关于KNN,有幸看到这篇文章,写的很好,这里就不在赘述。直接贴上代码了,有小的改动。(原来是python2版本的,这里改为python3的,主要就是print)
环境:win7 32bit + spyder + anaconda3.5
一、初阶
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
"""
Created on Sun Nov 6 16:09:00 2016
@author: Administrator
"""
#Input:
# newInput:待测的数据点(1xM)
# dataSet:已知的数据(NxM)
# labels:已知数据的标签(1xM)
# k:选取的最邻近数据点的个数
#
#Output:
# 待测数据点的分类标签
#
from numpy import *
# creat a dataset which contain 4 samples with 2 class
def createDataSet():
# creat a matrix: each row as a sample
group = array([[1.0, 0.9], [1.0, 1.0], [0.1, 0.2], [0.0, 0.1]])
labels = ['A', 'A', 'B', 'B']
return group, labels
#classify using KNN
def KNNClassify(newInput, dataSet, labels, k):
numSamples = dataSet.shape[0] # row number
# step1:calculate Euclidean distance
# tile(A, reps):Constract an array by repeating A reps times
diff = tile(newInput, (numSamples, 1)) - dataSet
squreDiff = diff**2
squreDist = sum(squreDiff, axis=1) # sum if performed by row
distance = squreDist ** 0.5
#step2:sort the distance
# argsort() returns the indices that would sort an array in a ascending order
sortedDistIndices = argsort(distance)
classCount = {}
for i in range(k):
# choose the min k distance
voteLabel = labels[sortedDistIndices[i]]
#step4:count the times labels occur
# when the key voteLabel is not in dictionary classCount,
# get() will return 0
classCount[voteLabel] = classCount.get(voteLabel, 0) + 1
#step5:the max vote class will return
maxCount = 0
for k, v in classCount.items():
if v > maxCount:
maxCount = v
maxIndex = k
return maxIndex
# test
dataSet, labels = createDataSet()
testX = array([1.2, 1.0])
k = 3
outputLabel = KNNClassify(testX, dataSet, labels, 3)
print("Your input is:", testX, "and classified to class: ", outputLabel)
testX = array([0.1, 0.3])
k = 3
outputLabel = KNNClassify(testX, dataSet, labels, 3)
print("Your input is:", testX, "and classified to class: ", outputLabel)
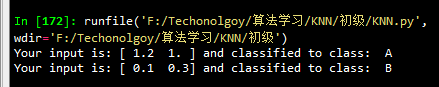
运行结果:
二、进阶
用到的手写识别数据库资料在这里下载。关于资料的介绍在上面的博文也已经介绍的很清楚了。
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
"""
Created on Sun Nov 6 16:09:00 2016
@author: Administrator
"""
#Input:
# newInput:待测的数据点(1xM)
# dataSet:已知的数据(NxM)
# labels:已知数据的标签(1xM)
# k:选取的最邻近数据点的个数
#
#Output:
# 待测数据点的分类标签
#
from numpy import *
#classify using KNN
def KNNClassify(newInput, dataSet, labels, k):
numSamples = dataSet.shape[0] # row number
# step1:calculate Euclidean distance
# tile(A, reps):Constract an array by repeating A reps times
diff = tile(newInput, (numSamples, 1)) - dataSet
squreDiff = diff**2
squreDist = sum(squreDiff, axis=1) # sum if performed by row
distance = squreDist ** 0.5
#step2:sort the distance
# argsort() returns the indices that would sort an array in a ascending order
sortedDistIndices = argsort(distance)
classCount = {}
for i in range(k):
# choose the min k distance
voteLabel = labels[sortedDistIndices[i]]
#step4:count the times labels occur
# when the key voteLabel is not in dictionary classCount,
# get() will return 0
classCount[voteLabel] = classCount.get(voteLabel, 0) + 1
#step5:the max vote class will return
maxCount = 0
for k, v in classCount.items():
if v > maxCount:
maxCount = v
maxIndex = k
return maxIndex
# convert image to vector
def img2vector(filename):
rows = 32
cols = 32
imgVector = zeros((1, rows * cols))
fileIn = open(filename)
for row in range(rows):
lineStr = fileIn.readline()
for col in range(cols):
imgVector[0, row * 32 + col] = int(lineStr[col])
return imgVector
# load dataSet
def loadDataSet():
## step 1: Getting training set
print("---Getting training set...")
dataSetDir = 'F:\Techonolgoy\算法学习\KNN\进阶\'
trainingFileList = os.listdir(dataSetDir + 'trainingDigits') # load the training set
numSamples = len(trainingFileList)
train_x = zeros((numSamples, 1024))
train_y = []
for i in range(numSamples):
filename = trainingFileList[i]
# get train_x
train_x[i, :] = img2vector(dataSetDir + 'trainingDigits/%s' % filename)
# get label from file name such as "1_18.txt"
label = int(filename.split('_')[0]) # return 1
train_y.append(label)
## step 2: Getting testing set
print("---Getting testing set...")
testingFileList = os.listdir(dataSetDir + 'testDigits') # load the testing set
numSamples = len(testingFileList)
test_x = zeros((numSamples, 1024))
test_y = []
for i in range(numSamples):
filename = testingFileList[i]
# get train_x
test_x[i, :] = img2vector(dataSetDir + 'testDigits/%s' % filename)
# get label from file name such as "1_18.txt"
label = int(filename.split('_')[0]) # return 1
test_y.append(label)
return train_x, train_y, test_x, test_y
# test hand writing class
def testHandWritingClass():
## step 1: load data
print("step 1: load data...")
train_x, train_y, test_x, test_y = loadDataSet()
## step 2: training...
print("step 2: training...")
pass
## step 3: testing
print("step 3: testing...")
numTestSamples = test_x.shape[0]
matchCount = 0
for i in range(numTestSamples):
predict = KNNClassify(test_x[i], train_x, train_y, 3)
if predict == test_y[i]:
matchCount += 1
accuracy = float(matchCount) / numTestSamples
## step 4: show the result
print("step 4: show the result...")
print('The classify accuracy is: %.2f%%' % (accuracy * 100))
testHandWritingClass()
运行结果:
