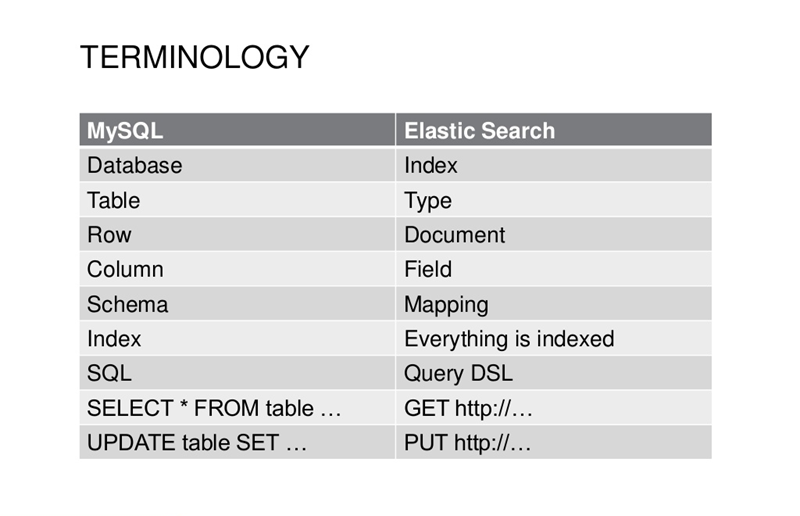
ES与数据库比较
查询操作
Elasticsearch中当我们设置Mapping(分词器、字段类型)完毕后,就可以按照设定的方式导入数据。
有了数据后,我们就需要对数据进行检索操作。根据实际开发需要,往往我们需要支持包含但不限于以下类型的检索:
1)精确匹配,类似mysql中的 “=”操作;
2)模糊匹配,类似mysql中的”like %关键词% “查询操作;
3)前缀匹配;
4)通配符匹配;
5)正则表达式匹配;
6)跨索引匹配;
7)提升精读匹配。
细数一下,我们的痛点在于:
1)ES究竟支持哪些检索操作?
2)如何实现ES精确值检索、指定索引检索、全文检索?
这些就是本文着重参考ES最新官方文档,针对ES5.X版本探讨的内容。
0、检索概览
检索子句的行为取决于查询应用于过滤(filter)上下文还是查询/分析(query)上下文。
过滤上下文——对应于结构化检索
1)核心回答的问题是:“这个文档是否符合这个查询条款?”
2)答案是简单的是或否,不计算分数。
3)过滤器上下文主要用于过滤结构化数据。类似于Mysql中判定某个字段是否存在:
例如:
a. 时间戳字段:是否属于2015年或2016年?
b. 状态字段:是否设置为“已发布”?
经常使用的过滤器将被Elasticsearch**自动缓存,以加快性能**。
分析上下文——对应于全文检索
1)核心回答了“本文档与此查询子句是否匹配?”的问题。
2)除了决定文档是否匹配之外,查询子句还会计算一个_score,表示文档与其他文档的匹配程度。
综合应用场景如下:
GET /_search
{ "query": { "bool": { "must": [
{ "match": { "title": "Search" }},
{ "match": { "content": "Elasticsearch" }}
], "filter": [
{ "term": { "status": "published" }},
{ "range": { "publish_date": { "gte": "2015-01-01" }}}
]
}
}
}以上检索,title中包含”Search”并且content中包含 “Elasticsearch”,status中精确匹配”published”,并且publish_date 大于“2015-01-01”的全部信息。
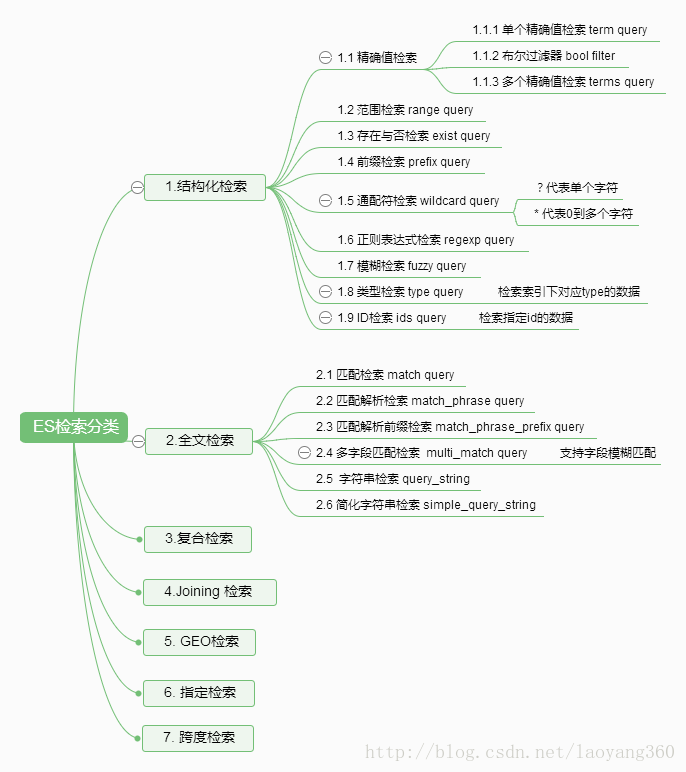
以下,以“脑图”的形式直观展示检索分类。
其中,3-7根据我随着我开发深入再做更新。
以下内容的原文需要参考ES官方文档(随着版本变化,后续会有更新)
1、结构化检索
针对字段类型: 日期、时间、数字类型,以及精确的文本匹配。
结构化检索特点:
* 1)结构化查询,我们得到的结果 总是 非是即否,要么存于集合之中,要么存在集合之外。
* 2)结构化查询不关心文件的相关度或评分;它简单的对文档包括或排除处理。
1.1 精确值查找
1.1.1 单个精确值查找(term query)
term 查询会查找我们指定的精确值。term 查询是简单的,它接受一个字段名以及我们希望查找的数值。
想要类似mysql中如下sql语句的查询操作:
SELECT document FROM products WHERE price = 20;
DSL写法:
GET /my_store/products/_search
{
"query" : {
"term" : {
"price" : 20
}
}
}当进行精确值查找时, 我们会使用过滤器(filters)。过滤器很重要,因为它们执行速度非常快,不会计算相关度(直接跳过了整个评分阶段)而且很容易被缓存。如下: 使用 constant_score 查询以非评分模式来执行 term 查询并以一作为统一评分。
GET /my_store/products/_search
{
"query" : {
"constant_score" : {
"filter" : {
"term" : {
"price" : 20
}
}
}
}
}注意:5.xES中,对于字符串类型,要进行精确值匹配。需要讲类型设置为text和keyword两种类型。mapping设置如下:
POST testindex/testtype/_mapping
{
"testtype ":{
"properties":{
"title":{
"type":"text",
"analyzer":"ik_max_word",
"search_analyzer":"ik_max_word",
"fields":{
"keyword":{
"type":"keyword"
}
}
}
}
}精确值java api jest使用方法:
searchSourceBuilder.query(QueryBuilders.termQuery(“text.keyword”, “来自新华社的报道”));
1.1.2 布尔过滤器
一个 bool 过滤器由三部分组成:
{
"bool" : {
"must" : [],
"should" : [],
"must_not" : [],
"filter": []
}
}must ——所有的语句都 必须(must) 匹配,与 AND 等价。
must_not ——所有的语句都 不能(must not) 匹配,与 NOT 等价。
should ——至少有一个语句要匹配,与 OR 等价。
filter——必须匹配,运行在非评分&过滤模式。
就这么简单! 当我们需要多个过滤器时,只须将它们置入 bool 过滤器的不同部分即可。
举例:
GET /my_store/products/_search
{
"query" : {
"filtered" : {
"filter" : {
"bool" : {
"should" : [
{ "term" : {"price" : 20}},
{ "term" : {"productID" : "XHDK-A-1293-#fJ3"}}
],
"must_not" : {
"term" : {"price" : 30}
}
}
}
}
}
}1.1.3 多个值精确查找(terms query)
{
"terms" : {
"price" : [20, 30]
}
}如上,terms是包含的意思,包含20或者包含30。
如下实现严格意义的精确值检索, tag_count代表必须匹配的次数为1。
GET /my_index/my_type/_search
{
"query": {
"constant_score" : {
"filter" : {
"bool" : {
"must" : [
{ "term" : { "tags" : "search" } },
{ "term" : { "tag_count" : 1 } }
]
}
}
}
}
}1.2 范围检索(range query)
range 查询可同时提供包含(inclusive)和不包含(exclusive)这两种范围表达式,可供组合的选项如下:
gt: > 大于(greater than)
lt: < 小于(less than)
gte: >= 大于或等于(greater than or equal to)
lte: <= 小于或等于(less than or equal to)类似Mysql中的范围查询:
SELECT document
FROM products
WHERE price BETWEEN 20 AND 40ES中对应的DSL如下:
GET /my_store/products/_search
{
"query" : {
"constant_score" : {
"filter" : {
"range" : {
"price" : {
"gte" : 20,
"lt" : 40
}
}
}
}
}
}1.3 存在与否检索(exist query)
mysql中,有如下sql:
SELECT tags FROM posts WHERE tags IS NOT NULL;
ES中,exist查询某个字段是否存在:
GET /my_index/posts/_search
{
"query" : {
"constant_score" : {
"filter" : {
"exists" : { "field" : "tags" }
}
}
}
}若想要exist查询能匹配null类型,需要设置mapping:
"user": {
"type": "keyword",
"null_value": "_null_"
}missing查询在5.x版本已经不存在,改成如下的判定形式:
GET /_search
{
"query": {
"bool": {
"must_not": {
"exists": {
"field": "user"
}
}
}
}
}1.4 前缀检索( Prefix Query )
匹配包含 not analyzed 的前缀字符:
GET /_search
{ "query": {
"prefix" : { "user" : "ki" }
}
}1.5 通配符检索( wildcard query)
匹配具有匹配通配符表达式( (not analyzed )的字段的文档。 支持的通配符:
1)*,它匹配任何字符序列(包括空字符序列);
2)?,它匹配任何单个字符。
请注意,此查询可能很慢,因为它需要遍历多个术语。
