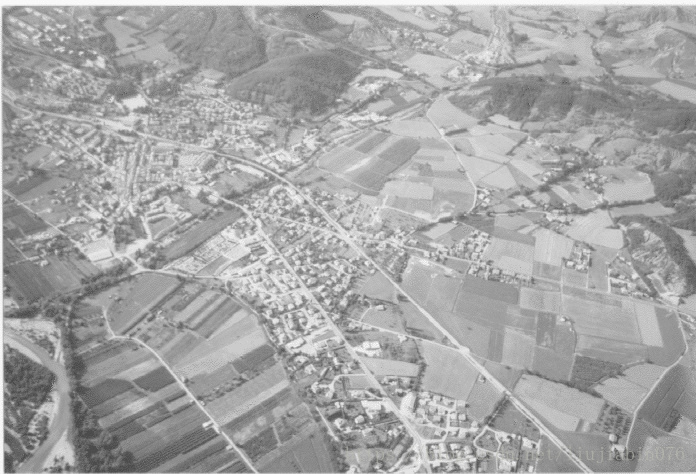
在处理二值图像,提取感兴趣目标时经常需要通过连通域的大小对候选目标进行初步筛选。OpenCV中findContour 方法可以返回轮廓并能够计算轮廓面积。可其局限性在对于非凸多边形的面积计算是不准确的。 此时,利用连通域计算面积的方法更可靠,然而 findContour方法并不返回连通域结果。
计算连通域基本方法主要有两种:1)Two-Pass法;2)Seed-Filling种子填充法;
参考了这篇文章的实现OpenCV_连通区域分析(Connected Component Analysis/Labeling)
其中,Two-Pass法步骤简单,易于理解。但是该博文的实现算法存在Bug, 会将连通的区域分割成不同标签。测试图如下:
使用其连通区域的结果如下:
不难发现,第二、四字符的连通区域计算出现了错误。 出错的原因是在于连通域的等价表上面。(equivalences )
其方法利用一维列表结构存储等价关系。例如存在一个具有等价性的标签组:{ 1,3,5,7};
则可以用一维数组表示: a[7] = 5, a[5] = 3, a[3] = 1,a[1] = 1, 或者更高效地是 a[7] = 1, a[5] = 1, a[3] = 1, a[1] = 1。 而前者的方式可以更准确地传递等价性,因为大多数时候 7 与 1 , 5 与1 的关系并不明确,或者很难获知。相对地, 3 与 1, 5 与 3 , 7 与 5的关系 更容易获得。 原因在于其标签值相近,代表空间相近,继而可通过邻域判断连通性。这里理解有困难可看这里Wiki: Connected-component labeling。
具体上面提到的参考算法的bug不细表,给出我的实现方法。
- 主算法
bool twoPass(cv::Mat pBinary, int background,int foreground, int border, cv::Mat& pLabel)
{
// connected component analysis (4- component)
// use two-pass algorithm
// 1. first pass: label each foreground pixel with a label
// 2. second pass: visit each labeled pixel and merge neighbor labels
if (pBinary.empty() || pBinary.channels() != 1)
return false;
int width = pBinary.cols;
int height = pBinary.rows;
pLabel.release();
pBinary.convertTo(pLabel, CV_32SC1);
int *data = pLabel.ptr<int>(0);
for (int i = 0; i < width*height; i++)
if (foreground == data[i]) data[i] = 1;
else data[i] = 0;
int label = 1;
//labelSet 连通域列表 比如连通队列{1,3,5,7} labelSet[7] = 5, labelSet[5] = 3, labelSet[3] = 1, labelSet[1] = 1
vector<int> labelSet;
labelSet.push_back(0);
labelSet.push_back(1);
border = MAX(1, border);
for (int i = border; i < height -border; i++)
{
int* curRowData = pLabel.ptr<int>(i);
int* preRowData = pLabel.ptr<int>(i - 1);
for (int j = border; j < width - border; j++)
{
int* cur_data = curRowData + j;
if (0 == *cur_data) continue;
int* left_data = curRowData + j - 1;
int* up_data = preRowData + j;
int* right_up_data = preRowData + j + 1;
int* left_up_data = preRowData + j - 1;
if (90 == i && 125 == j)
cout << "stop" << endl;
vector<int> neighborLabels;
if (*left_data > 1)
neighborLabels.push_back(*left_data);
if (*up_data > 1)
neighborLabels.push_back(*up_data);
// if (*right_up_data > 1)
// neighborLabels.push_back(*right_up_data);
// if (*left_up_data > 1)
// neighborLabels.push_back(*left_up_data);
if ( neighborLabels.empty() )
{
labelSet.push_back(++label);
*cur_data = label;
labelSet[label] = label;
}
else
{
sort(neighborLabels.begin(), neighborLabels.end());
*cur_data = neighborLabels[0];
for (size_t k = 1; k < neighborLabels.size(); k++)
{
int tmpLabel = neighborLabels[k];
int oldLabel = labelSet[tmpLabel];
if (oldLabel > *cur_data)
{
// 这里是关键
while ( oldLabel != tmpLabel)
{
int tmp = tmpLabel;
tmpLabel = oldLabel;
oldLabel = labelSet[tmpLabel];
labelSet[tmp] = *cur_data;
}
if (tmpLabel > *cur_data)
labelSet[tmpLabel] = *cur_data;
else
labelSet[*cur_data] = tmpLabel;
}
else if (oldLabel < *cur_data ) // 该有时语句不执行
