1、spring-data-commons项目
spring-data-commons项目是所有spring-data项目的核心,我们来看一下该项目下的repository包中的接口和注解。
2、Repository<T,ID>接口和@RepositoryDefinition注解
当中最重要的就是Repository接口了。它是做数据库操作的最底层的抽象接口、最顶级的父类,打开Repository接口看其源码,发现里面其实什么方法都没有,仅仅起到一个标识作用。捕获要管理的域类型和域类的id类型。用途是保存类型信息,并能够在类路径扫描期间发现继承该接口的接口,帮助我们创建代理类。
@Indexed public interface Repository<T, ID> { }
@Indexed 我们发现在Repository接口上有一个@Indexed 注解,是Spring5提供的注解,用于提升应用启动性能。这个注解单独存在不起作用,要想使其生效的话,要添加spring-context-indexer依赖。在编译时会将@CompoentScan扫描指定package中要生成的bean写在METE-INF/spring.components文件中,当项目启动时,就会读取这个文件,不会再扫描指定的package了,从而提升性能。
我们只要继承Repository接口,并根据它的规则来命名接口方法,就可以进行数据库操作。(与继承Repository接口相等价的就是,在接口上添加@RepositoryDefinition注解)
示例:
/**
* 书籍持久层
* @author caofanqi
* 使用@RepositoryDefinition注解与继承Repository具有相同的效果
*/
//@RepositoryDefinition(domainClass = Book.class,idClass = Long.class)
public interface BookRepository extends Repository<Book,Long>{
/**
* 根据书名查找书籍
* @param bookName 书籍名称
* @return 该书籍名称的书列表
*/
List<Book> findBooksByBookNameContains(String bookName);
}
@Transactional
@Rollback(false) @SpringBootTest class BookRepositoryTest { @Resource private BookRepository bookRepository; @Test void findBooksByBookNameContains() { System.out.println("bookRepository : " + bookRepository.getClass().getName()); List<Book> books = bookRepository.findBooksByBookNameContains("Java"); System.out.println(books); } }
这样就会根据我们传入的参数去like查询符合条件的书籍,生成的sql语句如下:

3、CrudRepository<T,ID>接口与注解@NoRepositoryBean
CrudRepository是Repository接口的子接口,提供了一套通用的CRUD方法。接口上的@NoRepositoryBean注解的意思是,不让Spring生成该类的代理类。
@NoRepositoryBean //不让Spring为该类生成代理类,仅仅提供一套通用的CRUD方法。 public interface CrudRepository<T, ID> extends Repository<T, ID> { /** * 保存方法*/ <S extends T> S save(S entity); /** * 保存*/ <S extends T> Iterable<S> saveAll(Iterable<S> entities); /** * 根据id进行查询*/ Optional<T> findById(ID id); /** * 判断给定id的数据是否存在*/ boolean existsById(ID id); /** * 查询全部,数据量很大的时候,谨慎使用*/ Iterable<T> findAll(); /** * 根据给定ids查询符合条件的数据 */ Iterable<T> findAllById(Iterable<ID> ids); /** * 统计条数*/ long count(); /** * 根据id删除*/ void deleteById(ID id); /** * 删除给定实体*/ void delete(T entity); /** * 删除给定实体*/ void deleteAll(Iterable<? extends T> entities); /** * 删除全部 */ void deleteAll(); }
我们要想使用这些方法,只需自己的Repository继承该接口即可。
4、PagingAndSortingRepository<T,ID>接口
是CrudRepository的子接口,也不会生成代理,只是提供分页和排序的方法。
@NoRepositoryBean public interface PagingAndSortingRepository<T, ID> extends CrudRepository<T, ID> { /** * 根据sort去所有对象排序的集合*/ Iterable<T> findAll(Sort sort); /** * 根据pageable进行分页,pageable中可以包含sort*/ Page<T> findAll(Pageable pageable); }
分页相关对象:
Sort查询的排序选项,至少提供一个属性列表来进行排序,不能是null或空,默认是升序ASC;
可以通过Sort.by 来构建Sort对象:
public static Sort by(String... properties) 根据给定的属性列表进行升序排序;
public static Sort by(Direction direction, String... properties) 指定属性和排序方向,Direction.ASC(升序)、Direction.DESC(降序);
public static Sort by(Order... orders)/public static Sort by(List<Order> orders) 根据给定的一组order进行排序。
可以通过Sort.and()方法将多个sort组合再一起,通过Sort.ascending()/Sort.descending指定排序方向。
还可以通过Sort.sort(Class<T> type) 来构造类型安全的排序对象:
public static <T> TypedSort<T> sort(Class<T> type) 根据指定class类型构造该类型的typeSort排序对象;
通过TypedSort.by 方法来构建排序字段,通过ascending()/descending指定排序方向,使用and()方法进行连接。
Order,实现一个排序对,提供方向和属性,为sort提供输入。也就是说,可以针对每一个属性设置不同的升序或降序。
可以通过一下方式来构建Order对象:
