原文链接:https://jiang-hao.com/articles/2020/algorithms-algorithms-merge-sort.html
算法介绍
归并排序(Merge sort)是建立在归并操作上的一种有效的排序算法。该算法是采用分治法(Divide and Conquer)的一个非常典型的应用。
作为一种典型的分而治之思想的算法应用,归并排序的实现由两种方法:
-
自上而下的递归:它从树的顶端开始,然后向下操作,每次操作都问同样的问题(我需要做什么来排序这个数组?)并回答它(分成两个子数组,进行递归调用,合并结果),直到我们到达树的底部。
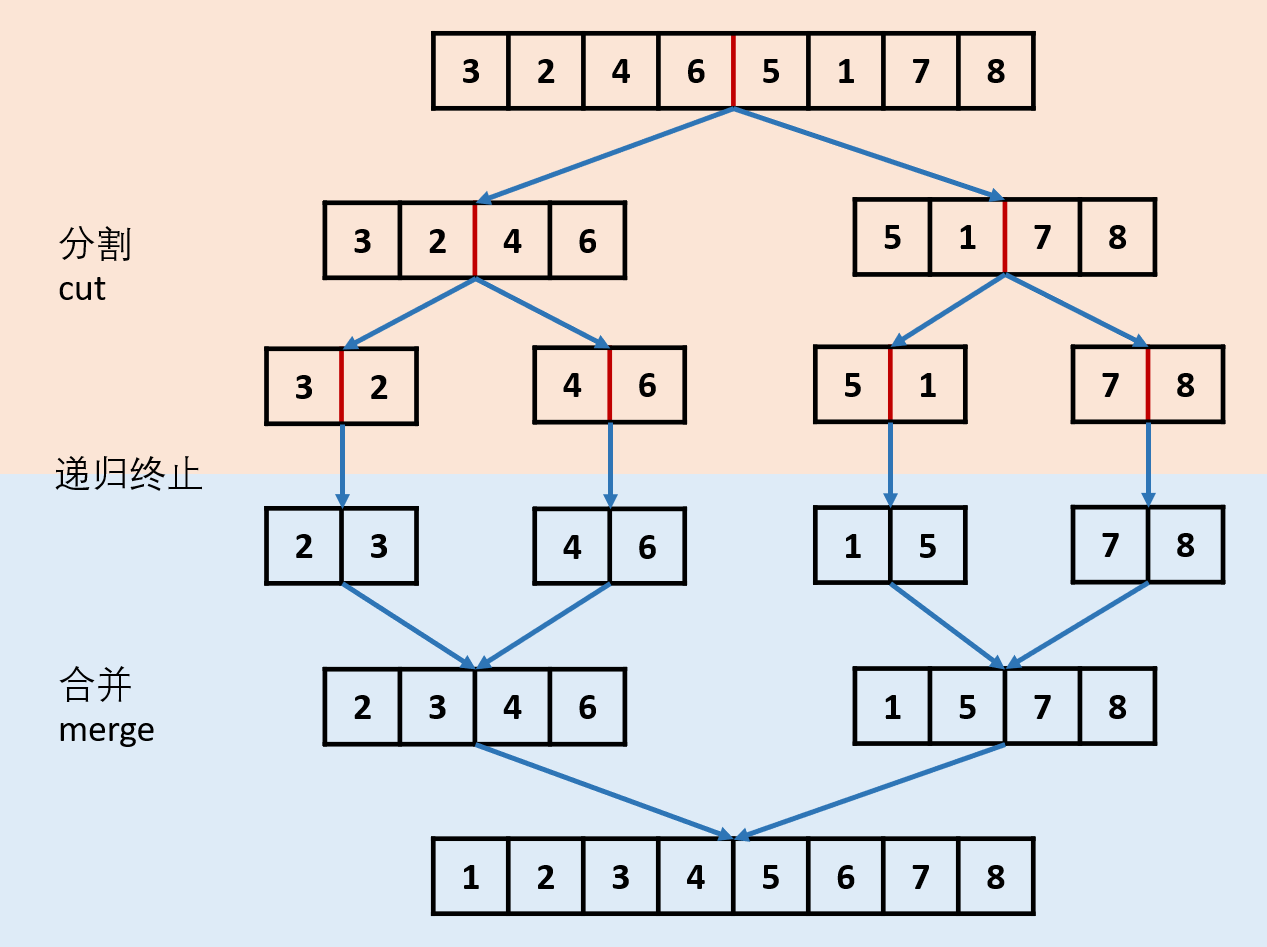
-
自下而上的迭代:不需要递归。它直接从树的底部开始,然后通过遍历这些片段再将它们合并起来。
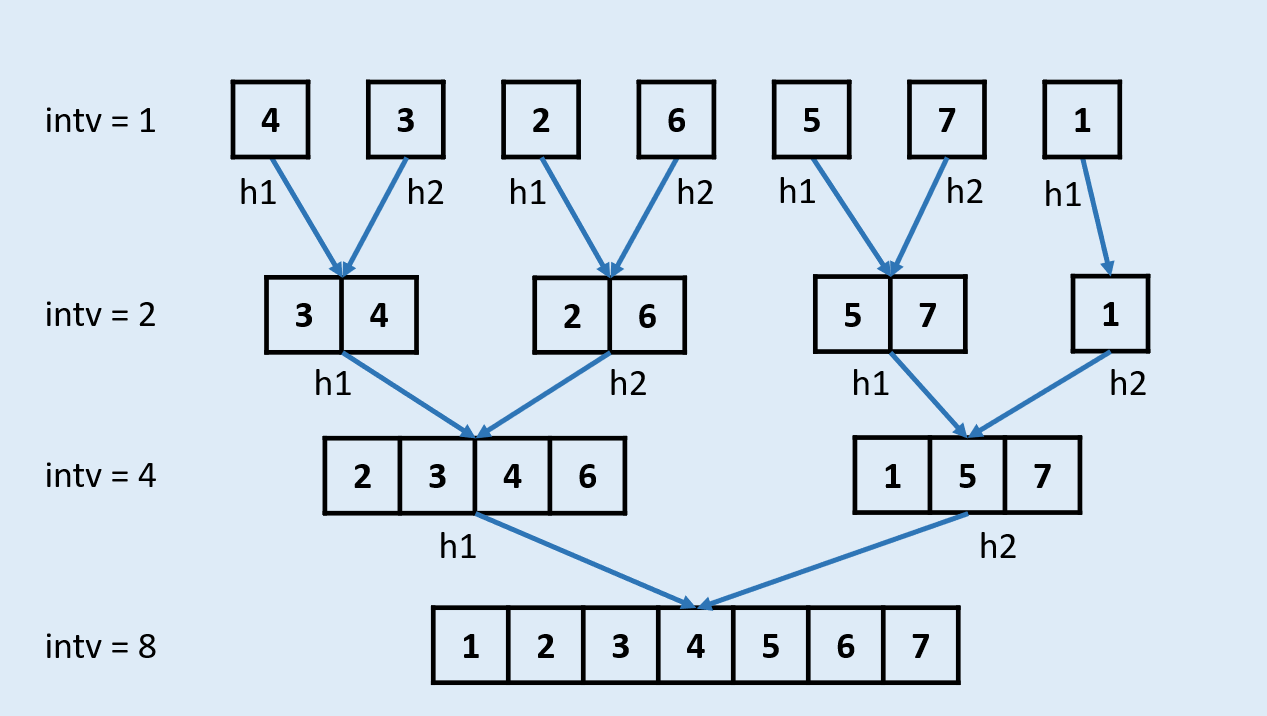
在《数据结构与算法 JavaScript 描述》中,作者给出了自下而上的迭代方法。但是对于递归法,作者却认为:
However, it is not possible to do so in JavaScript, as the recursion goes too deep for the language to handle.
