使用koa:
koa2是一个类,所以引入koa后,要创建实例化“对象”,才能使用koa内部封装的方法。

设置监听端口:

处理http请求:
1、http请求处理链
A、通过app.use()注册async异步函数
B、每收到一个http请求,koa就会调用通过app.use()注册的async异步函数,并传入ctx和next参数。
2、koa使用异步方法处理请求

async:异步函数
ctx:是由koa传入的封装了request和response的变量
3、next()
用await next()来调用下一个async函数
4、middleware
我们把每个async函数称为middleware
针对不同的url申请调用不同的异步函数:
底层的处理方式,是通过if判断请求的地址来进行区分的

使用if判断非常麻烦,使用koa-router省略这一个步骤

koa-router只能省略掉if判断的部分,最后要使用app.use()去调用koa-router这个异步函数

同理可以处理post请求
用post请求时,会遇到一个问题:post请求通常会发送一个表单,或者JSON,它作为request的body发送
但无论是Node.js提供的原始request对象,还是koa提供的request对象,都不提供解析request的body的功能!
引入另一个middleware ——koa-bodyparser解析request的body

用var name = ctx.request.body.name || ''拿到表单的name字段,如果该字段不存在,默认值设置为''
随着需要处理的url越来越多,app.js会显得特别的臃肿
在controller文件中集中描写url:
app.js不再放置url的异步函数处理方式
app.js只用于将所有controller文件夹中的url异步函数,引入,并使用app.use为其注册
引入+注册:就两个函数封装这一些功能

进一步简化app.js
将处理引入与注册url异步函数的方法,作为一个
Controller Middleware
进一步封装到controller.js中,去处理controller文件夹中的url异步函数
const fs = require('fs');
// add url-route in /controllers:
function addMapping(router, mapping) {
for (var url in mapping) {
if (url.startsWith('GET ')) {
var path = url.substring(4);
router.get(path, mapping[url]);
console.log(`register URL mapping: GET ${path}`);
} else if (url.startsWith('POST ')) {
var path = url.substring(5);
router.post(path, mapping[url]);
console.log(`register URL mapping: POST ${path}`);
} else if (url.startsWith('PUT ')) {
var path = url.substring(4);
router.put(path, mapping[url]);
console.log(`register URL mapping: PUT ${path}`);
} else if (url.startsWith('DELETE ')) {
var path = url.substring(7);
router.del(path, mapping[url]);
console.log(`register URL mapping: DELETE ${path}`);
} else {
console.log(`invalid URL: ${url}`);
}
}
}
function addControllers(router, dir) {
fs.readdirSync(__dirname + '/' + dir).filter((f) => {
return f.endsWith('.js');
}).forEach((f) => {
console.log(`process controller: ${f}...`);
let mapping = require(__dirname + '/' + dir + '/' + f);
addMapping(router, mapping);
});
}
module.exports = function (dir) {
let
controllers_dir = dir || 'controllers',
router = require('koa-router')();
addControllers(router, controllers_dir);
return router.routes();
};
这样app.js中只需要引入这个middleware,再调用就可以完成url的处理
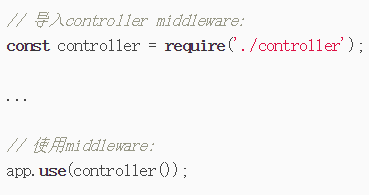
操作数据库:
ORM技术:Object-Relational Mapping,把关系数据库的表结构映射到js对象上。
ORM框架:Sequelize
数据库配置信息,在使用Sequelize操作MySQL需要放在参数里,告诉函数应该如何做
将其保存在config.js中
var config = { database: 'test', // 使用哪个数据库 username: 'www', // 用户名 password: 'www', // 口令 host: 'localhost', // 主机名 port: 3306 // 端口号,MySQL默认3306 }; module.exports = config;
1、创建Sequelize对象实例
//引入
const Sequelize = require('sequelize'); const config = require('./config'); //对象实例化 var sequelize = new Sequelize(config.database, config.username, config.password, { host: config.host, dialect: 'mysql', pool: { max: 5, min: 0, idle: 30000 } });
new Sequelize(database, [username=null], [password=null], [options={}])
//option可选填


