Android的智能指针方案是浸入式方案,管理引用计数的部分放在基类Refbase里(其他类继承这个类就自动拥有管理引用基数的能力了),配套的句柄类sp、wp会重载相应运算符使这些对外部类进行包装的句柄类被操纵的时候更像一个指针运算符,并使用RAII技术在构造和析构的时候调用Refbase的引用基数管理接口。
一.相关code文件
涉及到三个文件
system/core/include/utils/RefBase.h
system/core/include/utils/StrongPointer.h
system/core/libutils/RefBase.cpp
二.code具体分析
各个类的关系图如下
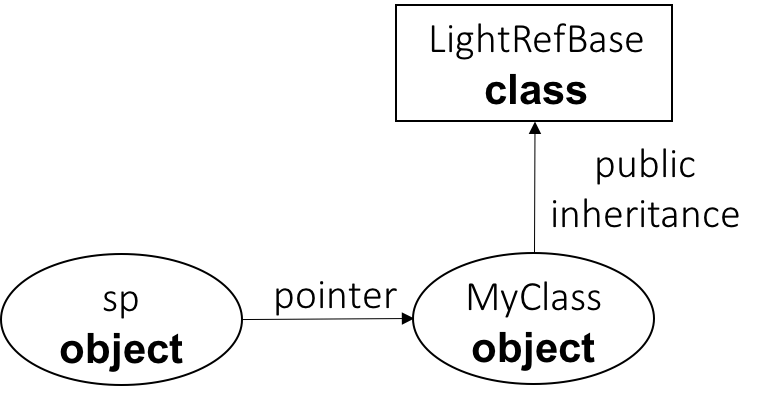
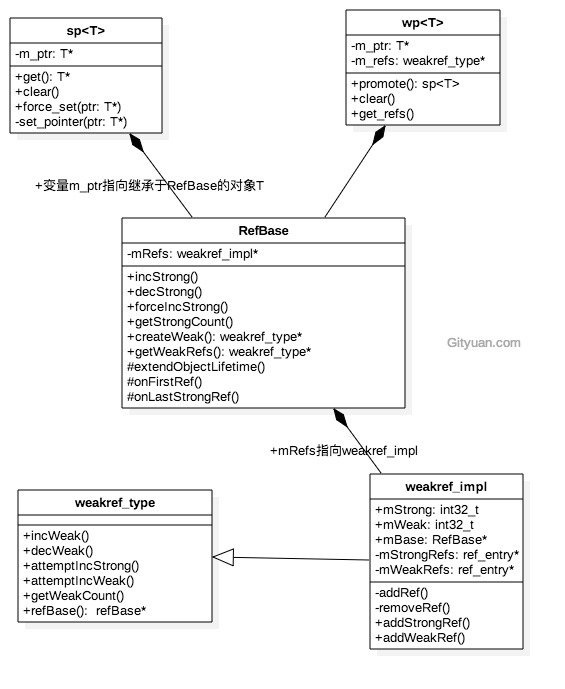
LightRefBase:
先是声明模版类
1 170 2 171// --------------------------------------------------------------------------- 3 172 4 173template <class T> 5 174class LightRefBase 6 175{ 7 176public:
这所以是模版类,是因为
当派生类的对象经由基类指针被删除时,基类必须有虚析构函数,否则会导致未定义的行为,通常是对象的devrived成分没被销毁。
如果由基类指针删除派生类对象,需要有虚析构函数,这会引入虚表,带来性能消耗,所以这里不用虚析构函数,而是在decStrong函数里通过模版参数T来做相应的类型转换,直接转化为子类类型,然后delete掉
核心数据是引用计数,用atomic相应函数来操作
1 203private: 2 204 mutable std::atomic<int32_t> mCount;
构造函数初始化mCount为0
1 176public: 2 177 inline LightRefBase() : mCount(0) { }
析构函数什么也不做
1 194protected: 2 195 inline ~LightRefBase() { }
定义LightRefBase<T>为一个新的类型,basetype
1 192 typedef LightRefBase<T> basetype;
getStrongCount获取引用计数,只为debug
1 187 //! DEBUGGING ONLY: Get current strong ref count. 2 188 inline int32_t getStrongCount() const { 3 189 return mCount.load(std::memory_order_relaxed); 4 190 } 5 191
incStrong用原子函数给引用计数加1
1 178 inline void incStrong(__attribute__((unused)) const void* id) const { 2 179 mCount.fetch_add(1, std::memory_order_relaxed); 3 180 }
decStrong则用原子函数给引用计数减1,并且如果减到0了,就删除自己,注意这里的删除用到了模版参数T来做类型转换
1 181 inline void decStrong(__attribute__((unused)) const void* id) const { 2 182 if (mCount.fetch_sub(1, std::memory_order_release) == 1) { 3 183 std::atomic_thread_fence(std::memory_order_acquire); 4 184 delete static_cast<const T*>(this); 5 185 } 6 186 }
ReferenceMover搜索代码,没有用到,renameRefs和renameRefId都是空函数
1 197private: 2 198 friend class ReferenceMover; 3 199 inline static void renameRefs(size_t n, const ReferenceRenamer& renamer) { } 4 200 inline static void renameRefId(T* ref, 5 201 const void* old_id, const void* new_id) { }
带纯虚函数的版本(没有模版参数) 是VirtualLightRefBase
1 207// This is a wrapper around LightRefBase that simply enforces a virtual 2 208// destructor to eliminate the template requirement of LightRefBase 3 209class VirtualLightRefBase : public LightRefBase<VirtualLightRefBase> { 4 210public: 5 211 virtual ~VirtualLightRefBase() {} 6 212};
sp:
sp是个模版类,也是个句柄类,是其存储对象的一个包装,因此会重载很多运算符,使对其的操作转向对其指向对象的操作(*,->,get函数,!=,==,>,<,>=,<=);并定义很多构造函数与一个析构函数调整其指向对象的强引用计数,重载了=号运算符做赋值时自己和右值相应强引用计数的调制,force_set给ProcessState类专用,clear函数reset。
1 56// --------------------------------------------------------------------------- 2 57 3 58template<typename T> 4 59class sp {
在文件开头声明了模版类wp
1 26// --------------------------------------------------------------------------- 2 27namespace android { 3 28 4 29template<typename T> class wp;
private里关键数据是T类型指针m_ptr
1 104private: 2 105 template<typename Y> friend class sp; 3 106 template<typename Y> friend class wp; 4 107 void set_pointer(T* ptr); 5 108 T* m_ptr; 6 109};
还有就是两个友元模版类sp,wp(其他类可以访问本类的m_ptr成员),set_pointer函数。函数内容如下
1 236template<typename T> 2 237void sp<T>::set_pointer(T* ptr) { 3 238 m_ptr = ptr; 4 239}
把m_ptr赋值为参数,这个函数没看见用过。
默认构造函数设置m_ptr为0
1 61 inline sp() : m_ptr(0) { }
析构函数会调用m_ptr的decStrong方法,这里是有隐形约定,穿进来的模版类必须实现这个方法。
1 70 ~sp(); 2 3 156template<typename T> 4 157sp<T>::~sp() { 5 158 if (m_ptr) 6 159 m_ptr->decStrong(this); 7 160}
clear方法会先把m_ptr decStrong,然后置零
1 85 // Reset 2 86 3 87 void clear(); 4 5 228template<typename T> 6 229void sp<T>::clear() { 7 230 if (m_ptr) { 8 231 m_ptr->decStrong(this); 9 232 m_ptr = 0; 10 233 } 11 234}
sp有六个带参构造函数和拷贝构造函数,三个不带模版参数,三个带模版参数
1 63 sp(T* other); 2 64 sp(const sp<T>& other); 3 65 sp(sp<T>&& other); 4 66 template<typename U> sp(U* other); 5 67 template<typename U> sp(const sp<U>& other); 6 68 template<typename U> sp(sp<U>&& other);
第一个构造函数是T类型的指针
1 113// --------------------------------------------------------------------------- 2 114// No user serviceable parts below here. 3 115 4 116template<typename T> 5 117sp<T>::sp(T* other) 6 118 : m_ptr(other) { 7 119 if (other) 8 120 other->incStrong(this); 9 121}
赋值m_ptr,通过other调用其incStrong
第二个构造函数是T类型的sp类的引用
1 123template<typename T> 2 124sp<T>::sp(const sp<T>& other) 3 125 : m_ptr(other.m_ptr) { 4 126 if (m_ptr) 5 127 m_ptr->incStrong(this); 6 128}
m_ptr会被赋值,并且T对象会被调用incStrong
第三个是移动构造函数,C++11的新标准
1 130template<typename T> 2 131sp<T>::sp(sp<T>&& other) 3 132 : m_ptr(other.m_ptr) { 4 133 other.m_ptr = nullptr; 5 134}
做了一次标准的堆内存替换,other的m_ptr指向的东西被赋予了m_ptr
第四个构造函数参数是其他类型的对象
1 136template<typename T> template<typename U> 2 137sp<T>::sp(U* other) 3 138 : m_ptr(other) { 4 139 if (other) 5 140 ((T*) other)->incStrong(this); 6 141}
m_ptr指向它,并调用他的incStrong
第五个构造函数是其他类型的sp为参数
1 143template<typename T> template<typename U> 2 144sp<T>::sp(const sp<U>& other) 3 145 : m_ptr(other.m_ptr) { 4 146 if (m_ptr) 5 147 m_ptr->incStrong(this); 6 148}
m_ptr为other.m_ptr,调用其incStrong
第六个构造函数是其他类型sp的移动构造函数
