在孤尽大佬的开课吧公开课视频(地址:https://www.kaikeba.com/open/item?c=681&channelCode=gjsh6ytvxy)中,有一道很有意思的题目:
首先,我们需要写出如何判断对称数和质数两个函数。
对于质数的判断,我们不难想到,如果可以整除,那么能被整除的因子至少有一个会小于等于这个数字的开平方。比如25,至少要有一个因子小于等于5。100,至少要有一个因子要与等于10。所以一个简单的思路就是:
1.判断是否为奇数(偶数肯定不是质数);
2.将该数开平方,得到的数字加1,以这个结果为最大值,如果从3开始,每隔2个数字一直到这个最大值进行除余,如果有任意数字除余结果为0,那么该数不为质数,如果全部不为0,那么该数为质数(此处使用了6n+-1法则,后续有说明);
最终代码如下:
private static boolean isPrime(int inputMaxNumber) { if (inputMaxNumber <= 1) { throw new RuntimeException("out of range"); } if (inputMaxNumber == 2 || inputMaxNumber == 3) { return false; } if (inputMaxNumber % 6 != 1 && inputMaxNumber % 6 != 5) { return false; } int sqrt = (int) Math.sqrt(inputMaxNumber); for (int i = 5; i <= sqrt; i += 6) { if (inputMaxNumber % i == 0 || inputMaxNumber % (i + 2) == 0) { return false; } } return true; }
对于对称数的判断,最简单的能想到的就是拆分为个位数字,然后头尾比较。但是这样的话,当数据量增大时,会出现大量的字符串对象,这种做法并不可取。这里用了一个办法,构造一个新数字,根据输入数字循环取余后除10,与此同时新数乘10并加上余数,最终如果新数与输入数字相等,那么判定为对称数。
最终代码如下:
private static boolean isBalanced(int source) { if (source <= 9) { throw new RuntimeException("out of range"); } int original = source; //构造新数字,以原数字的个位为最高位,十位为次,...依次到原数字的最高位成为本数字的个位 int buildNew = 0; while (source != 0) { buildNew = buildNew * 10 + source % 10; source /= 10; } if (buildNew == original) { return true; } return false; }
---------------------------------------------------------------
这道题,最不难想到的就是循环一个一个去找这些质数且对称的数字。但是考虑到性能,数据量稍微一大,那么耗时肯定会大大增加。怎么去优化这个过程呢?
视频中提到了几个优化点:
1.先判断是否为对称数,再判断是否为质数。因为对称数的判断比判断质数要简单得多,所以我们优先判断对称数,从消耗上会比小得多;
2.步长为1的循环优化的空间很大,这里的优化使用到了6N+-1法
6N+-1法则:任何一个自然数,总可以表示成如下形式之一:6N,6N+1,6N+2,6N+3,6N+4,6N+5 (N=0,1,2,3,..),显然,当N≥1时,6N,6N+2,6N+3,6N+4都不是素数,只有形如6N+1和6N+5的自然数才可能是素数,所以除了2,3外,所有的素数都可以表示成6N±1的形式(N=0,1,2,3,..)
到了这里,程序的性能已经比之前提升了很多。
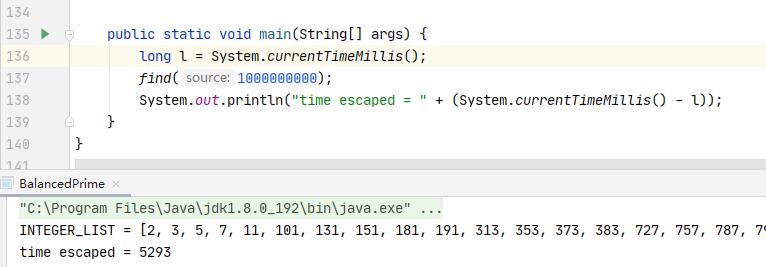
执行代码寻找10亿的结果并计时:

---------------------------------------------------------------
仔细想想,这个题目还是很有意思,继续思考,其实还会发现有进一步的优化空间。
这里找的既是对称数,又是质数,所以两位以上的数字,凡以2,4,5,6,8开头的数字都可以略过。如此一来,当数据量很大时,我们可以跳过很多不符合要求的数字段。比如寻找10亿以内符合要求的数字时,我们可以确定2000-3000,20000-30000,2亿-3亿...都不符合要求,所以可以直接跳过,这就节省了很多比较操作了。
这里给出代码,并与上面的执行结果进行比较:
public class BalancedPrime { public static final List<Integer> INTEGER_LIST = new ArrayList<>(); static { INTEGER_LIST.add(2); INTEGER_LIST.add(3); INTEGER_LIST.add(5); INTEGER_LIST.add(7); } private static void processNumberLtTen(int source) { ArrayList<Integer> integerArrayList = new ArrayList<>(); integerArrayList.add(2); if (source >= 3) { integerArrayList.add(3); } if (source >= 5) { integerArrayList.add(5); } if (source >= 7) { integerArrayList.add(7); } System.out.println("integerArrayList = " + integerArrayList.toString()); } public static void find(int source) { if (source <= 1) { throw new RuntimeException("out of range"); } if (source < 10) { processNumberLtTen(source); return; } //遇关键数字跳跃数字段,可提升接近50%性能 int ex = 0; int skipCount = 0; int limitSkipCount = -1; for (int i = 11; i <= source; i += 2) { if (skipCount == limitSkipCount || limitSkipCount == -1) { int current = i; while (current >= 10) { current /= 10; ex++; } limitSkipCount = ((int) Math.pow(10, ex)) / 2; if (current % 2 == 0 || current == 5) { i = calculateCurrent(current, ex); } else { limitSkipCount = (((current + 1) * (int) Math.pow(10, ex)) + 1 - i) / 2; } ex = 0; skipCount = 0; } skipCount++; compareAndProcess(i); } System.out.println("INTEGER_LIST = " + INTEGER_LIST.toString()); } private static int calculateCurrent(int current, int ex) { if (current == 2) { return (3 * (int) Math.pow(10, ex)) + 1; } else if (current == 4 || current == 5 || current == 6) { return (7 * (int) Math.pow(10, ex)) + 1; } else if (current == 8) { return (9 * (int) Math.pow(10, ex)) + 1; } else { throw new RuntimeException("out of range"); } } private static void compareAndProcess(int compare) { if (isBalanced(compare) && isPrime(compare)) { INTEGER_LIST.add(compare); } } private static boolean isBalanced(int source) { if (source <= 9) { throw new RuntimeException("out of range"); } int original = source; //构造新数字,以原数字的个位为最高位,十位为次,...依次到原数字的最高位成为本数字的个位 int buildNew = 0; while (source != 0) { buildNew = buildNew * 10 + source % 10; source /= 10; } if (buildNew == original) { return true; } return false; } private static boolean isPrime(int inputMaxNumber) { if (inputMaxNumber <= 1) { throw new RuntimeException("out of range"); } if (inputMaxNumber == 2 || inputMaxNumber == 3) { return false; } if (inputMaxNumber % 6 != 1 && inputMaxNumber % 6 != 5) { return false; } int sqrt = (int) Math.sqrt(inputMaxNumber); for (int i = 5; i <= sqrt; i += 6) { if (inputMaxNumber % i == 0 || inputMaxNumber % (i + 2) == 0) { return false; } } return true; } public static void main(String[] args) { long l = System.currentTimeMillis(); find(1000000000); System.out.println("time escaped = " + (System.currentTimeMillis() - l)); } }
执行结果:
另一个思路,我们不用循环比较定位符合要求的数字,而是直接通过构造出对称的数字,同时判断这个数字是否为质数。这样一来,比较的范围就大大减少,如果叠加之前想到的2,4,5,6,8的排除,那么程序的性能相比会更加优秀。
最终,将几个上述的关键点整合:
- 1.构造对称数
- 2.循环数字时,排除2,4,6,8,5开头的数字
- 3.判断素数时,开方后采用6N+-1法则
我们可以看看最终的结果:
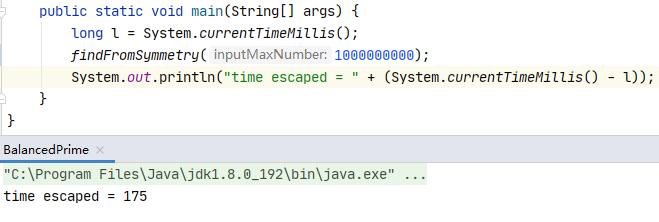
最后附上代码:
package com.changjiang.interesting; import java.util.ArrayList; import java.util.List; /** * @author changjiang.chen * @description 找出N内的所有质数且对称的数字,包含个位数。注意:0和1既不是质数也不是合数。 * @timestamp 2021-09-15 11:04:19 * <p> */ public class BalancedPrime { public static final List<Integer> INTEGER_LIST = new ArrayList<>(); static { INTEGER_LIST.add(2); INTEGER_LIST.add(3); INTEGER_LIST.add(5); INTEGER_LIST.add(7); } private static void processNumberLtTen(int source) { ArrayList<Integer> integerArrayList = new ArrayList<>(); integerArrayList.add(2); if (source >= 3) { integerArrayList.add(3); } if (source >= 5) { integerArrayList.add(5); } if (source >= 7) { integerArrayList.add(7); } System.out.println("integerArrayList = " + integerArrayList.toString()); } public static void find(int source) { if (source <= 1) { throw new RuntimeException("out of range"); } if (source < 10) { processNumberLtTen(source); return; } //遇关键数字跳跃数字段,可提升接近50%性能 int ex = 0; int skipCount = 0; int limitSkipCount = -1; for (int i = 11; i <= source; i += 2) { if (skipCount == limitSkipCount || limitSkipCount == -1) { int current = i; while (current >= 10) { current /= 10; ex++; } limitSkipCount = ((int) Math.pow(10, ex)) / 2; if (current % 2 == 0 || current == 5) { i = calculateCurrent(current, ex); } else { limitSkipCount = (((current + 1) * (int) Math.pow(10, ex)) + 1 - i) / 2; } ex = 0; skipCount = 0; } skipCount++; compareAndProcess(i); } System.out.println("INTEGER_LIST = " + INTEGER_LIST.toString()); } private static int calculateCurrent(int current, int ex) { if (current == 2) { return (3 * (int) Math.pow(10, ex)) + 1; } else if (current == 4 || current == 5 || current == 6) { return (7 * (int) Math.pow(10, ex)) + 1; } else if (current == 8) { return (9 * (int) Math.pow(10, ex)) + 1; } else { throw new RuntimeException("out of range"); } } private static void compareAndProcess(int compare) { if (isBalanced(compare) && isPrime(compare)) { INTEGER_LIST.add(compare); } } private static boolean isBalanced(int source) { if (source <= 9) { throw new RuntimeException("out of range" + source); } int original = source; //构造新数字,以原数字的个位为最高位,十位为次,...