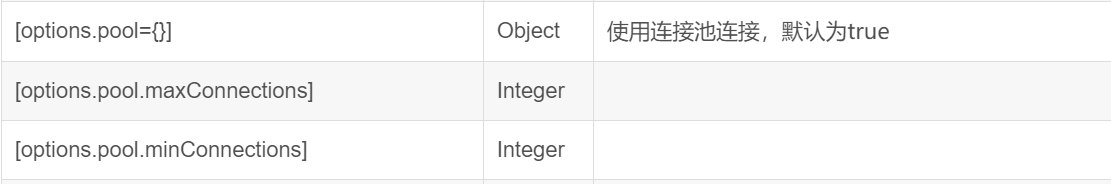

2、定义数据模型model让数据库可以创建表
//第一个参数传入名称Pet,默认的表名是Pets
//第二个参数指定列名和数据类型,如果是主键,需要更详细地指定。
//第三个参数是额外的配置,我们传入timestamps: false是为了关闭Sequelize的自动添加timestamp的功能
var Pet = sequelize.define('pet', { id: { type: Sequelize.STRING(50), primaryKey: true }, name: Sequelize.STRING(100), gender: Sequelize.BOOLEAN, birth: Sequelize.STRING(10), createdAt: Sequelize.BIGINT, updatedAt: Sequelize.BIGINT, version: Sequelize.BIGINT }, {
timestamps: false });
3、插入数据
promise方式
var now = Date.now(); Pet.create({ id: 'g-' + now, name: 'Gaffey', gender: false, birth: '2007-07-07', createdAt: now, updatedAt: now, version: 0 }).then(function (p) { console.log('created.' + JSON.stringify(p)); }).catch(function (err) { console.log('failed: ' + err); });
await方式
(async () => { var dog = await Pet.create({ id: 'd-' + now, name: 'Odie', gender: false, birth: '2008-08-08', createdAt: now, updatedAt: now, version: 0 }); console.log('created: ' + JSON.stringify(dog)); })();
4、查询数据
(async () => { var pets = await Pet.findAll({ where: { name: 'Gaffey' } }); console.log(`find ${pets.length} pets:`); for (let p of pets) { console.log(JSON.stringify(p)); } })();
5、更新数据
如果要更新数据,可以对查询到的实例调用save()方法: (async () => { var p = await queryFromSomewhere(); p.gender = true; p.updatedAt = Date.now(); p.version ++; await p.save(); })();
6、删除数据
(async () => { var p = await queryFromSomewhere(); await p.destroy(); })();
直接使用Sequelize虽然可以创建model,但是存在一些问题
混乱,不方便管理,不规范,无法复用
制定一个规范
A、model统一存放在models文件夹中
B、其次,每一个Model必须遵守一套规范:
- 统一主键,名称必须是
id,类型必须是STRING(50); - 主键可以自己指定,也可以由框架自动生成(如果为null或undefined);
- 所有字段默认为
NOT NULL,除非显式指定; - 统一timestamp机制,每个Model必须有
createdAt、updatedAt和version,分别记录创建时间、修改时间和版本号。其中,createdAt和updatedAt以BIGINT存储时间戳,最大的好处是无需处理时区,排序方便。version每次修改时自增。
这一套规范,不需要去记忆,而是通过一个db.js统一Model的定义:
const Sequelize = require('sequelize');
console.log('init sequelize...');
var sequelize = new Sequelize('dbname', 'username', 'password', {
host: 'localhost',
dialect: 'mysql',
pool: {
max: 5,
min: 0,
idle: 10000
}
});
const ID_TYPE = Sequelize.STRING(50);
function defineModel(name, attributes) {
var attrs = {};
for (let key in attributes) {
let value = attributes[key];
if (typeof value === 'object' && value['type']) {
value.allowNull = value.allowNull || false;
attrs[key] = value;
} else {
attrs[key] = {
type: value,
allowNull: false
};
}
}
attrs.id = {
type: ID_TYPE,
primaryKey: true
};
attrs.createdAt = {
type: Sequelize.BIGINT,
allowNull: false
};
attrs.updatedAt = {
type: Sequelize.BIGINT,
allowNull: false
};
attrs.version = {
type: Sequelize.BIGINT,
allowNull: false
};
return sequelize.define(name, attrs, {
tableName: name,
timestamps: false,
hooks: {
beforeValidate: function (obj) {
let now = Date.now();
if (obj.isNewRecord) {
if (!obj.id) {
obj.id = generateId();
}
obj.createdAt = now;
obj.updatedAt = now;
obj.version = 0;
} else {
obj.updatedAt = Date.now();
obj.version++;
}
}
}
});
}
怎么调用呢db.js创建model?举个例子!
//引入db.js
const db = require('../db'); //调用db.js中的defineModel,定义并暴露model module.exports = db.defineModel('users', { email: { type: db.STRING(100), unique: true }, passwd: db.STRING(100), name: db.STRING(100), gender: db.BOOLEAN });
在使用model进行数据库操作时候,每一次都要导入model,如果同时使用多个model,还要写多条语句去导入,显得特别麻烦
创建一个model.js自动化导入所有的model
const fs = require('fs');
const db = require('./db');
let files = fs.readdirSync(__dirname + '/models');
let js_files = files.filter((f)=>{
return f.endsWith('.js');
}, files);
module.exports = {};
for (let f of js_files) {
console.log(`import model from file ${f}...`);
let name = f.substring(0, f.length - 3);
module.exports[name] = require(__dirname + '/models/' + f);
}
module.exports.sync = () => {
db.sync();
};
使用model.js
//引入model.js
const model = require('./model'); //掉用导入 let Pet = model.Pet, User = model.User; var pet = await Pet.create({ ... });