link
D
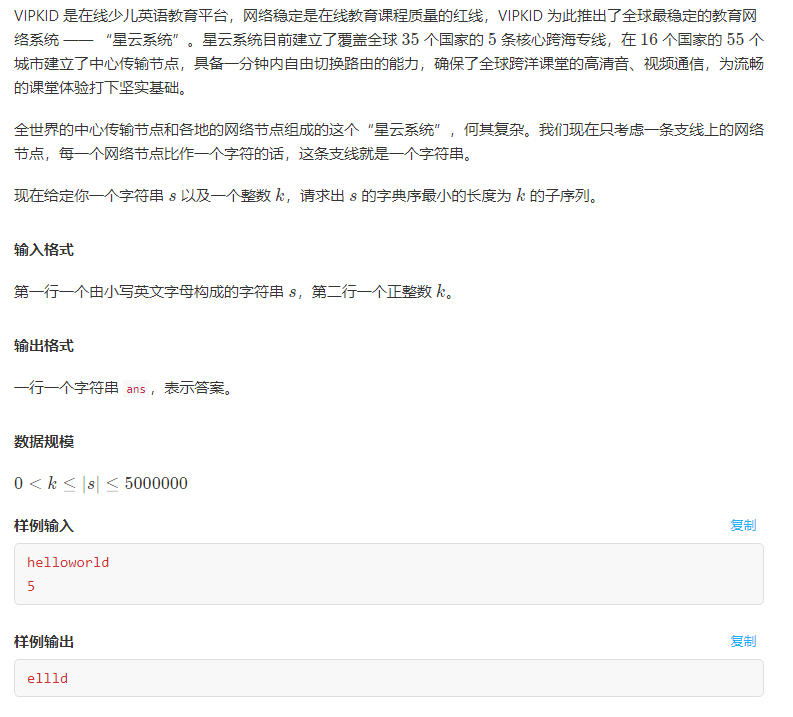
思路:开始的想法是用邻接表存住每个字母的下标,由于扫描顺序的缘故字母的下标表必然有序,然后二分。复杂度是(O(nlogn))。然后T一发...冥想了一会胡搞了一下又T了。算了一下规模差不多有15e7这样...后来改用单调栈维护一发过。其中单调栈中是维护一个字典序单调不减的序列。
Code:
//2019.6.16 by Caczhtus
//计蒜之道2019 D
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define maxn 5000005
#define repU(i, a, b) for (int i = a; i <= b; i++)
#define repD(i, a, b) for (int i = a; i >= b; i--)
#define repUk(i, a, b, k) for (int i = a; i <= b; i += k)
#define LL long long
#define fast_io ios::sync_with_stdio(false); cin.tie(0); cout.tie(0)
#define Mo 1000000009
#define debug1(x) cout << "debug : " << x << endl
#define debug2(x, y) cout << "debug : " << x << " " << y << endl
#define debug3(x, y, z) cout << "debug : " << x << " " << y << " " << z << endl
int k, len;
char s[maxn];
int stk[maxn], top;
int main() {
fast_io;
top = 0;
cin >> s >> k;
len = strlen(s);
repU(i, 0, len - 1) {
if (!top) stk[top++] = i;
else if (s[stk[0]] > s[i] && len-i >= k) {
top = 1;
stk[0] = i;
} else {
while (top && s[stk[top-1]]>s[i] && len-i > k-top) top--;
stk[top++] = i;
while (top > k) top--;
}
}
repU(i, 0, top - 1)
cout << s[stk[i]];
cout << endl;
return 0;
}
E
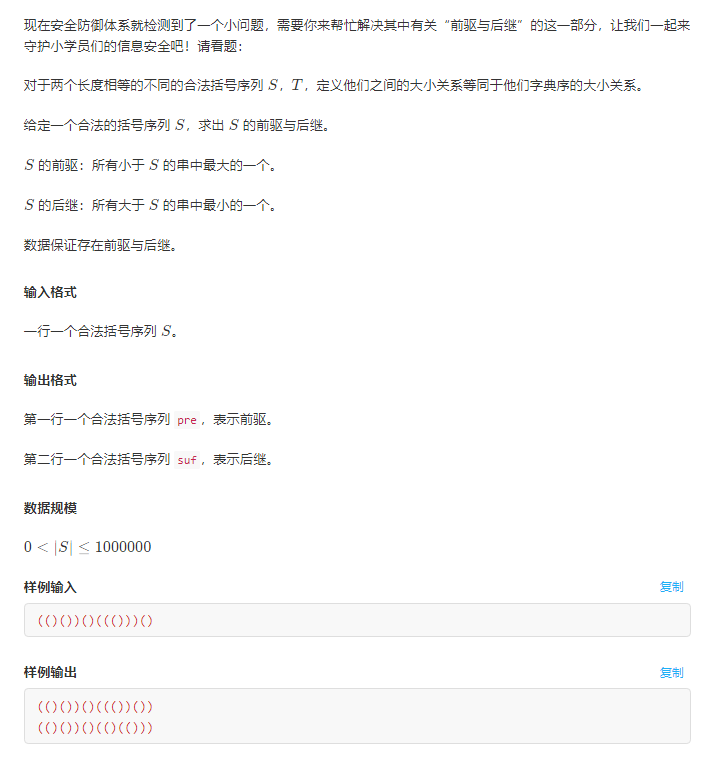
思路:括号匹配问题,匹配策略如下:
- 前驱,找最靠后的一组")("将其换成"()",由于修改了这个串的字典序(变小),所以后边的串的字典序在合法的前提下一定要尽量大。统计一下然后构造即可。复杂度(O(n))
- 后继,找最靠后的一组“()”将其换成")(",同理,后边的字典序在合法的情况下要尽量大。统计并计算即可。复杂度(O(n))
其实和数据结构的中序线索二叉树有点类似,把")("同"()"交换相当于把括号树的这颗合法子树合并或者拆分。
Code:
//2019.6.16 by Caczhtus
//计蒜之道2019 E
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define maxn 1000005
#define repU(i, a, b) for (int i = a; i <= b; i++)
#define repD(i, a, b) for (int i = a; i >= b; i--)
#define repUk(i, a, b, k) for (int i = a; i <= b; i += k)
#define LL long long
#define fast_io ios::sync_with_stdio(false); cin.tie(0); cout.tie(0)
#define Mo 1000000009
#define debug1(x) cout << "debug : " << x << endl
#define debug2(x, y) cout << "debug : " << x << " " << y << endl