依次到原数字的最高位成为本数字的个位 int buildNew = 0; while (source != 0) { buildNew = buildNew * 10 + source % 10; source /= 10; } if (buildNew == original) { return true; } return false; } private static boolean isPrime(int inputMaxNumber) { if (inputMaxNumber <= 1) { throw new RuntimeException("out of range"); } if (inputMaxNumber == 2 || inputMaxNumber == 3) { return false; } if (inputMaxNumber % 6 != 1 && inputMaxNumber % 6 != 5) { return false; } int sqrt = (int) Math.sqrt(inputMaxNumber); for (int i = 5; i <= sqrt; i += 6) { if (inputMaxNumber % i == 0 || inputMaxNumber % (i + 2) == 0) { return false; } } return true; } private static int buildBalanceByPrefix(int number, boolean isEven) { int process = number; if (!isEven) { process /= 10; } int inverse = 0; int ex = 0; while (process > 0) { int i = process % 10; inverse = inverse * 10 + i; ex++; process /= 10; } return (number * (int) Math.pow(10, ex) + inverse); } /** * 构建与输入数字长度相同的对称数 * * @param inputMaxNumber * @return */ private static List<Integer> buildSameLengthBalance(int inputMaxNumber) { if (inputMaxNumber < 10) { throw new RuntimeException("out of range" + inputMaxNumber); } int process = inputMaxNumber; //数字长度 int ex = 0; while (process > 0) { process /= 10; ex++; } //数字长度是否为偶数 boolean isEven = ex % 2 == 0; int prefixCount = ex / 2; if (!isEven) { prefixCount += 1; } List<Integer> integerList = new ArrayList<>(); boolean firstRounded = true; List<Integer> lastRounded = new ArrayList<>(); for (int i = 0; i < prefixCount; i++) { integerList.clear(); for (int j = 0; j < 10; j++) { if (firstRounded) { if (j % 2 == 0 || j == 5) { continue; } integerList.add(j); } else { for (int lastNumber : lastRounded) { integerList.add(lastNumber + j); } } } if (firstRounded) { firstRounded = false; } else { lastRounded.clear(); } for (int number : integerList) { lastRounded.add(number * 10); } } List<Integer> result = new ArrayList<Integer>(); for (int k : integerList) { //避免溢出 if ((isEven && k <= 21474) || (!isEven && ex / 2 <= 4)) { result.add(buildBalanceByPrefix(k, isEven)); } } return result; } /** * 1.如果大于10,那么结果集包含2,3,5,7 * 2.对于大于10的数字(两位以上的数字,含两位)的处理: * a.分析数字的位数,并判断这个位数的奇偶性。--构建所有可能的对称数 * a1.打头的数字不能为0,2,4,5,6,8 * a2.如果输入的是n位数,那么构建的n位数第一个数字不能比输入数字大 * * @param inputMaxNumber */ public static void findFromSymmetry(int inputMaxNumber) { if (inputMaxNumber <= 1) { throw new RuntimeException("out of range"); } if (inputMaxNumber < 10) { processNumberLtTen(inputMaxNumber); return; } int process = inputMaxNumber; while (process >= 10) { List<Integer> integers = buildSameLengthBalance(process); for (Integer integer : integers) { //构建的比原输入数字大时,跳过 if (integer > inputMaxNumber) { continue; } //首位数字为偶数或者5,则不进行比较了 int current = integer; while (current >= 10) { current /= 10; } if (current % 2 == 0 || current == 5) { continue; } //比较,并决定是否放入结果集 compareAndProcess(integer); } //减少一位,继续循环,直到降低到个位数字 process /= 10; } } public static void main(String[] args) { long l = System.currentTimeMillis(); findFromSymmetry(1000000000); System.out.println("time escaped = " + (System.currentTimeMillis() - l)); } }