1 150template<typename T> template<typename U> 2 151sp<T>::sp(sp<U>&& other) 3 152 : m_ptr(other.m_ptr) { 4 153 other.m_ptr = nullptr; 5 154}
然后是重载三个等号运算符的声明
1 78 template<typename U> sp& operator = (const sp<U>& other); 2 79 template<typename U> sp& operator = (sp<U>&& other); 3 80 template<typename U> sp& operator = (U* other);
等号运算符一共有六个实现
第一个是其他类型的sp引用
1 162template<typename T> 2 163sp<T>& sp<T>::operator =(const sp<T>& other) { 3 164 T* otherPtr(other.m_ptr); 4 165 if (otherPtr) 5 166 otherPtr->incStrong(this); 6 167 if (m_ptr) 7 168 m_ptr->decStrong(this); 8 169 m_ptr = otherPtr; 9 170 return *this; 10 171}
会先对other做incStrong操作,然后对m_ptr做decStrong操作,然后m_ptr赋值为otherPtr
第二个是移动等号
1 173template<typename T> 2 174sp<T>& sp<T>::operator =(sp<T>&& other) { 3 175 if (m_ptr) 4 176 m_ptr->decStrong(this); 5 177 m_ptr = other.m_ptr; 6 178 other.m_ptr = nullptr; 7 179 return *this; 8 180}
也是m_ptr做decStrong,然后转移到other.m_ptr里,并且other.mptr清空
第三个是T类型指针为参数
1 182template<typename T> 2 183sp<T>& sp<T>::operator =(T* other) { 3 184 if (other) 4 185 other->incStrong(this); 5 186 if (m_ptr) 6 187 m_ptr->decStrong(this); 7 188 m_ptr = other; 8 189 return *this; 9 190}
也一样,本对象的m_ptr decStrong,参数对象的m_ptr incStrong。m_ptr被赋值
第四个是其参数为他类型的sp
1 192template<typename T> template<typename U> 2 193sp<T>& sp<T>::operator =(const sp<U>& other) { 3 194 T* otherPtr(other.m_ptr); 4 195 if (otherPtr) 5 196 otherPtr->incStrong(this); 6 197 if (m_ptr) 7 198 m_ptr->decStrong(this); 8 199 m_ptr = otherPtr; 9 200 return *this; 10 201}
ohter先incStrong,m_ptr再decStrong,然后m_ptr赋值为other_ptr
第五个是移动赋值函数
1 203template<typename T> template<typename U> 2 204sp<T>& sp<T>::operator =(sp<U>&& other) { 3 205 if (m_ptr) 4 206 m_ptr->decStrong(this); 5 207 m_ptr = other.m_ptr; 6 208 other.m_ptr = nullptr; 7 209 return *this; 8 210}
第六个是其他类型指针对象
1 212template<typename T> template<typename U> 2 213sp<T>& sp<T>::operator =(U* other) { 3 214 if (other) 4 215 ((T*) other)->incStrong(this); 5 216 if (m_ptr) 6 217 m_ptr->decStrong(this); 7 218 m_ptr = other; 8 219 return *this; 9 220}
也是一样,其他的incStrong,m_ptr decStrong,m_ptr赋值为其他的对象地址
重载了*和->运算符,还有一个get函数,返回m_ptr或者m_ptr的引用
1 89 // Accessors 2 90 3 91 inline T& operator* () const { return *m_ptr; } 4 92 inline T* operator-> () const { return m_ptr; } 5 93 inline T* get() const { return m_ptr; } 6 94
定义了宏COMPARE,对于比较运算符,m_ptr会和六种运算符带的相应参数做比较,将sp与sp、wp、实体对象指针的比较转换为实体对象的比较,即m_ptr _op_ o.m_ptr。其中可比较的类型,o是sp<T>&, T*, sp<U>&, U*, wp<T>&, wp<U>&
1 33#define COMPARE(_op_) 2 34inline bool operator _op_ (const sp<T>& o) const { 3 35 return m_ptr _op_ o.m_ptr; 4 36} 5 37inline bool operator _op_ (const T* o) const { 6 38 return m_ptr _op_ o; 7 39} 8 40template<typename U> 9 41inline bool operator _op_ (const sp<U>& o) const { 10 42 return m_ptr _op_ o.m_ptr; 11 43} 12 44template<typename U> 13 45inline bool operator _op_ (const U* o) const { 14 46 return m_ptr _op_ o; 15 47} 16 48inline bool operator _op_ (const wp<T>& o) const { 17 49 return m_ptr _op_ o.m_ptr; 18 50} 19 51template<typename U> 20 52inline bool operator _op_ (const wp<U>& o) const { 21 53 return m_ptr _op_ o.m_ptr; 22 54}
涉及到6种比较运算符,==,!=,>,<,<=,>=
1 95 // Operators 2 96 3 97 COMPARE(==) 4 98 COMPARE(!=) 5 99 COMPARE(>) 6 100 COMPARE(<) 7 101 COMPARE(<=) 8 102 COMPARE(>=) 9 103
force_set函数仅仅是给ProcessState类使用的
1 82 //! Special optimization for use by ProcessState (and nobody else). 2 83 void force_set(T* other); 3 4 222template<typename T> 5 223void sp<T>::force_set(T* other) { 6 224 other->forceIncStrong(this); 7 225 m_ptr = other; 8 226}
可以看到会调用其他类的forceIncStrong增加强引用计数,然后m_ptr被赋值为other。与构造函数不同的是调用了forceIncStrong
LightRefBase只有强引用,会引来循环引用问题。
循环引用问题的本质是句柄类sp利用RAII机制,在其构造期引用计数加1,在其弹出堆栈析构期间给引用计数减1。而循环引用带来的问题是sp如果位于堆里,只会加1,不会自动析构,(没有人在外边调用delete删掉它),所以如果两个在堆的的sp互相指向对方,那么谁也不会被自动销毁,因为堆里的sp不会自动析构
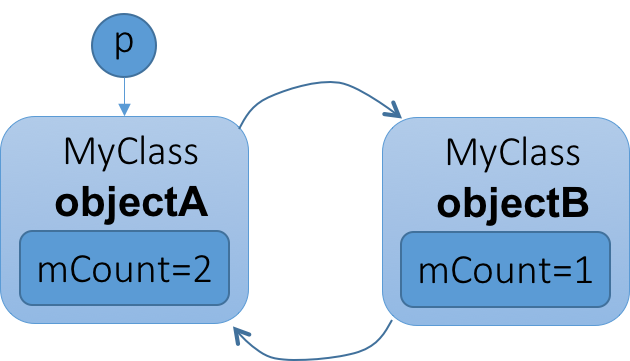
所以RefBase里支持了wp,堆里的引用指向可以使用weak引用计数。这是一种主从结构的指针,wp为从指针,只具有记录地址操作对象功能,sp为主指针,除了通过其操作对象,还可以管理对象的声明周期。

如果p不指向ObjectA,ObjectA就被销毁了,引起ObjectB也被销毁
但是这里有个问题,如果objectB还有其他指针指向他,那么objectB并不会被销毁,其中的从指针wp就会成为一个野指针,objectB并不知道其指向的对象已经被销毁了(如果是sp不会有这个问题,因为有sp指向就一定不会被销毁),objectA也不知道objectB的地址,没法通知objectB。
因此,这里需要一种机制让objectA被销毁的时候,objectB的wp还能感知到其已经成为一个野指针了(attemptIncStrong失败,这时就知道需要析构wp,不能再使用了,析构后ObjectA的weakref_impl也会消失)。
这就是weakref_type(具体实现为weakref_impl)的引入, 伴随着RefBase产生的一个影对象,但其生命周期可能比RefBase对象(主要是其继承对象)要长(RefBase有被wp指向的时候),同生不共死。weakref_type将记录强弱引用计数部分的code从实体类RefBase类里剥离出来。

因此强/弱引用计数部分都在weakref_impl(RefBase类里的mRefs对象,与RefBase互相指向)里维护,wp会同时指向weakref_impl和RefBase,sp引用计数为零默认flag情况下RefBase没了,wp引用计数为零的情况下weakref_impl才会跟着没了。(这个图不准确,sp指向的是objectB的地址,sp没了的情况下在decStrong函数里RefBase对象没了,weakref_impl对象的生存根据弱引用计数(sp减1弱引用也相应减1)情况而定;wp有两个字段同时指向RefBase和weakref_impl)
下面看看上面提到的weakref_impl和wp
weakref_impl:
这个类保存了强弱引用计数,sp和wp的构造析构对其中的强弱引用计数值的变化影响如下表格所示
| 引用类型 | 强引用计数 | 弱引用计数 |
|---|---|---|
| sp构造 | +1 | +1 |
| wp构造 | +1 | |
| sp析构 | -1 | -1 |
| wp析构 | -1 |
sp也会给弱引用计数加1是因为decWeak里只会判断弱引用计数是不是0,如果是0,直接删除weakref_impl
