%% ============ Part 2: Compute Cost and Gradient ============ % In this part of the exercise, you will implement the cost and gradient % for logistic regression. You neeed to complete the code in % costFunction.m % Setup the data matrix appropriately, and add ones for the intercept term [m, n] = size(X); % Add intercept term to x and X_test X = [ones(m, 1) X]; % Initialize fitting parameters initial_theta = zeros(n + 1, 1); % Compute and display initial cost and gradient [cost, grad] = costFunction(initial_theta, X, y);
难点1:X和theta的维度变化,怎么变得,为什么?
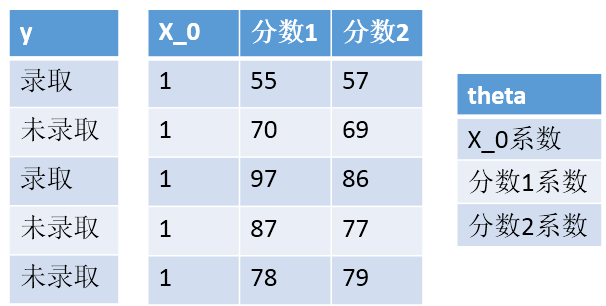
X加了一列1,θ加了一行θ0,因为最后边界是θ0+θ1X1+θ2X2,要符合矩阵运算
难点2:costFunction中grad是什么函数,有什么作用?
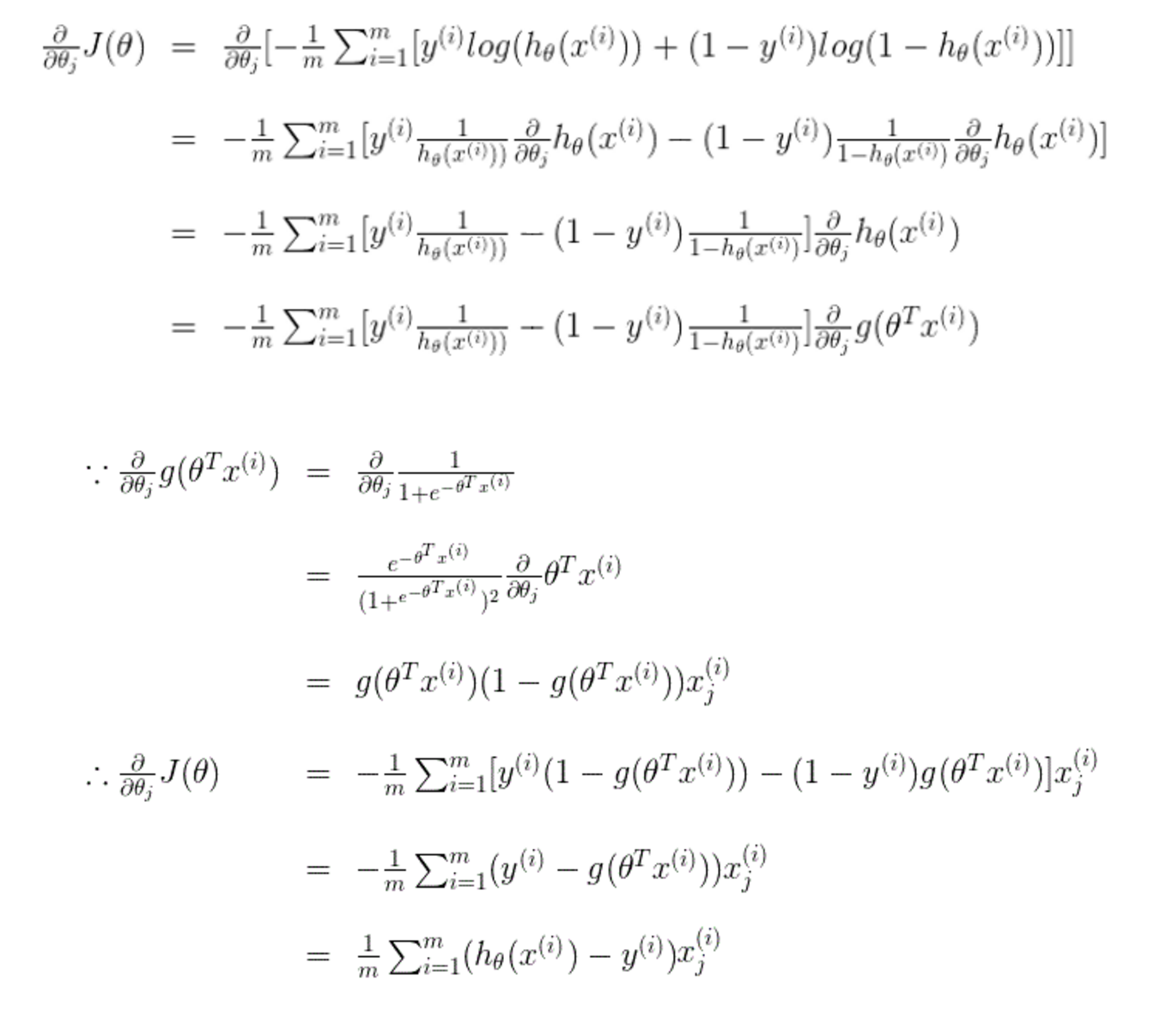
w.r.t 什么意思?
