After waking up at hh:mm, Andrew realised that he had forgotten to feed his only cat for yet another time (guess why there's only one cat). The cat's current hunger level is H points, moreover each minute without food increases his hunger by D points.
At any time Andrew can visit the store where tasty buns are sold (you can assume that is doesn't take time to get to the store and back). One such bun costs C roubles and decreases hunger by N points. Since the demand for bakery drops heavily in the evening, there is a special 20% discount for buns starting from 20:00 (note that the cost might become rational). Of course, buns cannot be sold by parts.
Determine the minimum amount of money Andrew has to spend in order to feed his cat. The cat is considered fed if its hunger level is less than or equal to zero.
The first line contains two integers hh and mm (00 ≤ hh ≤ 23, 00 ≤ mm ≤ 59) — the time of Andrew's awakening.
The second line contains four integers H, D, C and N (1 ≤ H ≤ 105, 1 ≤ D, C, N ≤ 102).
Output the minimum amount of money to within three decimal digits. You answer is considered correct, if its absolute or relative error does not exceed 10 - 4.
Formally, let your answer be a, and the jury's answer be b. Your answer is considered correct if 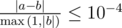 .
.
19 00 255 1 100 1
25200.0000
17 41 1000 6 15 11
1365.0000
In the first sample Andrew can visit the store at exactly 20:00. The cat's hunger will be equal to 315, hence it will be necessary to purchase 315 buns. The discount makes the final answer 25200 roubles.
In the second sample it's optimal to visit the store right after he wakes up. Then he'll have to buy 91 bins per 15 roubles each and spend a total of 1365 roubles.
思路:可以证明,如过当前时间不到20:00,那么最优支付方案一定是立刻购买和20:00购买中的一个。如果已经到了20:00,那里可购买就是最优的。
然后模拟就可以了。
#include<cstdio> #include<cstring> #include<iostream> #include<algorithm> using namespace std; int hh,mm,h,d,c,n; double work1(){ double tmp=h/n+(h%n>0?1:0);tmp*=c; return tmp; } double work2(){ int sum=20*60-hh*60-mm;h+=sum*d; double tmp=h/n+(h%n>0?1:0);tmp*=c; tmp*=0.8; return tmp; } int main(){ scanf("%d%d",&hh,&mm); scanf("%d%d%d%d",&h,&d,&c,&n); if(hh>=20){ double ans=h/n+(h%n>0?1:0); printf("%.4lf",ans*c*0.8); return 0; } double ans1=work1(); double ans2=work2(); printf("%.4lf",min(ans1,ans2)); }