为了防止非常慢的通配符查询,通配符不能以任何一个通配符*或?开头。
举例:
GET /_search
{
"query": {
"wildcard" : { "user" : "ki*y" }
}
}1.6 正则表达式检索(regexp query)
正则表达式查询允许您使用正则表达式术语查询。
举例如下:
GET /_search
{
"query": {
"regexp":{
"name.first": "s.*y"
}
}
}注意: *的匹配会非常慢,你需要使用一个长的前缀,
通常类似.*?+通配符查询的正则检索性能会非常低。
1.7 模糊检索(fuzzy query)
模糊查询查找在模糊度中指定的最大编辑距离内的所有可能的匹配项,然后检查术语字典,以找出在索引中实际存在待检索的关键词。
举例如下:
GET /_search
{
"query": {
"fuzzy" : { "user" : "ki" }
}
}1.8 类型检索(type query)
举例:
GET /my_index/_search
{
"query": {
"type" : {
"value" : "xext"
}
}
}已验证,检索索引my_index中,type为xext的全部信息。
1.9 Ids检索(ids query)
返回指定id的全部信息。
GET /my_index/_search
{
"query": {
"ids" : {
"type" : "xext",
"values" : ["2", "4", "100"]
}
}
}2、全文检索
高级全文查询通常用于在全文本字段(如电子邮件正文)上运行全文查询。他们了解如何对被查询的字段进行分析,并在执行前将每个字段的分析器(或search_analyzer)应用于查询字符串。
2.1 匹配检索(match query)
匹配查询接受文本/数字/日期类型,分析它们,并构造查询。
1)匹配查询的类型为boolean。 这意味着分析所提供的文本,并且分析过程从提供的文本构造一个布尔查询,
可以将运算符标志设置为或以控制布尔子句(默认为或);
2)文本分析取决于mapping中设定的analyzer(中文分词,我们默认选择ik分词器);
3) fuzziness——模糊性允许基于被查询的字段的类型进行模糊匹配;
4)”operator”: “and”——匹配与操作(默认或操作);
5) “minimum_should_match”: “75%”——这让我们可以指定必须匹配的词项数用来表示一个文档是否相关。
举例:
GET /_search
{
"query": {
"match" : {
"message" : {
"query" : "this is a test",
"operator" : "and"
}
}
}
}2.2 匹配解析检索 match_phrase query
match_phrase查询分析文本,并从分析文本中创建短语查询。
类似 match 查询, match_phrase 查询首先将查询字符串解析成一个词项列表,然后对这些词项进行搜索,但只保留那些包含 全部 搜索词项,且 位置 与搜索词项相同的文档。
举例如下:对于 quick fox 的短语搜索可能不会匹配到任何文档,因为没有文档包含的 quick 词之后紧跟着 fox 。
GET /my_index/my_type/_search
{
"query": {
"match_phrase": {
"title": "quick brown fox"
}
}
}2.3 匹配解析前缀检索(match_phrase_prefix)
用户已经渐渐习惯在输完查询内容之前,就能为他们展现搜索结果,这就是所谓的 即时搜索(instant search) 或 输入即搜索(search-as-you-type) 。
不仅用户能在更短的时间内得到搜索结果,我们也能引导用户搜索索引中真实存在的结果。
例如,如果用户输入 johnnie walker bl ,我们希望在它们完成输入搜索条件前就能得到:
Johnnie Walker Black Label 和 Johnnie Walker Blue Label 。
match_phrase_prefix与match_phrase相同,除了它允许文本中最后一个术语的前缀匹配。
举例:
GET / _search
{
“query”:{
“match_phrase_prefix”:{
“message”:“quick brown f”
}
}
}2.4 多字段匹配检索( multi_match query)
multi_match 查询为能在多个字段上反复执行相同查询提供了一种便捷方式。
默认情况下,查询的类型是 best_fields, 这表示它会为每个字段生成一个 match 查询。
举例1:”fields”: “*_title”
——任何与模糊模式正则匹配的字段都会被包括在搜索条件中, 例如可以左侧的方式同时匹配 book_title 、 chapter_title 和 section_title (书名、章名、节名)这三个字段。
举例2: “fields”: [ “*_title”, “chapter_title^2” ]
——可以使用 ^ 字符语法为单个字段提升权重,在字段名称的末尾添加 ^boost , 其中 boost 是一个浮点数。
举例3:”fields”: [ “first_name”, “last_name” ],
“operator”: “and”
——两个字段必须都包含。
GET /_search
{
"query": {
"multi_match" : {
"query": "this is a test",
"fields": [ "subject", "message" ]
}
}
}2.5 字符串检索(query_string)
一个使用查询解析器解析其内容的查询。
query_string查询提供了以简明的简写语法执行多匹配查询 multi_match queries ,布尔查询 bool queries ,提升得分 boosting ,模糊匹配 fuzzy matching ,通配符 wildcards ,正则表达式 regexp 和范围查询 range queries 的方式。
支持参数达10几种。
GET /_search
{
"query": {
"query_string" : {
"default_field" : "content",
"query" : "this AND that OR thus"
}
}
}2.6 简化字符串检索(simple_query_string)
一个使用SimpleQueryParser解析其上下文的查询。 与常规query_string查询不同,simple_query_string查询永远不会抛出异常,并丢弃查询的无效部分。
举例:
GET /_search
{
"query": {
"simple_query_string" : {
"fields" : ["content"],
"query" : "foo bar -baz"
}
}
}支持的操作如下:
1)+表示AND操作
2)| 表示OR操作
3)- 否定操作
4)*在术语结束时表示前缀查询
5)(和)表示优先
3 小结
有的博友可能会问,这和ES官网API有什么区别。
仔细对比你会发现,ES的中文文档是根据2.X版本翻译的,ES的英文文档一个版本是没有更新到5.X版本,另一个已经更新
===========================================================================
本节介绍以下 CRUD API:
单文档 APIs
多文档 APIs
Multi Get API
Bulk API
注意:所有的单文档的CRUD API,index参数只能接受单一的索引库名称,或者是一个指向单一索引库的alias。
Index API
Index API 允许我们存储一个JSON格式的文档,使数据可以被搜索。文档通过index、type、id唯一确定。我们可以自己提供一个id,或者也使用Index API 为我们自动生成一个。
这里有几种不同的方式来产生JSON格式的文档(document):
- 手动方式,使用原生的byte[]或者String
- 使用Map方式,会自动转换成与之等价的JSON
- 使用第三方库来序列化beans,如Jackson
- 使用内置的帮助类 XContentFactory.jsonBuilder()
手动方式
String json = "{" +
""user":"kimchy"," +
""postDate":"2013-01-30"," +
""message":"trying out Elasticsearch"" +
"}";
实例
/**
* 手动生成JSON
*/
@Test
public void CreateJSON(){
String json = "{" +
""user":"fendo"," +
""postDate":"2013-01-30"," +
""message":"Hell word"" +
"}";
IndexResponse response = client.prepareIndex("fendo", "fendodate")
.setSource(json)
.get();
System.out.println(response.getResult());
}
Map方式
Map是key:value数据类型,可以代表json结构.
