什么是线性表
所谓的线性表是由n个类型相同数据结构的有限序列(见下图)
线性表的特点
- 同一性
- 有穷性
- 有序性
存储结构
-
顺序存储结构
-
链式存储结构
顺序存储结构
存储结构样式
typedef struct
{
ElemType elem[MAXSIZE]; //线性表的占用的存储空间
int last;//记录表中最后一个元素所在的位置
}Seqlist;
这个比较简单,不做过多的解释直接上代码
代码样例
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
const int MAXSIZE = 100;
typedef struct
{
int elem[MAXSIZE];//ElemType
int last;
}Seqlist;
/*初始化线性表*/
bool InitList(Seqlist *l){
memset(l->elem,0,sizeof(l->elem));
l->last=-1;
return true;
}
/*删除指定位置i开始的k个元素*/
bool DelList(Seqlist *l,int i,int k){
if(i < 1 || i > l->last+1){
cout << "非法删除位置" << endl;
return false;
}
else if(k <= l->last+1-i){
for(int j=i-1; j < k+i-1; j++)
l->elem[j]=0;
for(int j=i-1; j < l->last-k+1; j++)
l->elem[j]=l->elem[j+k];
l->last-=k;
return true;
}
else{
for(int j=i-1; j <= l->last; j++)
l->elem[j]=0;
l->last=i-2;
return true;
}
}
/*输出线性表中所有元素*/
void PrintList(Seqlist *l){
for(int i=0; i <= l->last; i++)
cout << l->elem[i] << " ";
}
/*查找线性表中元素所在位置*/
int Locate(Seqlist L,int e){
int i=0;
while (i < L.last && L.elem[i] != e)
i++;
if(i < L.last)
return i+1;
else
return -1;
}
int main(){
Seqlist *l;
Seqlist _list;
l=&_list;
if(InitList(l)){
int i,k,book=0;
cin >> i >> k;
while(cin >> l->elem[book]){
book++;
}
l->last=book-1;
if(DelList(l,i,k)){
cout << "delete success" << endl;
PrintList(l);
}
else{
cout << "删除失败" << endl;
PrintList(l);
}
}
else
cout << "初始化失败" << endl;
system("pause");
return 0;
}
我们来讲讲这种存储结构的优缺点
优点
- 方便读取某个位置上元素
缺点
- 线性表长度需在确定,空间有限
- 插入删除某个元素效率低
链式存储结构
单链表
即每个结点中只存储数据和下一个结点地址(见下图),故只能从头开始依次访问链表中的节点
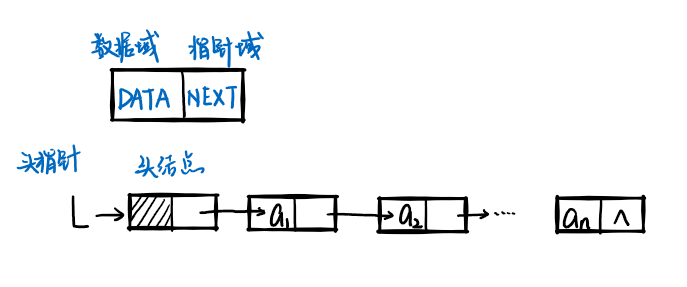
访问第一个存放数据的结点方法p=L->next
存储结构样式
struct Node{
ElemType data;
struct Node *next;
