方法说明
- oninvoke方法:必须具有与真实的被调用方法sayHello相同的入参列表:例如,oninvoke(String name)
- onreturn方法:至少要有一个入参且第一个入参必须与sayHello的返回类型相同,接收返回结果:例如,onreturnWithoutParam(String result),可以有多个参数,多个参数的情况下,第一个后边的所有参数都是用来接收sayHello入参的:例如, onreturn(String result, String name)
- onthrow方法:至少要有一个入参且第一个入参类型为Throwable或其子类,接收返回结果;例如,onthrow(Throwable ex),可以有多个参数,多个参数的情况下,第一个后边的所有参数都是用来接收sayHello入参的:例如,onthrow(Throwable ex, String name)
- 如果是consumer在调用provider的过程中,出现异常时不会走onthrow方法的,onthrow方法只会在provider返回的RpcResult中含有Exception对象时,才会执行。(dubbo中下层服务的Exception会被放在响应RpcResult的exception对象中传递给上层服务)
一、使用示例
服务消费者端
public interface Notify { void onreturnNoParam(String result); // 调用之后,没有参数的 void onreturn(String result, String name); // 调用之后 void onthrow(Throwable ex, String name); // 出现异常 } public class NotifyService implements Notify { @Override public void onreturnNoParam(String result) { System.out.println("======onreturnNoParam======, result: " + result); } @Override public void onreturn(String result, String name) { System.out.println("======onreturn======, param: " + name + ", result: " + result); } @Override public void onthrow(Throwable ex, String name) { System.out.println("======onthrow======, param: " + name + ", exception: " + ex.getMessage()); } }
测试结果输出:
main方法直接返回的结果:null
======onreturn======, param: world, result: Hello world, response form provider: 192.168.215.1:20880
注意:如果上面使用的是异步,则返回的结果为null
二、源码分析
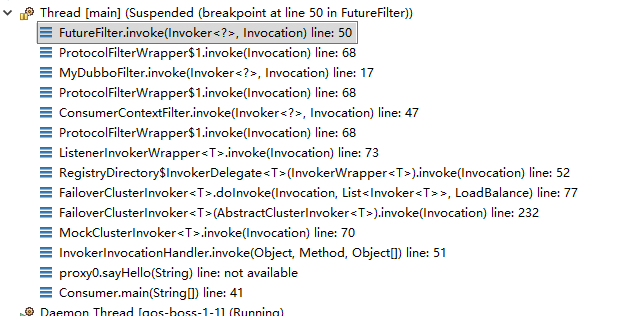
整个事件通知的逻辑都在FutureFilter中,来看一下源码:
public Result invoke(final Invoker<?> invoker, final Invocation invocation) throws RpcException { final boolean isAsync = RpcUtils.isAsync(invoker.getUrl(), invocation); // 1 调用服务之前:执行xxxService.oninvoke方法 fireInvokeCallback(invoker, invocation); // need to configure if there's return value before the invocation in order to help invoker to judge if it's // necessary to return future. // 2 调用服务 Result result = invoker.invoke(invocation); // 3 调用服务之后 if (isAsync) { asyncCallback(invoker, invocation); } else { syncCallback(invoker, invocation, result); } // 4 返回调用结果 return result; }
fireInvokeCallback
反射执行xxxService.oninvoke方法:必须具有与真实的被调用方法sayHello相同的入参列表。
