20165201 课下作业第三周(选做)
相关知识点总结
- 写递归函数最重要的是公式和终止条件!
- 递归函数的结构类似于这样:
public static int fact(int n) {
if (n == 0)
return 1;
else
return n * fact(n-1);
}
- Integer类中把字符串转为整数的方法(命令行参数):
a = Integer.parseInt(args[0]); - 递归函数可以嵌套调用,即递归函数既可以反复调用自己,也可以反复调用别的递归函数!
补做代码运行结果截图
代码:
public class buzuo2_1 {
public static void main(String args[]){
char a='你',b='我',c='他';
System.out.println("你在Unicode表中的位置的位置:"+(int)a);
System.out.println("我在Unicode表中的位置的位置:"+(int)b);
System.out.println("他在Unicode表中的位置的位置:"+(int)c);
}
}
运行结果:

代码:
public class buzuo2_2 {
public static void main(String[] args){
int i;
for(i=945;i<=969;i++){
if(i==962)
System.out.print(" ");
else
System.out.print((char)i+" ");
}
System.out.println();
for(i=913;i<=937;i++){
if(i==930)
System.out.print(" ");
else
System.out.print((char)i+" ");
}
}
}
运行结果:

代码:
public class buzuo3_1 {
public static void main(String [] args) {
int sum=0;
for(int i=1;i<=10;i++){
sum += fact(i);
}
System.out.println(sum);
}
public static int fact(int n) {
if (n == 0)
return 1;
else
return n * fact(n-1);
}
}
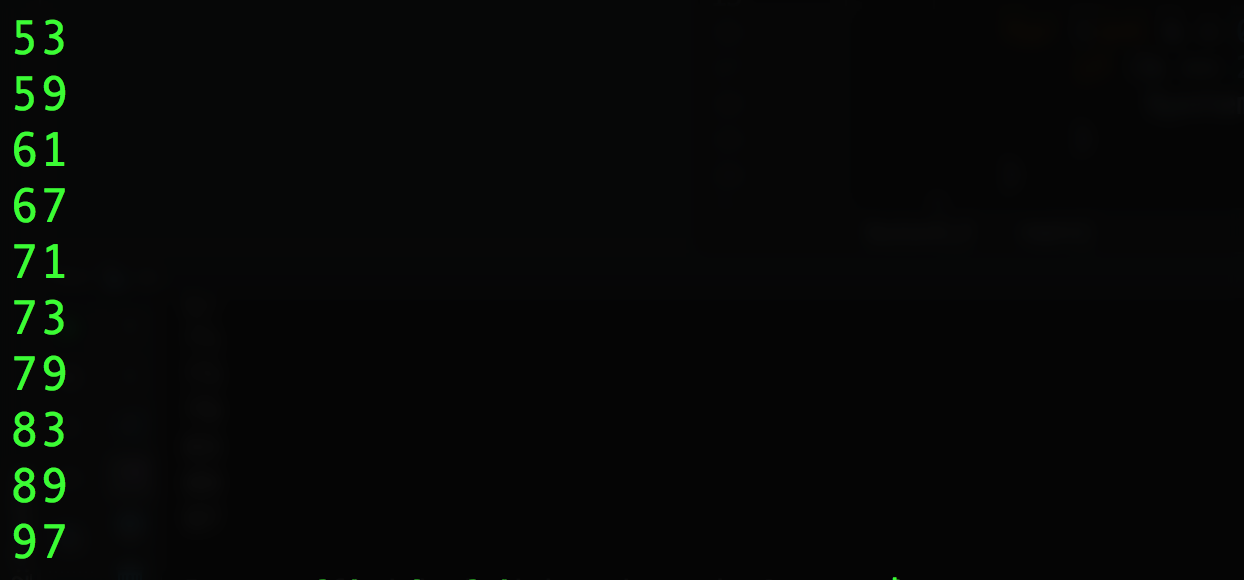
运行结果:

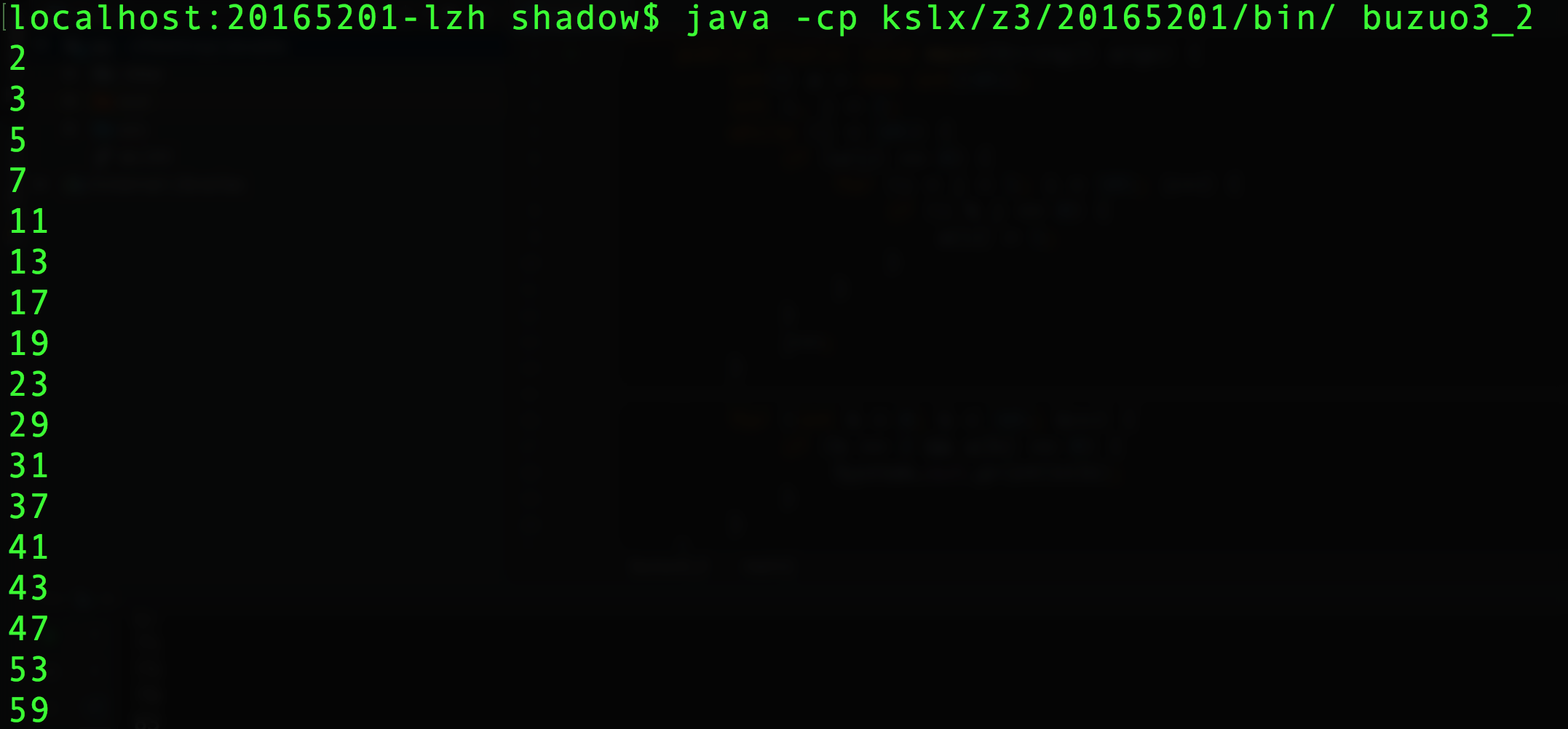
代码:
public class buzuo3_2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] a = new int[101];
int i, j = 2;
while (j < 101) {
if (a[j] == 0) {
for (i = j + 1; i < 101; i++) {
if (i % j == 0) {
a[i] = 1;
}
}
}
j++;
}
for (int k = 0; k < 101; k++) {
if (k >= 2 && a[k] == 0) {
System.out.println(k);
}
}
}
}
运行结果: