A:机器人
传送门:https://www.zhixincode.com/contest/1/problem/A
题意:地图是由A、B两根线组成的,机器人一开始是在A线上的S点,他初始时可以选择任意方向前进,但是除非碰见特殊点,否则是不能转弯的,他有r个必须经过的点分布在A线和B线上,有m个特殊点可以进行转向,这些特殊点对称分布在A、B两条线上,并且1,n这两个点也是特殊点,也就是说机器人一定可以转弯,A、B之间的距离是K,求机器人经过所有的必须经过的点后回到起点。
题解:画图.jpg
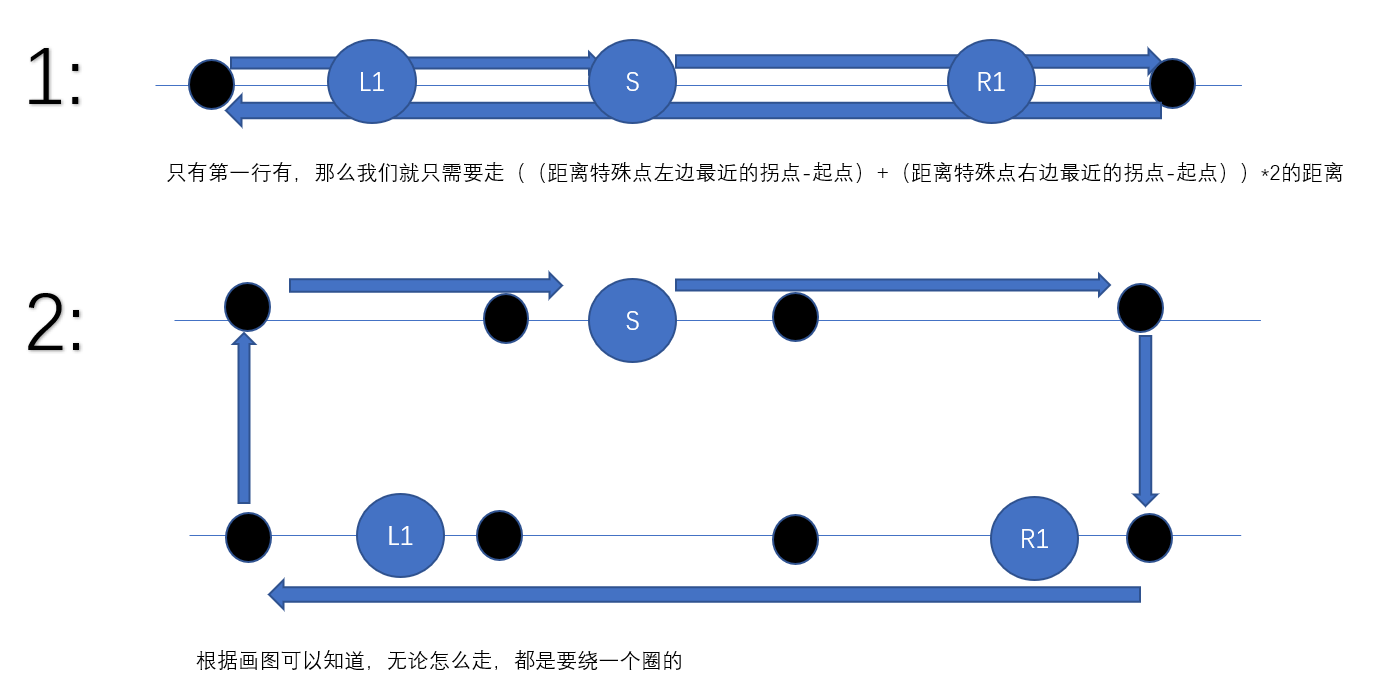

画图我们可以知道,我们要想经过所有的特殊点,只需要讨论两种情况,
一种是,B线上没有,那么只在A上走,
一种是B线上 有,那么我们只需要找到A的最左端,B的最左端、A的最右端、B的最右段的转折点即可,这样就可以保证走了一圈,肯定将所有的特殊点都经过了,并且路径最短
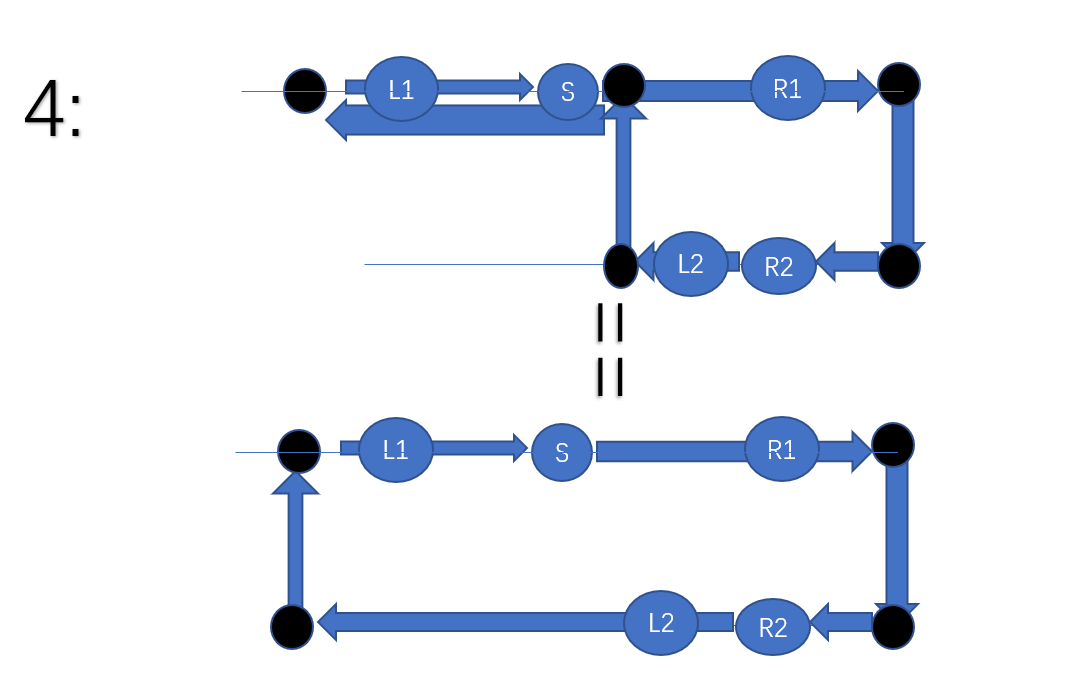
我们要特殊考虑一下如果只在起点S的左端有需要经过的点或者只在起点S右端怎么办呢
我们画图可以知道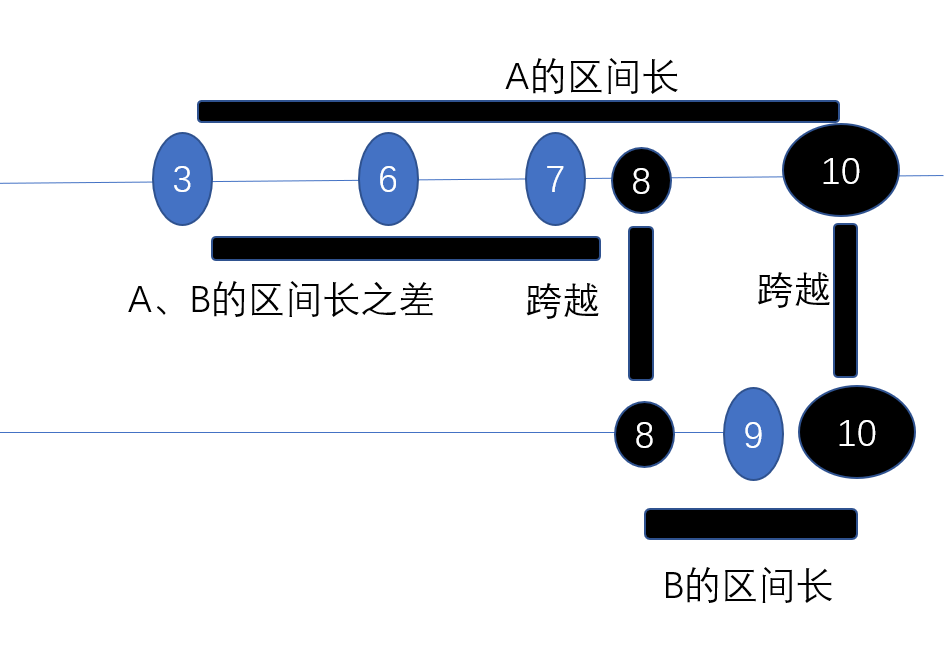
他是这样走的,所以我们需要计算出
①A、B的区间长lena,lenb
②A、B的区间长之差len2
这样就可以求出只在一边的情况
实际上,如果不在一边的话,A、B的区间长之差是0,所以这些都是可以分在同一种情况的,只需要对(0,len2)取一个max即可
代码如下:

#include <set> #include <map> #include <deque> #include <queue> #include <stack> #include <cmath> #include <ctime> #include <bitset> #include <cstdio> #include <string> #include <vector> #include <cstdlib> #include <cstring> #include <iostream> #include <algorithm> using namespace std; typedef long long LL; typedef pair<LL, LL> pLL; typedef pair<LL, int> pLi; typedef pair<int, LL> pil;; typedef pair<int, int> pii; typedef unsigned long long uLL; #define bug printf("********* ") #define debug(x) cout<<#x"=["<<x<<"]" <<endl #define FIN freopen("input.txt","r",stdin); #define IO ios::sync_with_stdio(false),cin.tie(0) const double eps = 1e-8; const int mod = 1000000007; const int maxn = 2e5 + 7; const double pi = acos(-1); const int inf = 0x3f3f3f3f; const LL INF = 0x3f3f3f3f3f3f3f3fLL; int a[maxn], b[maxn]; int flag = 0; vector<int> p; int n, r, m, k, s; int main() { #ifndef ONLINE_JUDGE FIN #endif scanf("%d%d%d%d%d", &n, &r, &m, &k, &s); int tot1 = 0, tot2 = 0; for(int i = 0; i < r; i++) { int x, tmp; scanf("%d%d", &x, &tmp); if(tmp == 0) { a[tot1++] = x; } else { b[tot2++] = x; } } for(int i = 0; i < m; i++) { int x; scanf("%d", &x); p.push_back(x); } p.push_back(1); p.push_back(n); sort(a, a + tot1); sort(b, b + tot2); sort(p.begin(), p.end()); int al = n, ar = 1, bl = n, br = 1; for(int i = 0; i < tot2; i++) { bl = min(bl, *(upper_bound(p.begin(), p.end(), b[i] ) - 1)); br = max(br, *lower_bound(p.begin(), p.end(), b[i])); } p.push_back(s); sort(p.begin(), p.end()); for(int i = 0; i < tot1; i++) { al = min(al, *(upper_bound(p.begin(), p.end(), a[i] ) - 1)); ar = max(ar, *lower_bound(p.begin(), p.end(), a[i])); } al = min(al, bl), ar = max(ar, br); //cout<<al<<" "<<ar<<endl; if(tot2 == 0) { // cout << (ar - al) * 2 << endl; //防止只在一边的情况 cout << (max(0, al - s) + max(0, s - ar) + ar - al) * 2 << endl; //s到a+a区间长*2 } else { //防止只在一边的情况 cout << (max(0, al - s) + max(0, s - ar)) * 2 + //s到a ar - al + br - bl + //ab区间长 bl - al + ar - br + //a超出b k * 2 << endl; //跨越 } return 0; }
B:吃豆豆
传送门:https://www.zhixincode.com/contest/1/problem/B
题意:有一个n*m的格子图,每个格子有一个时间戳t[i][j],代表这个格子每过时间t[i][j]会有一颗糖果,如果人刚好站在这个地方,人就可以得到这个糖果,人的起始位置是sx,sy,他需要移动到终点ex,ey处,问他至少吃C颗糖果所需要的最少的时间是多少
题解:我们考虑,图十分的小,最大是10*10,t[i][j]小于10,最多要吃 1018颗糖果,那么我即使呆在一个位置不动,我最多也只需要10180秒吃掉1018颗糖果,我们很显然可以暴力得到所有的状态的,就和dp联系起来了
我们定义dp[x][y][k]为在x,y这个位置,花费k的时间得到的糖果数量最多是多少
那么转移方程就是: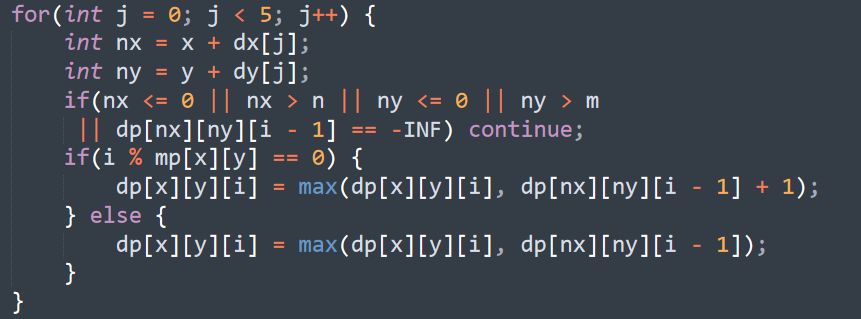
emmm奇妙的转移,不太好形容,有点bfs的意思在里面吧,还是很容易看懂的。如果这个位置的时间刚好取模当前位置的时间戳为0的话,那么由上一步转来的糖果数就可以+1
代码如下:

#include <set> #include <map> #include <deque> #include <queue> #include <stack> #include <cmath> #include <ctime> #include <bitset> #include <cstdio> #include <string> #include <vector> #include <cstdlib> #include <cstring> #include <iostream> #include <algorithm> using namespace std; typedef long long LL; typedef