with regard to
with reference to
关于的意思
难点3:linear regression的代价函数和logistic regression的代价函数,为什么不一样?
和幂次有关,如果还用原来的代价函数,那么会有很多局部最值,没有办法梯度下降到最小值。

另一个解读角度:从最大似然函数出发考虑。
下面的文章写得很好,参考链接:
http://blog.csdn.net/lu597203933/article/details/38468303
http://blog.csdn.net/it_vitamin/article/details/45625143
%% ============= Part 3: Optimizing using fminunc ============= % In this exercise, you will use a built-in function (fminunc) to find the % optimal parameters theta. % Set options for fminunc options = optimset('GradObj', 'on', 'MaxIter', 400); % Run fminunc to obtain the optimal theta % This function will return theta and the cost [theta, cost] = ... fminunc(@(t)(costFunction(t, X, y)), initial_theta, options);
难点4:optimset是什么作用?
options = optimset('GradObj', 'on', 'MaxIter', 400); //
通过optimset函数设置或改变这些参数。其中有的参数适用于所有的优化算法,有的则只适用于大型优化问题,另外一些则只适用于中型问题。
LargeScale – 当设为'on'时使用大型算法,若设为'off'则使用中型问题的算法。
适用于大型和中型算法的参数:
Diagnostics – 打印最小化函数的诊断信息。
Display – 显示水平。选择'off',不显示输出;选择'iter',显示每一步迭代过程的输出;选择'final',显示最终结果。打印最小化函数的诊断信息。
GradObj – 用户定义的目标函数的梯度。对于大型问题此参数是必选的,对于中型问题则是可选项。
MaxFunEvals – 函数评价的最大次数。
MaxIter – 最大允许迭代次数。
TolFun – 函数值的终止容限。
TolX – x处的终止容限。
options = optimset('param1',value1,'param2',value2,...) %设置所有参数及其值,未设置的为默认值
options = optimset('GradObj', 'on', 'MaxIter', 400);
在使用options的函数中,参数是由用户自行定义的,最大递归次数为400
难点5:[theta, cost] = fminunc(@(t)(costFunction(t, X, y)), initial_theta, options)是怎么实现功能?