Map<String, Object> json = new HashMap<String, Object>();
json.put("user","kimchy");
json.put("postDate",new Date());
json.put("message","trying out Elasticsearch");
实例
/**
* 使用集合
*/
@Test
public void CreateList(){
Map<String, Object> json = new HashMap<String, Object>();
json.put("user","kimchy");
json.put("postDate","2013-01-30");
json.put("message","trying out Elasticsearch");
IndexResponse response = client.prepareIndex("fendo", "fendodate")
.setSource(json)
.get();
System.out.println(response.getResult());
}
序列化方式
ElasticSearch已经使用了jackson,可以直接使用它把javabean转为json.
import com.fasterxml.jackson.databind.*;
// instance a json mapper
ObjectMapper mapper = new ObjectMapper(); // create once, reuse
// generate json
byte[] json = mapper.writeValueAsBytes(yourbeaninstance);
实例
/**
* 使用JACKSON序列化
* @throws Exception
*/
@Test
public void CreateJACKSON() throws Exception{
CsdnBlog csdn=new CsdnBlog();
csdn.setAuthor("fendo");
csdn.setContent("这是JAVA书籍");
csdn.setTag("C");
csdn.setView("100");
csdn.setTitile("编程");
csdn.setDate(new Date().toString());
// instance a json mapper
ObjectMapper mapper = new ObjectMapper(); // create once, reuse
// generate json
byte[] json = mapper.writeValueAsBytes(csdn);
IndexResponse response = client.prepareIndex("fendo", "fendodate")
.setSource(json)
.get();
System.out.println(response.getResult());
}
XContentBuilder帮助类方式
ElasticSearch提供了一个内置的帮助类XContentBuilder来产生JSON文档
// Index name
String _index = response.getIndex();
// Type name
String _type = response.getType();
// Document ID (generated or not)
String _id = response.getId();
// Version (if it's the first time you index this document, you will get: 1)
long _version = response.getVersion();
// status has stored current instance statement.
RestStatus status = response.status();
实例
/**
* 使用ElasticSearch 帮助类
* @throws IOException
*/
@Test
public void CreateXContentBuilder() throws IOException{
XContentBuilder builder = XContentFactory.jsonBuilder()
.startObject()
.field("user", "ccse")
.field("postDate", new Date())
.field("message", "this is Elasticsearch")
.endObject();
IndexResponse response = client.prepareIndex("fendo", "fendodata").setSource(builder).get();
System.out.println("创建成功!");
}
综合实例
import java.io.IOException;
import java.net.InetAddress;
import java.net.UnknownHostException;
import java.util.Date;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
import org.elasticsearch.action.index.IndexResponse;
import org.elasticsearch.client.transport.TransportClient;
import org.elasticsearch.common.settings.Settings;
import org.elasticsearch.common.transport.InetSocketTransportAddress;
import org.elasticsearch.common.xcontent.XContentBuilder;
import org.elasticsearch.common.xcontent.XContentFactory;
import org.elasticsearch.transport.client.PreBuiltTransportClient;
import org.junit.Before;
import org.junit.Test;
import com.fasterxml.jackson.core.JsonProcessingException;
import com.fasterxml.jackson.databind.ObjectMapper;
public class CreateIndex {
private TransportClient client;
@Before
public void getClient() throws Exception{
//设置集群名称
Settings settings = Settings.builder().put("cluster.name", "my-application").build();// 集群名
//创建client
client = new PreBuiltTransportClient(settings)
.addTransportAddress(new InetSocketTransportAddress(InetAddress.getByName("127.0.0.1"), 9300));
}
/**
* 手动生成JSON
*/
@Test
public void CreateJSON(){
String json = "{" +
""user":"fendo"," +
""postDate":"2013-01-30"," +
""message":"Hell word"" +
"}";
IndexResponse response = client.prepareIndex("fendo", "fendodate")
.setSource(json)
.get();
System.out.println(response.getResult());
}
/**
* 使用集合
*/
@Test
public void CreateList(){
Map<String, Object> json = new HashMap<String, Object>();
json.put("user","kimchy");
json.put("postDate","2013-01-30");
json.put("message","trying out Elasticsearch");
IndexResponse response = client.prepareIndex("fendo", "fendodate")
.setSource(json)
.get();
System.out.println(response.getResult());
}
/**
* 使用JACKSON序列化
* @throws Exception
*/
@Test
public void CreateJACKSON() throws Exception{
CsdnBlog csdn=new CsdnBlog();
csdn.setAuthor("fendo");
csdn.setContent("这是JAVA书籍");
csdn.setTag("C");
csdn.setView("100");
csdn.setTitile("编程");
csdn.setDate(new Date().toString());
// instance a json mapper
ObjectMapper mapper = new ObjectMapper(); // create once, reuse
// generate json
byte[] json = mapper.writeValueAsBytes(csdn);
IndexResponse response = client.prepareIndex("fendo", "fendodate")
.setSource(json)
.get();
System.out.println(response.getResult());
}
/**
* 使用ElasticSearch 帮助类
* @throws IOException
*/
@Test
public void CreateXContentBuilder() throws IOException{
XContentBuilder builder = XContentFactory.jsonBuilder()
.startObject()
.field("user", "ccse")
.field("postDate", new Date())
.field("message", "this is Elasticsearch")
.endObject();
IndexResponse response = client.prepareIndex("fendo", "fendodata").setSource(builder).get();
System.out.println("创建成功!");
}
}
你还可以通过startArray(string)和endArray()方法添加数组。.field()方法可以接受多种对象类型。你可以给它传递数字、日期、甚至其他XContentBuilder对象。
Get API
根据id查看文档:
GetResponse response = client.prepareGet("twitter", "tweet", "1").get();
更多请查看 rest get API 文档
配置线程
operationThreaded 设置为 true 是在不同的线程里执行此次操作
下面的例子是operationThreaded 设置为 false :
GetResponse response = client.prepareGet("twitter", "tweet", "1")
.setOperationThreaded(false)
.get();
Delete API
根据ID删除:
DeleteResponse response = client.prepareDelete("twitter", "tweet", "1").get();
更多请查看 delete API 文档
配置线程
operationThreaded 设置为 true 是在不同的线程里执行此次操作
下面的例子是operationThreaded 设置为 false :
GetResponse response = client.prepareGet("twitter", "tweet", "1")
.setOperationThreaded(false)
.get();
DeleteResponse response = client.prepareDelete("twitter", "tweet", "1")
.setOperationThreaded(false)
.get();
Delete By Query API
通过查询条件删除
BulkByScrollResponse response =
DeleteByQueryAction.INSTANCE.newRequestBuilder(client)
.filter(QueryBuilders.matchQuery("gender", "male")) //查询条件
