一、摘要
BlockingQueue通常用于一个线程在生产对象,而另外一个线程在消费这些对象的场景,例如在线程池中,当运行的线程数目大于核心的线程数目时候,经常就会把新来的线程对象放到BlockingQueue中去。
二、阻塞队列原理
原理简单的来讲:就是一个线程往队列里面放,而另外的一个线程从里面取
当线程持续的产生新对象并放入到队列中,直到队列达到它所能容纳的临界点。注意,队列的容量是有限的,不可能一直往里面插入对象。如果队列到达了临界点时,这个时候再想往队列中插入元素则会产生阻塞,直到另一端从队列中进行消费了,这个时候阻塞现象才不会发生。另外当去消费一个空的队列时候,这个线程也会产生阻塞现象,直到一个线程把对象插入到队列中
三、BlockingQueue常用方法总结
| 抛出异常 | 特殊值 | 阻塞 | 超时 | |
| 插入 | add(e) | offer(e) | put(e) | offer(e,time,unit) |
| 移除 | remove(e) | poll | take() | poll(time,unit) |
| 检查 | element(e) | peek | 不可用 | 不可用 |
四组不同的行为方式解释:
1. 抛异常:如果试图的操作无法立即执行,抛一个异常。
2. 特定值:如果试图的操作无法立即执行,返回一个特定的值(常常是 true / false)。
3. 阻塞:如果试图的操作无法立即执行,该方法调用将会发生阻塞,直到能够执行。
4. 超时:如果试图的操作无法立即执行,该方法调用将会发生阻塞,直到能够执行,但等
待时间不会超过给定值。返回一个特定值以告知该操作是否成功(典型的是 true / false)。
无法向一个 BlockingQueue 中插入 null。如果你试图插入 null,BlockingQueue 将会抛出
一个 NullPointerException。
四、BlockingQueue源码分析
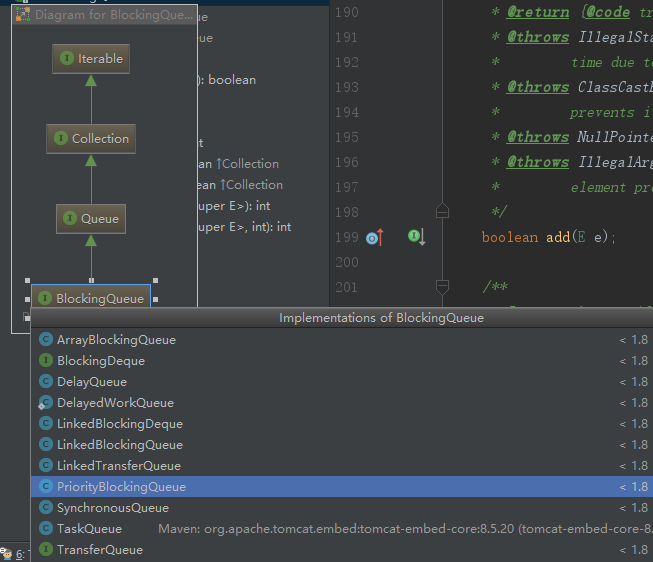
1、通过IDE可以明显的看到BlockingQueue是一个接口,我们在写代码的时候需要实现这个接口
java.util.concurrent 具有以下 BlockingQueue 接口的实现(Java 8):
五、数组阻塞队列ArrayBlockingQueue分析
1、原理分析
首先ArrayBlockingQueue 类实现了 BlockingQueue 接口。其次ArrayBlockingQueue 是一个有界的阻塞队列,其内部实现是将对象放到一个数组里,所以一旦创建了该队列,就不能再增加其容量了。最后ArrayBlockingQueue 内部以 FIFO(先进先出)的顺序对元素进行存储。
2、ArrayBlockingQueue的方法(下面着重分析put()和take()二者方法)
此构造方法中,我们能看到传入了两个参数,capacity代表着队列的容量大小,而boolean类型的参数则是判断是否为公平锁,如果为true,则先到的线程会先得到锁对象, 反之则有操作系统去决定哪个线程获得锁,大多数情况下都是设置为false,这样性能会高点
在put方法中,我们能看到在执行put方法时,我们必须要对其进行加锁操作,从而保证线程的安全性。其次会去判断其队列是否饱满了,饱满时则会发生阻塞现象,直到被其他线程唤醒时插入元素,接着会去调用notEmpty.signal()方法,间接的利用take方法将队列中的元素取走,最后将锁释放。
同理可以看出take()方法是相反的,不再做详细介绍,代码注释已给出
put()和take()精简源代码如下:
1 /** The queued items */ 2 final Object[] items; //利用数组来存储元素 3 /** Main lock guarding all access */ 4 final ReentrantLock lock; 5 6 /** Condition for waiting takes */ 7 private final Condition notEmpty; //定义一个Condition对象,用来对take进行操作 8 9 /** Condition for waiting puts */ 10 private final Condition notFull; //定义一个Condition对象,用来对put进行操作 11 12 /** 13 * Creates an {@code ArrayBlockingQueue} with the given (fixed) 14 * capacity and the specified access policy. 15 * 16 * @param capacity the capacity of this queue 17 * @param fair if {@code true} then queue accesses for threads blocked 18 * on insertion or removal, are processed in FIFO order; 19 * if {@code false} the access order is unspecified. 