}Node,*Linklist;
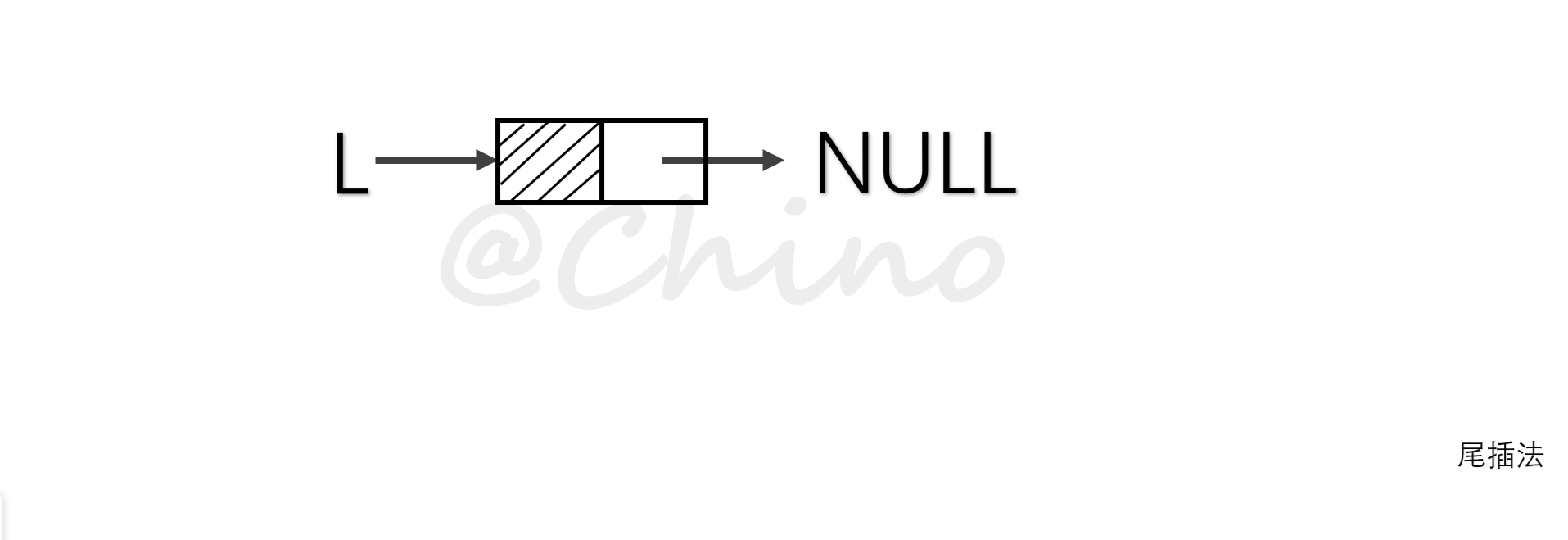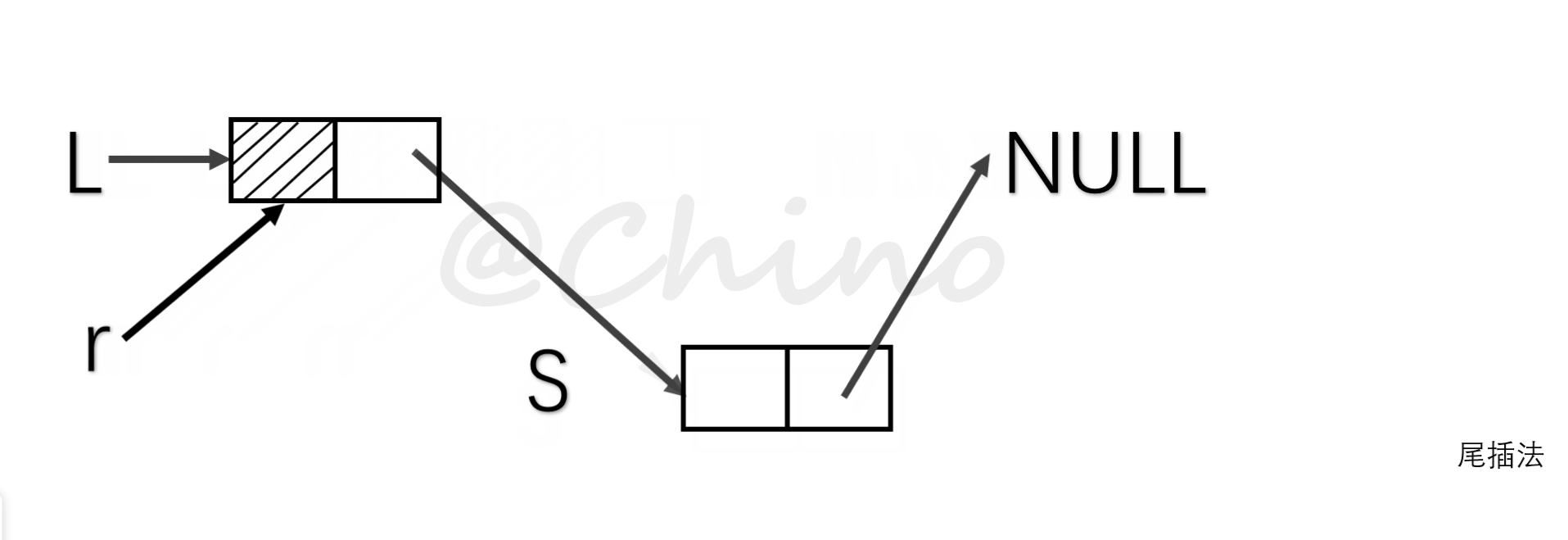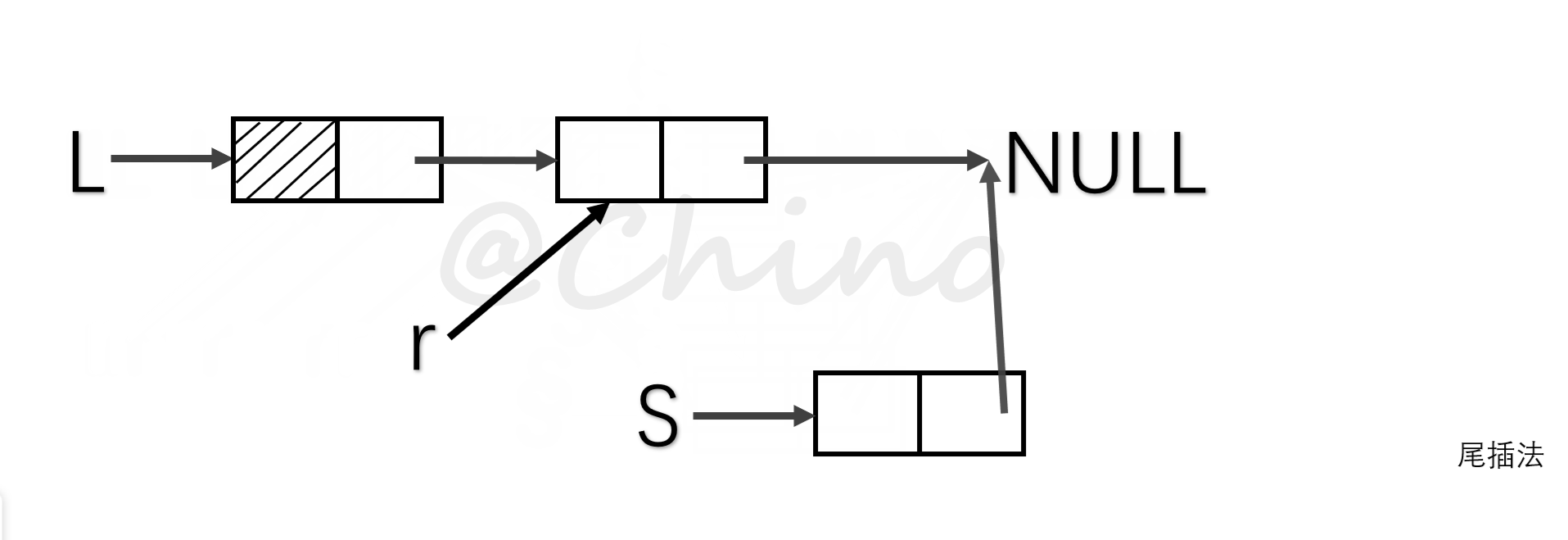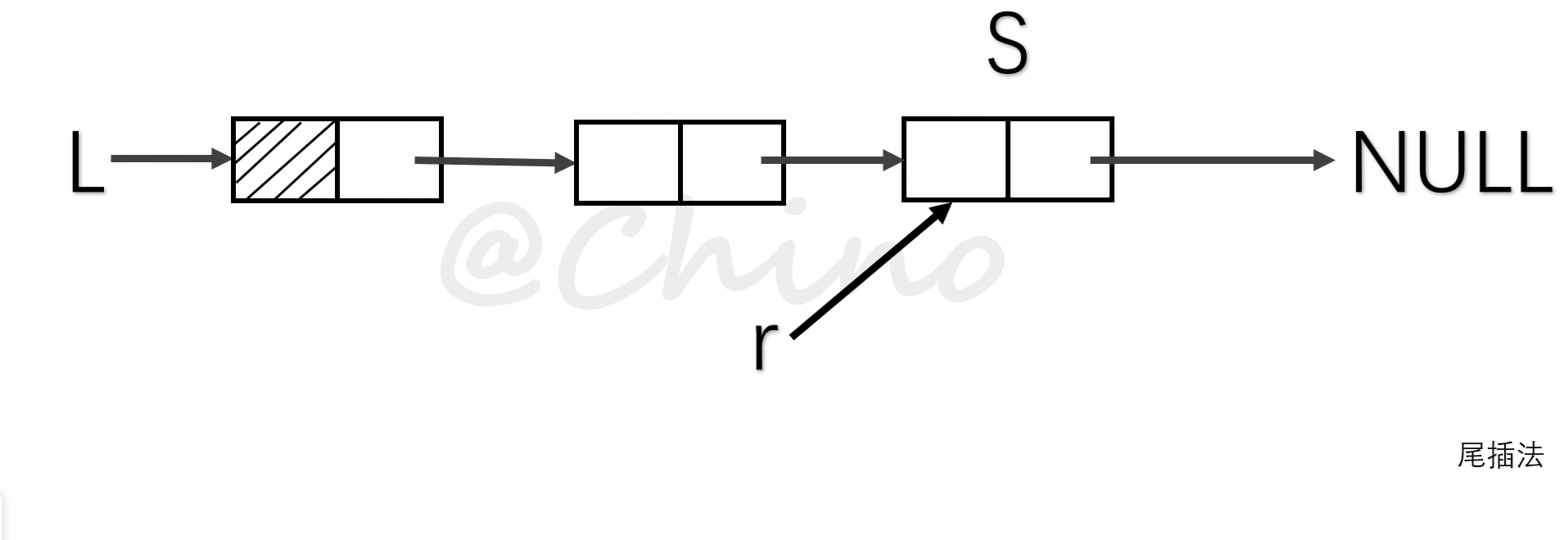
其中建表的方法有两种,一种是头插法,另一种是尾插法(见下图)

代码样例
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
typedef int ElemType;
typedef struct Node{
ElemType data;
struct Node *next;
}Node,*Linklist;
/*初始化链表*/
void InitList(Linklist *L){
*L=(Linklist)malloc(sizeof(Node));
(*L)->next = NULL;
}
/*头插法建立链表*/
void CreatFromHead(Linklist L){
Node *s;
ElemType num;//每个节点的数据,可以是其他数据类型
while (cin >> num)
{
s=(Node *)malloc(sizeof(Node));
s->data=num;
s->next=L->next;
L->next=s;
}
}
/*尾插法建立链表*/
void CreatFromTail(Linklist L){
Node *s,*r;
r=L;
ElemType num;//每个节点的数据,可以是其他数据类型
while (cin >> num)
{
s=(Node *)malloc(sizeof(Node));
s->data=num;
r->next=s;
r=s;
}
}
/*求链表的长度*/
int ListLength(Linklist L)
{
Node* p=L->next;
int i=0;
while(p != NULL){
i++;
p=p->next;
}
return i; //返回链表长度
}
/*删除第i个节点*/
bool Detele(Linklist L,int pos){
if(pos <= 0 && pos > ListLength(L))
return false;
Node *p, *r;
p=L;
int j=0;
while((p->next != NULL) && (j <= pos-1)){//找到该位置的前一个节点
p=p->next;
j++;
}
if(p->next == NULL)
return false;
r = p->next;
p->next = r->next;
free(r);
return true;
}
/*查询第i个节点*/
Node* Query(Linklist L,int pos){
if(pos <= 0 && pos > ListLength(L))
return NULL;
Node* p=L;
int j=0;
while((p->next != NULL) && (j != pos)){
p=p->next;
j++;
}
return p;
}
int main(){
Node *L;
InitList(&L);
return 0;
}
双向链表
即单链表每个节点中增加了存储前继指针域(用于存放前继结点的所在地址)(见下图),解决了单链表不能任意结点访问所有表中的元素的问题

存储结构样式
struct Node{
ElemType data;
struct Node *next ,*prior;
}Node,*Linklist;
循环表
*采用顺序存储结构的循环表(队列)
这里直接展示代码了,我们来讲一个应用——利用循环表(或者链表)输出杨辉三角形(过程见下图)