.source("persons") //index(索引名)
.get(); //执行
long deleted = response.getDeleted(); //删除文档的数量
如果需要执行的时间比较长,可以使用异步的方式处理,结果在回调里面获取
DeleteByQueryAction.INSTANCE.newRequestBuilder(client)
.filter(QueryBuilders.matchQuery("gender", "male")) //查询
.source("persons") //index(索引名)
.execute(new ActionListener<BulkByScrollResponse>() { //回调监听
@Override
public void onResponse(BulkByScrollResponse response) {
long deleted = response.getDeleted(); //删除文档的数量
}
@Override
public void onFailure(Exception e) {
// Handle the exception
}
});
Update API
有两种方式更新索引:
- 创建
UpdateRequest,通过client发送; - 使用
prepareUpdate()方法;
使用UpdateRequest
UpdateRequest updateRequest = new UpdateRequest();
updateRequest.index("index");
updateRequest.type("type");
updateRequest.id("1");
updateRequest.doc(jsonBuilder()
.startObject()
.field("gender", "male")
.endObject());
client.update(updateRequest).get();
使用 prepareUpdate() 方法
这里官方的示例有问题,new Script()参数错误,所以一下代码是我自己写的(2017/11/10)
client.prepareUpdate("ttl", "doc", "1")
.setScript(new Script("ctx._source.gender = "male"" ,ScriptService.ScriptType.INLINE, null, null))//脚本可以是本地文件存储的,如果使用文件存储的脚本,需要设置 ScriptService.ScriptType.FILE
.get();
client.prepareUpdate("ttl", "doc", "1")
.setDoc(jsonBuilder() //合并到现有文档
.startObject()
.field("gender", "male")
.endObject())
.get();
Update by script
使用脚本更新文档
UpdateRequest updateRequest = new UpdateRequest("ttl", "doc", "1")
.script(new Script("ctx._source.gender = "male""));
client.update(updateRequest).get();
Update by merging documents
合并文档
UpdateRequest updateRequest = new UpdateRequest("index", "type", "1")
.doc(jsonBuilder()
.startObject()
.field("gender", "male")
.endObject());
client.update(updateRequest).get();
Upsert
更新插入,如果存在文档就更新,如果不存在就插入
IndexRequest indexRequest = new IndexRequest("index", "type", "1")
.source(jsonBuilder()
.startObject()
.field("name", "Joe Smith")
.field("gender", "male")
.endObject());
UpdateRequest updateRequest = new UpdateRequest("index", "type", "1")
.doc(jsonBuilder()
.startObject()
.field("gender", "male")
.endObject())
.upsert(indexRequest); //如果不存在此文档 ,就增加 `indexRequest`
client.update(updateRequest).get();
如果 index/type/1 存在,类似下面的文档:
{
"name" : "Joe Dalton",
"gender": "male"
}
如果不存在,会插入新的文档:
{
"name" : "Joe Smith",
"gender": "male"
}
Multi Get API
一次获取多个文档
MultiGetResponse multiGetItemResponses = client.prepareMultiGet()
.add("twitter", "tweet", "1") //一个id的方式
.add("twitter", "tweet", "2", "3", "4") //多个id的方式
.add("another", "type", "foo") //可以从另外一个索引获取
.get();
for (MultiGetItemResponse itemResponse : multiGetItemResponses) { //迭代返回值
GetResponse response = itemResponse.getResponse();
if (response.isExists()) { //判断是否存在
String json = response.getSourceAsString(); //_source 字段
}
}
更多请浏览REST multi get 文档
Bulk API
Bulk API,批量插入:
import static org.elasticsearch.common.xcontent.XContentFactory.*;
BulkRequestBuilder bulkRequest = client.prepareBulk();
// either use client#prepare, or use Requests# to directly build index/delete requests
bulkRequest.add(client.prepareIndex("twitter", "tweet", "1")
.setSource(jsonBuilder()
.startObject()
.field("user", "kimchy")
.field("postDate", new Date())
.field("message", "trying out Elasticsearch")
.endObject()
)
);
bulkRequest.add(client.prepareIndex("twitter", "tweet", "2")
.setSource(jsonBuilder()
.startObject()
.field("user", "kimchy")
.field("postDate", new Date())
.field("message", "another post")
.endObject()
)
);
BulkResponse bulkResponse = bulkRequest.get();
if (bulkResponse.hasFailures()) {
// process failures by iterating through each bulk response item
//处理失败
}
使用 Bulk Processor
BulkProcessor 提供了一个简单的接口,在给定的大小数量上定时批量自动请求
创建BulkProcessor实例
首先创建BulkProcessor实例
import org.elasticsearch.action.bulk.BackoffPolicy;
import org.elasticsearch.action.bulk.BulkProcessor;
import org.elasticsearch.common.unit.ByteSizeUnit;
import org.elasticsearch.common.unit.ByteSizeValue;
import org.elasticsearch.common.unit.TimeValue;
BulkProcessor bulkProcessor = BulkProcessor.builder(
client, //增加elasticsearch客户端
new BulkProcessor.Listener() {
@Override
public void beforeBulk(long executionId,
BulkRequest request) { ... } //调用bulk之前执行 ,例如你可以通过request.numberOfActions()方法知道numberOfActions
@Override
public void afterBulk(long executionId,
BulkRequest request,
BulkResponse response) { ... } //调用bulk之后执行 ,例如你可以通过request.hasFailures()方法知道是否执行失败
@Override
public void afterBulk(long executionId,
BulkRequest request,
Throwable failure) { ... } //调用失败抛 Throwable
})
.setBulkActions(10000) //每次10000请求
.setBulkSize(new ByteSizeValue(5, ByteSizeUnit.MB)) //拆成5mb一块
.setFlushInterval(TimeValue.timeValueSeconds(5)) //无论请求数量多少,每5秒钟请求一次。
.setConcurrentRequests(1) //设置并发请求的数量。值为0意味着只允许执行一个请求。值为1意味着允许1并发请求。
.setBackoffPolicy(
BackoffPolicy.exponentialBackoff(TimeValue.timeValueMillis(100), 3))//设置自定义重复请求机制,最开始等待100毫秒,之后成倍更加,重试3次,当一次或多次重复请求失败后因为计算资源不够抛出 EsRejectedExecutionException 异常,可以通过BackoffPolicy.noBackoff()方法关闭重试机制
.build();
BulkProcessor 默认设置
- bulkActions 1000
- bulkSize 5mb
- 不设置flushInterval
- concurrentRequests 为 1 ,异步执行
- backoffPolicy 重试 8次,等待50毫秒
增加requests
然后增加requests到BulkProcessor
bulkProcessor.add(new IndexRequest("twitter", "tweet", "1").source(/* your doc here */));
bulkProcessor.add(new DeleteRequest("twitter", "tweet", "2"));
关闭 Bulk Processor
当所有文档都处理完成,使用awaitClose 或 close 方法关闭BulkProcessor:
bulkProcessor.awaitClose(10, TimeUnit.MINUTES);
或
bulkProcessor.close();
在测试中使用Bulk Processor
如果你在测试种使用Bulk Processor可以执行同步方法
BulkProcessor bulkProcessor = BulkProcessor.builder(client, new BulkProcessor.Listener() { /* Listener methods */ })
.setBulkActions(10000)
.setConcurrentRequests(0)
.build();
// Add your requests
bulkProcessor.add(/* Your requests */);
// Flush any remaining requests
bulkProcessor.flush();
// Or close the bulkProcessor if you don't need it anymore
bulkProcessor.close();
// Refresh your indices
client.admin().indices().prepareRefresh().get();
// Now you can start searching!