这个类实现了RefBase里声明的weakref_type
1 123// --------------------------------------------------------------------------- 2 124 3 125class RefBase::weakref_impl : public RefBase::weakref_type 4 126{
mStrong和mWeak原子变量记录强/弱引用计数
1 128 std::atomic<int32_t> mStrong; 2 129 std::atomic<int32_t> mWeak;
mBase指向RefBase
1 130 RefBase* const mBase;
原子变量mFlags记录RefBase对象生存期行为,强弱引用哪个决定其生存期
1 131 std::atomic<int32_t> mFlags;
如果非DEBUG_REFS的,非调试版本,相应的log追踪记录函数都是空的
1 143 void addStrongRef(const void* /*id*/) { } 2 144 void removeStrongRef(const void* /*id*/) { } 3 145 void renameStrongRefId(const void* /*old_id*/, const void* /*new_id*/) { } 4 146 void addWeakRef(const void* /*id*/) { } 5 147 void removeWeakRef(const void* /*id*/) { } 6 148 void renameWeakRefId(const void* /*old_id*/, const void* /*new_id*/) { } 7 149 void printRefs() const { } 8 150 void trackMe(bool, bool) { }
然后构造函数如下
1 135 weakref_impl(RefBase* base) 2 136 : mStrong(INITIAL_STRONG_VALUE) 3 137 , mWeak(0) 4 138 , mBase(base) 5 139 , mFlags(0) 6 140 { 7 141 }
mWeak为0,mBase指向RefBase,mFlags为0,mStrong为INITIAL_STRONG_VALUE,之所以是这个值来标志初始状态,而非0,是用来表明RefBase对象被初始化以后没有被sp对象引用过,这样mStrong为0只有一种可能——sp释放后强引用计数变成0。
INITIAL_STRONG_VALUE如下
1 121#define INITIAL_STRONG_VALUE (1<<28)
再看看其基类wearef_type,这个类是一些函数声明,要子类weakref_impl实现
1 80 class weakref_type 2 81 { 3 82 public: 4 83 RefBase* refBase() const;
refBase获取RefBase对象
incWeak,decWeak加减弱引用对象
1 85 void incWeak(const void* id); 2 86 void decWeak(const void* id);
attemptIncStrong和attemptIncWeak尝试增加强/弱引用数量
1 88 // acquires a strong reference if there is already one. 2 89 bool attemptIncStrong(const void* id); 3 90 4 91 // acquires a weak reference if there is already one. 5 92 // This is not always safe. see ProcessState.cpp and BpBinder.cpp 6 93 // for proper use. 7 94 bool attemptIncWeak(const void* id); 8 95
但是可能会失败,为何会失败看code
下面几个函数只为debug用,不管
1 96 //! DEBUGGING ONLY: Get current weak ref count. 2 97 int32_t getWeakCount() const; 3 98 4 99 //! DEBUGGING ONLY: Print references held on object. 5 100 void printRefs() const; 6 101 7 102 //! DEBUGGING ONLY: Enable tracking for this object. 8 103 // enable -- enable/disable tracking 9 104 // retain -- when tracking is enable, if true, then we save a stack trace 10 105 // for each reference and dereference; when retain == false, we 11 106 // match up references and dereferences and keep only the 12 107 // outstanding ones. 13 108 14 109 void trackMe(bool enable, bool retain); 15 110 };
refBase函数返回mBase,注意这里是RefBase::weakref_type,this要转换为实际new出来的weakref_impl
1 464RefBase* RefBase::weakref_type::refBase() const 2 465{ 3 466 return static_cast<const weakref_impl*>(this)->mBase; 4 467}
然后是incWeak函数
1 469void RefBase::weakref_type::incWeak(const void* id) 2 470{ 3 471 weakref_impl* const impl = static_cast<weakref_impl*>(this); 4 472 impl->addWeakRef(id); 5 473 const int32_t c __unused = impl->mWeak.fetch_add(1, 6 474 std::memory_order_relaxed); 7 475 ALOG_ASSERT(c >= 0, "incWeak called on %p after last weak ref", this); 8 476}
先把this转换为weakref_impl,其addWeakRef非debug版是个空函数不用管,然后对weakref_impl里的弱引用计数做原子加1操作
然后是decWeak函数
1 479void RefBase::weakref_type::decWeak(const void* id) 2 480{ 3 481 weakref_impl* const impl = static_cast<weakref_impl*>(this); 4 482 impl->removeWeakRef(id); 5 483 const int32_t c = impl->mWeak.fetch_sub(1, std::memory_order_release); 6 484 ALOG_ASSERT(c >= 1, "decWeak called on %p too many times", this); 7 485 if (c != 1) return; 8 486 atomic_thread_fence(std::memory_order_acquire); 9 487 10 488 int32_t flags = impl->mFlags.load(std::memory_order_relaxed); 11 489 if ((flags&OBJECT_LIFETIME_MASK) == OBJECT_LIFETIME_STRONG) { 12 490 // This is the regular lifetime case. The object is destroyed 13 491 // when the last strong reference goes away. Since weakref_impl 14 492 // outlive the object, it is not destroyed in the dtor, and 15 493 // we'll have to do it here. 16 494 if (impl->mStrong.load(std::memory_order_relaxed) 17 495 == INITIAL_STRONG_VALUE) { 18 496 // Special case: we never had a strong reference, so we need to 19 497 // destroy the object now. 20 498 delete impl->mBase; 21 499 } else { 22 500 // ALOGV("Freeing refs %p of old RefBase %p ", this, impl->mBase); 23 501 delete impl; 24 502 } 25 503 } else { 26 504 // This is the OBJECT_LIFETIME_WEAK case. The last weak-reference 27 505 // is gone, we can destroy the object. 28 506 impl->mBase->onLastWeakRef(id); 29 507 delete impl->mBase; 30 508 } 31 509}
套路都一样,弱引用计数昨晚原子减1操作后,如果变成了0,那么读取mFlags,如果flag为默认常规的OBJECT_LIFETIME_STRONG,那么此时如果RefBase从来没有引用过,那么删除mBase,在RefBase的析构函数里会删掉impl,否则的话mBase已经由于sp的析构而被删除了,直接删除impl;如果flag为OBJECT_LIFETIME_WEAK(RefBase和影对象的删除由弱引用计数决定)的话,这里就要先调用RefBase的 onLastWEakRef,通知对象弱引用计数也不好用了,然后删除mBase,weakref会在RefBase的析构函数里被删除。
这个函数要和RefBase的析构函数一起看。
智能指针里RefBase会被三个地方delete,RefBase的析构函数要处理这三种情况,分别是sp为0,flag为weak,flag为strong但sp从来没被引用过。sp为0的话会在decStrong里delete掉RefBase,这个函数里也会减少弱引用计数来来触发删不删impl的决定。
如果RefBase没有被sp引用过,那么删除mRefs(只有wp引用导致被删或者外边直接delete)。否则的话,看flag,如果flag是OBJECT_LIFETIME_WEAK,那么获取弱引用计数,如果为0的话,删掉mRefs。最后设置mRefs为NULL。
1 665RefBase::~RefBase() 2 666{ 3 667 if (mRefs->mStrong.load(std::memory_order_relaxed) 4 668 == INITIAL_STRONG_VALUE) { 5 669 // we never acquired a strong (and/or weak) reference on this object. 6 670 delete mRefs; 7 671 } else { 8 672 // life-time of this object is extended to WEAK, in 9 673 // which case weakref_impl doesn't out-live the object and we 10 674 // can free it now. 11 675 int32_t flags = mRefs->mFlags.load(std::memory_order_relaxed); 12 676 if ((flags & OBJECT_LIFETIME_MASK) != OBJECT_LIFETIME_STRONG) { 13 677 // It's possible that the weak count is not 0 if the object 14 678 // re-acquired a weak reference in its destructor 15 679 if (mRefs->mWeak.load(std::memory_order_relaxed) == 0) { 16 680 delete mRefs; 17 681 } 18 682 } 19 683 } 20 684 // for debugging purposes, clear this. 21 685 const_cast<weakref_impl*&>(mRefs) = NULL; 22 686} 23 687
理论上讲,RefBase的存活期比影对象的短,但是这里有两个删除影对象的地方,即没有被sp引用过,就说明这个对象的析构是由影对象里弱引用计数为0导致的(或者外边直接删除),impl来删除这个RefBase,那么直接删除impl;flag是weak的话,那么这个析构一定是影对象带来的,直接删掉RefBase对象。即影对象decWeakRef里的两处删除会调用RefBase的析构函数。这两种情况意外RefBase是被decStrong给delete的。
RefBase的构造函数如下
1 660RefBase::RefBase() 2 661 : mRefs(new weakref_impl(this)) 3 662{ 4 663}
会初始化mRefs为weakref_impl
weakref_type的getWeakCount、printRefs和trackMe都是调试用的
1 632int32_t RefBase::weakref_type::getWeakCount() const 2 633{ 3 634 // Debug only! 4 635 return static_cast<const weakref_impl*>(this)->mWeak 5 636 .load(std::memory_order_relaxed); 6 637} 7 638 8 639void RefBase::weakref_type::printRefs() const 9 640{ 10 641 static_cast<const weakref_impl*>(this)->printRefs(); 11 642} 12 643 13 644void RefBase::weakref_type::trackMe(bool enable, bool retain) 14 645{ 15 646 static_cast<weakref_impl*>(this)->trackMe(enable, retain); 16 647}
剩下的两个函数attemptIncStrong和attemptIncWeak讲完RefBase再说
RefBase:
这了类声明如下
1 67// --------------------------------------------------------------------------- 2 68 3 69class RefBase 4 70{ 5 71public:
核心函数inStrong和decStrong被sp调用,forceIncStrong仅仅为ProcessState对象使用
1 72 void incStrong(const void* id) const; 2 73 void decStrong(const void* id) const; 3 74 4 75 void forceIncStrong(const void* id) const;
getStrongCount仅为调试用
1 77 //! DEBUGGING ONLY: Get current strong ref count. 2 78 int32_t getStrongCount() const;
然后定义了类weakref_type
1 80 class weakref_type 2 81 { 3 82 public: 4 83 RefBase* refBase() const; 5 84 6 85 void incWeak(const void* id); 7 86 void decWeak(const void* id); 8 87 9 88 // acquires a strong reference if there is already one. 10 89 bool attemptIncStrong(const void* id); 11 90 12 91 // acquires a weak reference if there is already one. 13 92 // This is not always safe. see ProcessState.cpp and BpBinder.cpp 14 93 // for proper use. 15 94 bool attemptIncWeak(const void* id); 16 95 17 96 //! DEBUGGING ONLY: Get current weak ref count. 18 97 int32_t getWeakCount() const; 19 98 20 99 //! DEBUGGING ONLY: Print references held on object. 21 100 void printRefs() const; 22 101 23 102 //! DEBUGGING ONLY: Enable tracking for this object. 24 103 // enable -- enable/disable tracking 25 104 // retain -- when tracking is enable, if true, then we save a stack trace 26 105 // for each reference and dereference; when retain == false, we 27 106 // match up references and dereferences and keep only the 28 107 // outstanding ones. 29 108 30 109 void trackMe(bool enable, bool retain); 31 110 }; 32 111
然后是函数createWeak和getWeakRefs声明
1 112 weakref_type* createWeak(const void* id) const; 2 113 3 114 weakref_type* getWeakRefs() const; 4 115
内联函数printRefs和trackMe仅仅是为了调试,调用weakref_type的实现
1 116 //! DEBUGGING ONLY: Print references held on object. 2 117 inline void printRefs() const { getWeakRefs()->printRefs(); } 3 118 4 119 //! DEBUGGING ONLY: Enable tracking of object. 5 120 inline void trackMe(bool enable, bool retain) 6 121 { 7 122 getWeakRefs()->trackMe(enable, retain); 8 123 } 9 124
typedef RefBase 为basetype
1 125 typedef RefBase basetype;
protected里,有构造函数和纯析构函数
1 127protected: 2 128 RefBase(); 3 129 virtual ~RefBase();
然后是生命周期的flag,有strong和weak,RefBase的lifetime分别有强引用计数和弱引用计数是否为0决定,mask掩码用于运算到底是哪个flag
1 131 //! Flags for extendObjectLifetime() 2 132 enum { 3 133 OBJECT_LIFETIME_STRONG = 0x0000, 4 134 OBJECT_LIFETIME_WEAK = 0x0001, 5 135 OBJECT_LIFETIME_MASK = 0x0001 6 136 };
extendOjbectLifetime修改flag
1 138 void extendObjectLifetime(int32_t mode);
再为onIncStrongAttempted定义一个flag FIRST_INC_STRONG
1 140 //! Flags for onIncStrongAttempted()
2 141 enum {
3 142 FIRST_INC_STRONG = 0x0001
4 143 };
5 144
然后是四个纯虚函数回调,onFirstRef,onLastStrongRef,onIncStrongAttempted,onLastWeakRef,给子类提供添加自己逻辑的机会
1 145 virtual void onFirstRef(); 2 146 virtual void onLastStrongRef(const void* id); 3 147 virtual bool onIncStrongAttempted(uint32_t flags, const void* id); 4 148 virtual void onLastWeakRef(const void* id);
private区域里,weakref_type为友元类,声明了class weakref_impl
1 151 friend class weakref_type; 2 152 class weakref_impl;
拷贝构造函数和=都是private的
1 154 RefBase(const RefBase& o); 2 155 RefBase& operator=(const RefBase& o); 3 156
RefBase对象只能new了,没有办法当右值,要用sp和wp来使用指针对象
下面这几个都是为了debug用
1 157private: 2 158 friend class ReferenceMover; 3 159 4 160 static void renameRefs(size_t n, const ReferenceRenamer& renamer); 5 161 6 162 static void renameRefId(weakref_type* ref, 7 163 const void* old_id, const void* new_id); 8 164 9 165 static void renameRefId(RefBase* ref, 10 166 const void* old_id, const void* new_id);
最要的一个对象是影子对象mRefs
1 168 weakref_impl* const mRefs;
再看函数的具体实现
extendOjbectLifetime通过原子or操作,修改mFlags为传入的参数,一般就是OBJECT_LIFETIME_WEAK,让弱引用计数决定RefBase对象的存活
1 688void RefBase::extendObjectLifetime(int32_t mode) 2 689{ 3 690 // Must be happens-before ordered with respect to construction or any 4 691 // operation that could destroy the object. 5 692 mRefs->mFlags.fetch_or(mode, std::memory_order_relaxed); 6 693}
回调函数onFirstRef,onLastStrongRef,onLastWeakRef(这一个函数仅仅在flag为weak的时候被调用)都是空的
1 695void RefBase::onFirstRef() 2 696{ 3 697} 4 698 5 699void RefBase::onLastStrongRef(const void* /*id*/) 6 700{ 7 701} 8 9 708void RefBase::onLastWeakRef(const void* /*id*/) 10 709{ 11 710}
onIncStrongAttempted回调函数会返回传进来的flag是不是FIRST_INC_STRONG,在weakref_impl的attemptIncStrong里被调用
1 703bool RefBase::onIncStrongAttempted(uint32_t flags, const void* /*id*/) 2 704{ 3 705 return (flags&FIRST_INC_STRONG) ? true : false; 4 706}
renameRefs和renameRefId都是debug用的
1 712// --------------------------------------------------------------------------- 2 713 3 714#if DEBUG_REFS 4 715void RefBase::renameRefs(size_t n, const ReferenceRenamer& renamer) { 5 716 for (size_t i=0 ; i<n ; i++) { 6 717 renamer(i); 7 718 } 8 719} 9 720#else 10 721void RefBase::renameRefs(size_t /*n*/, const ReferenceRenamer& /*renamer*/) { } 11 722#endif 12 723 13 724void RefBase::renameRefId(weakref_type* ref, 14 725 const void* old_id, const void* new_id) { 15 726 weakref_impl* const impl = static_cast<weakref_impl*>(ref); 16 727 impl->renameStrongRefId(old_id, new_id); 17 728 impl->renameWeakRefId(old_id, new_id); 18 729} 19 730 20 731void RefBase::renameRefId(RefBase* ref, 21 732 const void* old_id, const void* new_id) { 22 733 ref->mRefs->renameStrongRefId(old_id, new_id); 23 734 ref->mRefs->renameWeakRefId(old_id, new_id); 24 735} 25 736 26 737}; // namespace android
getStrongCount返回mRefs里的mStrong
1 458int32_t RefBase::getStrongCount() const 2 459{ 3 460 // Debugging only; No memory ordering guarantees. 4 461 return mRefs->mStrong.load(std::memory_order_relaxed); 5 462}
incStrong会先调用mRefs的incWeak,增加弱引用计数,再增加mStrong,然后判断是不是第一次增加强引用计数,如果是就设置其为1,然后调用回调onFirstRef。对于初次引用的情况,如果在onFirstRef之前调用了decStrong的话(其他线程里有这个可能),那么就会有ALOG_ASSERT,直接打log后crash
1 381// --------------------------------------------------------------------------- 2 382 3 383void RefBase::incStrong(const void* id) const 4 384{ 5 385 weakref_impl* const refs = mRefs; 6 386 refs->incWeak(id); 7 387 8 388 refs->addStrongRef(id); 9 389 const int32_t c = refs->mStrong.fetch_add(1, std::memory_order_relaxed); 10 390 ALOG_ASSERT(c > 0, "incStrong() called on %p after last strong ref", refs); 11 391#if PRINT_REFS 12 392 ALOGD("incStrong of %p from %p: cnt=%d ", this, id, c); 13 393#endif 14 394 if (c != INITIAL_STRONG_VALUE) { 15 395 return; 16 396 } 17 397 18 398 int32_t old = refs->mStrong.fetch_sub(INITIAL_STRONG_VALUE, 19 399 std::memory_order_relaxed); 20 400 // A decStrong() must still happen after us. 21 401 ALOG_ASSERT(old > INITIAL_STRONG_VALUE, "0x%x too small", old); 22 402 refs->mBase->onFirstRef(); 23 403} 24 404
decStrong函数,先减少强引用计数,要是减到0的话,如果mFlags是OBJECT_LIFETIME_STRONG,先调用回调onLastStrongRef,然后直接delete掉RefBase,最后调用影对象的decWeak
1 405void RefBase::decStrong(const void* id) const 2 406{ 3 407 weakref_impl* const refs = mRefs; 4 408 refs->removeStrongRef(id); 5 409 const int32_t c = refs->mStrong.fetch_sub(1, std::memory_order_release); 6 410#if PRINT_REFS 7 411 ALOGD("decStrong of %p from %p: cnt=%d ", this, id, c); 8 412#endif 9 413 ALOG_ASSERT(c >= 1, "decStrong() called on %p too many times", refs); 10 414 if (c == 1) { 11 415 std::atomic_thread_fence(std::memory_order_acquire); 12 416 refs->mBase->onLastStrongRef(id); 13 417 int32_t flags = refs->mFlags.load(std::memory_order_relaxed); 14 418 if ((flags&OBJECT_LIFETIME_MASK) == OBJECT_LIFETIME_STRONG) { 15 419 delete this; 16 420 // Since mStrong had been incremented, the destructor did not 17 421 // delete refs. 18 422 } 19 423 } 20 424 // Note that even with only strong reference operations, the thread 21 425 // deallocating this may not be the same as the thread deallocating refs. 22 426 // That's OK: all accesses to this happen before its deletion here, 23 427 // and all accesses to refs happen before its deletion in the final decWeak. 24 428 // The destructor can safely access mRefs because either it's deleting 25 429 // mRefs itself, or it's running entirely before the final mWeak decrement. 26 430 refs->decWeak(id); 27 431}