#define debug3(x, y, z) cout << "debug : " << x << " " << y << " " << z << endl
char str[maxn], pre[maxn], suf[maxn];
int len; //串的长度
int prefix[maxn], suffix[maxn]; //前缀、后缀 剩余待配数量,不包含自己
void init() {
memset(prefix, 0, sizeof(prefix));
memset(suffix, 0, sizeof(suffix));
repU(i, 2, len-1) {
if (str[i-1] == '(') prefix[i] = prefix[i-1] + 1;
else prefix[i] = prefix[i-1] - 1;
}
repD(i, len-1, 1) {
if (str[i+1] == ')') suffix[i] = suffix[i+1] + 1;
else suffix[i] = suffix[i+1] - 1;
}
}
int main() {
cin >> str+1;
len = strlen(str+1);
strcpy(pre+1, str+1);
strcpy(suf+1, str+1);
init(); //预处理 方便判断匹配的合法性
int idx;
repD(i, len-1, 2) {
if (pre[i] == '(' && pre[i-1] == ')') {
pre[i] ^= pre[i-1], pre[i-1] ^= pre[i], pre[i] ^= pre[i-1];
//排序的方案复杂度过高 可以根据后面的括号数量进行构造
//构造策略是合法合法情况下使')'往前靠
int left = 0, right = 0;
repU(j, i+1, len) {
if (pre[j] == '(') left++;
else right++;
}
repU(j, 1, right-left) pre[++i] = ')';
repU(j, 1, left) pre[++i] = '(', pre[++i] = ')';
break;
}
}
repD(i, len-1, 2) {
if (suf[i] == ')' && suf[i-1] == '(' && prefix[i-1] && suffix[i] && prefix[i]-1 == suffix[i] && prefix[i-1] == suffix[i-1]-1) {
suf[i] ^= suf[i-1], suf[i-1] ^= suf[i], suf[i] ^= suf[i-1];
//排序的方案复杂度过高 这里可以用快排优化 不过由于类型只有两种 扫一遍即可
//构造策略是合法合法情况下使')'往前靠
int left = 0, right = 0;
repU(j, i+1, len) {
if (suf[j] == '(') left++;
else right++;
}
repU(j, 1, left) suf[++i] = '(';
repU(j, 1, right) suf[++i] = ')';
break;
}
}
cout << pre+1 << endl;
cout << suf+1 << endl;
return 0;
}
B

思路:枚举麻将的听牌,然后搜索。将牌应先于面子枚举。题目只考虑n4+21的胡法,并且不考虑杠的情况,所以十三幺等一些特殊胡法不用考虑。注意测试点有多组...(ps:坑了我好发wa),还有不合法的check。
Code:
//2019.6.16 by Caczhtus
//计蒜之道2019 B
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define maxn 5000005
#define repU(i, a, b) for (int i = a; i <= b; i++)
#define repD(i, a, b) for (int i = a; i >= b; i--)
#define repUk(i, a, b, k) for (int i = a; i <= b; i += k)
#define LL long long
#define fast_io ios::sync_with_stdio(false); cin.tie(0); cout.tie(0)
#define Mo 1000000009
#define debug1(x) cout << "debug : " << x << endl