client.prepareSearch().get();
所有实例 参见Git
===============================================================================================
为了讲解不同类型ES检索,我们将要对包含以下类型的文档集合进行检索:
1. title 标题;
2. authors 作者;
3. summary 摘要;
4. release data 发布日期;
5. number of reviews 评论数。
首先,让我们借助 bulk API批量创建新的索引并提交数据。
PUT /bookdb_index
{ "settings": { "number_of_shards": 1 }}
POST /bookdb_index/book/_bulk
{ "index": { "_id": 1 }}
{ "title": "Elasticsearch: The Definitive Guide", "authors": ["clinton gormley", "zachary tong"], "summary" : "A distibuted real-time search and analytics engine", "publish_date" : "2015-02-07", "num_reviews": 20, "publisher": "oreilly" }
{ "index": { "_id": 2 }}
{ "title": "Taming Text: How to Find, Organize, and Manipulate It", "authors": ["grant ingersoll", "thomas morton", "drew farris"], "summary" : "organize text using approaches such as full-text search, proper name recognition, clustering, tagging, information extraction, and summarization", "publish_date" : "2013-01-24", "num_reviews": 12, "publisher": "manning" }
{ "index": { "_id": 3 }}
{ "title": "Elasticsearch in Action", "authors": ["radu gheorge", "matthew lee hinman", "roy russo"], "summary" : "build scalable search applications using Elasticsearch without having to do complex low-level programming or understand advanced data science algorithms", "publish_date" : "2015-12-03", "num_reviews": 18, "publisher": "manning" }
{ "index": { "_id": 4 }}
{ "title": "Solr in Action", "authors": ["trey grainger", "timothy potter"], "summary" : "Comprehensive guide to implementing a scalable search engine using Apache Solr", "publish_date" : "2014-04-05", "num_reviews": 23, "publisher": "manning" }1、基本匹配检索( Basic Match Query)
1.1 全文检索
有两种方式可以执行全文检索:
1)使用包含参数的检索API,参数作为URL的一部分。
举例:以下对”guide”执行全文检索。
GET /bookdb_index/book/_search?q=guide
[Results]
"hits": [
{
"_index": "bookdb_index",
"_type": "book",
"_id": "1",
"_score": 0.28168046,
"_source": {
"title": "Elasticsearch: The Definitive Guide",
"authors": [
"clinton gormley",
"zachary tong"
],
"summary": "A distibuted real-time search and analytics engine",
"publish_date": "2015-02-07",
"num_reviews": 20,
"publisher": "manning"
}
},
{
"_index": "bookdb_index",
"_type": "book",
"_id": "4",
"_score": 0.24144039,
"_source": {
"title": "Solr in Action",
"authors": [
"trey grainger",
"timothy potter"
],
"summary": "Comprehensive guide to implementing a scalable search engine using Apache Solr",
"publish_date": "2014-04-05",
"num_reviews": 23,
"publisher": "manning"
}
}
]2)使用完整的ES DSL,其中Json body作为请求体。
其执行结果如方式1)结果一致。
{
"query": {
"multi_match" : {
"query" : "guide",
"fields" : ["_all"]
}
}
}解读:使用multi_match关键字代替match关键字,作为对多个字段运行相同查询的方便的简写方式。 fields属性指定要查询的字段,在这种情况下,我们要对文档中的所有字段进行查询。
1.2 指定特定字段检索
这两个API也允许您指定要搜索的字段。 例如,要在标题字段中搜索带有“in action”字样的图书,
1)URL检索方式
如下所示:
GET /bookdb_index/book/_search?q=title:in action
[Results]
"hits": [
{
"_index": "bookdb_index",
"_type": "book",
"_id": "4",
"_score": 0.6259885,
"_source": {
"title": "Solr in Action",
"authors": [
"trey grainger",
"timothy potter"
],
"summary": "Comprehensive guide to implementing a scalable search engine using Apache Solr",
"publish_date": "2014-04-05",
"num_reviews": 23,
"publisher": "manning"
}
},
{
"_index": "bookdb_index",
"_type": "book",
"_id": "3",
"_score": 0.5975345,
"_source": {
"title": "Elasticsearch in Action",
"authors": [
"radu gheorge",
"matthew lee hinman",
"roy russo"
],
"summary": "build scalable search applications using Elasticsearch without having to do complex low-level programming or understand advanced data science algorithms",
"publish_date": "2015-12-03",
"num_reviews": 18,
"publisher": "manning"
}
}
]2)DSL检索方式
然而,full body的DSL为您提供了创建更复杂查询的更多灵活性(我们将在后面看到)以及指定您希望的返回结果。 在下面的示例中,我们指定要返回的结果数、偏移量(对分页有用)、我们要返回的文档字段以及属性的高亮显示。
结果数的表示方式:size;
偏移值的表示方式:from;
指定返回字段 的表示方式 :_source;
高亮显示 的表示方式 :highliaght。
POST /bookdb_index/book/_search
{
"query": {
"match" : {
"title" : "in action"
}
},
"size": 2,
"from": 0,
"_source": [ "title", "summary", "publish_date" ],
"highlight": {
"fields" : {
"title" : {}
}
}
}
[Results]
"hits": {
"total": 2,
"max_score": 0.9105287,
"hits": [
{
"_index": "bookdb_index",
"_type": "book",
"_id": "3",
"_score": 0.9105287,
"_source": {
"summary": "build scalable search applications using Elasticsearch without having to do complex low-level programming or understand advanced data science algorithms",
"title": "Elasticsearch in Action",
"publish_date": "2015-12-03"
},
"highlight": {
"title": [
"Elasticsearch <em>in</em> <em>Action</em>"
]
}
},
{
"_index": "bookdb_index",
"_type": "book",
"_id": "4",
"_score": 0.9105287,
"_source": {
"summary": "Comprehensive guide to implementing a scalable search engine using Apache Solr",
"title": "Solr in Action",
"publish_date": "2014-04-05"
},
"highlight": {
"title": [
"Solr <em>in</em> <em>Action</em>"
]
}
}
]
}注意:对于 multi-word 检索,匹配查询允许您指定是否使用‘and’运算符,
而不是使用默认’or’运算符。
您还可以指定minimum_should_match选项来调整返回结果的相关性。
详细信息可以在Elasticsearch指南中查询Elasticsearch guide. 获取。
2、多字段检索 (Multi-field Search)
如我们已经看到的,要在搜索中查询多个文档字段(例如在标题和摘要中搜索相同的查询字符串),请使用multi_match查询。
POST /bookdb_index/book/_search
{
"query": {
"multi_match" : {
"query" : "elasticsearch guide",
"fields": ["title", "summary"]
}
}
}
[Results]
"hits": {
"total": 3,
"max_score": 0.9448582,
"hits": [
{
"_index": "bookdb_index",
"_type": "book",
"_id": "1",
"_score": 0.9448582,
"_source": {
"title": "Elasticsearch: The Definitive Guide",
"authors": [
"clinton gormley",
"zachary tong"
],
"summary": "A distibuted real-time search and analytics engine",
"publish_date": "2015-02-07",
"num_reviews": 20,
"publisher": "manning"
}
},
{
"_index": "bookdb_index",
"_type": "book",
"_id": "3",
"_score": 0.17312013,
"_source": {
"title": "Elasticsearch in Action",
"authors": [
"radu gheorge",
"matthew lee hinman",
"roy russo"
],
"summary": "build scalable search applications using Elasticsearch without having to do complex low-level programming or understand advanced data science algorithms",
"publish_date": "2015-12-03",
"num_reviews": 18,
"publisher": "manning"
}
},
{
"_index": "bookdb_index",
"_type": "book",
"_id": "4",
"_score": 0.14965448,
"_source": {
"title": "Solr in Action",
"authors": [
"trey grainger",
"timothy potter"
],
"summary": "Comprehensive guide to implementing a scalable search engine using Apache Solr",
"publish_date": "2014-04-05",
