在分布式调度中为了保证服务的高可用和容灾需求,通常都会讲服务在多个区域、机架、节点上平均分布,从而避免单点故障引起的服务不可用,在k8s中自然也实现了该算法即SelectorSpread, 本文就来学习下这个算法的底层实现细节
1. 设计要点
1.1 zone与node
zone即代表一个区域,node则是一个具体的节点,而该打散算法的目标就是将pod在zone和node之间进行打散操作
1.2 namespace
namespace是k8s中进行资源隔离的实现,同样的筛选也是如此,在筛选的过程中,不同namespace下面的pod并不会相互影响
1.3 计数与聚合
SelectorSpread算法是scheduler中优先级算法的一种,其实现了优先级算法的map/reduce方法,其中map阶段需要完成对各个节点亲和性的统计, 也就是统计该节点上的匹配的pod的数量,而reduce阶段则是聚合所有匹配的数量,进行统计打分
1.4 参考对象
在k8s中有很多上层对象诸如service、replicaSet、statefulset等,而算法打散的对象也是依据这些上层对象,让单个service的多个pod进行平均分布
1.5 选择器
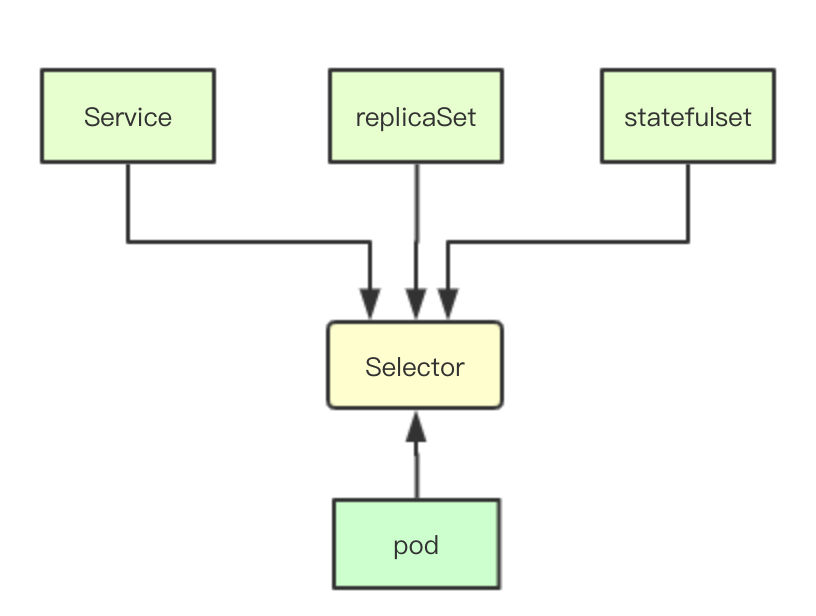
在传统的基于数据库的设计中,数据之间的关联关系通常是基于外键或者对象id来实现模型之间的关联,而在kubernetes中则是通过selector来进行这种关系的映射,通过给对象定义不同的label然后在label上构造选择器,从而实现各种资源之间的相互关联
2. 实现原理
2.1 选择器
2.1.1 选择器接口
选择器接口其关键方法主要是通过Matches来进行一组标签的匹配,先关注这些就可以了,后续需要再去关注其核心实现
type Selector interface {
// Matches returns true if this selector matches the given set of labels.
Matches(Labels) bool
// String returns a human readable string that represents this selector.