#define debug2(x, y) cout << "debug : " << x << " " << y << endl
#define debug3(x, y, z) cout << "debug : " << x << " " << y << " " << z << endl
int find(string& st) {
int res;
if (st[1] == 'm') {
res = st[0] - '1';
return res;
} else if (st[1] == 's') {
res = st[0] - '1';
return res + 9;
} else if (st[1] == 'p') {
res = st[0] - '1';
return res + 18;
} else {
res = st[0] - '1';
return res + 27;
}
}
string getAns(int k) {
string res = "m";
if (k < 9) res[0] = ('1'+k), res += "m";
else if (k < 18) res[0] = ('1'+k-9), res += "s";
else if (k < 27) res[0] = ('1'+k-18), res += "p";
else res[0] = ('1'+k-27), res += "z";
return res;
}
string str[13];
int cnt[105], T[105], K[105];
int st[14];
bool check() {
// memcpy(cnt, K, sizeof(K));
repU(i, 0, 33) cnt[i] = K[i];
int c = 0;
//枚举字牌除外的面子(顺子、刻子)
repU(i, 0, 2) {
repU(j, 0, 8) {
int idx = i * 9 + j;
if (cnt[idx] >= 3) {
cnt[idx] -= 3;
c++;
}
while (j < 7 && cnt[idx]>0 && cnt[idx+1]>0 && cnt[idx+2]>0) {
cnt[idx]--;
cnt[idx+1]--;
cnt[idx+2]--;
c++;
}
}
}
//枚举字牌的顺子或者将牌
repU(i, 27, 33) {
if (cnt[i] >= 3) {
cnt[i] -= 3;
c++;
}
}
if (c == 4) return true;
return false;
}
bool search(int id) {
// memcpy(K, T, sizeof(T));
repU(i, 0, 33) K[i] = T[i];
K[id]++;
//枚举将牌
repU(i, 0, 33) {
if (K[i] > 1) {
K[i] -= 2;
if (check()) return true;
K[i] += 2;
}
}
return false;
}
int main() {
int len = 0;
memset(T, 0, sizeof(T));
repU(i, 0, 12) cin >> str[i];
repU(i, 0, 12) T[find(str[i])]++;
repU(i, 0, 33) if (search(i)) st[len++] = i;;
repU(i, 0, len - 1) cout << getAns(st[i]) << endl;
return 0;
}
/*
3s 3s 3s 4s 4s 5s 5s 6s 6s 6s 7s 7s 7s
1s 1s 1s 2s 3s 4s 5s 6s 7s 8s 9s 9s 9s
3s 3s 3s 4s 4s 5s 5s 6s 6s 6s 8s 8s 8s
4s 4s 4s 5s 5s 6s 6s 7s 7s 7s 8s 8s 8s
*/
总结:开局看了A想了好长时间的概率,无果,然后转而看G,立马放弃。又去看了D起初无思路,看了挺多人在写这道,然后仔细想了想可以写个(O(n^2))的枚举,于是马上优化成二分了,想当然地以为复杂度够了没注意规模,T了几发后清醒了。于是转而想这个序列单调性,发现符合直接一发过。发现rank还不错,然后是漫长的B题与E题...过了B,赛后过了E。总的来说还是写代码的时候逻辑臭的锅...233。A题要用树状数组维护...C打表计算sg函数然后还要用fwt优化(不会)...F多重积分还要用到eular降幂(不会)...G是个dp+优化...