目录:
- 配置文件路径解析
- 环境和属性
- 源码分析
配置文件路径解析
在了解Spring容器如何解析配置文件路径前,我们先来看一段代码
1 <?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> 2 <beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" 3 xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" 4 xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd"> 5 6 <bean class="com.jdr.spring.TestBean" name="testBean"/> 7 8 </beans>
1 public class TestBean { 2 public void run() { 3 System.out.println("testBean run..."); 4 } 5 }
1 public class TestSpring { 2 public static void main(String[] args) { 3 ClassPathXmlApplicationContext ctx = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("beans.xml"); 4 TestBean testBean = (TestBean) ctx.getBean("testBean"); 5 testBean.run(); 6 } 7 }
上面这段代码通过ClassPathXmlApplicationContext来解析beans.xml,并且执行了TestBean的run方法,我相信有点Spring基础的同学都是能看懂的。
而本次学习的重点也不是如何使用ClassPathXmlApplicationContext,而是ClassPathXmlApplicationContext是如何解析beans.xml的。
废话不多说,我们先看看TestSpring的源码。
———————————————————————————————————————————————————————
通过查看源码我们可以发现,ClassPathXmlApplicationContext主要代码如下。
1 public ClassPathXmlApplicationContext(String[] configLocations, boolean refresh, ApplicationContext parent) 2 throws BeansException { 3 4 super(parent); 5 setConfigLocations(configLocations); 6 if (refresh) { 7 refresh(); 8 } 9 }
首先第5行先设置了Spring上下文的配置位置,然后调用了refresh函数,此函数执行了Spring容器启动前的一些操作,不是本次的重点,后续再说。
setConfigLocations的核心代码如下:
1 public void setConfigLocations(String... locations) { 2 if (locations != null) { 3 Assert.noNullElements(locations, "Config locations must not be null"); 4 this.configLocations = new String[locations.length]; 5 for (int i = 0; i < locations.length; i++) { 6 this.configLocations[i] = resolvePath(locations[i]).trim(); 7 } 8 } 9 else { 10 this.configLocations = null; 11 } 12 } 13 14 protected String resolvePath(String path) { 15 return getEnvironment().resolveRequiredPlaceholders(path); 16 }
其中,setConfigLocations函数的代码很简单,就必不再赘述。我们直接看下resolvePath做了一些什么事。
我们可以看到在调用了getEnvironment后,便又调用了resolveRequiredPlaceholders。这个地方就是占位符解析和替换的工作。接下来我们首先要了解的知识就是“Spring环境、属性和占位符”。
环境和属性
Spring环境和属性由四个部分组成:
- PropertySource:属性源。key-value 属性对抽象,用于配置数据。
- PropertyResolver:属性解析器。用于解析属性配置。
- Profile:剖面。只有被激活的Profile才会将其中所对应的Bean注册到Spring容器中
- Environment:环境。Profile和PropertyResolver的组合。
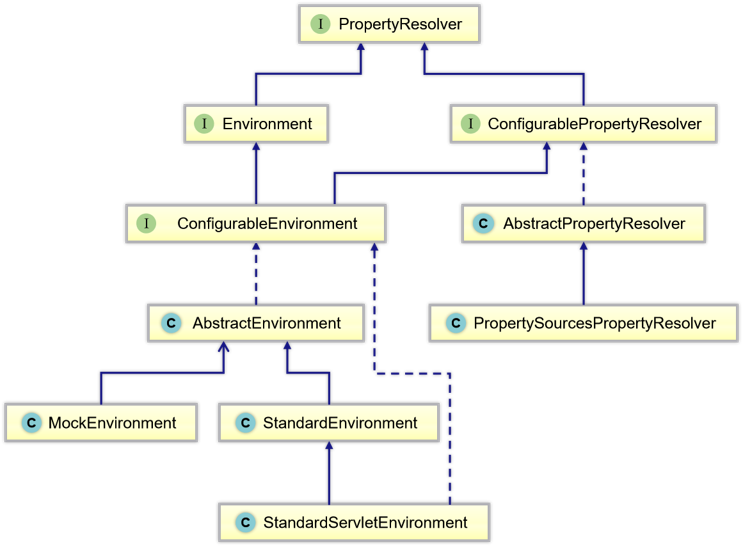
详解:
- PropertySource:提供了可配置属性源上的搜索操作。
- PropertyResolver:属性解析器,用于解析任何基础源的属性的接口。
- ConfigurablePropertyResolver:提供属性类型转换的功能。
- AbstractPropertyResolver:解析属性文件的抽象基类。设置了解析属性文件所需要ConversionService、prefix、suffix、valueSeparator等信息。
- PropertySourcesPropertyResolver:PropertyResolver的实现,对一组PropertySources提供属性解析服务。
- ConversionService:用于在运行时执行类型转换。
- Environment:集成在容器中的抽象,它主要包含两个方面,Profiles和Properties。
- ConfigurableEnvironment:设置激活的profile和默认的profile的功能以及操作Properties的工具。
———————————————————————————————————————————————————————
PropertySource:
PropertySource是在Spring Environment之上提供了可配置属性源上的搜索操作,其核心代码如下。
1 public abstract class PropertySource<T> { 2 3 // 属性值名 4 protected final String name; 5 6 // 属性对象 7 protected final T source; 8 9 // 获取属性名 10 public String getName() { 11 return this.name; 12 } 13 14 // 获取属性对象 15 public T getSource() { 16 return this.source; 17 } 18 19 // 属性名是否存在 20 public boolean containsProperty(String name) { 21 return (getProperty(name) != null); 22 } 23 24 // 根据属性名获取属性 25 public abstract Object getProperty(String name); 26 }
属性搜索过程是按照层次结构执行的。默认情况下,系统属性优先于环境变量。
因此,在调用env.getProperty("foo")时,如果在系统属性和环境变量中都设置了foo属性,则系统变量将优先于环境变量。
完整层次结构如下所示,优先级最高的条目位于顶部:
- ServletConfig参数
- ServletContext参数
- JNDI环境变量(如:"java:comp/env/")
- JVM system properties("-D"命令行参数,如-Dfoo="abcd")
- JVM system environment(操作系统环境变量)
注意:属性值不会被合并,而是会被前面的条目覆盖。
———————————————————————————————————————————————————————
PropertyResolver:
属性解析器,用于解析任何基础源的属性的接口,其接口定义如下:
1 public interface PropertyResolver { 2 3 // 是否包含指定key 4 boolean containsProperty(String key); 5 6 // 返回指定key对应的value,若没有则返回null 7 String getProperty(String key); 8 9 // 返回指定key对应的value,若没有则返回defaultValue 10 String getProperty(String key, String defaultValue); 11 12 // 返回指定key对应的value,并解析成指定类型。如果没有对应值则返回null 13 <T> T getProperty(String key, Class<T> targetType); 14 15 // 返回指定key对应的value,并解析成指定类型。如果没有对应值则返回defaultValue 16 <T> T getProperty(String key, Class<T> targetType, T defaultValue); 17 18 // 转换指定key的value为指定类型。如果没有则返回null 19 // 如果value不能转换成指定类型,则抛出ConversionException 20 @Deprecated 21 <T> Class<T> getPropertyAsClass(String key, Class<T> targetType); 22 23 // 返回指定key的value值,如果没有则抛出异常 24 String getRequiredProperty(String key) throws IllegalStateException; 25 26 // 转换指定key的value为指定类型,如果没有则抛出异常 27 <T> T getRequiredProperty(String key, Class<T> targetType) throws IllegalStateException; 28 29 // 解析${}占位符并替换为getProperty方法返回的结果,无法解析的占位符会被忽略 30 String resolvePlaceholders(String text); 31 32 // 解析${}占位符并替换为getProperty方法返回的结果,无法解析的占位符会抛异常 33 String resolveRequiredPlaceholders(String text) throws IllegalArgumentException; 34 }
源码分析
最后我们来看下Spring容器到底是如何解析配置的。
1 // 1、根据对应环境,解析path里的占位符 2 protected String resolvePath(String path) { 3 return getEnvironment().resolveRequiredPlaceholders(path); 4 } 5 6 // 2、对占位符进行解析 7 @Override 8 public String resolveRequiredPlaceholders(String text) throws IllegalArgumentException { 9 return this.propertyResolver.resolveRequiredPlaceholders(text); 10 } 11 12 // 3、创建占位符解析工具 13 @Override 14 public String resolveRequiredPlaceholders(String text) throws IllegalArgumentException { 15 if (this.strictHelper == null) { 16 this.strictHelper = createPlaceholderHelper(false); 17 } 18 return doResolvePlaceholders(text, this.strictHelper); 19 } 20 21 // 4、替换占位符 22 public String replacePlaceholders(String value, PlaceholderResolver placeholderResolver) { 23 Assert.notNull(value, "'value' must not be null"); 24 return parseStringValue(value, placeholderResolver, new HashSet<String>()); 25 }