pair<LL, LL> pLL; typedef pair<LL, int> pLi; typedef pair<int, LL> pil;; typedef pair<int, int> pii; typedef unsigned long long uLL; #define bug printf("********* ") #define debug(x) cout<<#x"=["<<x<<"]" <<endl #define FIN freopen("input.txt","r",stdin); #define IO ios::sync_with_stdio(false),cin.tie(0) const double eps = 1e-8; const int mod = 1000000007; const int maxn = 2e5 + 7; const double pi = acos(-1); const int INF = 0x3f3f3f3f; int dx[5] = {1, 0, -1, 0, 0}; int dy[5] = {0, 1, 0, -1, 0}; int dp[20][20][10301];//在i,j这个点,花费k的时间,可以得到的糖果 int mp[20][20]; int sx, sy, ex, ey; int main() { #ifndef ONLINE_JUDGE FIN #endif int n, m, C; scanf("%d%d%d", &n, &m, &C); for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++) { for(int j = 1; j <= m; j++) { scanf("%d", &mp[i][j]); } } memset(dp, -INF, sizeof(dp)); scanf("%d%d%d%d", &sx, &sy, &ex, &ey); dp[sx][sy][0] = 0; for(int i = 1; i <= 10300; i++) { for(int x = 1; x <= n; x++) { for(int y = 1; y <= m; y++) { for(int j = 0; j < 5; j++) { int nx = x + dx[j]; int ny = y + dy[j]; if(nx <= 0 || nx > n || ny <= 0 || ny > m || dp[nx][ny][i - 1] == -INF) continue; if(i % mp[x][y] == 0) { dp[x][y][i] = max(dp[x][y][i], dp[nx][ny][i - 1] + 1); } else { dp[x][y][i] = max(dp[x][y][i], dp[nx][ny][i - 1]); } } } } } int ans = INF; for(int i = 1; i <= 10300; i++) { if(dp[ex][ey][i] >= C) { ans = i; break; } } cout << ans << endl; return 0; }
C:拆拆拆数
传送门:https://www.zhixincode.com/contest/1/problem/C?problem_id=14
题意:将a、b分成ai和bi使得ai和bi互质并且ai、bi都要大于2
题解:两个相邻的数一定互质,那么我们就可以从a-2和b-2开始枚举,一定可以找到在10以内使得a-i与b-j互质(我也不知道我瞎说的)
代码如下:

#include <set> #include <map> #include <deque> #include <queue> #include <stack> #include <cmath> #include <ctime> #include <bitset> #include <cstdio> #include <string> #include <vector> #include <cstdlib> #include <cstring> #include <iostream> #include <algorithm> using namespace std; typedef long long LL; typedef pair<LL, LL> pLL; typedef pair<LL, int> pLi; typedef pair<int, LL> pil;; typedef pair<int, int> pii; typedef unsigned long long uLL; #define bug printf("********* ") #define debug(x) cout<<#x"=["<<x<<"]" <<endl #define FIN freopen("input.txt","r",stdin); #define IO ios::sync_with_stdio(false),cin.tie(0) const double eps = 1e-8; const int mod = 1000000007; const int maxn = 2e5 + 7; const double pi = acos(-1); const int inf = 0x3f3f3f3f; const LL INF = 0x3f3f3f3f3f3f3f3fLL; long long gcd(long long a, long long b) { return b ? gcd(b, a % b) : a; } int main() { #ifndef ONLINE_JUDGE FIN #endif int T; scanf("%d", &T); while(T--) { LL a, b; scanf("%lld%lld", &a, &b); int flag = 1; if(gcd(a,b)==1){ printf("1 %lld %lld ",a,b); continue; } for(int i = 2; i <= 10; i++) { if(flag) { for(int j = 2; j <= 10; j++) { if(gcd(i, j) == 1 && gcd(a - i, b - j) == 1) { printf("2 %d %d %lld %lld ", i, j, a - i, b - j); flag=0; break; } } } else { break; } } } return 0; }
F:爬爬爬山
传送门:https://www.zhixincode.com/contest/1/problem/F?problem_id=17
题意:上山会损耗体力值,下山会增加体力值,我们这样想,我们假设一开始就站在了h[1]+k这样的高度,如果前面的山比我还要高,我是一定要把前面的山给砍掉的,如果比我矮,我还是最后要爬上h[1]+k这样的高度,一加一减其实就抵消了,所以我们关心的就是高度高于h[1]+k的山峰,然后建立双向边跑最短路即可,起点是1,终点是n
代码如下:

#include <set> #include <map> #include <deque> #include <queue> #include <stack> #include <cmath> #include <ctime> #include <bitset> #include <cstdio> #include <string> #include <vector> #include <cstdlib> #include <cstring> #include <iostream> #include <algorithm> using namespace std; typedef long long LL; typedef pair<LL, LL> pLL; typedef pair<LL, int> pLi; typedef pair<int, LL> pil;; typedef pair<int, int> pii; typedef unsigned long long uLL; #define bug printf("********* ") #define debug(x) cout<<#x"=["<<x<<"]" <<endl #define FIN freopen("input.txt","r",stdin); #define IO ios::sync_with_stdio(false),cin.tie(0) const double eps = 1e-8; const int mod = 1000000007; const int maxn = 4e5 + 7; const double pi = acos(-1); const LL INF = 1e18; LL h[maxn]; struct EDGE { int v, nxt; LL w; } edge[maxn]; int head[maxn]; int tot; void add_edge(int u, int v, LL w) { edge[tot].v = v; edge[tot].w = w; edge[tot].nxt = head[u]; head[u] = tot++; } struct node { int s, dis; node (int _s, int _dis) { s = _s; dis = _dis; }; }; LL dis[maxn]; int vis[maxn]; void dijkstra(int st) { memset(dis, 0x3f, sizeof(dis)); memset(vis, 0, sizeof(vis)); priority_queue<pLL> q; dis[st] = 0; q.push(make_pair(0, st)); while(!q.empty()) { int x = q.top().second; q.pop(); if(vis[x]) continue; vis[x] = 1; for(int i = head[x]; i != -1; i = edge[i].nxt) { int v = edge[i].v; if(dis[v] > dis[x] + edge[i].w) { dis[v] = dis[x] + edge[i].w; q.push(make_pair(-dis[v], v)); } } } } int main() { #ifndef ONLINE_JUDGE FIN #endif int n, m; LL k; scanf("%d%d%lld", &n, &m, &k); for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++) { scanf("%lld", &h[i]); } memset(head, -1, sizeof(head)); tot = 0; k += h[1]; for(int i = 0; i < m; i++) { int u, v; LL w; scanf("%d%d%lld", &u, &v, &w); if(h[v] >= k) add_edge(u, v, w + (h[v] - k) * (h[v] - k)); else add_edge(u, v, w); if(h[u] >= k) add_edge(v, u, w + (h[u] - k) * (h[u] - k)); else add_edge(v, u, w); } dijkstra(1); printf("%lld ", dis[n]); return 0; }
J:夺宝奇兵
传送门:https://www.zhixincode.com/contest/1/problem/J?problem_id=21
题意:我们可以买别人的东西,最终要使得我们的东西是最多的,问最小的花费是多少