forceIncStrong函数给强弱引用计数加1,允许decStrong之后调用onFirstRef
1 433void RefBase::forceIncStrong(const void* id) const 2 434{ 3 435 // Allows initial mStrong of 0 in addition to INITIAL_STRONG_VALUE. 4 436 // TODO: Better document assumptions. 5 437 weakref_impl* const refs = mRefs; 6 438 refs->incWeak(id); 7 439 8 440 refs->addStrongRef(id); 9 441 const int32_t c = refs->mStrong.fetch_add(1, std::memory_order_relaxed); 10 442 ALOG_ASSERT(c >= 0, "forceIncStrong called on %p after ref count underflow", 11 443 refs); 12 444#if PRINT_REFS 13 445 ALOGD("forceIncStrong of %p from %p: cnt=%d ", this, id, c); 14 446#endif 15 447 16 448 switch (c) { 17 449 case INITIAL_STRONG_VALUE: 18 450 refs->mStrong.fetch_sub(INITIAL_STRONG_VALUE, 19 451 std::memory_order_relaxed); 20 452 // fall through... 21 453 case 0: 22 454 refs->mBase->onFirstRef(); 23 455 } 24 456}
weakref_type的attemptIncWeak函数,先获取弱引用计数,如果非0,那么在循环里使用compare_exchange_weak,确保弱引用计数加1
1 610bool RefBase::weakref_type::attemptIncWeak(const void* id) 2 611{ 3 612 weakref_impl* const impl = static_cast<weakref_impl*>(this); 4 613 5 614 int32_t curCount = impl->mWeak.load(std::memory_order_relaxed); 6 615 ALOG_ASSERT(curCount >= 0, "attemptIncWeak called on %p after underflow", 7 616 this); 8 617 while (curCount > 0) { 9 618 if (impl->mWeak.compare_exchange_weak(curCount, curCount+1, 10 619 std::memory_order_relaxed)) { 11 620 break; 12 621 } 13 622 // curCount has been updated. 14 623 } 15 624 16 625 if (curCount > 0) { 17 626 impl->addWeakRef(id); 18 627 } 19 628 20 629 return curCount > 0; 21 630}
最后是weakref_type的attemptIncStrong函数,先增加弱引用,对于已经被sp引用过的情况,在循环里确保强引用加1
1 511bool RefBase::weakref_type::attemptIncStrong(const void* id) 2 512{ 3 513 incWeak(id); 4 514 5 515 weakref_impl* const impl = static_cast<weakref_impl*>(this); 6 516 int32_t curCount = impl->mStrong.load(std::memory_order_relaxed); 7 517 8 518 ALOG_ASSERT(curCount >= 0, 9 519 "attemptIncStrong called on %p after underflow", this); 10 520 11 521 while (curCount > 0 && curCount != INITIAL_STRONG_VALUE) { 12 522 // we're in the easy/common case of promoting a weak-reference 13 523 // from an existing strong reference. 14 524 if (impl->mStrong.compare_exchange_weak(curCount, curCount+1, 15 525 std::memory_order_relaxed)) { 16 526 break; 17 527 } 18 528 // the strong count has changed on us, we need to re-assert our 19 529 // situation. curCount was updated by compare_exchange_weak. 20 530 } 21 531
对于强引用计数为0或者未被引用的情况
第一种情况,flag为strong
如果引用计数为0,这个时候Refbase已经被删了,直接调用decWeak,与本函数一开始的incWeak对冲。
1 532 if (curCount <= 0 || curCount == INITIAL_STRONG_VALUE) { 2 533 // we're now in the harder case of either: 3 534 // - there never was a strong reference on us 4 535 // - or, all strong references have been released 5 536 int32_t flags = impl->mFlags.load(std::memory_order_relaxed); 6 537 if ((flags&OBJECT_LIFETIME_MASK) == OBJECT_LIFETIME_STRONG) { 7 538 // this object has a "normal" life-time, i.e.: it gets destroyed 8 539 // when the last strong reference goes away 9 540 if (curCount <= 0) { 10 541 // the last strong-reference got released, the object cannot 11 542 // be revived. 12 543 decWeak(id); 13 544 return false; 14 545 }
如果count始终大于0,说明为未被sp引用,那么可以提升,给count加1
1 547 // here, curCount == INITIAL_STRONG_VALUE, which means 2 548 // there never was a strong-reference, so we can try to 3 549 // promote this object; we need to do that atomically. 4 550 while (curCount > 0) { 5 551 if (impl->mStrong.compare_exchange_weak(curCount, curCount+1, 6 552 std::memory_order_relaxed)) { 7 553 break; 8 554 } 9 555 // the strong count has changed on us, we need to re-assert our 10 556 // situation (e.g.: another thread has inc/decStrong'ed us) 11 557 // curCount has been updated. 12 558 } 13 559
如果上边的结果有count<=0,即这个时候恰好RefBase被删掉了,减少弱引用计数
1 560 if (curCount <= 0) { 2 561 // promote() failed, some other thread destroyed us in the 3 562 // meantime (i.e.: strong count reached zero). 4 563 decWeak(id); 5 564 return false; 6 565 }
对于flag为weak的,RefBase的生存周期做了延长。如果RefBase的onIncStrongAttempted返回0拒绝增加,那么就减少弱引用计数。默认的onIncStrongAttempted会检查参数是不是FIRST_INC_STRONG。这个之所以传这个参数,因为上边的强引用计数已经是0了,所以每次都要是这个参数。
1 else { 2 567 // this object has an "extended" life-time, i.e.: it can be 3 568 // revived from a weak-reference only. 4 569 // Ask the object's implementation if it agrees to be revived 5 570 if (!impl->mBase->onIncStrongAttempted(FIRST_INC_STRONG, id)) { 6 571 // it didn't so give-up. 7 572 decWeak(id); 8 573 return false; 9 574 }
然后给强引用计数加1。如果这个对象已经被其他人给增加了,那么要调用onLastStrongRef来感知到(里边取消onFirstRef做的操作)。codebase里用到onFirstRef和onLastStrongRef的,都是用在binder里。