我们假设需要输出4行
代码样例
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
const int MAXSIZE=50;//设定顺序表最大的顺序表,输出的杨辉三角的每层元素不能超过该最大长度-1
typedef struct{
int element[MAXSIZE];
int front;//队头
int rear;//队尾
}SeqQueue;
void InitQueue(SeqQueue *Q){
Q->front=Q->rear=0;
}
bool IsEmpty(SeqQueue *Q){
if(Q->front == Q->rear)
return true;
return false;
}
void GetHead(SeqQueue *Q, int *x)//取对头元素
{
if (Q->front == Q->rear)
return ;
*x = Q->element[Q->front];
return ;
}
void EnterQueue(SeqQueue *Q,int x){
if((Q->rear+1)%MAXSIZE == Q->front)
return ;
Q->element[Q->rear] = x;
Q->rear = (Q->rear + 1) % MAXSIZE;
return ;
}
void DeleteQueue(SeqQueue *Q,int *x){
if (Q->front == Q->rear)
return ;
*x = Q->element[Q->front];
Q->front = (Q->front + 1) % MAXSIZE;
return ;
}
void YangHuiTriangle(int N)
{
int n, i, x, temp;
SeqQueue Q;
InitQueue(&Q);
EnterQueue(&Q, 1); /* 第一行元素入队*/
for (n = 2; n <= N; n++) /* 产生第 n 行元素并入队,同时打印第 n-1 行的元素*/
{
EnterQueue(&Q, 1); /* 第 n 行的第一个元素入队*/
for (i = 1; i <= n - 2; i++) /* 利用队中第 n-1 行元素产生第 n 行的中间 n-2 个元素并入队*/
{
DeleteQueue(&Q, &temp);
printf("%d", temp); /* 打印第 n-1 行的元素*/
GetHead(&Q, &x);
temp = temp + x; /*利用队中第 n-1 行元素产生第 n 行元素*/
EnterQueue(&Q, temp);
}
DeleteQueue(&Q, &x);
printf("%d
", x); /* 打印第 n-1 行的最后一个元素 */
EnterQueue(&Q, 1); /* 第 n 行的最后一个元素入队 */
}
while (!IsEmpty(&Q)) /* 打印最后一行元素 */
{
DeleteQueue(&Q, &x);
printf("%d", x);
}
}
int main()
{
int num;
cin >> num;
YangHuiTriangle(num);
system("pause");
return 0;
}
循环链表
单向循环链表
即在单链表的基础上,在其尾结点的指针域指向头结点(形成一个环状的结构)
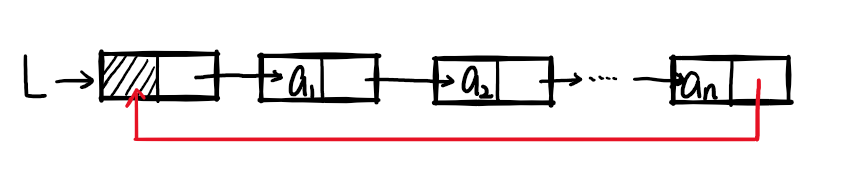
存储结构(同单向链表)
代码样例
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
typedef int ElemType;