public static Order by(String property) ,指定属性返回order对象,默认使用升序。
public static Order asc(String property),返回指定属性升序的order对象。
public static Order desc(String property),返回指定属性降序的order对象。
Pageable分页信息的抽象接口,实现类是PageRequest;
可以通过一下方式来构建Pageable对象:
public static PageRequest of(int page, int size),创建一个未排序的PageRequest,page从0开始;
public static PageRequest of(int page, int size, Direction direction, String... properties),创建一个根据给定方向和属性排序的分页对象。
public static PageRequest of(int page, int size, Sort sort),创建一个根据sort进行排序的分页对象。
Page,封装分页结果信息,可以通过如下方法获取分页信息。
page.getContent() ,分页查询结果列表;
page.getNumberOfElements(),当前分页结果列表中的元素个数;
page.getTotalElements(),当前条件下总条数;
page.getTotalPages(),总页数;
page.getNumber(),我们自己传的page;
page.getSize(),我们自己传入的size。
代码示例:
@Test
void testPagingAndSortingRepository(){
// Sort.Order id = Sort.Order.by("id");
// Sort.Order bookName = Sort.Order.desc("bookName");
// Sort sort = Sort.by(id,bookName);
//等价于上面三句代码
// Sort sort = Sort.by("id").ascending().and(Sort.by("bookName").descending());
//使用类型安全的排序
Sort.TypedSort<Book> bookTypedSort = Sort.sort(Book.class);
Sort sort = bookTypedSort.by(Book::getId).ascending()
.and(bookTypedSort.by(Book::getBookName).descending());
Pageable pageable = PageRequest.of(2,2, sort);
Page<Book> page = bookRepository.findAll(pageable);
System.out.println("分页查询结果列表:" + page.getContent());
System.out.println("当前分页结果列表中的元素个数:" + page.getNumberOfElements());
System.out.println("当前条件下总条数:" + page.getTotalElements());
System.out.println("总页数:" +page.getTotalPages());
System.out.println("我们自己传的page:" +page.getNumber());
System.out.println("我们自己传入的size:" +page.getSize());
}
5、QueryByExampleExecutor<T>接口
该接口位于spring-data-commons项目的repository.query包中,允许通过实例来进行查询,可以通过该接口来进行简单的动态查询。使用的话,自己的repository继承QueryByExampleExecutor并指定域类型,就可以使用它提供的功能了。
public interface QueryByExampleExecutor<T> { /** * 根据Example查找一个对象*/ <S extends T> Optional<S> findOne(Example<S> example); /** * 根据Example查找一批对象*/ <S extends T> Iterable<S> findAll(Example<S> example); /** * 根据Example查找一批对象,并排序*/ <S extends T> Iterable<S> findAll(Example<S> example, Sort sort); /** * 根据Example查找一批对象,并分页排序*/ <S extends T> Page<S> findAll(Example<S> example, Pageable pageable); /** * 根据Example查找,返回符合条件的对象个数*/ <S extends T> long count(Example<S> example); /** * 判断符合给定Example的对象是否存在*/ <S extends T> boolean exists(Example<S> example); }
ExampleMatcher源码分析:
package org.springframework.data.domain; import lombok.AccessLevel; import lombok.EqualsAndHashCode; import lombok.RequiredArgsConstructor; import lombok.experimental.FieldDefaults; import java.util.Collection; import java.util.LinkedHashMap; import java.util.Map; import java.util.Optional; import java.util.Set; import java.util.function.Function; import org.springframework.lang.Nullable; import org.springframework.util.Assert; /** * 用于示例查询(QBE)的属性路径匹配规范 */ public interface ExampleMatcher { /** * 创建一个新的匹配器,默认情况下,probe中所有的非空属性都匹配。即所有的属性条件用and连接。 */ static ExampleMatcher matching() { return matchingAll(); } /** * 创建一个新的匹配器,probe中所有的非空属性匹配一个即可。即所有的属性条件用or连接。 */ static ExampleMatcher matchingAny() { return new TypedExampleMatcher().withMode(MatchMode.ANY); } /** *创建一个新的匹配器,probe中所有的非空属性都匹配。即所有的属性条件用and连接。 */ static ExampleMatcher matchingAll() { return new TypedExampleMatcher().withMode(MatchMode.ALL); } /** * 返回一个新的匹配器,忽略给定路径的匹配。