"num_reviews": 23,
"publisher": "manning"
}
}
]
}注意:以上结果3匹配的原因是guide在summary存在。
3、 Boosting提升某字段得分的检索( Boosting)
由于我们正在多个字段进行搜索,我们可能希望提高某一字段的得分。 在下面的例子中,我们将“摘要”字段的得分提高了3倍,以增加“摘要”字段的重要性,从而提高文档 4 的相关性。
POST /bookdb_index/book/_search
{
"query": {
"multi_match" : {
"query" : "elasticsearch guide",
"fields": ["title", "summary^3"]
}
},
"_source": ["title", "summary", "publish_date"]
}
[Results]
"hits": [
{
"_index": "bookdb_index",
"_type": "book",
"_id": "1",
"_score": 0.31495273,
"_source": {
"summary": "A distibuted real-time search and analytics engine",
"title": "Elasticsearch: The Definitive Guide",
"publish_date": "2015-02-07"
}
},
{
"_index": "bookdb_index",
"_type": "book",
"_id": "4",
"_score": 0.14965448,
"_source": {
"summary": "Comprehensive guide to implementing a scalable search engine using Apache Solr",
"title": "Solr in Action",
"publish_date": "2014-04-05"
}
},
{
"_index": "bookdb_index",
"_type": "book",
"_id": "3",
"_score": 0.13094766,
"_source": {
"summary": "build scalable search applications using Elasticsearch without having to do complex low-level programming or understand advanced data science algorithms",
"title": "Elasticsearch in Action",
"publish_date": "2015-12-03"
}
}
]注意:Boosting不仅意味着计算得分乘法以增加因子。 实际的提升得分值是通过归一化和一些内部优化。参考 Elasticsearch guide.查看更多。
4、Bool检索( Bool Query)
可以使用AND / OR / NOT运算符来微调我们的搜索查询,以提供更相关或指定的搜索结果。
在搜索API中是通过bool查询来实现的。
bool查询接受”must”参数(等效于AND),一个must_not参数(相当于NOT)或者一个should参数(等同于OR)。
例如,如果我想在标题中搜索一本名为“Elasticsearch”或“Solr”的书,AND由“clinton gormley”创作,但NOT由“radu gheorge”创作:
POST /bookdb_index/book/_search
{
"query": {
"bool": {
"must": {
"bool" : { "should": [
{ "match": { "title": "Elasticsearch" }},
{ "match": { "title": "Solr" }} ] }
},
"must": { "match": { "authors": "clinton gormely" }},
"must_not": { "match": {"authors": "radu gheorge" }}
}
}
}
[Results]
"hits": [
{
"_index": "bookdb_index",
"_type": "book",
"_id": "1",
"_score": 0.3672021,
"_source": {
"title": "Elasticsearch: The Definitive Guide",
"authors": [
"clinton gormley",
"zachary tong"
],
"summary": "A distibuted real-time search and analytics engine",
"publish_date": "2015-02-07",
"num_reviews": 20,
"publisher": "oreilly"
}
}
]注意:您可以看到,bool查询可以包含任何其他查询类型,包括其他布尔查询,以创建任意复杂或深度嵌套的查询。
5、 Fuzzy 模糊检索( Fuzzy Queries)
在 Match检索 和多匹配检索中可以启用模糊匹配来捕捉拼写错误。 基于与原始词的Levenshtein距离来指定模糊度。
POST /bookdb_index/book/_search
{
"query": {
"multi_match" : {
"query" : "comprihensiv guide",
"fields": ["title", "summary"],
"fuzziness": "AUTO"
}
},
"_source": ["title", "summary", "publish_date"],
"size": 1
}
[Results]
"hits": [
{
"_index": "bookdb_index",
"_type": "book",
"_id": "4",
"_score": 0.5961596,
"_source": {
"summary": "Comprehensive guide to implementing a scalable search engine using Apache Solr",
"title": "Solr in Action",
"publish_date": "2014-04-05"
}
}
]“AUTO”的模糊值相当于当字段长度大于5时指定值2。但是,设置80%的拼写错误的编辑距离为1,将模糊度设置为1可能会提高整体搜索性能。 有关更多信息, Typos and Misspellingsch 。
6、 Wildcard Query 通配符检索
通配符查询允许您指定匹配的模式,而不是整个词组(term)检索。
- ? 匹配任何字符;
- *匹配零个或多个字符。
举例,要查找具有以“t”字母开头的作者的所有记录,如下所示:
POST /bookdb_index/book/_search
{
"query": {
"wildcard" : {
"authors" : "t*"
}
},
"_source": ["title", "authors"],
"highlight": {
"fields" : {
"authors" : {}
}
}
}
[Results]
"hits": [
{
"_index": "bookdb_index",
"_type": "book",
"_id": "1",
"_score": 1,
"_source": {
"title": "Elasticsearch: The Definitive Guide",
"authors": [
"clinton gormley",
"zachary tong"
]
},
"highlight": {
"authors": [
"zachary <em>tong</em>"
]
}
},
{
"_index": "bookdb_index",
"_type": "book",
"_id": "2",
"_score": 1,
"_source": {
"title": "Taming Text: How to Find, Organize, and Manipulate It",
"authors": [
"grant ingersoll",
"thomas morton",
"drew farris"
]
},
"highlight": {
"authors": [
"<em>thomas</em> morton"
]
}
},
{
"_index": "bookdb_index",
"_type": "book",
"_id": "4",
"_score": 1,
"_source": {
"title": "Solr in Action",
"authors": [
"trey grainger",
"timothy potter"
]
},
"highlight": {
"authors": [
"<em>trey</em> grainger",
"<em>timothy</em> potter"
]
}
}
]7、正则表达式检索( Regexp Query)
正则表达式能指定比通配符检索更复杂的检索模式。
举例如下:
POST /bookdb_index/book/_search
{
"query": {
"regexp" : {
"authors" : "t[a-z]*y"
}
},
"_source": ["title", "authors"],
"highlight": {
"fields" : {
"authors" : {}
}
}
}
[Results]
"hits": [
{
"_index": "bookdb_index",
"_type": "book",
"_id": "4",
"_score": 1,
"_source": {
"title": "Solr in Action",
"authors": [
"trey grainger",
"timothy potter"
]
},
"highlight": {
"authors": [
"<em>trey</em> grainger",
"<em>timothy</em> potter"
]
}
}
]8、匹配短语检索( Match Phrase Query)
匹配短语查询要求查询字符串中的所有词都存在于文档中,按照查询字符串中指定的顺序并且彼此靠近。
默认情况下,这些词必须完全相邻,但您可以指定偏离值(slop value),该值指示在仍然考虑文档匹配的情况下词与词之间的偏离值。
POST /bookdb_index/book/_search
{
"query": {
"multi_match" : {
"query": "search engine",
"fields": ["title", "summary"],
"type": "phrase",
"slop": 3
}
},
"_source": [ "title", "summary", "publish_date" ]
}
[Results]
"hits": [
{
"_index": "bookdb_index",
"_type": "book",
"_id": "4",
"_score": 0.22327082,
"_source": {
"summary": "Comprehensive guide to implementing a scalable search engine using Apache Solr",
"title": "Solr in Action",
"publish_date": "2014-04-05"
}
},
{
"_index": "bookdb_index",
"_type": "book",
"_id": "1",
"_score": 0.16113183,
"_source": {
"summary": "A distibuted real-time search and analytics engine",
"title": "Elasticsearch: The Definitive Guide",
"publish_date": "2015-02-07"
}
}
]注意:在上面的示例中,对于非短语类型查询,文档_id 1通常具有较高的分数,并且显示在文档_id 4之前,因为其字段长度较短。
然而,作为一个短语查询,词与词之间的接近度被考虑在内,所以文档_id 4分数更好。
9、匹配词组前缀检索
匹配词组前缀查询在查询时提供搜索即时类型或“相对简单”的自动完成版本,而无需以任何方式准备数据。
像match_phrase查询一样,它接受一个斜率参数,使得单词的顺序和相对位置没有那么“严格”。 它还接受max_expansions参数来限制匹配的条件数以减少资源强度。
POST /bookdb_index/book/_search
{
"query": {
"match_phrase_prefix" : {
"summary": {
"query": "search en",
"slop": 3,
"max_expansions": 10
}
}
},
"_source": [ "title", "summary", "publish_date" ]
}
[Results]
"hits": [
{
"_index": "bookdb_index",
"_type": "book",
"_id": "4",
"_score": 0.5161346,
"_source": {
"summary": "Comprehensive guide to implementing a scalable search engine using Apache Solr",
"title": "Solr in Action",
"publish_date": "2014-04-05"
}
},
{
"_index": "bookdb_index",
"_type": "book",
"_id": "1",
"_score": 0.37248808,
"_source": {
"summary": "A distibuted real-time search and analytics engine",
"title": "Elasticsearch: The Definitive Guide",
"publish_date": "2015-02-07"
}
}
]注意:查询时间搜索类型具有性能成本。
一个更好的解决方案是将时间作为索引类型。