typedef struct Node{
ElemType data;//ElemType
struct Node *next;
}Node,*Linklist;
/*初始化循环链表*/
void InitCList(Linklist *CL){
*CL=(Linklist)malloc(sizeof(Node));
*CL->next = *CL;
}
/*尾插法建立循环链表*/
void CreatFromTail(Linklist CL){
Node *s,*r;
r=CL;
ElemType num;//每个节点的数据,可以是其他数据类型
while (cin >> num)
{
s=(Node *)malloc(sizeof(Node));
s->data=num;
r->next=s;
r=s;
}
r->newxt=CL;
}
/*求链表的长度*/
int ListLength(Linklist CL)
{
Node* p=CL->next;
int i=0;
while(p != CL){
i++;
p=p->next;
}
return i; //返回链表长度
}
/*查询第i个节点*/
Node* Query(Linklist CL,int pos){
if(pos <= 0 && pos > ListLength(CL))
return NULL;
Node* p=CL;
int j=0;
while((p->next != CL) && (j != pos)){
p=p->next;
j++;
}
return p;
}
/*删除第i个节点*/
bool Detele(Linklist CL,int pos){
if(pos <= 0 && pos > ListLength(L))
return false;
Node *p, *r;
p=CL;
int j=0;
while((p->next != CL) && (j <= pos-1)){//找到该位置的前一个节点
p=p->next;
j++;
}
if(p->next == CL)
return false;
r = p->next;
p->next = r->next;
free(r);
return true;
}
int main(){
Node *CL;
InitList(&CL);
return 0;
}
循环单链表的合并算法(算法复杂度(O(1)))
Linklist mergeCL(Linklist CLA,Linklist CLB){
Node *p;
p=CLA->next;
CLA->next=CLB->next->next;
free(CLB->next);
CLB->next=p;
return CLB;
}
双向循环链表
即在双向链表的基础上,在其头结点前继指针域以及尾结点后即指针域分别指向尾结点和头结点(同样形成一个环状结构)

存储结构(同双向链表)
代码样例(略)
特殊的线性表
栈
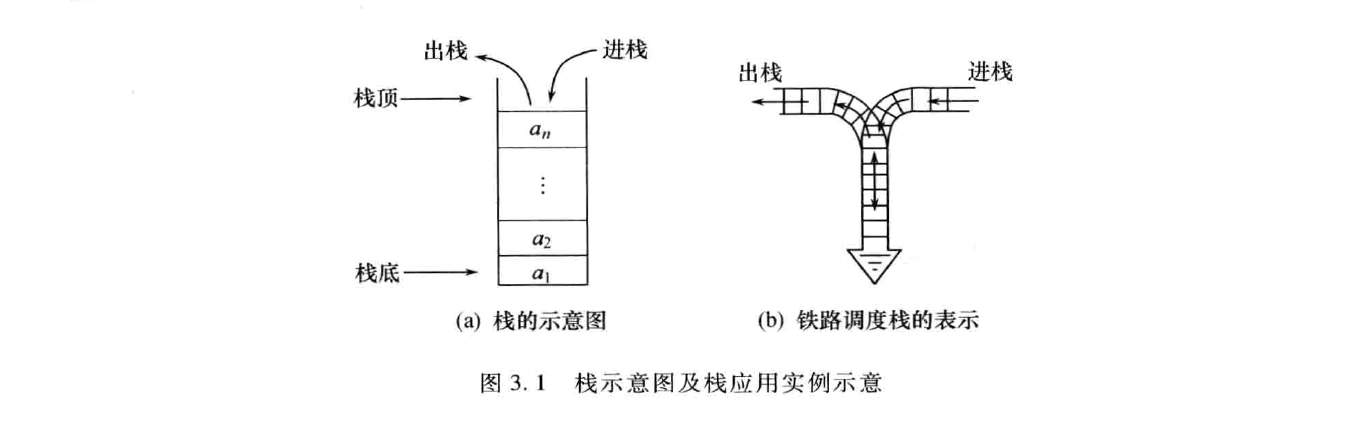
一种运算受限的线性表。限定只能在表尾进行插入和删除操作。同时也是递归的实现方法。
顺序栈·代码样例
/*
* @Author: Cafu-Chino
* @Date: 2020-05-21 20:07:41
* @Last Modified by: Cafu-Chino
* @Last Modified time: 2020-05-21 20:07:41
*/
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
const int maxn=50;
typedef int StackElementType;
typedef struct
{
/* data */
StackElementType elem[maxn];