关于句柄@,参考偏文章:http://blog.csdn.net/gzp444280620/article/details/49252491
关于fiminuc,参考这篇文章:http://blog.csdn.net/gzp444280620/article/details/49272977
fminunc(@(t)(costFunction(t, X, y)), initial_theta, options); %是为了当代码里面有这样的函数的时候,fminunc(1,θ,option)第一个参数,
会传递给costFunction(t, X, y)的第一个参数里面进行计算。
function plotDecisionBoundary(theta, X, y) %PLOTDECISIONBOUNDARY Plots the data points X and y into a new figure with %the decision boundary defined by theta % PLOTDECISIONBOUNDARY(theta, X,y) plots the data points with + for the % positive examples and o for the negative examples. X is assumed to be % a either % 1) Mx3 matrix, where the first column is an all-ones column for the % intercept. % 2) MxN, N>3 matrix, where the first column is all-ones % Plot Data plotData(X(:,2:3), y); hold on if size(X, 2) <= 3 % Only need 2 points to define a line, so choose two endpoints plot_x = [min(X(:,2))-2, max(X(:,2))+2]; % Calculate the decision boundary line//令theta装置乘以X等于0,即可 plot_y = (-1./theta(3)).*(theta(2).*plot_x + theta(1)); % Plot, and adjust axes for better viewing plot(plot_x, plot_y) % Legend, specific for the exercise legend('Admitted', 'Not admitted', 'Decision Boundary') axis([30, 100, 30, 100]) else % Here is the grid range u = linspace(-1, 1.5, 50); v = linspace(-1, 1.5, 50); z = zeros(length(u), length(v)); % Evaluate z = theta*x over the grid for i = 1:length(u) for j = 1:length(v) z(i,j) = mapFeature(u(i), v(j))*theta; end end z = z'; % important to transpose z before calling contour % Plot z = 0 % Notice you need to specify the range [0, 0] contour(u, v, z, [0, 0], 'LineWidth', 2) end hold off end
难点6:这个plotDecisionBoundary函数是怎么画出边界的?
plotDecisionBoundary中的下面的两行看不懂:
plot_x = [min(X(:,2))-2, max(X(:,2))+2]; //直线的参数其实已经得到,选划线的范围,把直线画出来即可。为了美观,扩大了两个单位
% Calculate the decision boundary line//令theta装置乘以X等于0,即可 plot_y = (-1./theta(3)).*(theta(2).*plot_x + theta(1));
plot_y = (-1./theta(3)).*(theta(2).*plot_x + theta(1));
function plotData(X, y) //会按照真类和假类分类 画出输入的点 %PLOTDATA Plots the data points X and y into a new figure % PLOTDATA(x,y) plots the data points with + for the positive examples % and o for the negative examples. X is assumed to be a Mx2 matrix. % Create New Figure figure; hold on; % ====================== YOUR CODE HERE ====================== % Instructions: Plot the positive and negative examples on a % 2D plot, using the option 'k+' for the positive % examples and 'ko' for the negative examples. % % Find Indices of Positive and Negative Examples //返回 y=1和y=0的位置,也就是行数 pos = find(y==1); neg = find(y == 0); //利用find的查找功能,把正类和负类分开,并把横纵坐标保存在pos里面 % Plot Examples plot(X(pos, 1), X(pos, 2), 'k+','LineWidth', 2, ... 'MarkerSize', 7); plot(X(neg, 1), X(neg, 2), 'ko', 'MarkerFaceColor', 'y', ... 'MarkerSize', 7); % ========================================================================= hold off; end
%% =========== Part 1: Regularized Logistic Regression ============ % In this part, you are given a dataset with data points that are not % linearly separable. However, you would still like to use logistic % regression to classify the data points. % % To do so, you introduce more features to use -- in particular, you add % polynomial features to our data matrix (similar to polynomial % regression). % % Add Polynomial Features % Note that mapFeature also adds a column of ones for us, so the intercept % term is handled X = mapFeature(X(:,1), X(:,2)); % Initialize fitting parameters initial_theta = zeros(size(X, 2), 1); % Set regularization parameter lambda to 1 lambda = 1; % Compute and display initial cost and gradient for regularized logistic % regression [cost, grad] = costFunctionReg(initial_theta, X, y, lambda);
难点7:mapFeature是怎么工作的,原理?
难点8:[cost, grad] = costFunctionReg(initial_theta, X, y, lambda);怎么工作?
%% ============= Part 2: Regularization and Accuracies ============= % Optional Exercise: % In this part, you will get to try different values of lambda and % see how regularization affects the decision coundart % % Try the following values of lambda (0, 1, 10, 100). % % How does the decision boundary change when you vary lambda? How does % the training set accuracy vary? % % Initialize fitting parameters initial_theta = zeros(size(X, 2), 1); % Set regularization parameter lambda to 1 (you should vary this) lambda = 1; % Set Options options = optimset('GradObj', 'on', 'MaxIter', 400); % Optimize [theta, J, exit_flag] = ... fminunc(@(t)(costFunctionReg(t, X, y, lambda)), initial_theta, options);
难点9:为什么fminunc可以返回三个变量?
ps:先把问题记录一下,稍后会一个个解决。