无论是「Sargan 检验」还是「Hansen J」检验都拒绝了「原假设:所有工具变量都外生」,表明存在一部分内生的工具变量。进一步,我们又构造了 统计量来检验工具变量 age 的外生性,检验结果显著拒绝了「原假设:工具变量 age 是外生的」。
3.2GMM 中过度识别的命令为 estat overid
若是 Sargen - Baseman 检验的统计量对应的 p 值大于 0.05 ,则认为所有的工具变量都是外生的,也就是有效的,反之则是无效的。(原假设是所有工具变量是外省的,若是 p 值小于 0.05 ,则拒绝原假设)
sysuse auto,clear ivregress gmm mpg gear_ratio (turn =weight length headroom),wmatrix(robust) small estat overid
过度识别检验( Sargen - Baseman 检验)的结果为:
Test of overidentifying restriction: Hansen's J chi2(2) = .54848 (p = 0.7601)
根据结果可知, Sargen - Baseman 检验统计量对应的 p 值大于 0.05 ,所有的工具变量都是外生有效的。
3.3 xtbond2 命令
以 mus08psidextract.dta 为例,该数据包含 595 名美国人 1976-1982 与工资相关的变量 (n = 595, T = 7),其中 lwage 为工资对数,wks 为工作周数,ms 为婚否,union 为是否由工会合同确定工资,occ 为是否是蓝领工人,south 为是否在美国南部,smsa 为是否住在大城市,ind 为是否在在制造业工作。
在使用 xtabond2 命令进行 GMM 回归时,Stata 同时提供 Sargan 检验、Hansen J 检验、以及 统计量。关于 Sargan 检验 和 Hansen J 检验,一般认为 Hansen J 检验结果更为稳健。
*-安装命令 ssc install xtabond2, replace *-动态面板过度识别检验 sysuse mus08psidextract.dta, clear xtabond2 lwage L(1/2).lwage L(0/1).wks ms union occ south smsa ind, \ gmm(lwage, lag(2 4)) gmm(wks ms union, lag(2 3)) \ iv(occ south smsa ind) nolevel twostep robust
上述命令中,L(1/2).lwage 表示 L1.wage L2.wage,L(0/1).wks 表示 wks L1.wks;gmm(lwage, lag(2 4)) 表示使用 lwage 的 2-4 阶作为 GMM 式工具变量,gmm(wks ms union, lag(2 3)) 表示使用 wks ms union 的 2-3 阶作为 GMM 式工具变量,iv(occ south smsa ind) 表示使用 occ south smsa ind 作为自身工具变量。
Dynamic panel-data estimation, two-step difference GMM ------------------------------------------------------------------------------ Group variable: id Number of obs = 2380 Time variable : t Number of groups = 595 Number of instruments = 39 Obs per group: min = 4 Wald chi2(10) = 1287.77 avg = 4.00 Prob > chi2 = 0.000 max = 4 ------------------------------------------------------------------------------ | Corrected lwage | Coef. Std. Err. z P>|z| [95% Conf. Interval] -------------+---------------------------------------------------------------- lwage | L1. | .611753 .0373491 16.38 0.000 .5385501 .6849559 L2. | .2409058 .0319939 7.53 0.000 .1781989 .3036127 | wks | --. | -.0159751 .0082523 -1.94 0.053 -.0321493 .000199 L1. | .0039944 .0027425 1.46 0.145 -.0013807 .0093695 | ms | .1859324 .144458 1.29 0.198 -.0972 .4690649 union | -.1531329 .1677842 -0.91 0.361 -.4819839 .1757181 occ | -.0357509 .0347705 -1.03 0.304 -.1038999 .032398 south | -.0250368 .2150806 -0.12 0.907 -.446587 .3965134 smsa | -.0848223 .0525243 -1.61 0.106 -.187768 .0181235 ind | .0227008 .0424207 0.54 0.593 -.0604422 .1058437 ------------------------------------------------------------------------------ Instruments for first differences equation Standard D.(occ south smsa ind) GMM-type (missing=0, separate instruments for each period unless collapsed) L(2/3).