20 * @throws IllegalArgumentException if {@code capacity < 1} 21 */ 22 public ArrayBlockingQueue(int capacity, boolean fair) { 23 if (capacity <= 0) //判断初始化的容量大小 24 throw new IllegalArgumentException(); 25 this.items = new Object[capacity]; 26 lock = new ReentrantLock(fair); 27 notEmpty = lock.newCondition(); 28 notFull = lock.newCondition(); 29 } 30 ====================================put()方法============================================== 31 /** 32 * Inserts the specified element at the tail of this queue, waiting 33 * for space to become available if the queue is full. 34 * 35 * @throws InterruptedException {@inheritDoc} 36 * @throws NullPointerException {@inheritDoc} 37 */ 38 public void put(E e) throws InterruptedException { 39 checkNotNull(e); 40 final ReentrantLock lock = this.lock; 41 lock.lockInterruptibly(); 42 try { 43 while (count == items.length) 44 notFull.await(); //队列饱满时,将使这个线程进入阻塞状态,直到被其他线程唤醒时插入元素 45 enqueue(e); //将元素插入到队列中 46 } finally { 47 lock.unlock(); 48 } 49 } 50 51 52 /** 53 * Inserts element at current put position, advances, and signals. 54 * Call only when holding lock. 55 */ 56 private void enqueue(E x) { 57 // assert lock.getHoldCount() == 1; 58 // assert items[putIndex] == null; 59 final Object[] items = this.items; 60 items[putIndex] = x; 61 if (++putIndex == items.length) 62 putIndex = 0; 63 count++; 64 notEmpty.signal(); //通知take那边消费其元素 65 } 66 67 ===================================================take()方法======================================================== 68 69 public E take() throws InterruptedException { 70 final ReentrantLock lock = this.lock; //加锁 71 lock.lockInterruptibly(); 72 try { 73 while (count == 0) 74 notEmpty.await(); //队列为空时,将使这个线程进入阻塞状态,直到被其他线程唤醒时取出元素 75 return dequeue(); //消费对头中的元素 76 } finally { 77 lock.unlock(); 78 } 79 } 80 81 /** 82 * Extracts element at current take position, advances, and signals. 83 * Call only when holding lock. 84 */ 85 private E dequeue() { 86 // assert lock.getHoldCount() == 1; 87 // assert items[takeIndex] != null; 88 final Object[] items = this.items; 89 @SuppressWarnings("unchecked") 90 E x = (E) items[takeIndex]; 91 items[takeIndex] = null; 92 if (++takeIndex == items.length) 93 takeIndex = 0; 94 count--; 95 if (itrs != null) 96 itrs.elementDequeued(); 97 notFull.signal(); //通知put那边消费其元素 98 return x; 99 }
六、链式阻塞队列LinkedBlockingQueue分析
1、原理分析
LinkedBlockingQueue 类实现了 BlockingQueue 接口。同时LinkedBlockingQueue 内部以一个链式结构(链接节点)对其元素进行存储。如果需要的话,这一链式结构可以选择一个上限。如果没有定义上限,将使用 Integer.MAX_VALUE 作为上限。LinkedBlockingQueue 内部以 FIFO(先进先出)的顺序对元素进行存储。
2、LinkedBlockingQueue方法分析
针对LinkedBlockingQueue的构造方法中,我们能看到没有定义上限时,会使用Integer.MAX_VALUE 作为上限
其次针对put等方法时,原理与ArrayBlockingQueue大致相同,只不过是基于链表去实现的
源码精简如下:
1 /** The capacity bound, or Integer.MAX_VALUE if none */ 2 //链表的容量 3 private final int capacity; 4 5 /** Current number of elements */ 6 //当前元素个数 7 private final AtomicInteger count = new AtomicInteger(); 8 9 /** 10 * Head of linked list. 11 * Invariant: head.item == null 12 */ 13 //链表头节点 14 transient Node<E> head; 15 16 /** 17 * Tail of linked list. 18 * Invariant: last.next == null 19 */ 20 //链表尾节点 21 private transient Node<E> last; 22 23 /** Lock held by take, poll, etc */ 24 //出队列锁 25 private final ReentrantLock takeLock = new ReentrantLock(); 26 27 /** Wait queue for waiting takes */ 28 private final Condition notEmpty = takeLock.newCondition(); 29 30 /** Lock held by put, offer, etc */ 31 //入队列锁 32 private final ReentrantLock putLock = new ReentrantLock(); 33 34 /** Wait queue for waiting puts */ 35 private final Condition notFull = putLock.newCondition(); 36 37 38 //默认构造方法,默认执行容量上限 39 public LinkedBlockingQueue() { 40 this(Integer.MAX_VALUE); 41 } 42 43 //指定队列的容量 44 public LinkedBlockingQueue(int capacity) { 45 if (capacity <= 0) throw new IllegalArgumentException(); 46 this.capacity = capacity; 47 //初始化头尾节点的值,设置均为null 48 last = head = new Node<E>(null); 49 } 50 51 //往对尾中插入元素,队列满时,则会发生阻塞,直到有元素消费了或者线程中断了 52 public void put(E e) throws InterruptedException { 53 if (e == null) throw new NullPointerException(); 54 int c = -1; 55 Node<E> node = new Node<E>(e); 56 final ReentrantLock putLock = this.putLock;//入队列锁 57 final AtomicInteger count = this.count;//获取当前队列中的元素个数 58 putLock.lockInterruptibly(); 59 try { 60 while (count.get() == capacity) { //条件:如果队列满了 61 notFull.await(); //则加入到出队列等待中,直到队列不满了,这时就会被其他线程notFull.signal()唤醒 62 } 63 enqueue(node);//将元素入队列 64 c = count.getAndIncrement(); //对当前队列元素个数加1 65 if (c + 1 < capacity) 66 notFull.signal(); 67 } finally { 68 putLock.unlock(); 69 } 70 if (c == 0) 71 signalNotEmpty(); 72 } 73 74 75 //出队列,大致原理与入队列相反,当队列为空时,则会阻塞,直到队列不为空或者线程中断 76 public E take() throws InterruptedException { 77 E x; 78 int c = -1; 79 final AtomicInteger count = this.count; 80 final ReentrantLock takeLock = this.takeLock; 81 takeLock.lockInterruptibly(); 82 try { 83 while (count.get() == 0) { 84 notEmpty.await(); 85 } 86 x = dequeue(); 87 c = count.getAndDecrement(); 88 if (c > 1) 89 notEmpty.signal(); 90 } finally { 91 takeLock.unlock(); 92 } 93 if (c == capacity) 94 signalNotFull(); 95 return x; 96 } 97 98 99
七、ArrayBlockingQueue和LinkedBlockingQueue源码比较
在上述源码过程我们能发现:
1、入队列时,当队列满了,则会发生阻塞,直到队列消费了数据或者线程被中断了才会唤醒
2、出队列时,当队列为空时,则会发生阻塞,直到队列中有数据了或者线程被中断了才会唤醒
源码注意:
ArrayBlockingQueue源码中,共用的是同一把锁
LinkedBlockingQueue源码中,则是用到了两把锁,一把是入队列锁,另一把是出队列锁
八、参考资料
https://www.cnblogs.com/java-zhao/p/5135958.html