String() string
// Add adds requirements to the Selector
Add(r ...Requirement) Selector
}
2.1.2 资源筛选
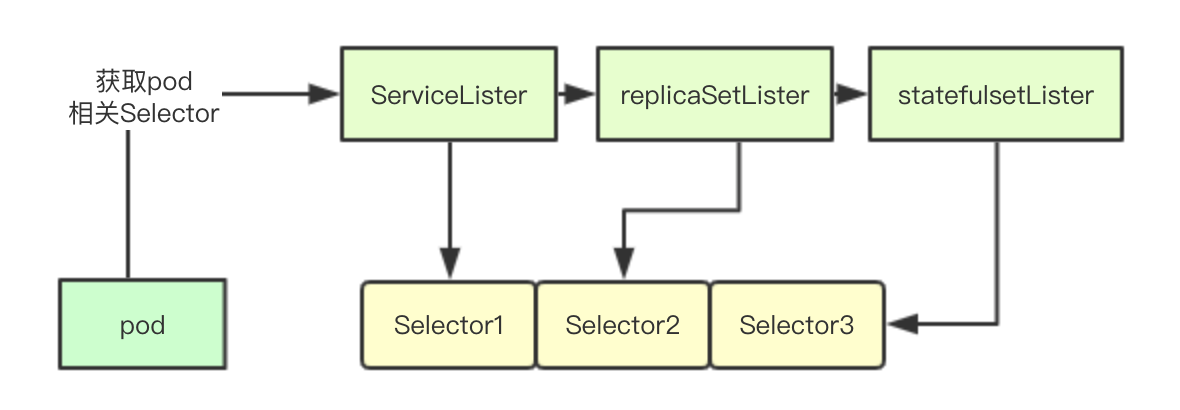
Selector数组的实现其实也很简单,就是遍历所有相关联的资源,然后用当前的pod上的Label标签去搜索,如果发现有资源包含当前pod的标签,就把对应资源的所有Selector都获取出来,加入到selectors数组中
func getSelectors(pod *v1.Pod, sl algorithm.ServiceLister, cl algorithm.ControllerLister, rsl algorithm.ReplicaSetLister, ssl algorithm.StatefulSetLister) []labels.Selector {
var selectors []labels.Selector
if services, err := sl.GetPodServices(pod); err == nil {
for _, service := range services {
selectors = append(selectors, labels.SelectorFromSet(service.Spec.Selector))
}
}
if rcs, err := cl.GetPodControllers(pod); err == nil {
for _, rc := range rcs {
selectors = append(selectors, labels.SelectorFromSet(rc.Spec.Selector))
}
}
if rss, err := rsl.GetPodReplicaSets(pod); err == nil {
for _, rs := range rss {
if selector, err := metav1.LabelSelectorAsSelector(rs.Spec.Selector); err == nil {
selectors = append(selectors, selector)
}
}
}
if sss, err := ssl.GetPodStatefulSets(pod); err == nil {
for _, ss := range sss {
if selector, err := metav1.LabelSelectorAsSelector(ss.Spec.Selector); err == nil {
selectors = append(selectors, selector)
}
}
}
return selectors
}
2.1 算法注册与初始化
2.1.1 算法注册
在构建算法的时候,首先会从参数中获取各种资源的Lister, 其实就是筛选对象的一个接口,可以从该接口中获取集群中对应类型的所有资源
factory.RegisterPriorityConfigFactory(
priorities.SelectorSpreadPriority,
factory.PriorityConfigFactory{
MapReduceFunction: func(args factory.PluginFactoryArgs) (priorities.PriorityMapFunction, priorities.PriorityReduceFunction) {
return priorities.NewSelectorSpreadPriority(args.ServiceLister, args.ControllerLister, args.ReplicaSetLister, args.StatefulSetLister)
},
Weight: 1,
},
)
2.1.2 算法初始化
算法初始化则是构建一个SelectorSpread对象,我们可以看到其map和reduce的关键实现分别对应内部的两个方法
func NewSelectorSpreadPriority(
serviceLister algorithm.ServiceLister,
controllerLister algorithm.ControllerLister,
replicaSetLister algorithm.ReplicaSetLister,
statefulSetLister algorithm.StatefulSetLister) (PriorityMapFunction, PriorityReduceFunction) {
selectorSpread := &SelectorSpread{
serviceLister: serviceLister,