int top;
}SeqStack;
void InitStack(SeqStack *S){
S->top = -1;
}
/*压入栈*/
bool Push (SeqStack *S,StackElementType a){
if(S->top == maxn-1)
return false;
S->top++;
S->elem[S->top] = a;
return true;
}
/*删除栈顶元素*/
bool Pop (SeqStack *S){
if(S->top == -1)
return false;
else
{
StackElementType a = S->top;
S->top--;
return true;
}
}
/*取栈顶*/
StackElementType GetTop(SeqStack *S){
if(S->top == -1){
return ;
}
else
{
StackElementType a = S->elem[S->top];
return a;
}
}
int main(){
SeqStack S;
InitStack(&S);
return 0;
}
双端栈·代码样例
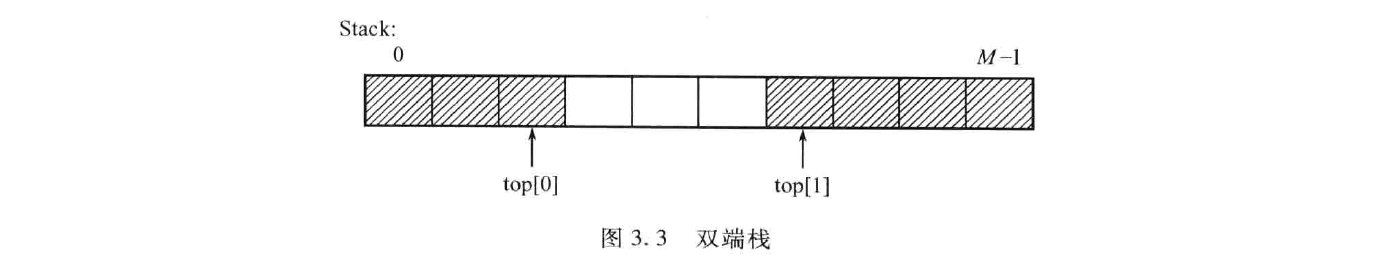
/*
* @Author: Cafu-Chino
* @Date: 2020-05-21 20:07:41
* @Last Modified by: Cafu-Chino
* @Last Modified time: 2020-05-21 20:07:41
*/
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
const int maxn=100;
typedef int StackElementType;
typedef struct
{
/* data */
StackElementType elem[maxn];
int top[2];
}DqStack;
void InitStack(SeqStack *S){
S->top[0] = -1;
S->top[1] = maxn;
}
/*压入栈*/
bool Push (SeqStack *S,StackElementType a,int i){
if(S->top[0]+1 == S->top[1])
return false;
if(i == 1){
S->top[0]++;
S->elem[S->top[0]] = a;
return true
}else if(i == 2){
S->top[1]--;
S->elem[S->top[1]] = a;
return true;
}
return false;
}
/*删除栈顶元素*/
bool Pop (SeqStack *S,int i){
if(i == 1){
if(S->top[0] == -1)
return false;
else
{
//StackElementType a = S->top[0];可以改为删除饼传回栈顶元素
S->top[0]--;
return true;
}
}
else if(i == 2){
if(S->top[1] == maxn)
return false;
else{
//StackElementType a = S->top[1];可以改为删除饼传回栈顶元素
S->top[1]++;
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
/*取栈顶*/
StackElementType GetTop(SeqStack *S,int i){
if(i == 1){
if(S->top[0] == -1)
return ;
else
{
StackElementType a = S->top[0];