然而,在 JavaScript 中这种方式不太可行,因为这个算法的递归深度对它来讲太深了。
和选择排序一样,归并排序的性能不受输入数据的影响,但表现比选择排序好的多,因为始终都是 O(nlogn) 的时间复杂度。代价是需要额外的内存空间。
归并排序分为三个过程:
- 将数列划分为两部分(在均匀划分时时间复杂度为 );
- 递归地分别对两个子序列进行归并排序;
- 合并两个子序列。
不难发现,归并排序的核心是如何合并两个子序列,前两步都很好实现。
其实合并的时候也不难操作。注意到两个子序列在第二步中已经保证了都是有序的了,第三步中实际上是想要把两个 有序 的序列合并起来。
算法步骤
- 申请空间,使其大小为两个已经排序序列之和,该空间用来存放合并后的序列;
- 设定两个指针,最初位置分别为两个已经排序序列的起始位置;
- 比较两个指针所指向的元素,选择相对小的元素放入到合并空间,并移动指针到下一位置;
- 重复步骤 3 直到某一指针达到序列尾;
- 将另一序列剩下的所有元素直接复制到合并序列尾。
代码实现
数组实现时间复杂度O(NlogN),空间复杂度O(N)
递归实现一:每次归并时都创建一个辅助数组
public static int[] sort(int[] nums) {
// 对数组进行拷贝,不改变参数内容
int[] arr = Arrays.copyOf(nums, nums.length);
if (arr.length<2) return arr;
int middle = (int) Math.floor(arr.length >> 1);
int[] left = Arrays.copyOfRange(arr, 0, middle);
int[] right = Arrays.copyOfRange(arr, middle, arr.length);
return merge(sort(left), sort(right));
}
public static int[] merge(int[] left, int[] right) {
// 创建一个辅助数组存储归并结果
int[] result = new int[left.length+right.length];
int i=0, j=0;
while (i+j < result.length) {
// 右侧数组全都转存完时,直接将左侧数组剩余的元素转存到结果数组
if (j==right.length) {
result[i+j] = left[i++];
}
// 左侧数组全都转存完时,直接将右侧数组剩余的元素转存到结果数组
else if (i==left.length) {
result[i+j] = right[j++];
}
// 否则,将两个子数组当前元素中较小的那个转存到结果数组中
else result[i+j] = left[i]<=right[j]? left[i++]: right[j++];
}
return result;
}
力扣运行结果:
执行用时:10 ms, 在所有 Java 提交中击败了30.97%的用户
内存消耗:44.2 MB, 在所有 Java 提交中击败了99.55%的用户
| 提交时间 | 提交结果 | 运行时间 | 内存消耗 | 语言 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 几秒前 | 通过 | 10 ms | 43.8 MB | Java |
| 几秒前 | 通过 | 10 ms | 43.9 MB | Java |
| 几秒前 | 通过 | 10 ms | 44.1 MB | Java |
递归实现二:仅创建一次一个等长的辅助数组,交替归并
/**
* 递归交替合并
* @param src 待合并的数组
* @param dst 合并结果数组
* @param start 数组 src 的 start 下标
* @param end 数组 src 的 end 下标
*/
public static void sort(int[] src, int[] dst, int start, int end) {
// 当待排序段[start,end)仅包含小于等于一个元素时,自然有序
if (end-start<2) {
dst[start]=src[start];
return;
}
// 将左右两段子数组分别排好序
int i = start + (end-start)/4;
int ii = start + (end-start)/2;
int iii = start + 3*(end-start)/4;
sort(src, dst, start, i);
sort(src, dst, i, ii);
sort(src, dst, ii, iii);
sort(src, dst, iii, end);
merge(dst, src, start, i, ii);
merge(dst, src, ii, iii, end);
// 最后归并
merge(src, dst, start, ii, end);
}
/**
* 归并方法:合并左右两段已分别排好序的 src[start:middle) 和 src[middle:end) 到 dst[start:end)
* 数组 src 的 [start:middle) 部分以及 [middle:end) 部分都已经各自排好序
* @param src 待合并的数组
* @param dst 合并结果数组
* @param start 数组 src 的 start 下标
* @param middle 数组 src 的 middle 下标