controllerLister: controllerLister,
replicaSetLister: replicaSetLister,
statefulSetLister: statefulSetLister,
}
return selectorSpread.CalculateSpreadPriorityMap, selectorSpread.CalculateSpreadPriorityReduce
}
2.2 CalculateSpreadPriorityMap
2.2.1 构建选择器
在进行Map核心统计阶段之前会先根据当前的pod获取其上的选择器Selector数组,即当前pod有那些选择器相关联,这个是在创建meta的时候完成
var selectors []labels.Selector
node := nodeInfo.Node()
if node == nil {
return schedulerapi.HostPriority{}, fmt.Errorf("node not found")
}
priorityMeta, ok := meta.(*priorityMetadata)
if ok {
// 在priorityMeta构建的时候已经完成
selectors = priorityMeta.podSelectors
} else {
// 获取当前pod的所有的selector 包括service rs rc
selectors = getSelectors(pod, s.serviceLister, s.controllerLister, s.replicaSetLister, s.statefulSetLister)
}
if len(selectors) == 0 {
return schedulerapi.HostPriority{
Host: node.Name,
Score: int(0),
}, nil
}
2.2.2 统计匹配计数
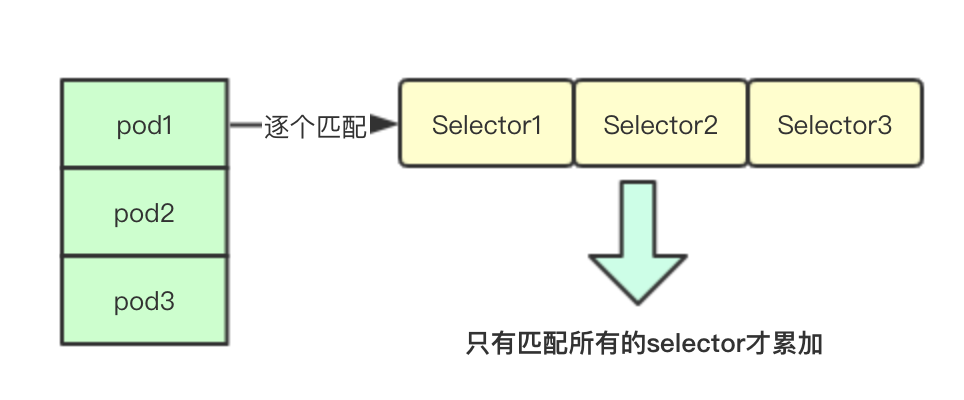
统计计数其实就是根据上面的selector数组逐个遍历当前node上面的所有pod如果发现全都匹配则计数一次,最后返回当前节点上匹配的pod的数量(这里的匹配是指的所有都匹配即跟当前的pod的所有label匹配都一样)
func countMatchingPods(namespace string, selectors []labels.Selector, nodeInfo *schedulernodeinfo.NodeInfo) int {
// 计算当前node上面匹配的node的数量
if nodeInfo.Pods() == nil || len(nodeInfo.Pods()) == 0 || len(selectors) == 0 {
return 0
}
count := 0
for _, pod := range nodeInfo.Pods() {
// 这里会跳过不同namespace和被删除的pod
if namespace == pod.Namespace && pod.DeletionTimestamp == nil {
matches := true
// 遍历所有的选择器,如果不匹配,则会立马跳出
for _, selector := range selectors {
if !selector.Matches(labels.Set(pod.Labels)) {
matches = false
break
}
}
if matches {
count++ // 记录当前节点上匹配的pod的数量
}
}
}
return count
}
2.2.3 返回统计结果
最后返回对应node的名字和node上的匹配的pod的数量
count := countMatchingPods(pod.Namespace, selectors, nodeInfo)
return schedulerapi.HostPriority{
Host: node.Name,
Score: count,
}, nil
2.4 CalculateAntiAffinityPriorityReduce
2.4.1 计数器
计数器主要包含三个:单个node上最大的pod数量、单个zone里面最大pod的数量、每个zone中pod的数量
countsByZone := make(map[string]int, 10)
maxCountByZone := int(0)
maxCountByNodeName := int(0)
2.4.2 单节点最大统计与zone区域聚合
for i := range result {
if result[i].Score > maxCountByNodeName {
