思路分析
实现 html parser 主要分为词法分析和语法分析两步。
词法分析
词法分析需要把每一种类型的 token 识别出来,具体的类型有:
- 开始标签,如 <div>
- 结束标签,如 </div>
- 注释标签,如 <!--comment-->
- doctype 标签,如 <!doctype html>
- text,如 aaa
这是最外层的 token,开始标签内部还要分出属性,如 id="aaa" 这种。
也就是有这几种情况:
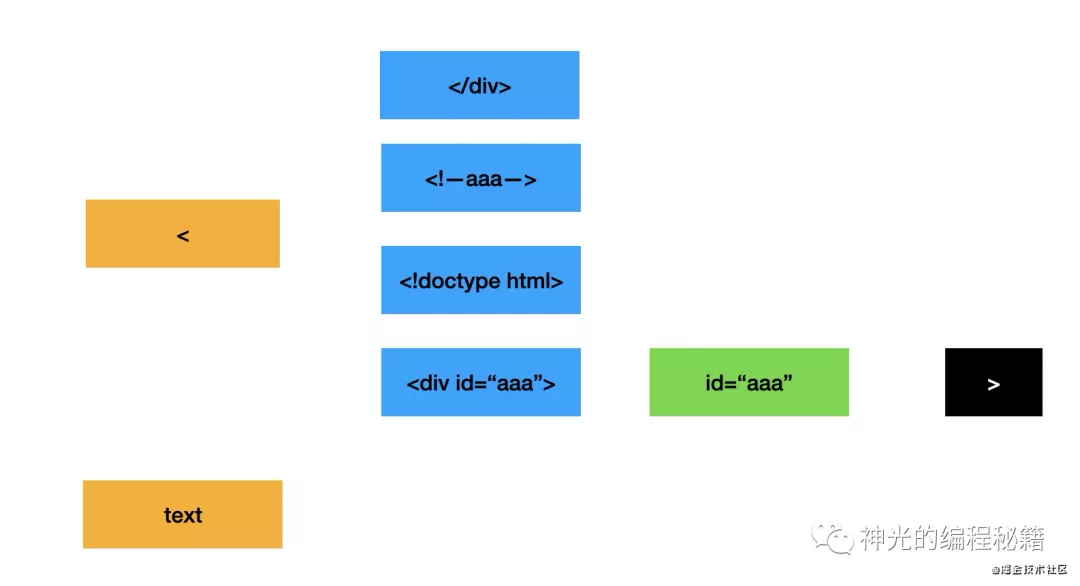
第一层判断是否包含 <,如果不包含则是 text,如果包含则再判断是哪一种,如果是开始标签,还要对其内容再取属性,直到遇到 > 就重新判断。
语法分析
语法分析就是对上面分出的 token 进行组装,生成 ast。
html 的 ast 的组装主要是考虑父子关系,记录当前的 parent,然后 text、children 都设置到当前 parent 上。
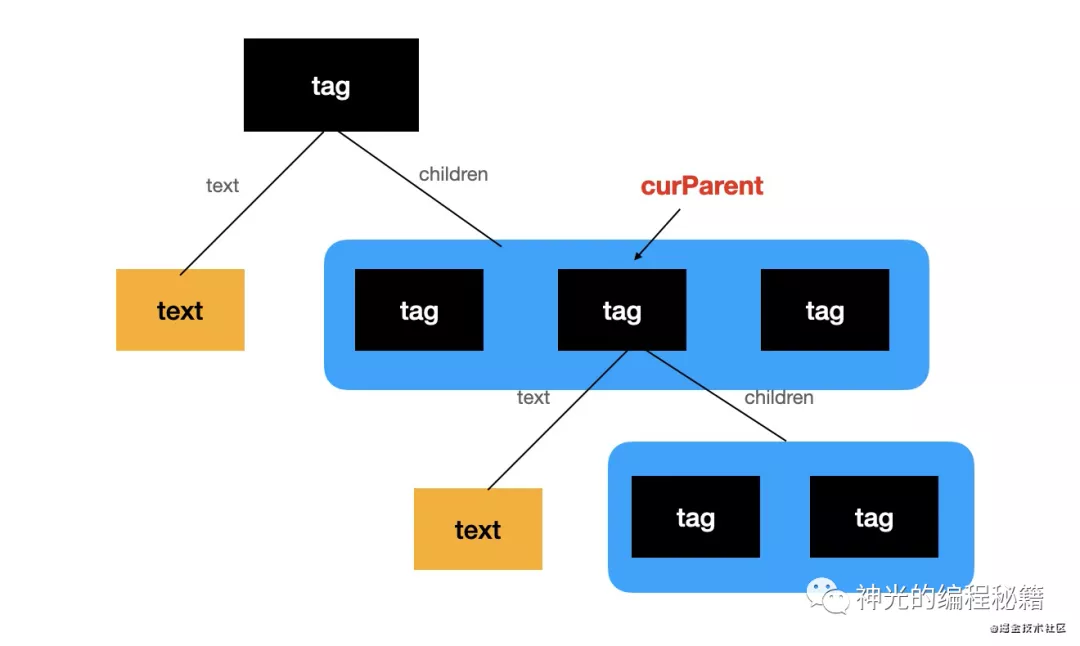
我们来用代码实现一下:
代码实现
词法分析
首先,我们要把 startTag、endTag、comment、docType 还有 attribute 的正则表达式写出来:
正则
- 结束标签就是 </ 开头,然后 a-zA-Z0-9 和 - 出现多次,之后是 >
const endTagReg = /^</([a-zA-Z0-9-]+)>/;
- 注释标签是 <!-- 和 --> 中间夹着非 --> 字符出现任意次
const commentReg = /^<!--[^(-->)]*-->/;
- doctype 标签是 <!doctype 加非 > 字符出现多次,加 >
const docTypeReg = /^<!doctype [^>]+>/;
- attribute 是多个空格开始,加 a-zA-Z0-9 或 - 出现多次,接一个 =,之后是非 > 字符出多次
const attributeReg = /^(?:[ ]+([a-zA-Z0-9-]+=[^>]+))/;
- 开始标签是 < 开头,接 a-zA-Z0-9 和 - 出现多次,然后是属性的正则,最后是 > 结尾
const startTagReg = /^<([a-zA-Z0-9-]+)(?:([ ]+[a-zA-Z0-9-]+=[^> ]+))*>/;