更多相关API查询 Completion Suggester API 或者 Edge-Ngram filters 。
10、字符串检索( Query String)
query_string查询提供了以简明的简写语法执行多匹配查询 multi_match queries ,布尔查询 bool queries ,提升得分 boosting ,模糊匹配 fuzzy matching ,通配符 wildcards ,正则表达式 regexp 和范围查询 range queries 的方式。
在下面的例子中,我们对“ search algorithm ”一词执行模糊搜索,其中一本作者是“ grant ingersoll ”或“tom morton”。 我们搜索所有字段,但将提升应用于文档2的摘要字段。
POST /bookdb_index/book/_search
{
"query": {
"query_string" : {
"query": "(saerch~1 algorithm~1) AND (grant ingersoll) OR (tom morton)",
"fields": ["_all", "summary^2"]
}
},
"_source": [ "title", "summary", "authors" ],
"highlight": {
"fields" : {
"summary" : {}
}
}
}
[Results]
"hits": [
{
"_index": "bookdb_index",
"_type": "book",
"_id": "2",
"_score": 0.14558059,
"_source": {
"summary": "organize text using approaches such as full-text search, proper name recognition, clustering, tagging, information extraction, and summarization",
"title": "Taming Text: How to Find, Organize, and Manipulate It",
"authors": [
"grant ingersoll",
"thomas morton",
"drew farris"
]
},
"highlight": {
"summary": [
"organize text using approaches such as full-text <em>search</em>, proper name recognition, clustering, tagging, information extraction, and summarization"
]
}
}
]11、简化的字符串检索 (Simple Query String)
simple_query_string查询是query_string查询的一个版本,更适合用于暴露给用户的单个搜索框,
因为 它分别用+ / | / - 替换了AND / OR / NOT的使用,并放弃查询的无效部分,而不是在用户出错时抛出异常。
POST /bookdb_index/book/_search
{
"query": {
"simple_query_string" : {
"query": "(saerch~1 algorithm~1) + (grant ingersoll) | (tom morton)",
"fields": ["_all", "summary^2"]
}
},
"_source": [ "title", "summary", "authors" ],
"highlight": {
"fields" : {
"summary" : {}
}
}
}12、Term/Terms检索(指定字段检索)
上面1-11小节的例子是全文搜索的例子。 有时我们对结构化搜索更感兴趣,我们希望在其中找到完全匹配并返回结果。
在下面的例子中,我们搜索Manning Publications发布的索引中的所有图书(借助 term和terms查询 )。
POST /bookdb_index/book/_search
{
"query": {
"term" : {
"publisher": "manning"
}
},
"_source" : ["title","publish_date","publisher"]
}
[Results]
"hits": [
{
"_index": "bookdb_index",
"_type": "book",
"_id": "2",
"_score": 1.2231436,
"_source": {
"publisher": "manning",
"title": "Taming Text: How to Find, Organize, and Manipulate It",
"publish_date": "2013-01-24"
}
},
{
"_index": "bookdb_index",
"_type": "book",
"_id": "3",
"_score": 1.2231436,
"_source": {
"publisher": "manning",
"title": "Elasticsearch in Action",
"publish_date": "2015-12-03"
}
},
{
"_index": "bookdb_index",
"_type": "book",
"_id": "4",
"_score": 1.2231436,
"_source": {
"publisher": "manning",
"title": "Solr in Action",
"publish_date": "2014-04-05"
}
}
]Multiple terms可指定多个关键词进行检索。
{
"query": {
"terms" : {
"publisher": ["oreilly", "packt"]
}
}
}13、Term排序检索-(Term Query - Sorted)
Term查询和其他查询一样,轻松的实现排序。多级排序也是允许的。
POST /bookdb_index/book/_search
{
"query": {
"term" : {
"publisher": "manning"
}
},
"_source" : ["title","publish_date","publisher"],
"sort": [
{ "publish_date": {"order":"desc"}},
{ "title": { "order": "desc" }}
]
}
[Results]
"hits": [
{
"_index": "bookdb_index",
"_type": "book",
"_id": "3",
"_score": null,
"_source": {
"publisher": "manning",
"title": "Elasticsearch in Action",
"publish_date": "2015-12-03"
},
"sort": [
1449100800000,
"in"
]
},
{
"_index": "bookdb_index",
"_type": "book",
"_id": "4",
"_score": null,
"_source": {
"publisher": "manning",
"title": "Solr in Action",
"publish_date": "2014-04-05"
},
"sort": [
1396656000000,
"solr"
]
},
{
"_index": "bookdb_index",
"_type": "book",
"_id": "2",
"_score": null,
"_source": {
"publisher": "manning",
"title": "Taming Text: How to Find, Organize, and Manipulate It",
"publish_date": "2013-01-24"
},
"sort": [
1358985600000,
"to"
]
}
]14、范围检索(Range query)
另一个结构化检索的例子是范围检索。下面的举例中,我们检索了2015年发布的书籍。
POST /bookdb_index/book/_search
{
"query": {
"range" : {
"publish_date": {
"gte": "2015-01-01",
"lte": "2015-12-31"
}
}
},
"_source" : ["title","publish_date","publisher"]
}
[Results]
"hits": [
{
"_index": "bookdb_index",
"_type": "book",
"_id": "1",
"_score": 1,
"_source": {
"publisher": "oreilly",
"title": "Elasticsearch: The Definitive Guide",
"publish_date": "2015-02-07"
}
},
{
"_index": "bookdb_index",
"_type": "book",
"_id": "3",
"_score": 1,
"_source": {
"publisher": "manning",
"title": "Elasticsearch in Action",
"publish_date": "2015-12-03"
}
}
]注意:范围查询适用于日期,数字和字符串类型字段。
15、过滤检索(Filtered query)5.0版本已不再存在,不必关注。
过滤的查询允许您过滤查询的结果。 如下的例子,我们在标题或摘要中查询名为“Elasticsearch”的图书,但是我们希望将结果过滤到只有20个或更多评论的结果。
POST /bookdb_index/book/_search
{
"query": {
"filtered": {
"query" : {
"multi_match": {
"query": "elasticsearch",
"fields": ["title","summary"]
}
},
"filter": {
"range" : {
"num_reviews": {
"gte": 20
}
}
}
}
},
"_source" : ["title","summary","publisher", "num_reviews"]
}
[Results]
"hits": [
{
"_index": "bookdb_index",
"_type": "book",
"_id": "1",
"_score": 0.5955761,
"_source": {
"summary": "A distibuted real-time search and analytics engine",
"publisher": "oreilly",
"num_reviews": 20,
"title": "Elasticsearch: The Definitive Guide"
}
}
]注意:已过滤的查询不要求存在要过滤的查询。 如果没有指定查询,则运行match_all查询,基本上返回索引中的所有文档,然后对其进行过滤。
实际上,首先运行过滤器,减少需要查询的表面积。 此外,过滤器在第一次使用后被缓存,这使得它非常有效。
更新:已筛选的查询已推出的Elasticsearch 5.X版本中移除,有利于布尔查询。 这是与上面重写的使用bool查询相同的示例。 返回的结果是完全一样的。
POST /bookdb_index/book/_search
{
"query": {
"bool": {
"must" : {
"multi_match": {
"query": "elasticsearch",
"fields": ["title","summary"]
}
},
"filter": {
"range" : {
"num_reviews": {
"gte": 20
}
}
}
}
},
"_source" : ["title","summary","publisher", "num_reviews"]
}16、多个过滤器检索(Multiple Filters)5.x不再支持,无需关注。
多个过滤器可以通过使用布尔过滤器进行组合。
在下一个示例中,过滤器确定返回的结果必须至少包含20个评论,不得在2015年之前发布,并且应该由oreilly发布。
POST /bookdb_index/book/_search
{
"query": {
"filtered": {
"query" : {
"multi_match": {
"query": "elasticsearch",
"fields": ["title","summary"]
}
},
"filter": {
"bool": {
"must": {
"range" : { "num_reviews": { "gte": 20 } }
},
"must_not": {
"range" : { "publish_date": { "lte": "2014-12-31" } }
},
"should": {
"term": { "publisher": "oreilly" }
}
}
}
}
},
"_source" : ["title","summary","publisher", "num_reviews", "publish_date"]
}
[Results]
"hits": [
{
"_index": "bookdb_index",
"_type": "book",
"_id": "1",
"_score": 0.5955761,
"_source": {
"summary": "A distibuted real-time search and analytics engine",
"publisher": "oreilly",
"num_reviews": 20,
"title": "Elasticsearch: The Definitive Guide",
"publish_date": "2015-02-07"
}
}
]17、 Function 得分:Field值因子( Function Score: Field Value Factor)
可能有一种情况,您想要将文档中特定字段的值纳入相关性分数的计算。 这在您希望基于其受欢迎程度提升文档的相关性的情况下是有代表性的场景。