可以从上述代码中得知,替换占位符的核心代码便是parseStringValue函数,我们来看看它的实现。
1 protected String parseStringValue( 2 String value, PlaceholderResolver placeholderResolver, Set<String> visitedPlaceholders) { 3 // ex: value = spring-${config}.xml 4 StringBuilder result = new StringBuilder(value); 5 6 // 找到占位符前缀下标(${) 7 int startIndex = value.indexOf(this.placeholderPrefix); 8 while (startIndex != -1) { 9 // 找到占位符前缀对应的后缀下标 10 int endIndex = findPlaceholderEndIndex(result, startIndex); 11 if (endIndex != -1) { 12 // 获取result中startIndex + this.placeholderPrefix.length()到endIndex的值 13 // 也就是占位符中的字符,spring-${config}.xml >>> config 14 String placeholder = result.substring(startIndex + this.placeholderPrefix.length(), endIndex); 15 String originalPlaceholder = placeholder; 16 if (!visitedPlaceholders.add(originalPlaceholder)) { 17 throw new IllegalArgumentException( 18 "Circular placeholder reference '" + originalPlaceholder + "' in property definitions"); 19 } 20 // 递归调用,解析占位符中包含的占位符(嵌套占位符) 21 placeholder = parseStringValue(placeholder, placeholderResolver, visitedPlaceholders); 22 // 获取占位符对应的值 23 String propVal = placeholderResolver.resolvePlaceholder(placeholder); 24 if (propVal == null && this.valueSeparator != null) { 25 int separatorIndex = placeholder.indexOf(this.valueSeparator); 26 if (separatorIndex != -1) { 27 String actualPlaceholder = placeholder.substring(0, separatorIndex); 28 String defaultValue = placeholder.substring(separatorIndex + this.valueSeparator.length()); 29 propVal = placeholderResolver.resolvePlaceholder(actualPlaceholder); 30 if (propVal == null) { 31 propVal = defaultValue; 32 } 33 } 34 } 35 if (propVal != null) { 36 // 递归调用,解析先前解析的占位符值中包含的占位符 37 // 也就是解析完propVal后,propVal可能是占位符(占位符嵌套) 38 propVal = parseStringValue(propVal, placeholderResolver, visitedPlaceholders); 39 result.replace(startIndex, endIndex + this.placeholderSuffix.length(), propVal); 40 if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) { 41 logger.trace("Resolved placeholder '" + placeholder + "'"); 42 } 43 startIndex = result.indexOf(this.placeholderPrefix, startIndex + propVal.length()); 44 } 45 else if (this.ignoreUnresolvablePlaceholders) { 46 // Proceed with unprocessed value. 47 startIndex = result.indexOf(this.placeholderPrefix, endIndex + this.placeholderSuffix.length()); 48 } 49 else { 50 throw new IllegalArgumentException("Could not resolve placeholder '" + 51 placeholder + "'" + " in value "" + value + """); 52 } 53 visitedPlaceholders.remove(originalPlaceholder); 54 } 55 else { 56 startIndex = -1; 57 } 58 } 59 60 return result.toString(); 61 } 62 63 private int findPlaceholderEndIndex(CharSequence buf, int startIndex) { 64 // 因为后缀的下标肯定在前缀之后,所以要加上前缀的长度,才能精准定位到对应的后缀下标 65 int index = startIndex + this.placeholderPrefix.length(); 66 int withinNestedPlaceholder = 0; 67 while (index < buf.length()) { 68 // StringUtils.substringMatch: buf的第index下标的字符是否为this.placeholderSuffix 69 if (StringUtils.substringMatch(buf, index, this.placeholderSuffix)) { 70 if (withinNestedPlaceholder > 0) { 71 withinNestedPlaceholder--; 72 index = index + this.placeholderSuffix.length(); 73 } 74 else { 75 return index; 76 } 77 } 78 else if (StringUtils.substringMatch(buf, index, this.simplePrefix)) { 79 withinNestedPlaceholder++; 80 index = index + this.simplePrefix.length(); 81 } 82 else { 83 index++; 84 } 85 } 86 return -1; 87 }
parseStringValue的核心逻辑在while循环中;从其循环逻辑来看,如果value入参不包含this.placeholderPrefix的话则直接返回value。
this.placeholderPrefix则是resolveRequiredPlaceholders函数中createPlaceholderHelper传入的,我们来看看其逻辑。
1 public static final String PLACEHOLDER_PREFIX = "${"; 2 public static final String PLACEHOLDER_SUFFIX = "}"; 3 public static final String VALUE_SEPARATOR = ":"; 4 5 private String placeholderPrefix = SystemPropertyUtils.PLACEHOLDER_PREFIX; 6 private String placeholderSuffix = SystemPropertyUtils.PLACEHOLDER_SUFFIX; 7 private String valueSeparator = SystemPropertyUtils.VALUE_SEPARATOR; 8 9 private PropertyPlaceholderHelper createPlaceholderHelper(boolean ignoreUnresolvablePlaceholders) { 10 return new PropertyPlaceholderHelper(this.placeholderPrefix, this.placeholderSuffix, 11 this.valueSeparator, ignoreUnresolvablePlaceholders); 12 }
从上述代码中,我们便可以知道parseStringValue中的几个属性值分别如下:
- private final String placeholderPrefix = "${";
- private final String placeholderSuffix = "}";
- private final String valueSeparator = ":";
- private final boolean ignoreUnresolvablePlaceholders = false;
———————————————————————————————————————————————————————
有了上面这些基础的东西后,就能轻松阅读parseStringValue的逻辑了。
所以我们上面的测试类TestSpring中的ClassPathXmlApplicationContext ctx = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("beans.xml");解析出来的便还是原值beans.xml。
如果我们改成下面这样,也是也是能够解析出来的。
1 public class TestSpring { 2 3 public static void main(String[] args) { 4 Properties properties = System.getProperties(); 5 properties.setProperty("config", "beans"); 6 ClassPathXmlApplicationContext xml = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("${config}.xml"); 7 TestBean testBean = (TestBean) xml.getBean("testBean"); 8 testBean.run(); 9 } 10 }
当然,如果你仔细分析了parseStringValue后,你会发现其实它是支持嵌套占位符的,比如这样:
1 public class TestSpring { 2 3 public static void main(String[] args) { 4 Properties properties = System.getProperties(); 5 properties.setProperty("config", "beans"); 6 properties.setProperty("prefix", "spring"); 7 properties.setProperty("prefix-config", "${prefix}"); 8 9 ClassPathXmlApplicationContext xml = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("${prefix-config}-${config}.xml"); 10 TestBean testBean = (TestBean) xml.getBean("testBean"); 11 testBean.run(); 12 } 13 }