1.图名,图例,轴标签,轴边界,轴刻度,轴刻度标签
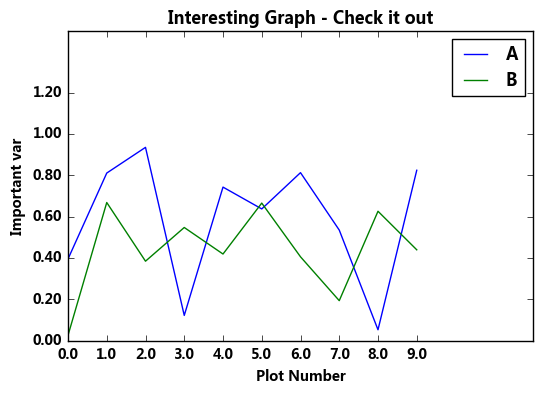
# 图名,图例,轴标签,轴边界,轴刻度,轴刻度标签等 df = pd.DataFrame(np.random.rand(10,2),columns=['A','B']) fig = df.plot(figsize=(6,4)) # figsize:创建图表窗口,设置窗口大小 # 创建图表对象,并赋值与fig plt.title('Interesting Graph - Check it out') # 图名 plt.xlabel('Plot Number') # x轴标签 plt.ylabel('Important var') # y轴标签 plt.legend(loc = 'upper right') # 显示图例,loc表示位置 # 'best' : 0, (only implemented for axes legends)(自适应方式) # 'upper right' : 1, # 'upper left' : 2, # 'lower left' : 3, # 'lower right' : 4, # 'right' : 5, # 'center left' : 6, # 'center right' : 7, # 'lower center' : 8, # 'upper center' : 9, # 'center' : 10, plt.xlim([0,12]) # x轴边界 plt.ylim([0,1.5]) # y轴边界 plt.xticks(range(10)) # 设置x刻度 plt.yticks([0,0.2,0.4,0.6,0.8,1.0,1.2]) # 设置y刻度 fig.set_xticklabels("%.1f" %i for i in range(10)) # x轴刻度标签 保留小数点后一位小数 fig.set_yticklabels("%.2f" %i for i in [0,0.2,0.4,0.6,0.8,1.0,1.2]) # y轴刻度标签 #保留小数点后2位小数
# 范围只限定图表的长度,刻度则是决定显示的标尺 → 这里x轴范围是0-12,但刻度只是0-9,刻度标签使得其显示1位小数 # 轴标签则是显示刻度的标签 print(fig,type(fig)) # 查看表格本身的显示方式,以及类别
输出结果:
Axes(0.125,0.125;0.775x0.775) <class 'matplotlib.axes._subplots.AxesSubplot'>
2.
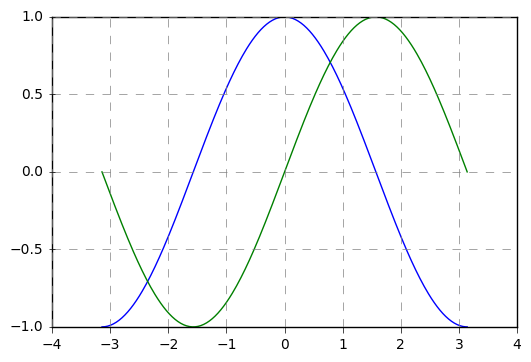
# 其他元素可视性 x = np.linspace(-np.pi,np.pi,256,endpoint = True) #linspace()通过指定开始值、终值和元素个数创建表示等差数列的一维数组,可以通过endpoint参数指定是否包含终值,默认值为True,即包含终值。 c, s = np.cos(x), np.sin(x) plt.plot(x, c) plt.plot(x, s) # 通过ndarry创建图表 plt.grid(True, linestyle = "--",color = "gray", linewidth = "0.5",axis = 'both') # 显示网格 # linestyle:线型 # color:颜色 # linewidth:宽度 # axis:x,y,both,显示x/y/两者的格网 plt.tick_params(bottom='on',top='off',left='on',right='off') # 显示刻度的那根轴线,凸出来的地方。设置为off时都不显示。默认为全显示 import matplotlib matplotlib.rcParams['xtick.direction'] = 'out' matplotlib.rcParams['ytick.direction'] = 'inout' # 设置刻度的方向,in,out,inout 设置为in,刻度突出的部分在里面显示,out在外面显示,inout在中间显示 # 这里需要导入matploltib,而不仅仅导入matplotlib.pyplot frame = plt.gca() #plt.axis('off') # 关闭坐标轴 #frame.axes.get_xaxis().set_visible(False) #frame.axes.get_yaxis().set_visible(False) # x/y 轴不可见
3.
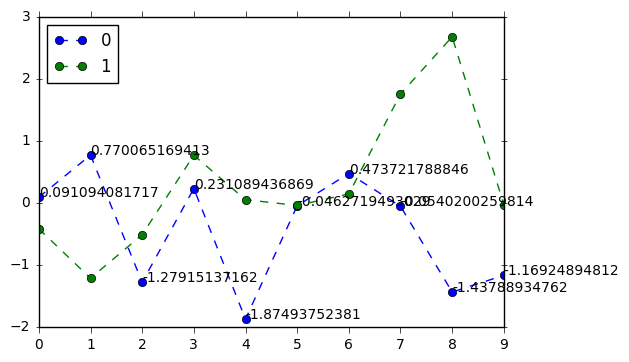
# 注解 df = pd.DataFrame(np.random.randn(10,2)) print(df) df.plot(style = '--o') # plt.text(5,0.5,'hahaha',fontsize=10) # 注解 → 横坐标,纵坐标,注解字符串 for i in range(10): plt.text(i,df[0].iloc[i],df[0].iloc[i],fontsize=10) #对0列的元素来说,标注y点的坐标。
输出:
0 1 0 0.091094 -0.417407 1 0.770065 -1.215896 2 -1.279151 -0.512889 3 0.231089 0.768293 4 -1.874938 0.051870 5 -0.046272 -0.041660 6 0.473722 0.144373 7 -0.054020 1.756313 8 -1.437889 2.679062 9 -1.169249 -0.029428
4. 图片保存
# 图表输出 df = pd.DataFrame(np.random.randn(1000, 4), columns=list('ABCD')) df = df.cumsum() df.plot(style = '--.',alpha = 0.5) plt.legend(loc = 'upper left') plt.savefig('C:/Users/Desktop/pdd.png', dpi=400, bbox_inches = 'tight', facecolor = 'g', edgecolor = 'b') # 可支持png,pdf,svg,ps,eps…等,以后缀名来指定 # dpi是分辨率 # bbox_inches:图表需要保存的部分。如果设置为‘tight’,则尝试剪除图表周围的空白部分。 # facecolor,edgecolor: 图像的背景色,默认为‘w’(白色)