maxCountByNodeName = result[i].Score // 寻找单节点上的最大pod数量
}
zoneID := utilnode.GetZoneKey(nodeNameToInfo[result[i].Host].Node())
if zoneID == "" {
continue
}
// 进行zone所有node匹配pod的聚合
countsByZone[zoneID] += result[i].Score
}
2.4.3 zone最大值统计
for zoneID := range countsByZone {
if countsByZone[zoneID] > maxCountByZone {
maxCountByZone = countsByZone[zoneID]
}
}
2.4.4 核心计算打分算法
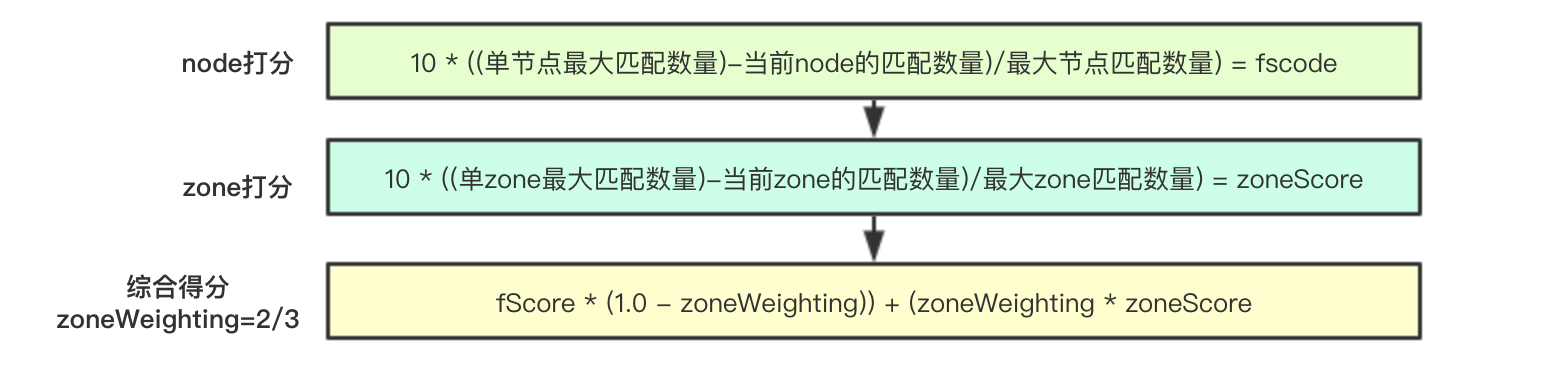
核心打分算法流程包含两个级别:node级别和zone级别,其算法为:
node: 10 * ((单节点最大匹配数量)-当前node的匹配数量)/最大节点匹配数量) = fscode
zone: 10 * ((单zone最大匹配数量)-当前zone的匹配数量)/最大zone匹配数量) = zoneScore
合并: fScore * (1.0 - zoneWeighting)) + (zoneWeighting * zoneScore (zoneWeighting=2/3)
即优先进行zone级别分布,其次再是node
比如分别有3个node其匹配pod数量分别为:
node1:3, node2:5, node3:10 则打分结果为:
node1: 10 * ((10-3)/10) = 7
node2: 10 * ((10-5)/10) = 5
node3: (10* ((10-5)/10) = 0
可以看到其上匹配的pod数量越多最终的优先级则越小
假设分别有3个zone(跟node编号相同), 则zone得分为:zone1=7, zone2=5, zone3=0
最终计分(zoneWeighting=2/3): node1=7, node2=5, node3=0
maxCountByNodeNameFloat64 := float64(maxCountByNodeName)
maxCountByZoneFloat64 := float64(maxCountByZone)
MaxPriorityFloat64 := float64(schedulerapi.MaxPriority)
for i := range result {
// initializing to the default/max node score of maxPriority
fScore := MaxPriorityFloat64
if maxCountByNodeName > 0 {
fScore = MaxPriorityFloat64 * (float64(maxCountByNodeName-result[i].Score) / maxCountByNodeNameFloat64)
}
// If there is zone information present, incorporate it
if haveZones {
zoneID := utilnode.GetZoneKey(nodeNameToInfo[result[i].Host].Node())
if zoneID != "" {
zoneScore := MaxPriorityFloat64
if maxCountByZone > 0 {
zoneScore = MaxPriorityFloat64 * (float64(maxCountByZone-countsByZone[zoneID]) / maxCountByZoneFloat64)
}
fScore = (fScore * (1.0 - zoneWeighting)) + (zoneWeighting * zoneScore)
}
}
result[i].Score = int(fScore)
if klog.V(10) {
klog.Infof(
"%v -> %v: SelectorSpreadPriority, Score: (%d)", pod.Name, result[i].Host, int(fScore),
)
}
}
今天就到这里吧,其实可以看出在分布的时候,是会优先尝试zone分布,然后在进行节点分布,我比较好奇zoneWeighting=2/3这个值是怎么来的,从注释上看,老外也没有证明,可能就是为了倾斜zone吧,大家周末愉快
微信号:baxiaoshi2020
关注公告号阅读更多源码分析文章
更多文章关注 www.sreguide.com
本文由博客一文多发平台 OpenWrite 发布