{
labelSet[*cur_data] = oldLabel;
// 后面的Label是有前面的 data决定的
//*cur_data = oldLabel;
}
}
} // neighbors
} // j
} // i
// 2. second pass
// input : {1,3,5,7} labelSet[7] = 5, labelSet[5] = 3, labelSet[3] = 1, labelSet[1] = 1
// out : labelSet[7] = 1, labelSet[5] = 1, labelSet[3] = 1, labelSet[1] = 1
for (size_t i = 2; i < labelSet.size(); i++)
{
if ( i == labelSet[i] )
continue;
int cur_label = labelSet[i];
int pre_label = labelSet[cur_label];
while (pre_label != cur_label)
{
cur_label = pre_label;
pre_label = labelSet[pre_label];
}
labelSet[i] = cur_label;
}
cout <<"label : "<< labelSet.size() << endl;
for (int i = 0; i < height; i++)
{
int* data = pLabel.ptr<int>(i);
for (int j = 0; j < width; j++)
{
int& pixelLabel = data[j];
pixelLabel = labelSet[pixelLabel];
}
}
return true;
}
结果:
2、 有条件选择连通域标签
void thresholdLabel(const cv::Mat& _labelImg, vector<int>& _labelList)
{
if (_labelImg.empty() || _labelImg.type() != CV_32SC1)
return;
std::map<int,int> labelCount;
int rows = _labelImg.rows;
int cols = _labelImg.cols;
for (int i = 0; i < rows; i++)
{
const int* data_src = (int*)_labelImg.ptr<int>(i);
for (int j = 0; j < cols; j++)
{
int pixelValue = data_src[j];
if (0 == pixelValue) continue;
if (labelCount.count(pixelValue) <= 0)
labelCount[pixelValue] = 1;
else
labelCount[pixelValue]++;
}
}
std::map<int, int>::iterator st = labelCount.begin();
std::map<int, int>::iterator et = labelCount.end();
for (; st != et; ++st)
{
if (st->second < 100 ) continue; // 连通域小于100,忽略
_labelList.push_back(st->first);
cout << "label " << st->first << ": " << st->second<<endl;
}
}
3、 随机着色
cv::Scalar randColor()
{
uchar r = 255 * (rand() / (1.0 + RAND_MAX));
uchar g = 255 * (rand() / (1.0 + RAND_MAX));
uchar b = 255 * (rand() / (1.0 + RAND_MAX));
return cv::Scalar(b, g, r);
}
void getLabelColor(const cv::Mat& _labelImg, vector<int>_labelList, cv::Mat& _colorLabelImg)
{
if (_labelImg.empty() || _labelImg.type() != CV_32SC1 || _labelList.empty())
return;
std::map<int, cv::Scalar> colors;
int rows = _labelImg.rows;
int cols = _labelImg.cols;
_colorLabelImg.release();
_colorLabelImg.create(rows, cols, CV_8UC3);
_colorLabelImg = cv::Scalar::all(0);
for (int i = 0; i < rows; i++)
{
const int* data_src = (int*)_labelImg.ptr<int>(i);
uchar* data_dst = _colorLabelImg.ptr<uchar>(i);
for (int j = 0; j < cols; j++)
{
int pixelValue = data_src[j];
vector<int>::iterator it = find(_labelList.begin(), _labelList.end(), pixelValue);
if (it == _labelList.end())
{
data_dst++;
data_dst++;
data_dst++;
continue;
}
if (pixelValue > 1)
{
if (colors.count(pixelValue) <= 0)
{
colors[pixelValue] = randColor();
}
cv::Scalar color = colors[pixelValue];
*data_dst++ = color[0];
*data_dst++ = color[1];
*data_dst++ = color[2];
}
else
{
data_dst++;
data_dst++;
data_dst++;
}
}
}
}
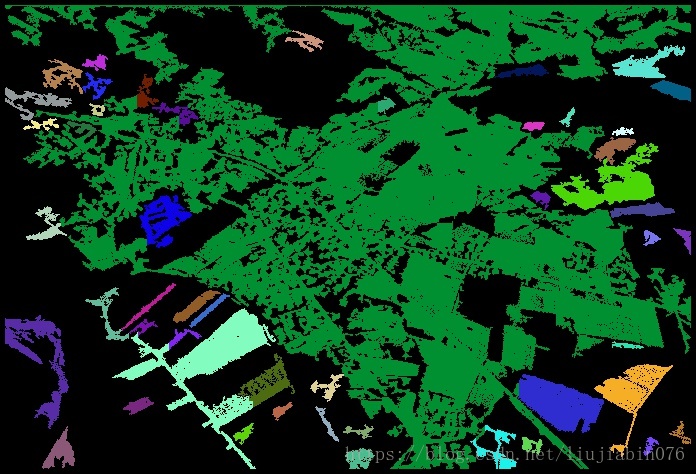
更多结果:
原图
结果:
此文仅讨论Two-Pass 实现问题。Two-Pass 方法相较于SeedFill ,运算效率比较低。
完。
Lewis, 2018-06-24