* @param end 数组 src 的 end 下标
*/
private static void merge(int [] src, int [] dst, int start, int middle, int end){
int i = start;
int j = middle;
int k = start;
while (k<end) {
// 右侧数组全都转存完时,直接将左侧数组剩余的元素转存到结果数组
if (j==end) {
dst[k++] = src[i++];
}
// 左侧数组全都转存完时,直接将右侧数组剩余的元素转存到结果数组
else if (i==middle) {
dst[k++] = src[j++];
}
// 否则,将两个子数组当前元素中较小的那个转存到结果数组中
else dst[k++] = src[i]<=src[j]? src[i++]: src[j++];
}
}
力扣运行结果:
执行用时:6 ms, 在所有 Java 提交中击败了64.16%的用户
内存消耗:45.7 MB, 在所有 Java 提交中击败了86.98%的用户
| 提交时间 | 提交结果 | 运行时间 | 内存消耗 | 语言 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 几秒前 | 通过 | 6 ms | 46.3 MB | Java |
| 几秒前 | 通过 | 6 ms | 45.9 MB | Java |
| 几秒前 | 通过 | 6 ms | 46 MB | Java |
非递归实现
/**
* 归并方法:合并左右两段已分别排好序的 src[start:middle) 和 src[middle:end) 到 dst[start:end)
* 数组 src 的 [start:middle) 部分以及 [middle:end) 部分都已经各自排好序
* @param src 待合并的数组
* @param dst 合并结果数组
* @param start 数组 src 的 start 下标
* @param middle 数组 src 的 middle 下标
* @param end 数组 src 的 end 下标
*/
private static void merge(int [] src, int [] dst, int start, int middle, int end){
int i = start;
int j = middle;
int k = start;
while (k < end) {
if (i==middle) dst[k++] = src[j++];
else if (j==end) dst[k++] = src[i++];
else dst[k++] = src[i] <= src[j] ? src[i++] : src[j++];
}
}
/**
* 用于合并排好序的相邻数组段
* 将 x 合并到 y
* @param x
* @param y
* @param s 合并大小
*/
private static void mergePass(int [] x,int [] y,int s){
//从第一个元素开始
int i = 0;
//i+2*s 要小于等于数组长度,也就是说未合并的元素个数要大于2*s
while (i + 2*s <= x.length) {
//合并大小为s的相邻2段子数组
merge(x, y, i, i+s, i+2*s);
i += 2*s;
}
//此循环执行的次数为: x.length/(2*s) 次 9/(2*1)=4
//若未合并的元素个数大于 1*s,则合并最后两个序列
if (i+s < x.length) merge(x, y, i, i+s, x.length);
//否则直接复制到y
else {
while (i < x.length) {
y[i] = x[i++];
}
}
}
/**
* 消去递归后的归并排序算法
* @param a
*/
public static void mergeSort(int []a ){
//申请个大小和a相等的数组b
int[] tmp = new int[a.length];
int s = 1;
//这里不能为<=
while (s < a.length) {
//交替合并
mergePass(a, tmp, s);
s *= 2;
mergePass(tmp, a, s);
s *= 2;
}
}
力扣执行结果:
执行用时:7 ms, 在所有 Java 提交中击败了55.19%的用户
内存消耗:45.8 MB, 在所有 Java 提交中击败了75.00%的用户
| 提交时间 | 提交结果 | 运行时间 | 内存消耗 | 语言 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 几秒前 | 通过 | 7 ms | 45.8 MB | Java |
| 几秒前 | 通过 | 8 ms | 45.7 MB | Java |
| 几秒前 | 通过 | 7 ms | 45.7 MB | Java |
链表实现时间复杂度O(NlogN),空间复杂度O(1)
递归实现
static class ListNode {
int val;
ListNode next;
ListNode() {}
ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
ListNode(int val, ListNode next) { this.val = val; this.next = next; }
}