return a;
}
}
else if(i == 2){
if(S->top[1] == maxn)
return ;
else{
StackElementType a = S->top[1];
return a;
}
}
return ;
}
int main(){
SeqStack S;
InitStack(&S);
return 0;
}
链栈·代码样例
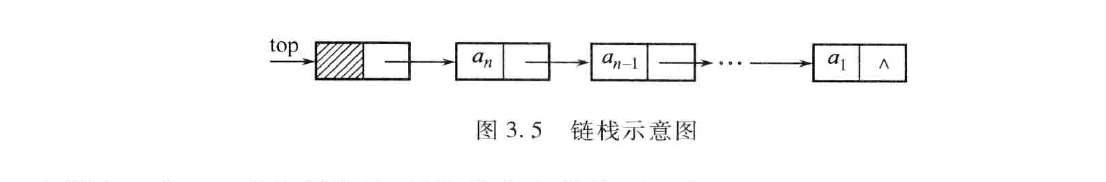
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<stdio.h>
const int maxn = 50;
typedef int StackElementType;
typedef struct node
{
StackElementType data;
struct node *next;
}LinkStackNode;
typedef LinkStackNode *LinkStack;
/*初始化栈*/
void InitStack(LinkStack *top){
top=(LinkStackNode *)malloc(sizeof(LinkStackNode));
(*top)->next=NULL;
}
/*压入栈*/
bool Push(LinkStack top,StackElementType a){
LinkStackNode *p;
p=(LinkStackNode *)malloc(sizeof(LinkStackNode));
if(p == NULL)
return false;
p->data = a;
p->next = top->next;
top->next = p;
return true;
}
/*删除栈顶元素*/
bool Pop(LinkStack top,StackElementType *a){
LinkStackNode *p;
p = top->next;
if(p == NULL)
return false;
top->next == p->next;
*a = p->data;
free(p);
return true;
}
/*判断栈是否为空*/
bool IsEmpty(LinkStack top){
if(top->next == NULL)
return true;
else
return false;
}
int main(){
LinkStack top;
InitStack(&top);
return 0;
}
队列
是一种运算受限的线性表。限定只能在表尾进行插入;只能在表头进行删除操作。
循环队列·代码样例(略,见上文杨辉三角)
链式队列·代码样例
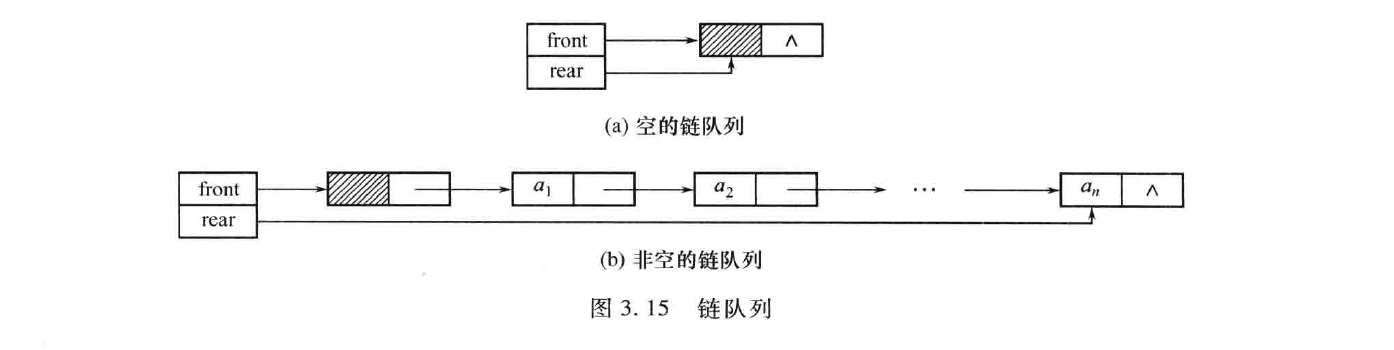
/*
* @Author: Cafu-Chino
* @Date: 2020-05-20 21:01:52
* @Last Modified by: Cafu-Chino
* @Last Modified time: 2020-05-20 21:01:52
* @Website: https://www.cnblogs.com/cafu-chino/
*/
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
typedef int QueueElementType;
typedef struct Node
{
QueueElementType data;
struct Node *next;
}LinkQueueNode;
typedef struct
{
LinkQueueNode *front;
LinkQueueNode *rear;
}LinkQueue;