属性传入这个方法,生成的条件中就不会包含该属性。一般用于基本数据类型。 */ ExampleMatcher withIgnorePaths(String... ignoredPaths); /** * 返回一个新的匹配器,设置默认的字符串的匹配规则。默认是StringMatcher.DEFAULT(=) 。 * */ ExampleMatcher withStringMatcher(StringMatcher defaultStringMatcher); /** * 返回一个新的匹配器,忽略大小写匹配(还要看数据库是否支持大小写区分)。 */ default ExampleMatcher withIgnoreCase() { return withIgnoreCase(true); } /** * 返回一个新的匹配器,设置是否忽略大小写匹配(还要看数据库是否支持大小写区分)。 */ ExampleMatcher withIgnoreCase(boolean defaultIgnoreCase); /** * 返回一个新的匹配器,设置指定属性的匹配方式(使用lambda方式)。 */ default ExampleMatcher withMatcher(String propertyPath, MatcherConfigurer<GenericPropertyMatcher> matcherConfigurer) { Assert.hasText(propertyPath, "PropertyPath must not be empty!"); Assert.notNull(matcherConfigurer, "MatcherConfigurer must not be empty!"); GenericPropertyMatcher genericPropertyMatcher = new GenericPropertyMatcher(); matcherConfigurer.configureMatcher(genericPropertyMatcher); return withMatcher(propertyPath, genericPropertyMatcher); } /** * 返回一个新的匹配器,设置指定属性的匹配方式(原始方式)。 */ ExampleMatcher withMatcher(String propertyPath, GenericPropertyMatcher genericPropertyMatcher); /** * 属性转换器 */ ExampleMatcher withTransformer(String propertyPath, PropertyValueTransformer propertyValueTransformer); /** * 返回一个新的匹配器,指定属性忽略大小写。 */ ExampleMatcher withIgnoreCase(String... propertyPaths); /** * 返回一个新的匹配器,将probe中的null属性也作为过滤条件。如:bookName is null。 * */ default ExampleMatcher withIncludeNullValues() { return withNullHandler(NullHandler.INCLUDE); } /** * 返回一个新的匹配器,将probe中的null属性忽略,不作为过滤条件。 */ default ExampleMatcher withIgnoreNullValues() { return withNullHandler(NullHandler.IGNORE); } /** * 返回一个新的匹配器,设置null值处理器。 */ ExampleMatcher withNullHandler(NullHandler nullHandler); /** * 获得null处理器。 */ NullHandler getNullHandler(); /** * 获取默认的字符串匹配器。 */ StringMatcher getDefaultStringMatcher(); /** * 如果忽略字符串大小写,返回true。 */ boolean isIgnoreCaseEnabled(); /** * 判断是否是忽略属性。 */ default boolean isIgnoredPath(String path) { return getIgnoredPaths().contains(path); } /** * 获取忽略属性集合。 */ Set<String> getIgnoredPaths(); /** * 属性特定查询方式。 */ PropertySpecifiers getPropertySpecifiers(); /** * 是否是全匹配。 */ default boolean isAllMatching() { return getMatchMode().equals(MatchMode.ALL); } /** * 是否是任意匹配。 */ default boolean isAnyMatching() { return getMatchMode().equals(MatchMode.ANY); } /** * 获取匹配方式。 */ MatchMode getMatchMode(); /** * null处理器枚举。 */ enum NullHandler { INCLUDE, IGNORE } /** * 回调配置匹配器。 */ interface MatcherConfigurer<T> { void configureMatcher(T matcher); } /** * 通用属性匹配。 */ @EqualsAndHashCode class GenericPropertyMatcher { @Nullable StringMatcher stringMatcher = null; @Nullable Boolean ignoreCase = null; PropertyValueTransformer valueTransformer = NoOpPropertyValueTransformer.INSTANCE; public GenericPropertyMatcher() {} /** * 通过字符串匹配器,是否忽略大小写构建GenericPropertyMatcher。 */ public static GenericPropertyMatcher of(StringMatcher stringMatcher, boolean ignoreCase) { return new GenericPropertyMatcher().stringMatcher(stringMatcher).ignoreCase(ignoreCase); } /** *通过字符串匹配器构建GenericPropertyMatcher。 */ public static GenericPropertyMatcher of(StringMatcher stringMatcher) { return new GenericPropertyMatcher().stringMatcher(stringMatcher); } /** * 设置忽略大小写。 */ public GenericPropertyMatcher ignoreCase() { this.ignoreCase = true; return this; } /** * 设置是否忽略大小写。 */ public GenericPropertyMatcher ignoreCase(boolean ignoreCase) { this.ignoreCase = ignoreCase; return this; } /** * 设置区分大小写。 */ public GenericPropertyMatcher caseSensitive() { this.ignoreCase = false; return this; } /** * 包含给定属性值。 */ public GenericPropertyMatcher contains() { this.stringMatcher = StringMatcher.CONTAINING; return this; } /** * 以给定属性值结尾。 */ public GenericPropertyMatcher endsWith() { this.stringMatcher = StringMatcher.ENDING; return this; } /** * 以给定属性值开头。 */ public GenericPropertyMatcher startsWith() { this.stringMatcher = StringMatcher.STARTING; return this; } /** * 精确匹配。 */ public GenericPropertyMatcher exact() { this.stringMatcher = StringMatcher.EXACT; return this; } /** * 默认规则。 */ public GenericPropertyMatcher storeDefaultMatching() { this.stringMatcher = StringMatcher.DEFAULT; return this; } /** * 正则匹配。 */ public GenericPropertyMatcher regex() { this.stringMatcher = StringMatcher.REGEX; return this; } /** * 给定string匹配器。 */ public GenericPropertyMatcher stringMatcher(StringMatcher stringMatcher) { Assert.notNull(stringMatcher, "StringMatcher must not be null!"); this.stringMatcher = stringMatcher; return this; } /** * 设置属性转换器 */ public GenericPropertyMatcher transform(PropertyValueTransformer propertyValueTransformer) { Assert.notNull(propertyValueTransformer, "PropertyValueTransformer must not be null!"); this.valueTransformer = propertyValueTransformer; return this; } } /** * 用于创建GenericPropertyMatcher。 */ class GenericPropertyMatchers { /** * 忽略大小写的。 */ public static GenericPropertyMatcher ignoreCase() { return new GenericPropertyMatcher().ignoreCase(); } /** * 不忽略大小写的。 */ public static GenericPropertyMatcher caseSensitive() { return new GenericPropertyMatcher().caseSensitive(); } /** * 包含。 */ public static GenericPropertyMatcher contains() { return new GenericPropertyMatcher().contains(); } /** * 以结尾。 */ public static GenericPropertyMatcher endsWith() { return new GenericPropertyMatcher().endsWith(); } /** * 以开始。 */ public static GenericPropertyMatcher startsWith() { return new GenericPropertyMatcher().startsWith(); } /** * 精确匹配。 */ public static GenericPropertyMatcher exact() { return new GenericPropertyMatcher().exact(); } /** * 默认方式。 */ public static GenericPropertyMatcher storeDefaultMatching() { return new GenericPropertyMatcher().storeDefaultMatching(); } /** * 正则。 */ public static GenericPropertyMatcher regex() { return new GenericPropertyMatcher().regex(); } } /** * 字符串匹配模式。 */ enum StringMatcher { /** * 默认,效果同EXACT。 */ DEFAULT, /** * 精确,相等。 */ EXACT, /** * 开头匹配。 */ STARTING, /** * 结尾匹配。 */ ENDING, /** * 包含,模糊匹配。 */ CONTAINING, /** * 正则匹配。 */ REGEX; } /** * 属性转换器,一般不需要设置。 */ interface PropertyValueTransformer extends Function<Optional<Object>, Optional<Object>> {} /** */ enum NoOpPropertyValueTransformer implements ExampleMatcher.PropertyValueTransformer { INSTANCE; @Override @SuppressWarnings("null") public Optional<Object> apply(Optional<Object> source) { return source; } } /** * 属性特定查询方式 */ @FieldDefaults(makeFinal = true, level = AccessLevel.PRIVATE) @RequiredArgsConstructor(access = AccessLevel.PRIVATE) @EqualsAndHashCode class PropertySpecifier { String path; @Nullable