- 实现mypwd
- 任务要求:
1 学习pwd命令
2 研究pwd实现需要的系统调用(man -k; grep),写出伪代码
3 实现mypwd
4 测试mypwd
提交过程博客的链接
- 实现过程:
- 学习pwd命令
-
功能:查看”当前工作目录“的完整路径
-
命令格式:pwd
-
使用man命令查看pwd

- 实现pwd
- 研究pwd实现需要的系统调用(man -k; grep),写出伪代码
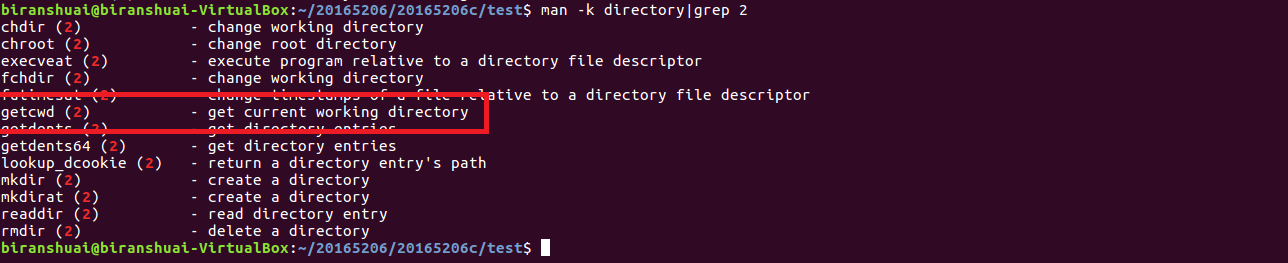
- man -k directory|grep 2
因为pwd是查看当前工作目录的路径,因此应该查找有关目录的有关信息,即directory。使用命令
man -k directory|grep 2 查找,可发现getcwd的功能是“得到当前工作目录”。符合要求,通过man命令查看其帮助文档。
- man getcwd