private void fireInvokeCallback(final Invoker<?> invoker, final Invocation invocation) { final Method onInvokeMethod = (Method) StaticContext.getSystemContext().get(StaticContext.getKey(invoker.getUrl(), invocation.getMethodName(), Constants.ON_INVOKE_METHOD_KEY)); final Object onInvokeInst = StaticContext.getSystemContext().get(StaticContext.getKey(invoker.getUrl(), invocation.getMethodName(), Constants.ON_INVOKE_INSTANCE_KEY)); if (onInvokeMethod == null && onInvokeInst == null) { return; } if (onInvokeMethod == null || onInvokeInst == null) { throw new IllegalStateException("service:" + invoker.getUrl().getServiceKey() + " has a onreturn callback config , but no such " + (onInvokeMethod == null ? "method" : "instance") + " found. url:" + invoker.getUrl()); } if (onInvokeMethod != null && !onInvokeMethod.isAccessible()) { onInvokeMethod.setAccessible(true); } // 获取真实方法sayHello传入的参数 Object[] params = invocation.getArguments(); try { onInvokeMethod.invoke(onInvokeInst, params); } catch (InvocationTargetException e) { fireThrowCallback(invoker, invocation, e.getTargetException()); } catch (Throwable e) { fireThrowCallback(invoker, invocation, e); } }
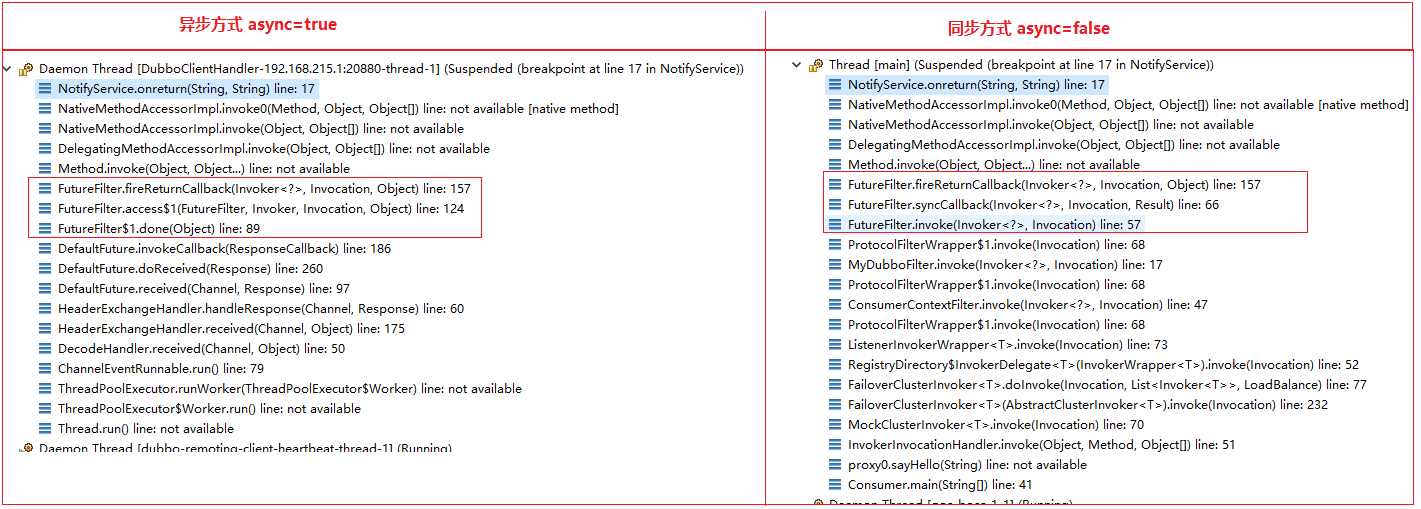
再来看一下同步调用和异步调用
private void asyncCallback(final Invoker<?> invoker, final Invocation invocation) { Future<?> f = RpcContext.getContext().getFuture(); if (f instanceof FutureAdapter) { ResponseFuture future = ((FutureAdapter<?>) f).getFuture(); // 3.1 调用服务之后:设置回调ResponseCallback对象到DefaultFuture中, // 当provider返回响应时,执行DefaultFuture.doReceived方法,该方法会调用ResponseCallback对象的done或者caught方法 future.setCallback(new ResponseCallback() { public void done(Object rpcResult) { if (rpcResult == null) { logger.error(new IllegalStateException("invalid result value : null, expected " + Result.class.getName())); return; } ///must be rpcResult if (!(rpcResult instanceof Result)) { logger.error(new IllegalStateException("invalid result type :" + rpcResult.getClass() + ", expected " + Result.class.getName())); return; } Result result = (Result) rpcResult; if (result.hasException()) { fireThrowCallback(invoker, invocation, result.getException()); } else { fireReturnCallback(invoker, invocation, result.getValue()); } } public void caught(Throwable exception) { fireThrowCallback(invoker, invocation, exception); } }); } }
private void syncCallback(final Invoker<?> invoker, final Invocation invocation, final Result result) { if (result.hasException()) { //3.1 调用服务之后:如果返回结果异常信息(注意:如果是consumer自己throw的异常,会在2的时候直接抛走,不会走到这里),直接执行xxxService.onthrow方法 fireThrowCallback(invoker, invocation, result.getException()); } else { //3.2 调用服务之后:如果返回值正常,执行xxxService.onreturn方法 fireReturnCallback(invoker, invocation, result.getValue()); } }
异步与同步的区别