StringMatcher stringMatcher; @Nullable Boolean ignoreCase; PropertyValueTransformer valueTransformer; PropertySpecifier(String path) { Assert.hasText(path, "Path must not be null/empty!"); this.path = path; this.stringMatcher = null; this.ignoreCase = null; this.valueTransformer = NoOpPropertyValueTransformer.INSTANCE; } public PropertySpecifier withStringMatcher(StringMatcher stringMatcher) { Assert.notNull(stringMatcher, "StringMatcher must not be null!"); return new PropertySpecifier(this.path, stringMatcher, this.ignoreCase, this.valueTransformer); } public PropertySpecifier withIgnoreCase(boolean ignoreCase) { return new PropertySpecifier(this.path, this.stringMatcher, ignoreCase, this.valueTransformer); } public PropertySpecifier withValueTransformer(PropertyValueTransformer valueTransformer) { Assert.notNull(valueTransformer, "PropertyValueTransformer must not be null!"); return new PropertySpecifier(this.path, this.stringMatcher, this.ignoreCase, valueTransformer); } public String getPath() { return path; } @Nullable public StringMatcher getStringMatcher() { return stringMatcher; } @Nullable public Boolean getIgnoreCase() { return ignoreCase; } public PropertyValueTransformer getPropertyValueTransformer() { return valueTransformer == null ? NoOpPropertyValueTransformer.INSTANCE : valueTransformer; } public Optional<Object> transformValue(Optional<Object> source) { return getPropertyValueTransformer().apply(source); } } /** * 特定属性查询方式集合 */ @EqualsAndHashCode class PropertySpecifiers { private final Map<String, PropertySpecifier> propertySpecifiers = new LinkedHashMap<>(); PropertySpecifiers() {} PropertySpecifiers(PropertySpecifiers propertySpecifiers) { this.propertySpecifiers.putAll(propertySpecifiers.propertySpecifiers); } public void add(PropertySpecifier specifier) { Assert.notNull(specifier, "PropertySpecifier must not be null!"); propertySpecifiers.put(specifier.getPath(), specifier); } public boolean hasSpecifierForPath(String path) { return propertySpecifiers.containsKey(path); } public PropertySpecifier getForPath(String path) { return propertySpecifiers.get(path); } public boolean hasValues() { return !propertySpecifiers.isEmpty(); } public Collection<PropertySpecifier> getSpecifiers() { return propertySpecifiers.values(); } } /** * 匹配方式。 */ enum MatchMode { ALL, ANY; } }
示例代码:
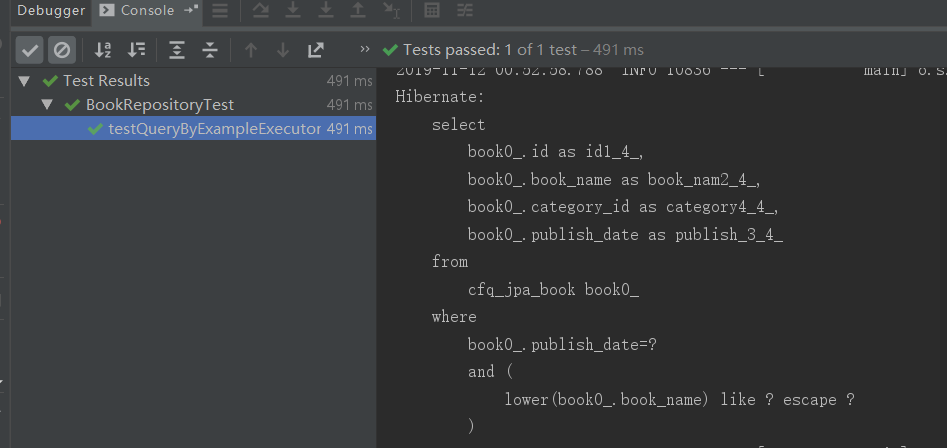
@Test void testQueryByExampleExecutor(){ Book book = Book.builder().bookName("java").publishDate(LocalDate.of(2019,11,11)).id(1L).build(); ExampleMatcher matcher = ExampleMatcher.matching() .withIgnorePaths("id") //忽略id属性,不管id有没有值,都不作为查询条件。 .withIgnoreNullValues() //忽略属性为null的,不作为查询条件。 .withMatcher("bookName",m -> m.startsWith().ignoreCase()) //设置bookName属性,前包含,忽略大小写。 .withTransformer("publishDate",value -> Optional.of(LocalDate.of(2019,11,12))); //转换属性值 Example<Book> example = Example.of(book,matcher); List<Book> books = bookRepository.findAll(example); }
生成的sql语句:
Spring-Data-Jpa官网的字符串匹配举例

QueryByExampleExecutor最佳实践:
首先要判断是否需要我们自己构建匹配器,如果默认匹配器,可以完成,我们就不需要创建。
判断null值是否要作为条件,一般都是忽略的,如果null值作为条件,将不想作为条件的null属性添加到忽略列表。
基本类型是有默认值的,如果不作为条件,要加入到忽略列表。
不同的字符串属性,如果需要不同的匹配方式,进行单独设置。
不是特别复杂的动态查询,使用QBE,还是很方便的。
源码地址:https://github.com/caofanqi/study-spring-data-jpa