题解:要想使我们的东西最多,我们的东西应该是比当前拥有最多物品的人的物品还多,所以我们可以枚举我们需要买的物品数量,然后将其余所有人的物品数量降到这个数量级以内,如果将所有人的物品降到这个数量级以内还是没有让我的物品到达这个数量时,我就将物品从便宜的开始买,一直买到我的物品的数量达到我规定的这个量级位置,枚举时每次更新使得所有人达到当前量级以下需要花费的最小值,更新答案
代码如下:

#include <set> #include <map> #include <deque> #include <queue> #include <stack> #include <cmath> #include <ctime> #include <bitset> #include <cstdio> #include <string> #include <vector> #include <cstdlib> #include <cstring> #include <iostream> #include <algorithm> using namespace std; typedef long long LL; typedef pair<LL, LL> pLL; typedef pair<LL, int> pLi; typedef pair<int, LL> pil;; typedef pair<int, int> pii; typedef unsigned long long uLL; #define bug printf("********* ") #define debug(x) cout<<#x"=["<<x<<"]" <<endl #define FIN freopen("input.txt","r",stdin); #define IO ios::sync_with_stdio(false),cin.tie(0) const double eps = 1e-8; const int mod = 1000000007; const int maxn = 2e5 + 7; const double pi = acos(-1); const int inf = 0x3f3f3f3f; const LL INF = 0x3f3f3f3f3f3f3f3fLL; int n, m; vector<int> vec[maxn]; LL check(int cnt) { vector<int> res; LL tmp = 0; int cnt1 = 0; for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++) { int sz=vec[i].size(); for(int j = 0; j < sz; j++) { if(j < sz-(cnt-1)) { tmp += vec[i][j]; cnt1++; } else { res.push_back(vec[i][j]); } } } // cout<<res.size()<<endl; sort(res.begin(), res.end()); for(int i = 0; i < res.size() && cnt1 < cnt; i++) { tmp += res[i]; cnt1++; } return tmp; } int main() { #ifndef ONLINE_JUDGE FIN #endif scanf("%d%d", &n, &m); for(int i = 1; i <= m; i++) { int a, c; scanf("%d%d", &a, &c); vec[c].push_back(a); } for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++) { sort(vec[i].begin(), vec[i].end()); } LL ans = INF; for(int i = 1; i <= m; i++) { ans = min(ans, check(i)); } cout << ans << endl; return 0; }