1 575 // grab a strong-reference, which is always safe due to the 2 576 // extended life-time. 3 577 curCount = impl->mStrong.fetch_add(1, std::memory_order_relaxed); 4 578 // If the strong reference count has already been incremented by 5 579 // someone else, the implementor of onIncStrongAttempted() is holding 6 580 // an unneeded reference. So call onLastStrongRef() here to remove it. 7 581 // (No, this is not pretty.) Note that we MUST NOT do this if we 8 582 // are in fact acquiring the first reference. 9 583 if (curCount != 0 && curCount != INITIAL_STRONG_VALUE) { 10 584 impl->mBase->onLastStrongRef(id); 11 585 } 12 586 } 13 587 }
最后,对于从来没有引用过的情况,给强引用计数设置为1
1 589 impl->addStrongRef(id); 2 590 3 591#if PRINT_REFS 4 592 ALOGD("attemptIncStrong of %p from %p: cnt=%d ", this, id, curCount); 5 593#endif 6 594 7 595 // curCount is the value of mStrong before we incremented it. 8 596 // Now we need to fix-up the count if it was INITIAL_STRONG_VALUE. 9 597 // This must be done safely, i.e.: handle the case where several threads 10 598 // were here in attemptIncStrong(). 11 599 // curCount > INITIAL_STRONG_VALUE is OK, and can happen if we're doing 12 600 // this in the middle of another incStrong. The subtraction is handled 13 601 // by the thread that started with INITIAL_STRONG_VALUE. 14 602 if (curCount == INITIAL_STRONG_VALUE) { 15 603 impl->mStrong.fetch_sub(INITIAL_STRONG_VALUE, 16 604 std::memory_order_relaxed); 17 605 } 18 606 19 607 return true;
wp:
wp指向的是mRefs和RefBase,mRefs专为wp不成为野指针而生,与其息息相关。所以在RefBase.h里,定义了wp和其实现,便于在wp类里直接定义引用weakref_type的东西。
先看声明,这是一个模版类
1 214// --------------------------------------------------------------------------- 2 215 3 216template <typename T> 4 217class wp 5 218{ 6 219public: 7 220 typedef typename RefBase::weakref_type weakref_type;
私有数据里,先声明其他同参数的sp和wp为友元类
1 298private: 2 299 template<typename Y> friend class sp; 3 300 template<typename Y> friend class wp;
然后是最重要的两个数据,m_ptr和m_refs,分别指向实体类和影对象
1 302 T* m_ptr; 2 303 weakref_type* m_refs; 3 304}; 4 305
默认构造函数如下
1 222 inline wp() : m_ptr(0) { } 2 223 3 224 wp(T* other); 4 225 wp(const wp<T>& other); 5 226 wp(const sp<T>& other); 6 227 template<typename U> wp(U* other); 7 228 template<typename U> wp(const sp<U>& other); 8 229 template<typename U> wp(const wp<U>& other);
析构函数如下
1 231 ~wp(); 2 232
重载了等号运算符
1 233 // Assignment 2 234 3 235 wp& operator = (T* other); 4 236 wp& operator = (const wp<T>& other); 5 237 wp& operator = (const sp<T>& other); 6 238 7 239 template<typename U> wp& operator = (U* other); 8 240 template<typename U> wp& operator = (const wp<U>& other); 9 241 template<typename U> wp& operator = (const sp<U>& other); 10 242
声明了set_object_and_refs方法
1 243 void set_object_and_refs(T* other, weakref_type* refs);
promote方法,返回一个构造的sp,并增加影对象里的强弱引用计数,要是实体对象被删除了,这个sp里的m_ptr就是NULL
1 245 // promotion to sp 2 246 3 247 sp<T> promote() const;
clear方法reset
1 248 2 249 // Reset 3 250 4 251 void clear();
get_refs和unsafe_get返回影对象地址和实体对象地址
1 253 // Accessors 2 254 3 255 inline weakref_type* get_refs() const { return m_refs; } 4 256 5 257 inline T* unsafe_get() const { return m_ptr; }
宏COMPARE_WEAK定义了一系列的比较运算符不同参数的函数体
1 36// --------------------------------------------------------------------------- 2 37 3 38#define COMPARE_WEAK(_op_) 4 39inline bool operator _op_ (const sp<T>& o) const { 5 40 return m_ptr _op_ o.m_ptr; 6 41} 7 42inline bool operator _op_ (const T* o) const { 8 43 return m_ptr _op_ o; 9 44} 10 45template<typename U> 11 46inline bool operator _op_ (const sp<U>& o) const { 12 47 return m_ptr _op_ o.m_ptr; 13 48} 14 49template<typename U> 15 50inline bool operator _op_ (const U* o) const { 16 51 return m_ptr _op_ o; 17 52}
是不同模版参数的sp和T*、U*类型指针,比较的是m_ptr
这里一共有六个比较运算符
1 259 // Operators 2 260 3 261 COMPARE_WEAK(==) 4 262 COMPARE_WEAK(!=) 5 263 COMPARE_WEAK(>) 6 264 COMPARE_WEAK(<) 7 265 COMPARE_WEAK(<=) 8 266 COMPARE_WEAK(>=) 9 267
每个运算符还有两个用wp做参数的版本,一个本类一个其他类的模版参数。注意比较的对象,以m_ptr为主,如果二者相同,就比较m_refs
1 268 inline bool operator == (const wp<T>& o) const { 2 269 return (m_ptr == o.m_ptr) && (m_refs == o.m_refs); 3 270 } 4 271 template<typename U> 5 272 inline bool operator == (const wp<U>& o) const { 6 273 return m_ptr == o.m_ptr; 7 274 } 8 275 9 276 inline bool operator > (const wp<T>& o) const { 10 277 return (m_ptr == o.m_ptr) ? (m_refs > o.m_refs) : (m_ptr > o.m_ptr); 11 278 } 12 279 template<typename U> 13 280 inline bool operator > (const wp<U>& o) const { 14 281 return (m_ptr == o.m_ptr) ? (m_refs > o.m_refs) : (m_ptr > o.m_ptr); 15 282 } 16 283 17 284 inline bool operator < (const wp<T>& o) const { 18 285 return (m_ptr == o.m_ptr) ? (m_refs < o.m_refs) : (m_ptr < o.m_ptr); 19 286 } 20 287 template<typename U> 21 288 inline bool operator < (const wp<U>& o) const { 22 289 return (m_ptr == o.m_ptr) ? (m_refs < o.m_refs) : (m_ptr < o.m_ptr); 23 290 } 24 291 inline bool operator != (const wp<T>& o) const { return m_refs != o.m_refs; } 25 292 template<typename U> inline bool operator != (const wp<U>& o) const { return !operator == (o); } 26 293 inline bool operator <= (const wp<T>& o) const { return !operator > (o); } 27 294 template<typename U> inline bool operator <= (const wp<U>& o) const { return !operator > (o); } 28 295 inline bool operator >= (const wp<T>& o) const { return !operator < (o); } 29 296 template<typename U> inline bool operator >= (const wp<U>& o) const { return !operator < (o); }