(wks ms union) L(2/4).lwage ------------------------------------------------------------------------------ Arellano-Bond test for AR(1) in first differences: z = -4.52 Pr > z = 0.000 Arellano-Bond test for AR(2) in first differences: z = -1.60 Pr > z = 0.109 ------------------------------------------------------------------------------ Sargan test of overid. restrictions: chi2(29) = 59.55 Prob > chi2 = 0.001 (Not robust, but not weakened by many instruments.) Hansen test of overid. restrictions: chi2(29) = 39.88 Prob > chi2 = 0.086 (Robust, but weakened by many instruments.) Difference-in-Hansen tests of exogeneity of instrument subsets: gmm(lwage, lag(2 4)) Hansen test excluding group: chi2(18) = 23.59 Prob > chi2 = 0.169 Difference (null H = exogenous): chi2(11) = 16.29 Prob > chi2 = 0.131 gmm(wks ms union, lag(2 3)) Hansen test excluding group: chi2(5) = 6.43 Prob > chi2 = 0.266 Difference (null H = exogenous): chi2(24) = 33.44 Prob > chi2 = 0.095 iv(occ south smsa ind) Hansen test excluding group: chi2(25) = 28.00 Prob > chi2 = 0.308 Difference (null H = exogenous): chi2(4) = 11.87 Prob > chi2 = 0.018
可以看出,工具变量总的个数为 39,而内生变量的个数为 10。同时,扰动项的差分存在一阶自相关,而不存在二阶自相关,故不能拒绝原假设「扰动项无自相关」,可以使用差分 GMM。
Sargan 统计量和 Hansen 统计量在 10% 的水平上都拒绝了「所有工具变量都外生」的原假设。值得注意的是,Sargan 统计量并不稳健,但不受工具变量过多的影响,而 Hansen 统计量虽然稳健,但受工具变量过多的影响。

4. 过度识别检验统计量无法计算
4.1 原因
在使用 ivreg2 命令进行估计时,我们经常会发现 Sargan 检验或 Hansen J 检验始终无法通过。这可能是由于「工具变量过多」造成的,如模型中控制了年份固定效应、地区固定效应和行业固定效应等虚拟变量。
但是,当「虚拟变量的个数 < (外生变量个数 + 工具变量个数)」时,正交条件对应的方差-协方差矩阵 有可能是非满秩矩阵,此时我们无法计算出 矩阵的逆矩阵 ,从而导致过度识别检验的统计量无法计算。更为详细的介绍,可通过 help ivreg2 查看。
4.2 解决方法
利用 Frisch-Waugh-Lovell (FWL) 定理,我们可以尝试「partial out」一定数量的外生变量 (通常主要是虚拟变量),以保证 矩阵满秩。在使用 ivreg2 命令执行 2SLS 或 GMM 估计时,我们可以加入 partial() 选项,选项中先填入所有外生的虚拟变量,如有必要,可以进一步加入其它外生的解释变量。
4.3 Stata 实现
接下来,以案例形式简要介绍「partial out」的原理。
范例 1:partial out 连续变量
sysuse "auto.dta", clear rename (price length weight) (Y X1 X2) ivregress 2sls Y X1 X2 est store m0 //原始结果 *-Partial out X2 ivregress 2sls Y X2 //从 y 中除去 X2 的影响 predict e_y, res ivregress 2sls X1 X2 //从 X1 中除去 X2 的影响 predict e_x1, res ivregress 2sls e_y e_x1 //partial out 后的的回归结果 est store m1 esttab m0 m1, nogap restore
-------------------------------------------- (1) (2) Y e_y -------------------------------------------- X1 -97.96* (-2.55) X2 4.699*** (4.27) e_x1 -97.96* (-2.55) _cons 10386.5* 2.04e-12 (2.46) (0.00) -------------------------------------------- N 74 74 -------------------------------------------- t statistics in parentheses * p<0.05, ** p<0.01, *** p<0.001 *-Notes: (1) 如果采用 regress 进行回归,SE 会有微小差异, 主要是因为 regress 会针对小样本进行自由度调整。 (2) 采用 IV/GMM 估计,即 ivregress 命令就不会有这个问题了。
范例 2:partial out 虚拟变量
sysuse auto, clear drop if rep78==. global yx "price wei len mpg" ivregress 2sls $yx i.rep78 est store m0 bysort rep78: center $yx, inplace //prefix(c_) ivregress 2sls $yx est store m1 esttab m0 m1, nogap nobase restore
-------------------------------------------- (1) (2) price price -------------------------------------------- weight 5.187*** 5.187*** (4.74) (4.74) length -124.2*** -124.2*** (-3.29) (-3.29) mpg -126.8 -126.8 (-1.60) (-1.60) 2.rep78 1137.3 (0.67) 3.rep78 1254.6 (0.80) 4.rep78 2267.2 (1.42) 5.rep78 3850.8* (2.29) _cons 14614.5* 0.0000116 (2.52) (0.00) -------------------------------------------- N 69 69 -------------------------------------------- t statistics in parentheses * p<0.05, ** p<0.01, *** p<0.001 *-Note: FE 模型其实就是先 partial out 公司虚拟变量,然后再对转换后的数据执行 OLS 回归。