分词
之后,我们就可以基于这些正则来分词,第一层处理 < 和 text:
function parse(html, options) { function advance(num) { html = html.slice(num); } while(html){ if(html.startsWith('<')) { //... } else { let textEndIndex = html.indexOf('<'); options.onText({ type: 'text', value: html.slice(0, textEndIndex) }); textEndIndex = textEndIndex === -1 ? html.length: textEndIndex; advance(textEndIndex); } } }
第二层处理 <!-- 和 <!doctype 和结束标签、开始标签:
const commentMatch = html.match(commentReg); if (commentMatch) { options.onComment({ type: 'comment', value: commentMatch[0] }) advance(commentMatch[0].length); continue; } const docTypeMatch = html.match(docTypeReg); if (docTypeMatch) { options.onDoctype({ type: 'docType', value: docTypeMatch[0] }); advance(docTypeMatch[0].length); continue; } const endTagMatch = html.match(endTagReg); if (endTagMatch) { options.onEndTag({ type: 'tagEnd', value: endTagMatch[1] }); advance(endTagMatch[0].length); continue; } const startTagMatch = html.match(startTagReg); if(startTagMatch) { options.onStartTag({ type: 'tagStart', value: startTagMatch[1] }); advance(startTagMatch[1].length + 1); let attributeMath; while(attributeMath = html.match(attributeReg)) { options.onAttribute({ type: 'attribute', value: attributeMath[1] }); advance(attributeMath[0].length); } advance(1); continue; }
经过词法分析,我们能拿到所有的 token:
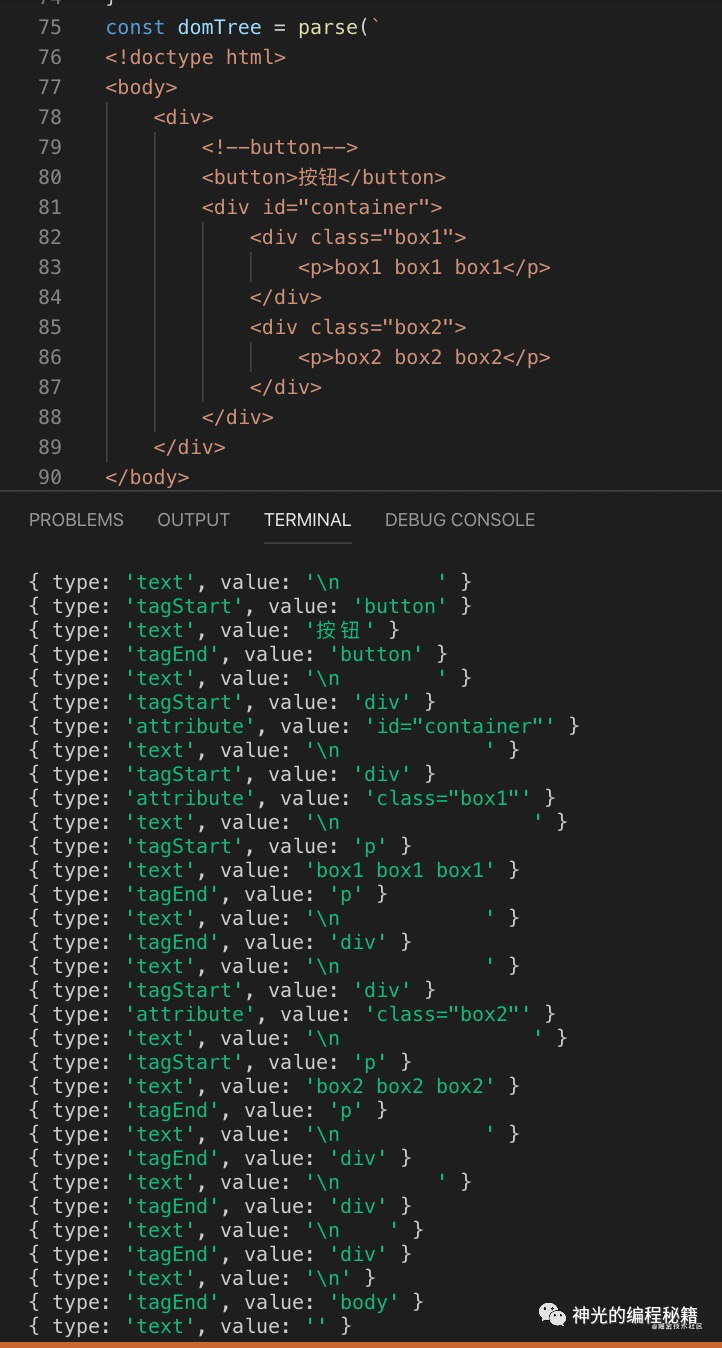
语法分析
token 拆分之后,我们需要再把这些 token 组装在一起,只处理 startTag、endTag 和 text 节点。通过 currentParent 记录当前 tag。
- startTag 创建 AST,挂到 currentParent 的 children 上,然后 currentParent 变成新创建的 tag
- endTag 的时候把 currentParent 设置为当前 tag 的 parent
- text 也挂到 currentParent 上
function htmlParser(str) { const ast = { children: [] }; let curParent = ast; let prevParent = null; const domTree = parse(str,{ onComment(node) { }, onStartTag(token) { const tag = { tagName: token.value, attributes: [], text: '', children: [] }; curParent.children.push(tag); prevParent = curParent; curParent = tag; }, onAttribute(token) { const [ name, value ] = token.value.split('='); curParent.attributes.push({ name, value: value.replace(/^['"]/, '').replace(/['"]$/, '') }); }, onEndTag(token) { curParent = prevParent; }, onDoctype(token) { }, onText(token) { curParent.text = token.value; } }); return ast.children[0]; }
我们试一下效果:
const htmlParser = require('./htmlParser');
const domTree = htmlParser(`
<!doctype html>
<body>
<div>
<!--button-->
<button>按钮</button>
<div id="container">
<div class="box1">
<p>box1 box1 box1</p>
</div>
<div class="box2">
<p>box2 box2 box2</p>
</div>
</div>
</div>
</body>
`);
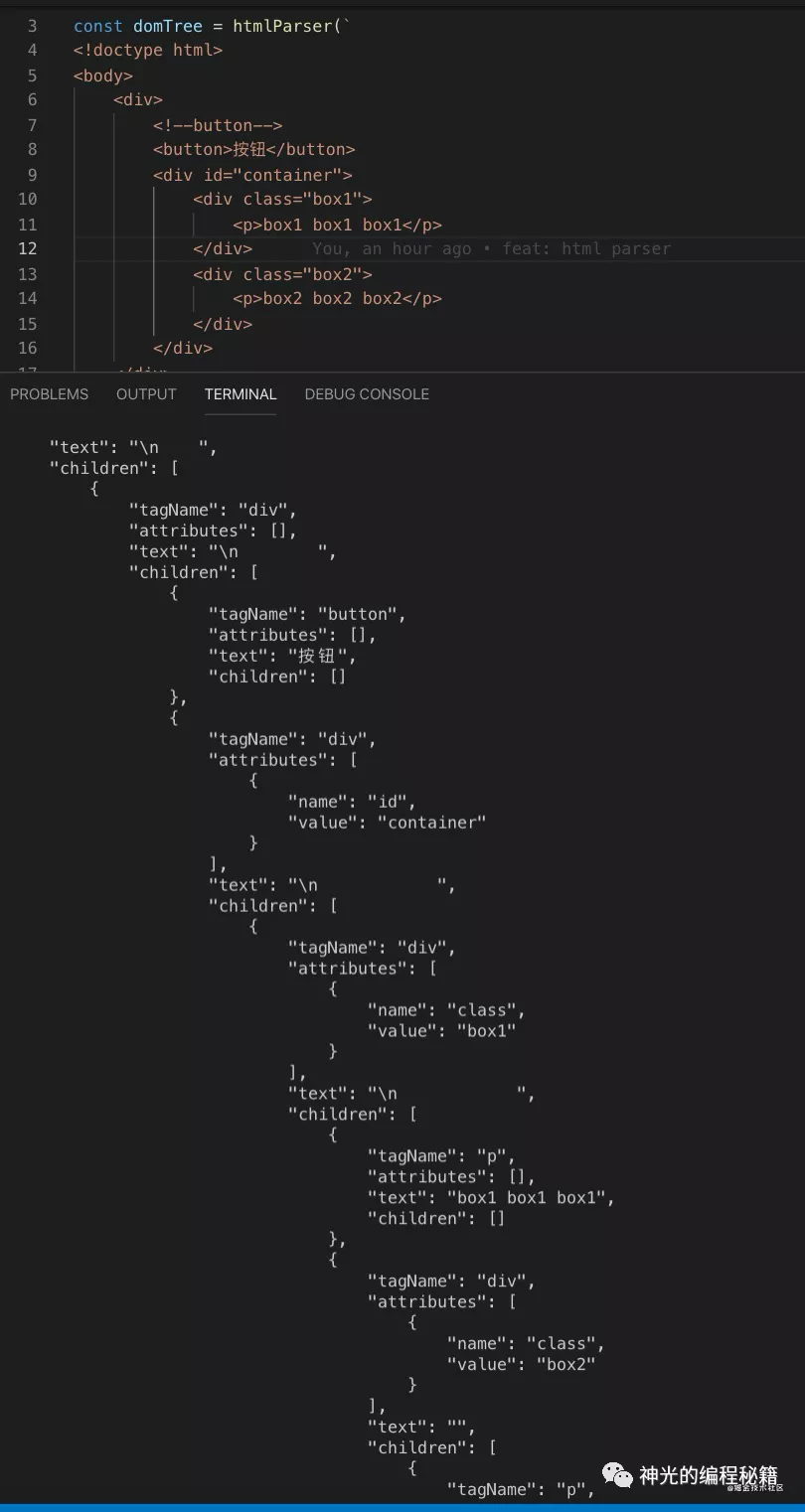
console.log(JSON.stringify(domTree, null, 4));
成功生成了正确的 AST。
总结
这篇是简易浏览器中 html parser 的实现,少了自闭合标签的处理,就是差一个 if else,后面会补上。
我们分析了思路并进行了实现:通过正则来进行 token 的拆分,把拆出的 token 通过回调函数暴露出去,之后进行 AST 的组装,需要记录当前的 parent,来生成父子关系正确的 AST。
html parser 其实也是淘系前端的多年不变的面试题之一,而且 vue template compiler 还有 jsx 的 parser 也会用到类似的思路。还是有必要掌握的。希望本文能帮大家理清思路。
代码在 github:https://github.com/QuarkGluonPlasma/tiny-browser
转自https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/ku6yNZqIKH9wBSGbUdhW0A