构造函数会根据参数不同,决定是用createWeak和incWeak来创建m_refs,同时也会初始化m_ptr。使用前会先判断下穿进来的指针是不是空指针
1 310 2 311// --------------------------------------------------------------------------- 3 312// No user serviceable parts below here. 4 313 5 314template<typename T> 6 315wp<T>::wp(T* other) 7 316 : m_ptr(other) 8 317{ 9 318 if (other) m_refs = other->createWeak(this); 10 319} 11 320 12 321template<typename T> 13 322wp<T>::wp(const wp<T>& other) 14 323 : m_ptr(other.m_ptr), m_refs(other.m_refs) 15 324{ 16 325 if (m_ptr) m_refs->incWeak(this); 17 326} 18 327 19 328template<typename T> 20 329wp<T>::wp(const sp<T>& other) 21 330 : m_ptr(other.m_ptr) 22 331{ 23 332 if (m_ptr) { 24 333 m_refs = m_ptr->createWeak(this); 25 334 } 26 335} 27 336 28 337template<typename T> template<typename U> 29 338wp<T>::wp(U* other) 30 339 : m_ptr(other) 31 340{ 32 341 if (other) m_refs = other->createWeak(this); 33 342} 34 343 35 344template<typename T> template<typename U> 36 345wp<T>::wp(const wp<U>& other) 37 346 : m_ptr(other.m_ptr) 38 347{ 39 348 if (m_ptr) { 40 349 m_refs = other.m_refs; 41 350 m_refs->incWeak(this); 42 351 } 43 352} 44 353 45 354template<typename T> template<typename U> 46 355wp<T>::wp(const sp<U>& other) 47 356 : m_ptr(other.m_ptr) 48 357{ 49 358 if (m_ptr) { 50 359 m_refs = m_ptr->createWeak(this); 51 360 } 52 361}
析构函数先判断m_ptr不为空,然后调用decWeak。
1 363template<typename T> 2 364wp<T>::~wp() 3 365{ 4 366 if (m_ptr) m_refs->decWeak(this); 5 367}
clear方法把m_ptr清零,并调用decWeak
1 458template<typename T> 2 459void wp<T>::clear() 3 460{ 4 461 if (m_ptr) { 5 462 m_refs->decWeak(this); 6 463 m_ptr = 0; 7 464 } 8 465}
set_object_and_refs方法增加外部对象的弱引用计数,把旧的弱引用计数减1,设置m_ptr和m_refs
1 439template<typename T> 2 440void wp<T>::set_object_and_refs(T* other, weakref_type* refs) 3 441{ 4 442 if (other) refs->incWeak(this); 5 443 if (m_ptr) m_refs->decWeak(this); 6 444 m_ptr = other; 7 445 m_refs = refs; 8 446}
promote函数构建一个sp,根据attemptIncStrong来决定要不要把m_ptr传给sp
1 448template<typename T> 2 449sp<T> wp<T>::promote() const 3 450{ 4 451 sp<T> result; 5 452 if (m_ptr && m_refs->attemptIncStrong(&result)) { 6 453 result.set_pointer(m_ptr); 7 454 } 8 455 return result; 9 456}
=运算符增加外部对象的弱引用计数,把旧的弱引用计数减1,设置m_ptr和m_refs,类似set_object_and_refs
1 369template<typename T> 2 370wp<T>& wp<T>::operator = (T* other) 3 371{ 4 372 weakref_type* newRefs = 5 373 other ? other->createWeak(this) : 0; 6 374 if (m_ptr) m_refs->decWeak(this); 7 375 m_ptr = other; 8 376 m_refs = newRefs; 9 377 return *this; 10 378} 11 379 12 380template<typename T> 13 381wp<T>& wp<T>::operator = (const wp<T>& other) 14 382{ 15 383 weakref_type* otherRefs(other.m_refs); 16 384 T* otherPtr(other.m_ptr); 17 385 if (otherPtr) otherRefs->incWeak(this); 18 386 if (m_ptr) m_refs->decWeak(this); 19 387 m_ptr = otherPtr; 20 388 m_refs = otherRefs; 21 389 return *this; 22 390} 23 391 24 392template<typename T> 25 393wp<T>& wp<T>::operator = (const sp<T>& other) 26 394{ 27 395 weakref_type* newRefs = 28 396 other != NULL ? other->createWeak(this) : 0; 29 397 T* otherPtr(other.m_ptr); 30 398 if (m_ptr) m_refs->decWeak(this); 31 399 m_ptr = otherPtr; 32 400 m_refs = newRefs; 33 401 return *this; 34 402} 35 403 36 404template<typename T> template<typename U> 37 405wp<T>& wp<T>::operator = (U* other) 38 406{ 39 407 weakref_type* newRefs = 40 408 other ? other->createWeak(this) : 0; 41 409 if (m_ptr) m_refs->decWeak(this); 42 410 m_ptr = other; 43 411 m_refs = newRefs; 44 412 return *this; 45 413} 46 414 47 415template<typename T> template<typename U> 48 416wp<T>& wp<T>::operator = (const wp<U>& other) 49 417{ 50 418 weakref_type* otherRefs(other.m_refs); 51 419 U* otherPtr(other.m_ptr); 52 420 if (otherPtr) otherRefs->incWeak(this); 53 421 if (m_ptr) m_refs->decWeak(this); 54 422 m_ptr = otherPtr; 55 423 m_refs = otherRefs; 56 424 return *this; 57 425} 58 426 59 427template<typename T> template<typename U> 60 428wp<T>& wp<T>::operator = (const sp<U>& other) 61 429{ 62 430 weakref_type* newRefs = 63 431 other != NULL ? other->createWeak(this) : 0; 64 432 U* otherPtr(other.m_ptr); 65 433 if (m_ptr) m_refs->decWeak(this); 66 434 m_ptr = otherPtr; 67 435 m_refs = newRefs; 68 436 return *this; 69 437}
三.使用注意事项
不能在把目标对象赋给一个长久存在的sp对象之前赋给一个短生命周期的sp对象,因为一旦短生命周期的sp对象被析构了,相应的引用计数对象就死亡了
四.总结
Android的RefBase和LightRefBase类是侵入式智能指针方案的基类,sp是配套的句柄类,为了解决堆里的sp对象没有RAII可用无法自动析构,引入了不完全句柄类wp,wp不影响实体RefBase对象的生存期,只能记录地址,阉割了对实体对象RefBase的包装能力(没有*,->,get函数),使用前需要成为sp,这时就可以通过weakref_impl感知到wp是否为野指针,weakref_impl对象记录了强弱引用计数(之所以也记录强引用计数而不是把它放进RefBase里是因为sp没了实体对象也就没了,实体对象里边的强引用对象自然也没了,而影子对象要根据强引用计数来判断实体对象的生存情况,所以影子对象里必须保存强引用计数),在实体类RefBase死了的情况下仍然存在,在wp升级为sp的过程中(attemptIncStrong函数)根据其中记录的强引用计数的值而让wp感知到是不是野指针(强引用计数为0),如果弱引用计数也没了,weakref_impl对象也可以析构了。所以强弱引用计数中,强引用计数决定的是RefBase实体类的生存(顺带也有weakref_impl);弱引用计数则决定了weakref_impl的生存,可以防止wp在不知情的情况下成为野指针。