在我们的例子中,我们希望增加更受欢迎的书籍(按评论数量判断)。 这可以使用field_value_factor函数得分。
POST /bookdb_index/book/_search
{
"query": {
"function_score": {
"query": {
"multi_match" : {
"query" : "search engine",
"fields": ["title", "summary"]
}
},
"field_value_factor": {
"field" : "num_reviews",
"modifier": "log1p",
"factor" : 2
}
}
},
"_source": ["title", "summary", "publish_date", "num_reviews"]
}
[Results]
"hits": [
{
"_index": "bookdb_index",
"_type": "book",
"_id": "1",
"_score": 0.44831306,
"_source": {
"summary": "A distibuted real-time search and analytics engine",
"num_reviews": 20,
"title": "Elasticsearch: The Definitive Guide",
"publish_date": "2015-02-07"
}
},
{
"_index": "bookdb_index",
"_type": "book",
"_id": "4",
"_score": 0.3718407,
"_source": {
"summary": "Comprehensive guide to implementing a scalable search engine using Apache Solr",
"num_reviews": 23,
"title": "Solr in Action",
"publish_date": "2014-04-05"
}
},
{
"_index": "bookdb_index",
"_type": "book",
"_id": "3",
"_score": 0.046479136,
"_source": {
"summary": "build scalable search applications using Elasticsearch without having to do complex low-level programming or understand advanced data science algorithms",
"num_reviews": 18,
"title": "Elasticsearch in Action",
"publish_date": "2015-12-03"
}
},
{
"_index": "bookdb_index",
"_type": "book",
"_id": "2",
"_score": 0.041432835,
"_source": {
"summary": "organize text using approaches such as full-text search, proper name recognition, clustering, tagging, information extraction, and summarization",
"num_reviews": 12,
"title": "Taming Text: How to Find, Organize, and Manipulate It",
"publish_date": "2013-01-24"
}
}
]注1:我们可以运行一个常规的multi_match查询,并按num_reviews字段排序,但是我们失去了相关性得分的好处。
注2:有许多附加参数可以调整对原始相关性分数
(如“ modifier ”,“ factor ”,“boost_mode”等)的增强效果的程度。
详见 Elasticsearch guide.
18、 Function 得分:衰减函数( Function Score: Decay Functions )
假设,我们不是想通过一个字段的值逐渐增加得分,以获取理想的结果。 举例:价格范围、数字字段范围、日期范围。 在我们的例子中,我们正在搜索2014年6月左右出版的“ search engines ”的书籍。
POST /bookdb_index/book/_search
{
"query": {
"function_score": {
"query": {
"multi_match" : {
"query" : "search engine",
"fields": ["title", "summary"]
}
},
"functions": [
{
"exp": {
"publish_date" : {
"origin": "2014-06-15",
"offset": "7d",
"scale" : "30d"
}
}
}
],
"boost_mode" : "replace"
}
},
"_source": ["title", "summary", "publish_date", "num_reviews"]
}
[Results]
"hits": [
{
"_index": "bookdb_index",
"_type": "book",
"_id": "4",
"_score": 0.27420625,
"_source": {
"summary": "Comprehensive guide to implementing a scalable search engine using Apache Solr",
"num_reviews": 23,
"title": "Solr in Action",
"publish_date": "2014-04-05"
}
},
{
"_index": "bookdb_index",
"_type": "book",
"_id": "1",
"_score": 0.005920768,
"_source": {
"summary": "A distibuted real-time search and analytics engine",
"num_reviews": 20,
"title": "Elasticsearch: The Definitive Guide",
"publish_date": "2015-02-07"
}
},
{
"_index": "bookdb_index",
"_type": "book",
"_id": "2",
"_score": 0.000011564,
"_source": {
"summary": "organize text using approaches such as full-text search, proper name recognition, clustering, tagging, information extraction, and summarization",
"num_reviews": 12,
"title": "Taming Text: How to Find, Organize, and Manipulate It",
"publish_date": "2013-01-24"
}
},
{
"_index": "bookdb_index",
"_type": "book",
"_id": "3",
"_score": 0.0000059171475,
"_source": {
"summary": "build scalable search applications using Elasticsearch without having to do complex low-level programming or understand advanced data science algorithms",
"num_reviews": 18,
"title": "Elasticsearch in Action",
"publish_date": "2015-12-03"
}
}
]19、Function得分:脚本得分( Function Score: Script Scoring )
在内置计分功能不符合您需求的情况下,可以选择指定用于评分的Groovy脚本。
在我们的示例中,我们要指定一个考虑到publish_date的脚本,然后再决定考虑多少评论。 较新的书籍可能没有这么多的评论,所以他们不应该为此付出“代价”。
得分脚本如下所示:
``
publish_date = doc['publish_date'].value
num_reviews = doc['num_reviews'].value
if (publish_date > Date.parse('yyyy-MM-dd', threshold).getTime()) {
my_score = Math.log(2.5 + num_reviews)
} else {
my_score = Math.log(1 + num_reviews)
}
return my_score要动态使用评分脚本,我们使用script_score参数:
POST /bookdb_index/book/_search
{
"query": {
"function_score": {
"query": {
"multi_match" : {
"query" : "search engine",
"fields": ["title", "summary"]
}
},
"functions": [
{
"script_score": {
"params" : {
"threshold": "2015-07-30"
},
"script": "publish_date = doc['publish_date'].value; num_reviews = doc['num_reviews'].value; if (publish_date > Date.parse('yyyy-MM-dd', threshold).getTime()) { return log(2.5 + num_reviews) }; return log(1 + num_reviews);"
}
}
]
}
},
"_source": ["title", "summary", "publish_date", "num_reviews"]
}
[Results]
"hits": {
"total": 4,
"max_score": 0.8463001,
"hits": [
{
"_index": "bookdb_index",
"_type": "book",
"_id": "1",
"_score": 0.8463001,
"_source": {
"summary": "A distibuted real-time search and analytics engine",
"num_reviews": 20,
"title": "Elasticsearch: The Definitive Guide",
"publish_date": "2015-02-07"
}
},
{
"_index": "bookdb_index",
"_type": "book",
"_id": "4",
"_score": 0.7067348,
"_source": {
"summary": "Comprehensive guide to implementing a scalable search engine using Apache Solr",
"num_reviews": 23,
"title": "Solr in Action",
"publish_date": "2014-04-05"
}
},
{
"_index": "bookdb_index",
"_type": "book",
"_id": "3",
"_score": 0.08952084,
"_source": {
"summary": "build scalable search applications using Elasticsearch without having to do complex low-level programming or understand advanced data science algorithms",
"num_reviews": 18,
"title": "Elasticsearch in Action",
"publish_date": "2015-12-03"
}
},
{
"_index": "bookdb_index",
"_type": "book",
"_id": "2",
"_score": 0.07602123,
"_source": {
"summary": "organize text using approaches such as full-text search, proper name recognition, clustering, tagging, information extraction, and summarization",
"num_reviews": 12,
"title": "Taming Text: How to Find, Organize, and Manipulate It",
"publish_date": "2013-01-24"
}
}
]
}注1:要使用动态脚本,必须为config / elasticsearch.yml文件中的Elasticsearch实例启用它。 也可以使用已经存储在Elasticsearch服务器上的脚本。 查看 Elasticsearch reference docs 以获取更多信息。
**注2:**JSON不能包含嵌入的换行符,因此分号用于分隔语句。
转自:https://blog.csdn.net/laoyang360/article/details/76769208?utm_source=copy
参考:https://github.com/quanke/elasticsearch-java
https://es.xiaoleilu.com/040_Distributed_CRUD/00_Intro.html
https://github.com/elasticsearch-cn/elasticsearch-definitive-guide