/*初始化队列*/
bool InitQueue(LinkQueue *Q){
Q->front=(LinkQueueNode *)malloc(sizeof(LinkQueueNode));
if(Q->front != NULL){
Q->rear=Q->front;
Q->front->next=NULL;
return true;
}
return false;
}
/*入队*/
bool AddQueue(LinkQueue *Q,QueueElementType a){
LinkQueueNode * Node;
Node=(LinkQueueNode *)malloc(sizeof(LinkQueueNode));
if(Node!=NULL){
Node->data=a;
Node->next=NULL;
Q->rear->next=Node;
Q->rear=Node;
return true ;
}
return false;
}
/*出队*/
QueueElementType DeleteQueue(LinkQueue *Q){
LinkQueueNode * p;
if (Q->front == Q->rear){
return false;
}
p=Q->front->next;
Q->front->next=p->next;
if(Q->rear == p){
Q->rear=Q->front;
}
QueueElementType a;
a=p->data;
free(p);
return a;
}
/*判断队列是否为空*/
bool IsEmpty(LinkQueue Q){
if(Q.front->next==NULL){
return true;
}
return false;
}
/*打印队列*/
void OutputQueue(LinkQueue Q){
LinkQueueNode *p;
p=Q.front->next;
while (p!=NULL)
{
cout << p->data << endl;
p=p->next;
}
}
int main(){
LinkQueue Q;
InitQueue(&Q);
return 0;
}
综合应用
单链表的倒置
就是把现象表的所有元素翻转,我们采用头插法的思想。(如图演示步骤)
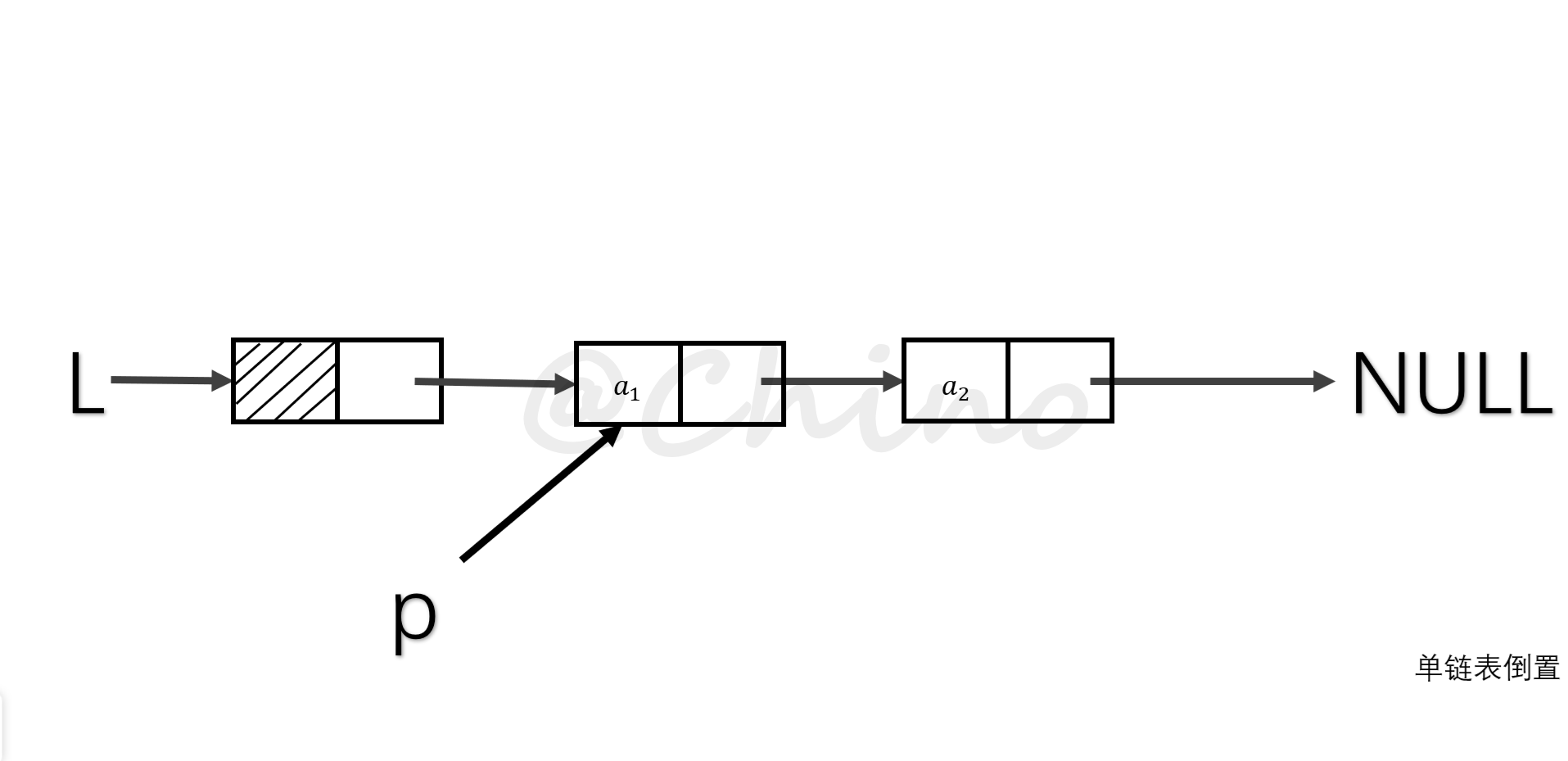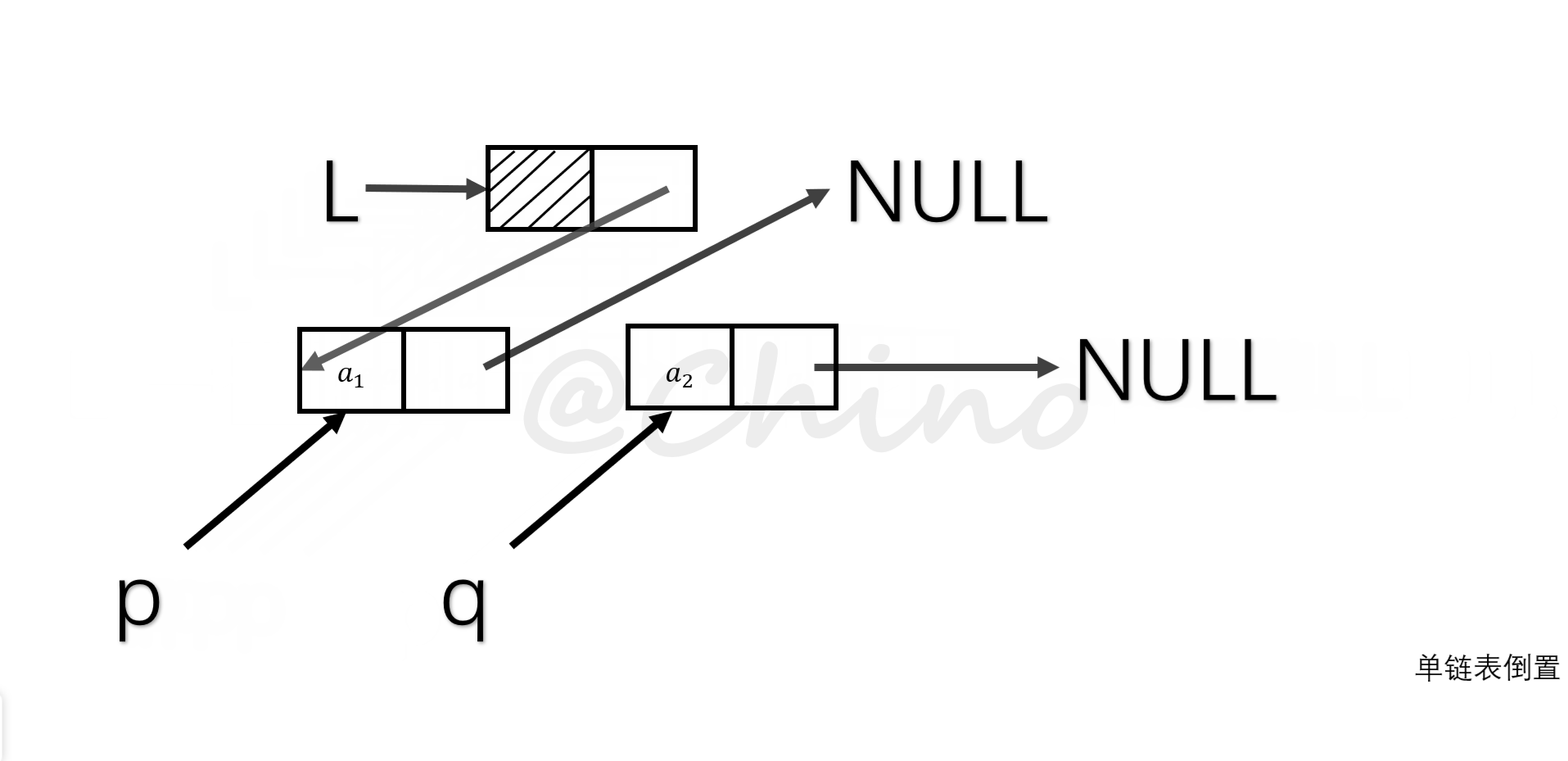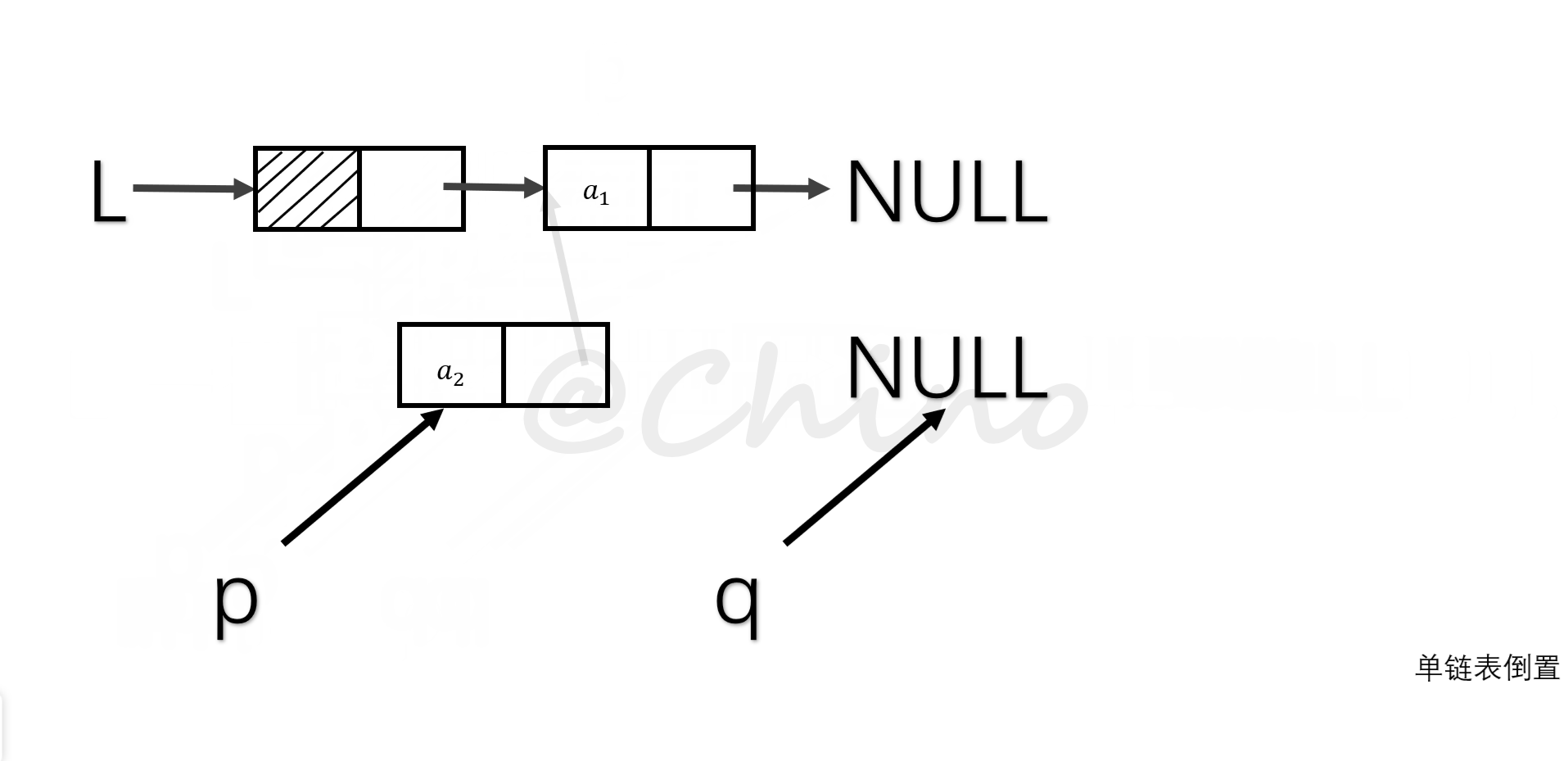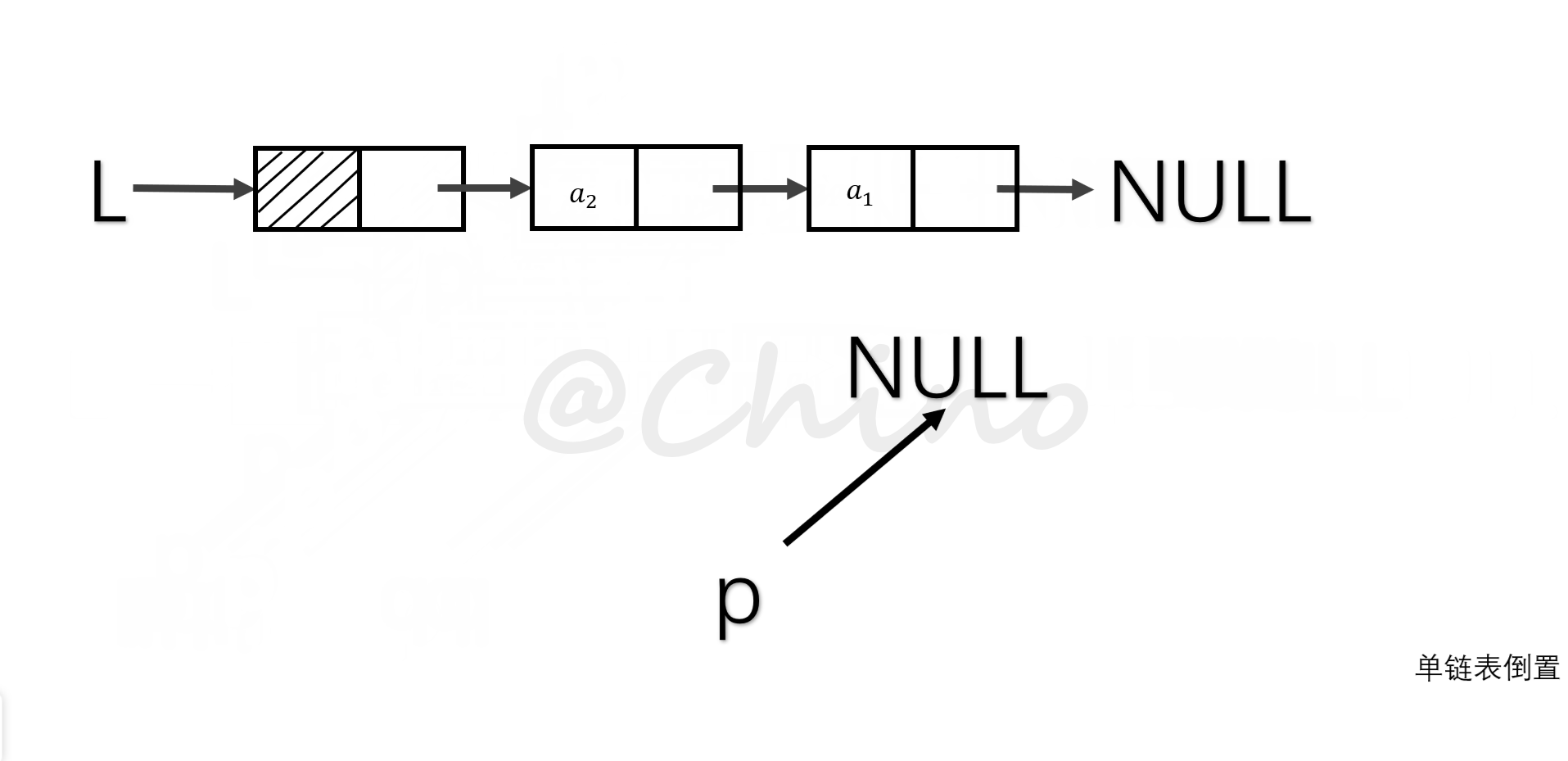
关键代码
/*翻转表内元素*/
void ReverseList(LinkList L){
LinkList p=L->next;
L->next=NULL;
while (p != NULL)
{
LinkList q=p->next;
p->next=L->next;
L->next=p;
p=q;
}
}
转逆波兰表达式(中缀表达式转后缀表达式)
所谓的转逆波兰表达式就是将我们常见的数学运算表达式5+6*1-2/2转成5 6 1 * + 2 2 / - #即成了逆波兰表达式
代码样例
/*
* @Author: Cafu-Chino
* @Date: 2020-04-30 16:01:28
* @Last Modified by: Cafu-Chino
* @Last Modified time: 2020-04-30 18:35:32
*/
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
queue<string>num;
stack<string>oper;
// void Initoper(){
