You are given a tree (a graph with n vertices and n - 1 edges in which it's possible to reach any vertex from any other vertex using only its edges).
A vertex can be destroyed if this vertex has even degree. If you destroy a vertex, all edges connected to it are also deleted.
Destroy all vertices in the given tree or determine that it is impossible.
The first line contains integer n (1 ≤ n ≤ 2·105) — number of vertices in a tree.
The second line contains n integers p1, p2, ..., pn (0 ≤ pi ≤ n). If pi ≠ 0 there is an edge between vertices i and pi. It is guaranteed that the given graph is a tree.
If it's possible to destroy all vertices, print "YES" (without quotes), otherwise print "NO" (without quotes).
If it's possible to destroy all vertices, in the next n lines print the indices of the vertices in order you destroy them. If there are multiple correct answers, print any.
5
0 1 2 1 2
YES
1
2
3
5
4
4
0 1 2 3
NO
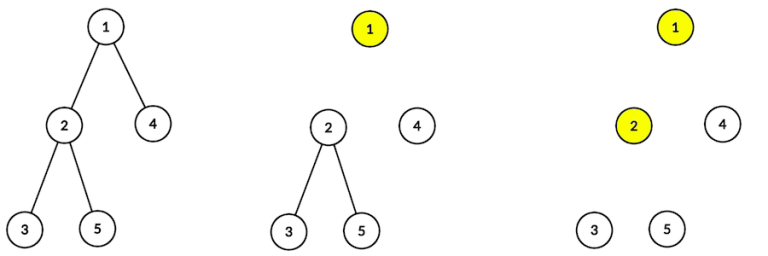
In the first example at first you have to remove the vertex with index 1 (after that, the edges (1, 2) and (1, 4) are removed), then the vertex with index 2 (and edges (2, 3) and (2, 5) are removed). After that there are no edges in the tree, so you can remove remaining vertices in any order.
题目大意:给你一棵树,只能删除度数为偶数的节点,节点删除后,与它相连的边也会删除。问你能否把所有点删除。
解题思路:只要你能想到,如果一棵树,有偶数条边,那么他一定能被删除完!或者说,一棵树有奇数个节点,那么他肯定能被删除完!因为,如果边为奇数,每次删除偶数条边,最后肯定剩奇数个边啊!如果边为偶数,每次删除偶数条边,最后肯定能删除完!所以基于这个思想,我们递归的删除点即可。从根节点开始,如果某一棵子树他的节点个数为偶数(加上当前节点就为奇数了),那么就深搜这颗子树,递归删除。
#include <bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std; vector<int> ch[200005]; int sz[200005]; void getsize(int u, int pre) { sz[u] = 1; for (int i = 0; i < ch[u].size(); ++i) { if (ch[u][i] != pre) { getsize(ch[u][i], u); sz[u] += sz[ch[u][i]]; } } } void dfs(int u, int pre) { for (int i = 0; i < ch[u].size(); i++) { if (ch[u][i] != pre) { if (sz[ch[u][i]] % 2 == 0) { dfs(ch[u][i], u); } } } printf("%d ", u); for (int i = 0; i < ch[u].size(); i++) { if (ch[u][i] != pre) { if (sz[ch[u][i]] % 2 == 1) { dfs(ch[u][i], u); } } } } int main() { int N; scanf("%d", &N); int temp; int root; for (int i = 1; i <= N; i++) { scanf("%d", &temp); if (temp != 0) { ch[i].push_back(temp); ch[temp].push_back(i); } else { root = i; } } if (N % 2 == 0) { printf("NO "); } else { getsize(root,-1); printf("YES "); dfs(root, -1); } return 0; }
我wa的代码,原因是,我的写法是每次找出边是偶数的,删掉,再继续,仔细思考找到了可以把我wa的样例:
 先删1的话,会导致输出“NO”
先删1的话,会导致输出“NO”

#include <iostream> #include<cstring> #include<string> #include<cstdio> #include<algorithm> #include<cmath> #include<deque> #include<vector> #include<queue> #define ll unsigned long long #define inf 0x3f3f3f3f using namespace std; vector<int>v[200005]; bool us[200005]; int in[200005]; queue<int>q; int main() { int n; cin>>n; memset(us,0,sizeof(us)); memset(in,0,sizeof(in)); while(!q.empty()) q.pop(); for(int i=1;i<=n;i++) { int x; cin>>x; if(x!=0) { v[x].push_back (i); v[i].push_back (x); in[i]++; in[x]++; } } if(n%2==0) cout<<"NO"<<endl; else { while(1) { int k=-1; for(int i=1;i<=n;i++) { if(!us[i]&&in[i]%2==0) { k=i; break; } } if(k==-1) break; q.push(k); us[k]=1; for(int j=0;j<v[k].size ();j++) { int y=v[k][j]; if(us[y]) continue; in[y]--; } } bool f=1; for(int i=1;i<=n;i++) { if(!us[i]) { f=0; break; } } if(!f) cout<<"NO"; else { cout<<"YES"<<endl; while(!q.empty ()) { cout<<q.front()<<endl; q.pop(); } } } return 0; }