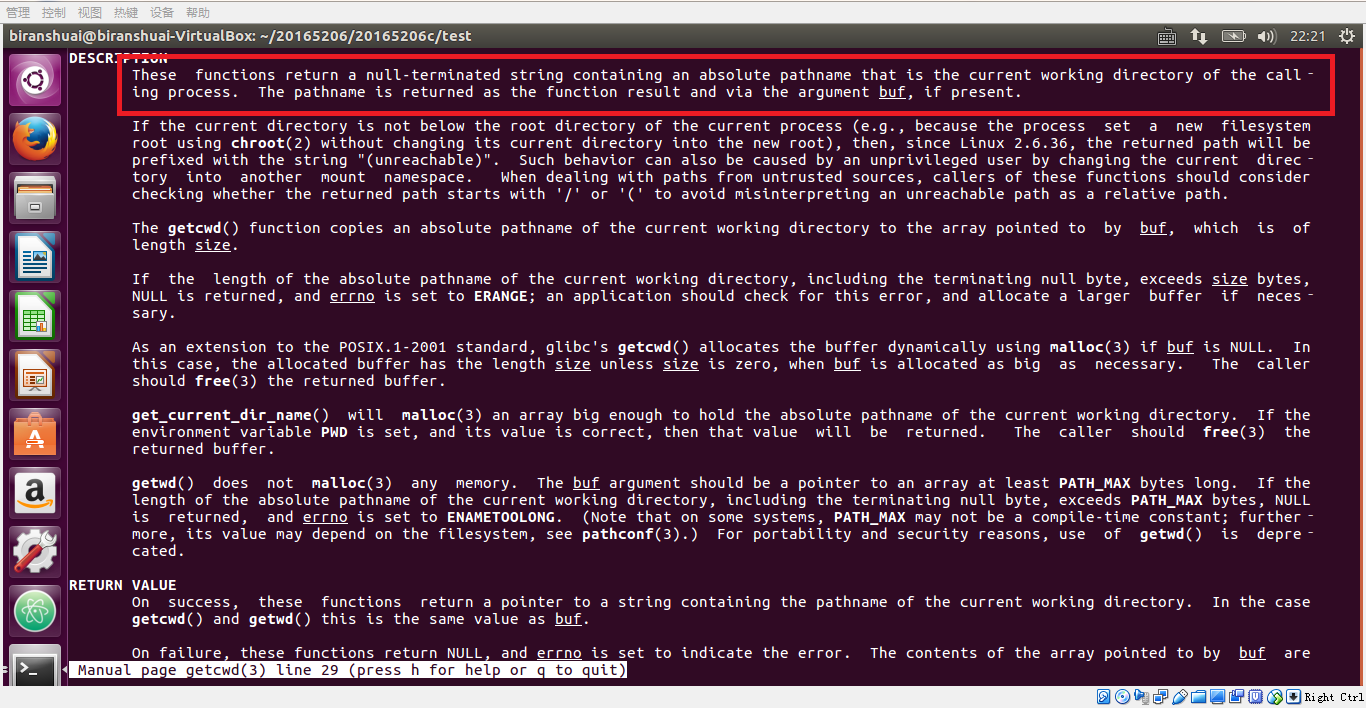
这里可发现getcwd的工作原理:这些函数返回一个以空结尾的字符串,该字符串包含一个绝对路径名,该路径名是调用进程的当前工作目录。路径名作为函数结果返回,如果存在,则通过参数BUF返回。
我们需要的就是这个参数BUF,而BUF是一个定义的指针,所以可据此写伪代码。
- 伪代码
定义一个字符串数组,用于存放绝对路径;
定义一个指针BUF;
getcwd();
if(BUF)
打印存放的路径名;
else
出错;
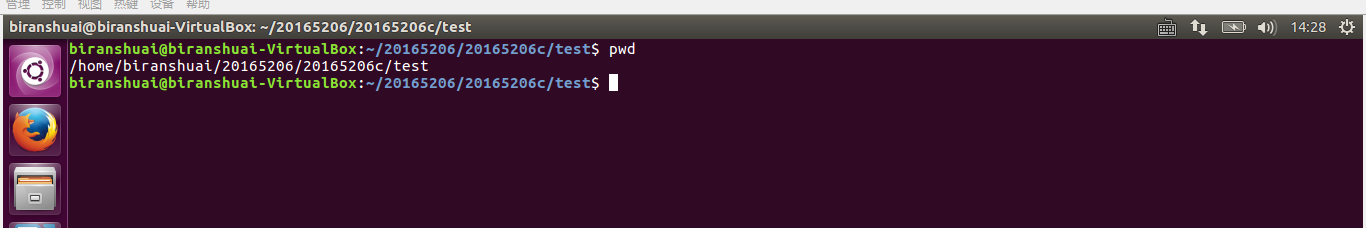
- 实现mypwd
-
int getinode(char *);
该函数功能是显示当前目录的inode。功能实现是调用了stat,stat用于显示文件或文件系统的详细信息。此处返回当前目录的inode。 -
char *inode_to_name(int);
该函数功能是存储绝对路径。功能实现是调用了dir、dirent、opendir、readdir等,将每一次获取的文件夹目录内容进行复制,存储并返回。 -
void printpath();
该函数功能是打印路径。功能实现是调用了getinode函数和inode_to_name函数,即从当前目录开始,不断返回上一层目录,比较当前目录与上一层目录的inode是否相同,若相同则表明返回到了根目录,然后将指针中存储的路径返回并打印。 -
mypwd代码:
#include<stdio.h>
#include<sys/stat.h>
#include<dirent.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<string.h>
#include<sys/types.h>
void printpath();
char *inode_to_name(int);
int getinode(char *);
int main()
{
printpath();
putchar('
');
return ;
}
void printpath()
{
int inode,up_inode;
char *str;
inode = getinode(".");
up_inode = getinode("..");
chdir("..");
str = inode_to_name(inode);
if(inode == up_inode) {
return;
}
printpath();
printf("/%s",str);
}
int getinode(char *str)
{
struct stat st;
if(stat(str,&st) == -1){
perror(str);
exit(-1);
}
return st.st_ino;
}
char *inode_to_name(int inode)
{
char *str;
DIR *dirp;
struct dirent *dirt;
if((dirp = opendir(".")) == NULL){
perror(".");
exit(-1);
}
while((dirt = readdir(dirp)) != NULL)
{
if(dirt->d_ino == inode){
str = (char *)malloc(strlen(dirt->d_name)*sizeof(char));
strcpy(str,dirt->d_name);
return str;
}
}
perror(".");
exit(-1);
}
- 测试mypwd

- 体会
这次是利用c语言实现pwd命令,思路还算比较清晰,但在编写代码上还是存在困难,我学习并借鉴了网上的代码,实现了mypwd,收获还是挺大的。