// oper.push("#");
// }
// void ptnq(queue<string>q){
// while (!q.empty())
// {
// cout << q.front() <<" ";
// /* code */
// q.pop();
// }
// cout <<endl;
// }
// void ptns(stack<string>q){
// while (!q.empty())
// {
// cout << q.top() <<" ";
// /* code */
// q.pop();
// }
// cout <<endl;
// }
int main(){
string str;
cin >> str;
// Initoper();
for(int i=0; i < str.length(); i++){
if(str[i] <= '9' && str[i] >= '0'){
// cout << str[i] << endl;
string tstr;
int j=0;
while(str[i+j] <= '9' && str[i+j] >= '0'){
string temp;
temp=str[i+j];
tstr+=temp;
j++;
}
i+=j-1;
// cout << tstr.length() << endl;
// cout << tstr << endl;
num.push(tstr);
}
else{
string temp;
temp=str[i];
// if(temp == "/"){
// cout << "----" << endl;
// }
if(temp == "(")//处理(
oper.push(temp);
else if(temp == ")"){//处理)
while(!oper.empty()){
if(oper.top() == "("){
oper.pop();
break;
}
string top=oper.top();
num.push(top);
oper.pop();
}
}
else if(temp == "+" || temp == "-")//处理+-
{
if(oper.empty())
oper.push(temp);
else{
while ((!oper.empty()) && (oper.top() == "+" || oper.top() == "-" || oper.top() == "*" || oper.top() == "/")){
string top=oper.top();
num.push(top);
oper.pop();
}
oper.push(temp);
}
}
else if (temp == "*" || temp == "/"){//处理*/
if(oper.empty())
oper.push(temp);
else{
while((!oper.empty()) && (oper.top() == "*" || oper.top() == "/")){
string top=oper.top();
num.push(top);
oper.pop();
}
oper.push(temp);
}
}
else//增加对字母表达式支持
{
num.push(temp);
}
}
}
while (!oper.empty())//将剩下的符号导入结果中
{
string top=oper.top();
num.push(top);
oper.pop();
}
while (!num.empty())
{
cout << num.front() << " ";
num.pop();
}
cout << "#" << endl;
system("pause");
return 0;
}