范例 3:是否加入 partial() 选项无影响
*-数据下载地址 * https://gitee.com/arlionn/data/blob/master/data01/Acem_data_done.dta use Acem_data_done.dta, clear global y "change_gdp" global x "change_dependency" global z "devo1990 lpop1990 base_dependency" // 控制变量 global IVs "birthrate1960_1965 birthrate1965_1970 birthrate1970_1975 birthrate1975_1980 birthrate1980_1985 birthrate1985_1990"// 工具变量 ivregress 2sls $y ($x=$IVs) $z i.region_code, robust //官方命令 est store a1 ivreg2 $y ($x=$IVs) $z i.region_code, robust // 等价-外部命令 est store a2 // without -partial()- option ivreg2 $y ($x=$IVs) $z i.region_code, robust /// partial(lpop1990 i.region_code base_dependency) est store c5 // with -partial()- option *-手动计算:(特别注意:此时的 SE 是错误的!) * Step1: reg $x $IVs $z i.region_code cap drop xhat predict xhat * Step2: reg $y xhat $z i.region_code est store a3 *-对比结果: local m "a1 a2 c5 a3" esttab `m' `s', nogap replace /// b(%6.3f) s(N r2_a rkf j jp) /// star(* 0.1 ** 0.05 *** 0.01) /// order(change_dependency xhat) /// indicate("Region Dummies =*.region_code") /// addnotes("*** 1% ** 5% * 10%") nobase ---------------------------------------------------------------------------- (a1) (a2) (c5) (a3) no-parital no-partial partial-out by-hand CMD ivregress ivreg2 ivreg2 regress ---------------------------------------------------------------------------- change_dep~y 1.703*** 1.703*** 1.703*** (4.14) (4.14) (4.14) xhat 1.703*** (3.80) devo1990 -0.190*** -0.190*** -0.190*** -0.190*** (-4.22) (-4.22) (-4.22) (-4.58) lpop1990 -0.017 -0.017 -0.017 (-0.83) (-0.83) (-0.96) base_depen~y -0.041 -0.041 -0.041 (-0.14) (-0.14) (-0.13) _cons 1.899*** 1.899*** 1.899*** (4.99) (4.99) (5.54) Region Dum~s Yes Yes No Yes ---------------------------------------------------------------------------- N 169.000 169.000 169.000 169.000 r2_a 0.179 0.179 -0.024 0.261 rkf 19.365 19.365 j 4.280 4.280 jp 0.510 0.510 ---------------------------------------------------------------------------- t statistics in parentheses, p<0.1, ** p<0.05, *** p<0.01
Notes:(1) a1 与 c5 结果完全相同,因此 partial out 部分变量不影响系数估计值;(2) partial out 的目的是为了减少干扰项的方差协方差矩阵 的维度,以便合理计算 Sargan 和 Hansen J 统计量。
范例4:是否加入 partial 选项有显著影响
我们将通过下例来演示加入 partial 选项引起的变化。
use http://fmwww.bc.edu/ec-p/data/hayashi/griliches76.dta, clear ivreg2 lw s expr tenure rns smsa i.year (iq=med kww age), cluster(year)
执行完上述命令后,会出现如下提示,即由于矩条件的协方差矩阵非满秩,过度识别检验的结果无法显示。在此情况下,可筛除一些虚拟变量。
Warning: estimated covariance matrix of moment conditions not of full rank.overidentification statistic not reported, and standard errors and model tests should be interpreted with caution.
Possible causes: number of clusters insufficient to calculate robust covariance matrix singleton dummy variable (dummy with one 1 and N-1 0s or vice versa).
partial option may address problem.
下面利用 partial() 选项筛除年份虚拟变量后回归,即可呈现 Hansen J 的检验结果。
ivreg2 lw s expr tenure rns smsa i.year (iq=med kww age), cluster(year) partial(i.year)