public static ListNode sortList(ListNode head) {
if (head==null || head.next==null) return head;
//链表的快慢指针二分法
ListNode slow = head;
ListNode fast = head.next;
while (fast != null && fast.next != null) {
slow = slow.next;
fast = fast.next.next;
}
//找到中间节点
ListNode tmp = slow.next;
//二分切割链表
slow.next = null;
//递归调用归并
return merge(sortList(head), sortList(tmp));
}
public static ListNode merge(ListNode left, ListNode right) {
//创建哨兵节点,存放归并结果
ListNode sentinel = new ListNode(-1);
//创建指针,维护尾节点
ListNode tail = sentinel;
//两个子链都还存在节点时,进入循环体
while (left!=null && right!=null) {
//较小的节点放入结果链表,对应子链去头
if (left.val <= right.val) {
tail.next = left;
left = left.next;
} else {
tail.next = right;
right = right.next;
}
//更新尾节点
tail = tail.next;
}
//将还有剩余节点的子链直接尾接到结果链
tail.next = left==null? right: left;
//返回归并结果
return sentinel.next;
}
力扣执行结果:
执行用时:6 ms, 在所有 Java 提交中击败了53.76%的用户
内存消耗:46.5 MB, 在所有 Java 提交中击败了23.27%的用户
| 提交时间 | 提交结果 | 运行时间 | 内存消耗 | 语言 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 几秒前 | 通过 | 6 ms | 46.5 MB | Java |
| 2 分钟前 | 通过 | 6 ms | 47 MB | Java |
| 2 分钟前 | 通过 | 6 ms | 46.6 MB | Java |
非递归实现(从底至顶直接合并)
public static ListNode sortList(ListNode head) {
// 求链表长度
ListNode h = head;
int length = 0;
while (h != null) {
h = h.next;
length+=1;
}
// 初始化准备
int blockSize = 1;
// 结果链表哨兵
ListNode res = new ListNode(-1);
res.next = head;
// 从1到length迭代单元块大小
while (blockSize<length) {
// 结果链表游标
ListNode pre = res;
h = res.next;
// 两两遍历所有单元块
while (h != null) {
// 求第一个子链
ListNode h1 = h;
int i = blockSize;
while (i>0 && h!=null) {
h = h.next;
i-=1;
}
if (i>0) break;
// 求第二个子链
ListNode h2 = h;
i = blockSize;
while (i>0 && h!=null) {
h = h.next;
i-=1;
}
// 合并两个子链
int c1 = blockSize;
int c2 = blockSize-i;
while (c1>0 && c2>0) {
if(h1.val <= h2.val) {
pre.next = h1;
h1 = h1.next;
c1-=1;
} else {
pre.next = h2;
h2 = h2.next;
c2-=1;
}
pre = pre.next;
}
// 将比较完后其中剩下的那个子链所有节点直接尾接到结果链表
pre.next = c1>0 ? h1 : h2;
// 归正游标
while (c1>0 || c2>0) {
pre = pre.next;
c1-=1;
c2-=1;
}
// 归正归并后的链表尾节点回原链表
pre.next = h;
}
blockSize *= 2;
}
return res.next;
}
力扣执行结果:
执行用时:8 ms, 在所有 Java 提交中击败了41.64%的用户
内存消耗:43.1 MB, 在所有 Java 提交中击败了66.86%的用户
| 提交时间 | 提交结果 | 运行时间 | 内存消耗 | 语言 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 几秒前 | 通过 | 8 ms | 43.1 MB | Java |
| 3 分钟前 | 通过 | 9 ms | 43.1 MB | Java |
| 7 分钟前 | 通过 | 8 ms | 42.8 MB | Java |
算法复杂度
最优时间复杂度:O(n*log(n))
最坏时间复杂度:O(n*log(n))
平均时间复杂度:O(n*log(n))
最坏空间复杂度:总共O(n),辅助O(n);当使用linked list,辅助空间为O(1).